Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medications
Uploaded by
Shaz ChindhyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medications
Uploaded by
Shaz ChindhyCopyright:
Available Formats
Anesthesiology Medication Orientation
Induction Agents:
Propofol: sedative-hypnotic, with enhancement of GABA at its receptors.
Hepatic metabolism. Quick emergence after bolus is related to redistribution. Short half-
life compared to barbiturates. Dose dependant depression of ventilation. No analgesia.
Decreased incidence of nausea seen when run as an infusion. Pain upon injection.
Possibility for bacterial contamination. Dose for induction is 1.5-2.5mg/kg. Infusion rate
for general anesthesia is 100-300 mcg/kg/min.
Thiopental: similar effects as propofol. Redistribution again accounts for prompt emergence after
bolus. Hepatic metabolism. Increased duration of effect with repeat dosing. Dose 3-
5mg/kg. Usually not used as infusion. Used for burst suppression in some neurosurgical
cases.
Etomidate: similar effects as propofol and barbiturates. Pain on injection. Can see myoclonus after
injection. Possibility of adrenal suppression after single bolus or infusions. Minimal
cardiovascular effects after injection. (Not always true). Induction Dose .2-.4mg/kg.
Ketamine: phencyclidine derivative that produce dissociative anesthesia. NMDA antagonist. Has
both analgesic and amnesic qualities. Does not depress ventilation. 1-2 mg/kg.
Emergence delirium, nightmares, Increased ICP. Increased BP and HR, increased oral
secretions. Increased IOP. Used IM to sedation/stun child who needs IV access prior to
surgery, who can or will not take oral versed.
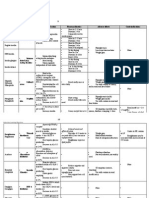
Drug Blood
Pressure
Heart Rate SVR ICP CBF
Propofol
Thiopental
Etomidate
Ketamine
Benzodiazepines: Work to enhance GABA action via a chloride channel. Amnesia, Anxiolysis, sedation.
Minimal CV/Resp effects.
Midazolam: short acting, quick on set. 1-2mg IV. .5mg/kg orally about 30min
Before surgery. Water-soluble.
Lorazepam, Diazepam: Longer acting, build up of propylene glycerol with lorazepam.
Limit use of lorazepam in renal failure patients.
Narcotics: MU receptor agonists. Multiple MU/kappa/delta receptors. Analgesia, respiratory depression.
Nausea/vomiting.
Fentanyl: Synthetic opioid. Potent. Usually does not cause hypotension.
May see decrease in BP when accompanied by benzodiazepines.
Like some of the induction agents, redistribution accounts for short action of effect after
single bolus. Hepatic metabolism p450system. 1-2mcg/kg for analgesia. 2-20mcg/kg for
adjutant to inhalational or intravenous anesthesia.
Hydromorphone: No histamine release, longer acting narcotic. Usual dose 2-.4mg bolus. Also
used in epidural infusions. Onset of action is longer than that of fentanyl. (ie must wait
a bit longer if you do see immediate effect.
Morphine: Histamine release. 1-5mg bolus. Like dilaudid action is slower than fentanyl in onset.
Merperidine: Synthetic opioid . Active metabolites have CNS toxicity and can accumulate with use of
infusions and in patients with renal failure. Used for shivering in the recovery room. Has
some local anesthetic properties. Avoid in patients using MAOI.
Muscle Relaxants:
Depolarizing Muscle Relaxant
Succinylcholine. Associated with increase of .5-1meq of potassium. Triggering agent for MH.
Increased ICP, IOP, intra gastric pressure, and increased LES pressure. Short action 10-15min.
Rapid onset less than one minute.
Non Depolarizing Agents
Vercuronium, Pancuronium, Rocuronium, Atracurium, Mivacurium
Drug Dose Clearance Onset Duration
Succinylcholine 1-2mg IV, 4mg
IM
Pseudo-
cholinesterase
Less than a min 10-15 min
Pancuronium .1mg/kg Renal 3-5 min 60-90 min
Vecuronium .08-1 mg/kg Renal 3-5 min 20-35 min
Rocuronium .6-1.2mg/kg Renal 1-2 min 20-45 min
Atracurium .5mg/kg Hoffman,
Hydrolysis
3-5 min 20-35 min
Mivacurium .25mg/kg Hydrolysis,
Enzymatic
12-20 min 2-3 min
Volatile Anesthetics:
Review in Miller. Agents used for mask induction are Halothane, Sevoflurane.
