Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adverbial Clauses (Reparado)
Uploaded by
Magalí Serri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views9 pagesAdverbial Clauses (Reparado)
Uploaded by
Magalí SerriCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
1
Type: Adverbial clause
of
Subordinators Functioning as..
1) Time
Time AFTER: after - once since - when -
whenever now (that) - as soon as immediately
(that) directly (that) The moment/minute (that)
Time BEFORE: before by the time that till until
SAME Time: as when whenever as long as
so long as while whilst now (that)
To inf: outcome of a situation (time+result) Final
Verbless: only introduced by: as soon as, once, till,
until -- when , whenever, while, whilst + prep ph
Initial or Final Position
Most of them are
Sentence Adjunct
BUT unless, as long as,
so long as are
Predication Adjunct;
BUT when
(time+concession),
now that
(time+reason), no
sooner than are
Content Disjunct.
2) Place
Where (specific) wherever (non-specific)
Remember place+contrast: When a did this, b did
that.
Archaic forms: whence (from where) whither (to
where).
When Initial position is
Sentence Adjunct,
when Final position
Predication Adjunct.
3) Direct Condition
Conditional
clauses in
general may
have S-OP
inversion without
a subordinator if
the operator is:
WERE-SHOULD-
HAD.
As long as, provided (that), providing (that), so long
as: mean if and only if, condition+exception:
Content Disjunct.
Assuming that, given that, if, in case, in the event
that, just so (that), on condition that, supposing
that.
Unless: except if (a menos que).
Only if: a will not happen unless b happens.
In case: the meaning is different according to:
BrE means: if it should happen that.
AmE means: on condition that.
Non-finite: if, unless.
Verbless: if, unless, with, without.
Verbless and ed participle clauses with exp. Subj.
Are introduced with with/without.
Mainly Initial position
and Sentence Adjunct.
2
4) Indirect
Condition
Condition not related to the situation in the matrix
clause.
In case: (si acaso)
Initial or Final position.
Style Disjunct.
5) Concession
(Says the contrary of what one might expect).
Although, though, when, whereas, while,
If can be replaced by
Although
Formal style:
Subordinator THOUGH, the predication or C.S. may
be fronted.
Subordinator AS, the predication or C.S. must be
fronted.
Subordinator THAT, the C.S. must be fronted.
Subordinator MUCH AS to talk about a strong
feeling or desire.
Non-finite: although, though, while, whilst.
Initial position as a
tendency. Content
Disjunct.
6) Condition and
concession
Finite: even if, even though (if: when it means even
if, even though).
6.1. Alternative (uno o el otro) conditional
concessive clauses:
Whether or (whether), it doesnt matter whether
(initial), no matter whether
Verbless: with... or without... NP or (no) NP.
6.2. Universal ( Indicate a free choice from any
number of conditions) conditional concessive
clauses
-WH words combined with EVER. The
subordinator (a rel pron or adv) has a function and
must have initial position.
No matter+WH element.
Sentence Adjunct.
Initial or Final position
Sentence Adjunct
Initial position
7) Contrast
Convey a contrast bet 2 situations and compares
them when dissimilar to show differences.
Whereas, while, whilst
Initial as a tendency or
Final position. Content
Disjunct
3
8) Contingency
(Siempre que)
Denote habitual contingency expressed in clauses
of:
Time: whenever, once.
Place: wherever.
Condition: if+past participle.
Non-finite: -ing or ed part.
Verbless: once+adj.
Adj ph
Initial position.
Sentence Adjunct.
9) Exception
Except that, excepting that, except: solo que, si no
fuera porque.
Except for the fact that, apart from the fact that.
Save that, but for (both formal): sub. Cl. take
obligatory should.
Non-finite: to inf, -ing part
But for (a no ser porque, a menos que)
Final position. Content
Disjunct.
10) Reason:
a- Direct
b- Indirect
A- Direct reason:
1. Because, because of +NPh.
2. Because, since.
3. For
4. Circumstances and consequence:
premise in the sub, conclusion in the
matrix. Used to say why a statement
you just have said is true.
5. As: predication/C.S. may be optionally
fronted.
6. In case: introduces a possibility against
which a precaution is needed in
advance, which is the reason why sth
else is done. (Por si, caso que).
7. In that: reason+point of view.
Final position.
Predication Adjunct.
Initial position. Cont
Disjunct/Sent Adjunct
Final position. Content
Disjunct.
Content Disjunct.
Final position.
Predication Adjunct.
Predication Adjunct.
4
8. That: the matrix is normally a neg
exclamation or a rhetorical quest. C.S.
obligatory fronted.
9. While: time+reason.
Non-finite: -ing part & to infinitive.
If only: (aunque ms no sea para) to introduce that
what you think is a fairly good reason for doing sth.
