Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 11, 12 & 13 Offers and After
Uploaded by
testtest1Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 11, 12 & 13 Offers and After
Uploaded by
testtest1Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11-13 Outline
Article I. Offers
Offerer Gives te offeree the power of acceptance Offeree Acceptee to K formation because there is an
offer and an acceptance
Offers v Preliminary Negotiations
a) Language Define and certain v not define and certain
b) Objective Test Looks like the parties meant to enter a K v not
c) Communication Offer is communicated to the offeree v not
d) End Result K v Negotiation
Elements of an offer
a) Language must be definite and certain
i) (I offer, promise, will) v (Im considering, might, thinking about)
b) It must appear to a reasonable third party that the parties intended to enter a K
i) Objective Test Did it look like the parties meant to enter into a K?
ii) Lucy v Zehmer Offer written on napkin so there was a K and farm was sold
(1) Rule of intoxication Voids K but hard to prove
c) The offer must be communicated to the offeree
i) Usually communicated directly
ii) Large communicating medium Communication to the masses via media
(1) Exceptions: Limited Class of Offerees Limits the number of the power of acceptances
(a) First Come First Serve Limits the number of offerees to one
(b) Reward K Unilateral, only the person providing the info can collect the award
Terms and Conditions (specific promises)
a) C/L Price term how much the goods will cost to buy
i) Delivery term What time of delivery
ii) Quantity term How many willing to sell
iii) Warranty term How long is the guarantee
(1) Exceptions: Real estate contracts no specific terms that have to be in a contract except an
adequate description of the property so the price can be left out
b) U.C.C. Rule of quantity Must contain the term of quantity
i) Exception: Output Requirement Ks (I might require, might use, might produce)
ii) Rule of gap filling If no price n K, the court would fill the price in
(1) Vague Ks Under the UCC, if parties enter into a K and put in the term but are vague, the K s
not enforceable
Summary
a) The language must be definite and certain exception: Output Requirement K
b) It must appear to a reasonable third party that the parties intended to enter a K (Objective Test) exception:
gap filling
c) The offer must be communicated to the offeree If you put vague terms, court might find no K exists
After an offer
a) Lapse The offer was made and the offeree did nothing in response so the offer dies or lapses
i) Good for time agreed upon or a Reasonable Time which depends on what you are selling
(1) Rapidly changing market Offer is only good for a few minutes
ii) Offer will stay open through Option K which keeps the offer for the time stated
(1) Offeree pay for option K and offeree may not revoke but to hold open the offer for the time stated
b) Termination by operation of law The offer automatically dies because before acceptance offeree
(1) dies (Death)
(2) does insane (Insanity)
(3) what is being sold becomes illegal (Illegality)
c) Express Rejection Offeree expressively declines the offer therefore the offeree no longer has the power
of acceptance
i) Counter-offer (switching powers of acceptance) Offer then counter-offer then acceptance, rejection
or counter-offer
d) Revocation Offerer takes back the offer prior to acceptance so the original offer is killed
i) Three contracts that may not be revoked
(1) Unilateral Contracts If the offeree starts the act, the acceptance has begun
(2) Option Contracts Guaranteeing that the offer wont be revoked
(3) Merchants Firm Offers under U.C.C. Section 2-205 reasonable amount of time if not, stated
in terms
(a) Must be a K under the UCC for the sale of goods
(b) The offerer must be merchant
(c) The offere must promise in a signed writing to hold open the offer
(4) Acceptance
Article II. Acceptance (CL v UCC)
Mode How offer is conveyed or the form of acceptance
Rule UCC S2-207 & Mirror Image
UCC Any reasonable Mode
a) Rule UCC S2-207 Acceptance under the UCC depends on the parties to the transaction (Non-Merchants
v Merchants)
(1) Acceptance sent within a reasonable amount of time even though it states terms additional to or