Desflurane acts quickly and is quickly eliminated when turned off. All of the volatile agents cause
bronchodilation at high levels.
Nitrous Oxide Halothane Isoflurane Desflurane Sevoflurane
Cardiovascular
BP
HR
SVR
CO
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC/
NC/
NC
Respiratory
TV
RR
PaCO2
NC
Cerebral
CBF
ICP
CMRO
Seizures
Neuromuscular
blockade
Renal
RBF
GFR
UO
?
?
?
?
Hepatic
Blood flow
?
?
Metabolism .004% 15-20% .2% <.1% 2-3%
MAC 105-110 .75 1.15 6.0-7.25 2.05
Local Anesthetics:
Concentration: For Local anesthetics 1%=10mg/cc. Hence
.25%bupivicaine=2.5mg/cc. Always read bottles.
Toxic Doses for peripheral blocks: Lidocaine 5mg/kg plain 7mg/kg with epi
Bupivicaine 2mg/kg plain 3mg/kg with epi
Ropivicaine same as bupivicaine
Other Commonly used drugs:
Phenylephrine: direct acting sympathomimetic drug with predominately effects
Making: Standard concentration is 100mcg/ml. Provided as 10mg/cc.
Method 1: dilute 10mg (1cc) into 100cc of .9%saline.
Method 2: 10mg into 9cc saline/water.
Take 1 cc of this mixture (1mg/cc)
And add to another 9cc of saline/water.
Final concentration is .1mg (100mcg)/cc.
Usually see increase in BP, SVR with a decrease in HR.
Ephedrine: Indirect acting sympathomimetic that increases release of NE. has both and effects
(mainly 1 effects). Making: Standard concentration is 5mg/ml. Provided as
50mg/cc. Dilute 1cc (50mg) into 9cc water/saline) final concentration 5mg/ml.
Usually see a increase in BP,HR, SVR
Dopamine: Dose dependant effects. Dopamine at doses of 1-3 mcg/kg/min predominately have
renal effects. Doses of 3-10 mcg/kg/min have more effects (increased contractility)
with only modest increases in blood pressure and pulse. Doses of 10-20mcg/kg min.
Increase BP/pulse. Doses over 20mcg/kg/min have predominately effects.
Norepinephrine: Is an endogenous catecholamine/neurotransmitter with and effects. Increases
SVR. More than .
Epinephrine: Is an endogenous catecholamine with and effects, with more effects on increased
contractility and heart rate, with modest increase in blood pressure. Also has effect on
metabolism effects stimulate lipolysis and liver glycogenolysis and effects inhibit
insulin release; resulting in hyperglycemia. Used with local anesthetics to decrease
absorption of the anesthetic by vasoconstriction. Also used to treat anaphylaxis and
anaphylactoid reactions. Racemic epinephrine used as a nebulized medication to treat
stridor cause by upper airway swelling.
Nitroglycerine: Venodilatation >arteriolar dilatation. Reduces myocardial oxygen consumption.
Nitroprusside: Similar to Nitroglycerine in peripheral dilatation, but has more arterial dilatation than
nitroglycerine. Thiocyanate and cyanide toxicity are possible with high dose infusions
and prolonged use of nitroprusside.
Labetalol: Selective 1 and nonselective receptor antagonists. Less likely to have
bronchospasm than with other nonselective antagonists. Dose is usually 5-10mg
initially. Usually see decrease BP, HR
Esmolol: Selective 1 antagonists.
Dose is usually between 10-30mg initially.
Usually see decrease HR, with some decrease in BP.