It means roughly: even if the only reason is.
Verbless: subordinate introduced by WITH to
mention only one circumstance or WHAT WITH
(Entre una cosa y la otra) to mention one or more
circumstances of an unspecified set.
B- Indirect reason:
The reason not related to the situation in the
matrix, but a motivation for the implicit speech act
of the utterance to explain how is that you come
to know sth.
As, as long as
Because, For
Since
Content Disjunct.
Content Disjunct.
Content Disjunct.
Initial position.
Final position.
Initial or Final position.
11) Circumstance
(Reason given in
certain
circumstances, in
certain
occasions; not at
any time. El
hablante le da
matiz de
circunstancia,
una situacin
determinada).
Express reason + fulfilled condition (contains a
premise in the sub cl. and a conclusion drawn for it
in the matrix.
As, as long as, seeing that (formal informal usage).
Since introducing a particular situation.
Inasmuch (formal): por cuanto. (In the degree that,
in view of the fact that). Used to introduce a clause
in which you mention sth relevant to the truth of
the preceding or following statement, e.g. sth that
gives a reason for it.
Now that: (ahora que) reason+temporal meaning.
May be used to indicate simultaneity.
Content Disjunct.
Content Disjunct.
Content Disjunct.
Initial and Final
position.
Content Disjunct.
12) Purpose
The result is yet to be achieved. Therefore they
generally take a modal.
Final position.
Sentence Adjunct.
5
Finite:
These clauses introduce a negative purpose and
therefore take non-assertive form (para que no).
For fear that, in case, in order that... not, lest.
She turned her face, lest he should see her tears.
If+ be (going) to: If I am to be there on time, Id
better leave at once.
In order that
So (that): Go quietly so no one can hear you.
That: He eats that he may live. (Come para vivir.)
Non-finite:
To infinitive - with subordinators: in order (not), so
as (not)
-without subordinators
Both can have their expressed subject of the to inf
introduced by FOR.
13) Result
Factual. The result is achieved.
Finite:
So that
So (formal)
Such that: result+manner (de modo tal que)
That
Until: result+time
Non-finite: -ing participle (and). He died, leaving 3
fatherless children.
Content Disjunct.
14) Manner -
Similarity
When the verb is dynamic theres a blend with
manner.
Finite:
As: in a way that is similar to the way that.
The sub can be intensified by just & exactly.
When the clause is in Final or Mid position, there is
S-Op Inversion. He was a lawyer, as were several of
his brothers.
Initial or Final position.
Predication Adjunct.
Sentence Adjunct.
Can be obligatory
Predication Adjunct: It
was just as I imagined
it would be.
Makes it obligatory.
6
As... so+matrix in literary style. The Cl. can express
an analogy.
How: Do it how I tell you.
Like: inf AmE.
In (the-any) way (that): free syntactic
constructions. (In such a way that).
Non-finite: -ed part introduced by As.
-ing part.
Verbless: He sauntered down the lane, (with) his
hands in his pockets.
15) Comparison
Finite:
As if, as though
Like (inf. AmE)
If the comparison is factual, the verbs in the
comparison follow the normal rules of temporal
reference and are indicative. (Cuando el tiempo se
mantiene son factual: pr+pr, past+past).
If the comp is hypothetical (lack of reality) a
subjunctive or hypothetical past may be used as an
alternative. (pr+past, el tiempo cambia).
Non-finite: to-inf., -ing part, -ed part
As if, As though
Verbless: As if, As though.
She shivered as though with cold.
Final position.
Predication Adjunct.
16) Proportion
Cl. involves a kind of comparison: proportionality
or equivalence of a tendency or degree bet 2
situations.
Finite: As...so (matrix cl.) formal
The+comp... the+comp. The sub is the 1
st
one.
The more she thought about it, the worse she felt.
Non-finite: The+comp... the+comp. The sub is the
1
st
one.
The less said about that, the happier I will be.
Initial or Final position.
Sentence Adjunct.
7
Verbless: The+comp... the+comp. The sub is the 1
st
one.
The simpler the business, the better off you are.
17) Extent or degree
Inasmuch as: formal,(en tanto y en cuanto hasta
donde).
Insofar as
Insofar that: formal, rare.
These subord are used to introduce a clause in
which you mention sth that is relevant to the truth
of the preceding or following statement, for
example sth that gives extent.
Only to the extent that.
Initial or Final position.
Sentence Adjunct.
18) Preference
The matrix expresses the preference.
The sub expresses the rejected alternative.
Non-finite: The y are usually non-finite bare inf.
With or without expressed subject.
Rather than + bare infinitive.
Sooner than
A preposition meaning instead of.
Finite: rare and formal, with obligatory should.
Rather than she should feel lonely, her friends
arranged to take her with them on the trip.