different from those offered or agreed upon unless acceptance is conditional to additional or
different terms
(2) Additional terms are considered proposals unless the Merchants:
(a) Offer expressly limits acceptance to the offer
(b) Materially alter it
(c) Give notification of objections already or given the objections within a reasonable time when
received
i) Non-Merchants
(1) If offeree says I accept
(2) There is a K
(3) To the terms agreed upon
(a) Terms not agreed upon = proposal requiring further negotiation
(b) Unable to agree = Original terms of offer
(c) Conditional acceptance (Only If Rule) Only if in sentence then it becomes a counter offer
ii) Merchants One who normally deals in goods of that kind
(1) If offeree says I accept
(2) There is a K
(3) New terms are part of the K unless:
(a) New terms are part of the K
(b) New terms cause a significant economic change
(c) Offerer objects to new terms in a timely manner
b) Rule UCC S2-205 If terms are written gives assurance and it will be held open, is not revocable, for lack
of consideration during the time stated if not for a reasonable of time (max 3 months)
i) Form must be signed separately by offeree and offeror
Common Law Mirror Image Modes must match
a) Mirror Image Rule Acceptance encompasses all terms in the offer and must match
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Bilderberg GroupDocument35 pagesThe Bilderberg GroupTimothy100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Assignment 7 - Clarkson LumberDocument5 pagesAssignment 7 - Clarkson Lumbertesttest1No ratings yet
- Taylor Campbell FeatureDocument5 pagesTaylor Campbell Featureapi-666625755No ratings yet
- Understanding Your Family LegacyDocument81 pagesUnderstanding Your Family LegacyKimberly Verendia100% (2)
- LP DLL Entrep W1Q1 2022 AujeroDocument5 pagesLP DLL Entrep W1Q1 2022 AujeroDENNIS AUJERO100% (1)
- Lupo Lupangco Vs CA G.R. No. 77372 April 29, 1988 160 SCRA 848Document2 pagesLupo Lupangco Vs CA G.R. No. 77372 April 29, 1988 160 SCRA 848Emil Bautista100% (2)
- Symphonological Bioethical Theory: Gladys L. Husted and James H. HustedDocument13 pagesSymphonological Bioethical Theory: Gladys L. Husted and James H. HustedYuvi Rociandel Luardo100% (1)
- Trigonometric Identities - TRIG - RIDGE STYLEDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Identities - TRIG - RIDGE STYLEtesttest1No ratings yet
- BH FFM13 PPT ch01Document11 pagesBH FFM13 PPT ch01testtest1No ratings yet
- Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Total Points Score MATH 2331 Exam 1 Name____Solution____ Summer II 2014 (A) (Show All Your Work. Circle AnswersDocument5 pagesProblem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Total Points Score MATH 2331 Exam 1 Name____Solution____ Summer II 2014 (A) (Show All Your Work. Circle Answerstesttest1No ratings yet
- SSN 7e 01 StudentDocument19 pagesSSN 7e 01 Studenttesttest1No ratings yet
- Ans Chapter2 Even# ProblemsDocument2 pagesAns Chapter2 Even# Problemstesttest1No ratings yet
- 1 Problems in Oksendal's BookDocument22 pages1 Problems in Oksendal's Booktesttest10% (1)
- Ti Tools Ti Cellsheet Converter: Convert and Send To Connected Ti DeviceDocument6 pagesTi Tools Ti Cellsheet Converter: Convert and Send To Connected Ti Devicetesttest1No ratings yet
- Ans Chapter1 Even# ProblemsDocument3 pagesAns Chapter1 Even# Problemstesttest1No ratings yet
- CH 5 HW SolutionsDocument4 pagesCH 5 HW Solutionstesttest1No ratings yet
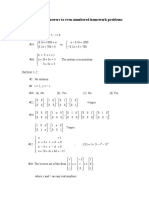
- MATH 2331: Chapter 3 Answers To Even-Numbered Homework ProblemsDocument1 pageMATH 2331: Chapter 3 Answers To Even-Numbered Homework Problemstesttest1No ratings yet
- Prob 8Document1 pageProb 8testtest1No ratings yet
- Prob 6Document1 pageProb 6testtest1No ratings yet
- Ch. 3 HW SolutionsDocument8 pagesCh. 3 HW Solutionstesttest1No ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Versus Bjerksund and Stensland Approximations For American Options PricingDocument9 pagesNumerical Methods Versus Bjerksund and Stensland Approximations For American Options Pricingtesttest1No ratings yet
- Ch.2 HW SolutionsDocument4 pagesCh.2 HW Solutionstesttest1No ratings yet