Catecholamines MAP HR CO SVR RBF Cardiac
dysrhythmias
Dopamine + + +++ + +++ +
Norepinephrine +++ - - +++ --- +
Epinephrine + ++ ++ ++ -- +++
Dobutamine + + +++ - ++ -
In the OR Events:
I. Preop evaluation / Events
a. Chart review/interview the night before
b. Meet patient in holding prior to surgery
c. Discuss Anesthesia plan with patient
d. Start IV
e. Sedation after patient has been seen by OR nurse and Staff
f. Blocks before surgery
II. OR
a. Assist patient to the OR table
b. Place standard monitors
c. Preoxygenation
d. Induction
e. Mask airway
f. Airway
g. Protect eyes
h. Other monitors
i. Positioning
j. Protection of pressure points
III. End of Case/Emergence/Recovery
a. Return of TOF
b. Reversal of Muscle Relaxation if necessary
c. Antiemetics
d. Spontaneous Ventilation
e. Pain control
f. Extubation
g. Transport to Recovery with Oxygen and monitors
h. Report in Recovery and post op orders
IV. PACU
a. Airway
b. Breathing
c. Circulation
d. Pain control
e. Urine output
Keys for Tables:
MAP=mean arterial pressure
SBP=systolic blood pressure
CBF=cerebral blood flow
ICP=intracranial pressure
SVR=systemic vascular resistance
CO=cardiac output
RBF=renal blood flow
PaCo2=partial pressure arterial carbon dioxide
TV=tidal volume
CMRO=cerebral metabolic rate
RR=respiratory rate
GFR=glomerular filtration rate
You might also like
- Cardiac TranspDocument30 pagesCardiac TranspShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Essential MeditationDocument61 pagesEssential MeditationShaz Chindhy100% (2)
- Cong HeartDocument7 pagesCong HeartShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Me 1Document74 pagesMe 1Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Cushings SyndromeDocument12 pagesCushings SyndromeEligius UsiNo ratings yet
- Pericardial Disease: Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1Document5 pagesPericardial Disease: Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- ACCP Board Review 21st EditionDocument491 pagesACCP Board Review 21st Editionphathands_311721694100% (2)
- Step CSDocument20 pagesStep CSShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Admit Card 11Document5 pagesAdmit Card 11Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Ventilation PDFDocument8 pagesBasic Mechanical Ventilation PDFPabloIgLopezNo ratings yet
- 110 Questions UCSF Students Were Asked in A Residency Interview PDFDocument3 pages110 Questions UCSF Students Were Asked in A Residency Interview PDFShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Lac+Usc Internal Medicine Residency Survival Guide 2013-2014Document226 pagesLac+Usc Internal Medicine Residency Survival Guide 2013-2014Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- AC SaDocument1 pageAC SaShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Housestaff Survival GuideDocument61 pagesInternal Medicine Housestaff Survival Guidesgod34No ratings yet
- MediDocument63 pagesMediShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- M3 Resources List for Surgery, PCC, Medicine & MoreDocument2 pagesM3 Resources List for Surgery, PCC, Medicine & MoreShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Improving Your Residency Interview Skills 2009Document24 pagesImproving Your Residency Interview Skills 2009Ram60% (5)
- Admit Card 1Document5 pagesAdmit Card 1Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- I. Definition/General Consideration: Acute Asthma ExacerbationDocument2 pagesI. Definition/General Consideration: Acute Asthma ExacerbationShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Antimicrobial GuideDocument89 pagesMicrobiology Antimicrobial GuideShaz Chindhy100% (1)
- 3Document7 pages3Shaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- IMDocument128 pagesIMShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- I. Definition/General Considerations: Colon CancerDocument2 pagesI. Definition/General Considerations: Colon CancerShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Learning ObjDocument2 pagesEndocrine Learning ObjShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Improving Your Residency Interview Skills 2009Document24 pagesImproving Your Residency Interview Skills 2009Ram60% (5)