Before: They would starve before they would
surrender unconditionally.
Initial or Final position.
Sentence Adjunct.
COMMENT CLAUSES
Can be Initial or Final
position.
Types:
A- Like the matrix of the main clause:
contains a transitive verb or adjective
which elsewhere is followed by a that-
clause as complementation.
He never actually took the money, I
believe.
I believe that he... (Comment cl. + that-cl.)
B- Introduced by As: like an adv finite cl.
I am a good writer, as you know.
Style Disjunct.
Style Disjunct.
8
C- Introduced by What: like a nom-rel cl.
Whats more, weve lost all our belongings.
What is even more remarkable, ...
D- Like a to-infinitive Cl.:
I dont know what to do, to be honest.
E- Like an ing-part Cl.:
Putting it at its lowest terms, it has little
market value.
F- Like an ed part. Cl.:
Stated bluntly, he had no chance of
winning.
Conjunct.
Style Disjunct.
Style Disjunct.
Style Disjunct.
SENTENTIAL RELATIVE
CLAUSES
- They modify the whole clause, and are like
a comment of the matrix in which the
writer/speaker shows an opinion but still
refers to what it is said in the matrix.
ALWAYS introduced by a WH
pronoun/adverb (element).
Content Disjunct.
ADJECTIVE VERBLESS
CLAUSES
- The Cl. refers to an attribute of the subject.
(Clauses realised by adjective phrases).
- The clause is mobile. (I-M-E position).
- Its implied subj. is the subj. of the matrix,
unless the clause contains additional clause
constituents, and therefore the clause can
be related to a NPh other than the subj.
Attribute of the subject
Anxious for a quick decision, the chairman called
for a vote.
implied subject
She glanced with disgust at the cat, now quiet in
her daughters lap.
implied subject
Attribute of the
object
- The implied subj. can be the whole of the
matrix clause.
Strange, it was she who initiated divorce
proceedings.
Modifier of the
subject of the matrix.
COMPARATIVE CLAUSES
A proposition expressed in the matrix is compared
with a proposition expressed in the subordinate.
9
Las Comparative Clauses
tienen que ser FINITE
para que sean clauses,
sino son prepositional
phrase.
Comparative Element: COMP element: the clause
element that specifies the standard of comparison
and is the hinge (nexo) bet the matrix and the
Comparative Clause.
Basis of comparison expressed in the Comparative
Cl.
The Comparative Cl. is the complement to the
Comparative element.
Comparative Clauses of:
a- Equivalence:
- as... as ...
- Not so/as... as ...
b- Of Non-equivalence:
- To a higher degree: more / -er... than ...
- To a lower degree: less/ -er... than ...
c- Of Sufficiency: enough... to infinitive
d- Of Excess: too... to infinitive
COMPARATIVE CLAUSES
OF DEGREE AND RESULT
Introduce constructions that combine the notion of
sufficiency or excess with that of result. They
express a high degree in the matrix and the
subordinate clause conveys a notion of result.
Degree in the matrix, result in the subordinate.
SO: adverb premodifier of an adverb or adjective.
SUCH: predeterminer.
SUCH + a + noun... that ...
SO + adj./verb... that ...
Non-finite:
SUCH + (as) to-infinitive
SO
He was such a fool to doubt you.
You might also like
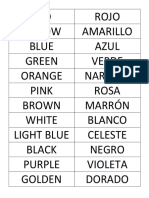
- Lista de Verbos para Present PerfectDocument1 pageLista de Verbos para Present PerfectMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
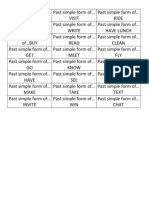
- Past Simple IrregularDocument3 pagesPast Simple IrregularSkye LucionNo ratings yet
- Ejercitación - Módulo 1 Clase 4Document7 pagesEjercitación - Módulo 1 Clase 4Magalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Technical English - Ejercitación - Módulo - 1 - Clase - 1Document5 pagesTechnical English - Ejercitación - Módulo - 1 - Clase - 1Magalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Short Long and Irregular AdjectivesDocument2 pagesShort Long and Irregular AdjectivesMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect With Just (LISTENING)Document1 pagePresent Perfect With Just (LISTENING)Magalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Test On QuantifiersDocument1 pageTest On Quantifiersmilenerato2240No ratings yet
- The PluralsDocument2 pagesThe PluralsMagalí Serri0% (1)
- Back To School Plurals Grade 3Document1 pageBack To School Plurals Grade 3Magalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense ExplainedDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Tense ExplainedJae ClefNo ratings yet