- American: Memorandum (SAMPLE ONLY)Document8 pagesAmerican: Memorandum (SAMPLE ONLY)testtest1No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting CH 08 - Problems - 31, 36, 39Document15 pagesCost Accounting CH 08 - Problems - 31, 36, 39testtest1No ratings yet
- Ch. 3 HW SolutionsDocument8 pagesCh. 3 HW Solutionstesttest1No ratings yet
- TI-89 Finance PDFDocument18 pagesTI-89 Finance PDFtesttest1No ratings yet
- Fixed Income PSA ModelDocument4 pagesFixed Income PSA Modeltesttest1No ratings yet
- American BjerksundStenslandDocument1 pageAmerican BjerksundStenslandtesttest1No ratings yet
- Linear Algrebra PracticeDocument61 pagesLinear Algrebra Practicetesttest1No ratings yet
- General Addition Rule - Two Probabilities of Either Who Are Not Disjoint. P (A or B) P (A) +Document1 pageGeneral Addition Rule - Two Probabilities of Either Who Are Not Disjoint. P (A or B) P (A) +testtest1No ratings yet
- Mortgage Back Securities: 0 N N N 0 NDocument1 pageMortgage Back Securities: 0 N N N 0 Ntesttest1No ratings yet
- Neu Example CmoDocument33 pagesNeu Example Cmotesttest1No ratings yet
- Fixed Income PSA ModelDocument4 pagesFixed Income PSA Modeltesttest1No ratings yet
- HTMMIS1Document1 pageHTMMIS1testtest1No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Competitors: Burberry Group (BRBY) Ralph Lauren Corp (RL)Document8 pagesTopic 1: Competitors: Burberry Group (BRBY) Ralph Lauren Corp (RL)testtest1No ratings yet
- ExhibitsDocument3 pagesExhibitstesttest1No ratings yet
- Construction Equipments Operations and MaintenanceDocument1 pageConstruction Equipments Operations and MaintenanceQueenie PerezNo ratings yet
- List of Solar Energy Operating Applications 2020-03-31Document1 pageList of Solar Energy Operating Applications 2020-03-31Romen RealNo ratings yet
- 19 Preposition of PersonalityDocument47 pages19 Preposition of Personalityshoaibmirza1No ratings yet
- Question Classify The Different Concepts in Preventing Accidental Compromise of DataDocument1 pageQuestion Classify The Different Concepts in Preventing Accidental Compromise of DataCrystal Marie Jordan Aguhob100% (1)
- 420jjpb2wmtfx0 PDFDocument19 pages420jjpb2wmtfx0 PDFDaudSutrisnoNo ratings yet
- In - Gov.uidai ADHARDocument1 pageIn - Gov.uidai ADHARvamsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Imc 407Document14 pagesChapter 1 Imc 407Mayson Chua ShangNo ratings yet
- Directory-Of-Doctors UNEPDocument34 pagesDirectory-Of-Doctors UNEPPerera KusalNo ratings yet
- Promoting a school walkathon for weight lossDocument3 pagesPromoting a school walkathon for weight lossDamon HelthNo ratings yet
- Receivable Financing Pledge Assignment ADocument34 pagesReceivable Financing Pledge Assignment AJoy UyNo ratings yet
- Investment Evaluation MethodDocument13 pagesInvestment Evaluation MethodBAo TrAmNo ratings yet
- Early Registration FormDocument2 pagesEarly Registration FormMylene PilongoNo ratings yet
- MPRC - OGSE100 FY2020 Report - 0Document48 pagesMPRC - OGSE100 FY2020 Report - 0adamNo ratings yet
- 1.1.a New Attitude For A New YearDocument8 pages1.1.a New Attitude For A New YearMatthew LopezNo ratings yet
- Criminal Investigation 11th Edition Swanson Test BankDocument11 pagesCriminal Investigation 11th Edition Swanson Test BankChristopherWaltonnbqyf100% (14)
- Active Directory Infrastructure DesigndocumentDocument6 pagesActive Directory Infrastructure Designdocumentsudarshan_karnatiNo ratings yet
- Definition, Nature, Scope, Subject MatterDocument7 pagesDefinition, Nature, Scope, Subject MatterNikon SonuNo ratings yet
- Winchel RM Stanley MDocument13 pagesWinchel RM Stanley MMariola AlamoNo ratings yet
- AIDA Model in AdvertisingDocument3 pagesAIDA Model in AdvertisingHằng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Pak Steel Product Price ListDocument6 pagesPak Steel Product Price ListHamid NaveedNo ratings yet
- G. Rappaport: Grammatical Role of Animacy in A Formal Model of Slavic MorphologyDocument28 pagesG. Rappaport: Grammatical Role of Animacy in A Formal Model of Slavic Morphologyanon_315959073No ratings yet
- The Ancient CeltsDocument2 pagesThe Ancient CeltsArieh Ibn GabaiNo ratings yet
- 01082023-Stapled Visa ControversyDocument2 pages01082023-Stapled Visa Controversyakulasowjanya574No ratings yet
- AccountancyDocument18 pagesAccountancyMeena DhimanNo ratings yet