- Alcohol counseling + drug combo best for dependence vs abuseDocument4 pagesAlcohol counseling + drug combo best for dependence vs abuseShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Common SymptsDocument7 pagesCommon SymptsShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- All of Medicine FlashcardsDocument142 pagesAll of Medicine FlashcardsShaz Chindhy100% (2)
- Christopher Kol's Guide to Third Year ClerkshipsDocument10 pagesChristopher Kol's Guide to Third Year ClerkshipsShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- GIDocument44 pagesGIShaz ChindhyNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- MAX Carter: Plus Daddy Issues XXL Bear Pride Hiv Self TestingDocument48 pagesMAX Carter: Plus Daddy Issues XXL Bear Pride Hiv Self TestingShane Erasmus50% (22)
- Emotional Neglect Complex PTSDDocument11 pagesEmotional Neglect Complex PTSDtheplatinumlife736493% (14)
- NABH Newsletter - Sept 2021Document73 pagesNABH Newsletter - Sept 2021rpohamrclehNo ratings yet
- SMA Bahasa Inggris 2012Document12 pagesSMA Bahasa Inggris 2012soe_barn64No ratings yet
- Mouth Breathing and Facial Morphological PatternDocument6 pagesMouth Breathing and Facial Morphological PatternAlejandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis PDFDocument1 pageUrinalysis PDFPT Mirielle MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Perforation 2Document6 pagesGastrointestinal Perforation 2shat bidNo ratings yet
- Research Papers Clinical Governance Leads Roles and Responsibilities PDFDocument6 pagesResearch Papers Clinical Governance Leads Roles and Responsibilities PDFYuli FitriantiNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 6 - On of Vitamin B Complex Skin TestingDocument2 pagesExercise No 6 - On of Vitamin B Complex Skin TestingpharmaebooksNo ratings yet
- ANS - Toxic Syndromes PDFDocument74 pagesANS - Toxic Syndromes PDFARNo ratings yet
- Human Insulin Immunoassay Procedure ManualDocument13 pagesHuman Insulin Immunoassay Procedure ManualRajeev PareekNo ratings yet
- Courses That Count For WGS Credit - Studies of Women, Gender, and SexualityDocument3 pagesCourses That Count For WGS Credit - Studies of Women, Gender, and SexualityganiesoktavianaNo ratings yet
- 457 Fact Sheet - Chef (Commercial Cookery)Document5 pages457 Fact Sheet - Chef (Commercial Cookery)Kemal Adhi Pradana100% (1)
- Blood Products For Transfusion WorksheetDocument2 pagesBlood Products For Transfusion Worksheetlexie irvinNo ratings yet
- Training Methods ReviewDocument10 pagesTraining Methods ReviewIhsan LashleyNo ratings yet
- Nurses Progress NotesDocument2 pagesNurses Progress NotesCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Role of Drugs in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument239 pagesRole of Drugs in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Approach To Nasal Tip Shaping: The Five-Suture TechniqueDocument5 pagesA Simplified Approach To Nasal Tip Shaping: The Five-Suture TechniqueroyvillafrancaNo ratings yet
- 22145Document3 pages22145adolphoparaNo ratings yet
- World Energy Outlook Special Report 2016 Energyand Air PollutionDocument266 pagesWorld Energy Outlook Special Report 2016 Energyand Air PollutionCarlosNo ratings yet
- Diesel Free Ebook Auto RegulationDocument15 pagesDiesel Free Ebook Auto RegulationFrank_the_Tank100% (1)
- Ey Making Quality Cancer Care More Accessible and Affordable in IndiaDocument160 pagesEy Making Quality Cancer Care More Accessible and Affordable in Indiaabhiyan0008494No ratings yet
- Mikroba Saluran PencernaanDocument70 pagesMikroba Saluran PencernaanAde Yurga TonaraNo ratings yet
- What A Palanca Means To This Doctor - Ronibats - PHDocument16 pagesWhat A Palanca Means To This Doctor - Ronibats - PHsteth16No ratings yet
- Acl InjuriesDocument2 pagesAcl InjuriesFrnz RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1-Evidence Based Midwifery Care PDFDocument11 pages1-Evidence Based Midwifery Care PDFsinarNo ratings yet
- s41598 018 35903 5Document9 pagess41598 018 35903 5leartaNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Approval FrameworkDocument85 pagesRegulatory Approval FrameworkAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Enzymes Acquires 70% Stake in API Maker JC Biotech (Company Update)Document2 pagesAdvanced Enzymes Acquires 70% Stake in API Maker JC Biotech (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Compassion FatigueDocument14 pagesCompassion Fatigueapi-331878226No ratings yet