- Plural+ HomeworkDocument3 pagesPlural+ HomeworkliesbethelbersNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Irregular VerbsDocument2 pages1.1 - Irregular VerbsMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Some, Any, No: A - Circle The Correct WordDocument2 pagesSome, Any, No: A - Circle The Correct WordMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Travel and TransportDocument5 pagesTravel and TransportMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - First DayDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - First DayMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 Past Simple Present Perfect Simple and ContDocument2 pagesTEST 1 Past Simple Present Perfect Simple and ContMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - First DayDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - First DayMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- 2 - When My Dad Was A Teenager - March 15Document2 pages2 - When My Dad Was A Teenager - March 15Magalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Water in Florida - Level 2: Flooding Affect FleeDocument2 pagesRadioactive Water in Florida - Level 2: Flooding Affect FleeMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- RevisiónDocument2 pagesRevisiónMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Colours BOARD GAMEDocument2 pagesColours BOARD GAMEMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- 1 - GAME First ClassDocument3 pages1 - GAME First ClassMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - First DayDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - First DayMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Verb (Base Form) Spanish Translation Past SimpleDocument3 pagesVerb (Base Form) Spanish Translation Past SimpleMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- A Pizza ReadingDocument2 pagesA Pizza Readingfernando50% (2)
- RevisiónDocument2 pagesRevisiónMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Water in Florida - Level 2: Flooding Affect FleeDocument2 pagesRadioactive Water in Florida - Level 2: Flooding Affect FleeMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Geographical Features For The TestDocument1 pageGeographical Features For The TestMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Verb (Base Form) Spanish Translation Past SimpleDocument3 pagesVerb (Base Form) Spanish Translation Past SimpleMagalí SerriNo ratings yet
- Preposiciones de Lugar - Practice PDFDocument3 pagesPreposiciones de Lugar - Practice PDFMagalí Serri0% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Present PerfectDocument2 pagesPresent Perfectcesar barreraNo ratings yet
- French Prepositions With Countries Continents US StatesDocument13 pagesFrench Prepositions With Countries Continents US StatesTeluguvilan HaHaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document80 pagesLecture 11MisAlNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Indefinite Pronouns Aug 16Document4 pagesLesson Plan - Indefinite Pronouns Aug 16aria jen05100% (2)
- Friends New Year's ResolutionsDocument5 pagesFriends New Year's Resolutionsleo2009No ratings yet
- ENGLISH IV - STUDENT - S TEXTBOOK Ultima VersionDocument84 pagesENGLISH IV - STUDENT - S TEXTBOOK Ultima VersionDaniel José JiménezNo ratings yet
- Level of Competency in Subject-Verb Agreement Among 4Th Year Bsed Students in Gov. Alfonso D. Tan CollegeDocument7 pagesLevel of Competency in Subject-Verb Agreement Among 4Th Year Bsed Students in Gov. Alfonso D. Tan CollegeMem ReecsNo ratings yet
- OEGCA AnswersDocument17 pagesOEGCA AnswersCatrava ThomasNo ratings yet
- Technology Work Buddies British English Teacher Ver2Document7 pagesTechnology Work Buddies British English Teacher Ver2Fernanda SilvaNo ratings yet
- Bài tập To-infinitive và Bare infinitive tiếng Anh lớp 11Document7 pagesBài tập To-infinitive và Bare infinitive tiếng Anh lớp 11ellisj152No ratings yet
- Skills 2nd Prep 2023 ShaarawyDocument48 pagesSkills 2nd Prep 2023 ShaarawyMaster TarekNo ratings yet
- Four Corners Students Book4 Scope and Sequence PDFDocument4 pagesFour Corners Students Book4 Scope and Sequence PDFStephen Albán100% (1)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesPurposive CommunicationASTRA FAYE QUEENA DELENANo ratings yet
- Giao An BD HSG Anh 9 HaymiencheDocument112 pagesGiao An BD HSG Anh 9 Haymienchethethanh0402No ratings yet
- Simple, Compound, and Complex Sentences inDocument14 pagesSimple, Compound, and Complex Sentences inMul Yadi100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Literature AutosavedDocument20 pagesLesson Plan in Literature AutosavedArlene Caguicla100% (7)
- Types of Nouns Explained in DetailDocument3 pagesTypes of Nouns Explained in DetailRajgopal IyerNo ratings yet
- Extra English Lesson: Class 12KTC & 12VPCDocument76 pagesExtra English Lesson: Class 12KTC & 12VPChoangtuan14102412No ratings yet
- Open Mind Elementary Unit 02 Grammar 2Document12 pagesOpen Mind Elementary Unit 02 Grammar 2khatuna sharashidzeNo ratings yet
- Zadnja Priprema Za DRUGI Reading Test 1abcDocument14 pagesZadnja Priprema Za DRUGI Reading Test 1abcLana GrujićNo ratings yet
- Learn Shona - FSI Basic CourseDocument536 pagesLearn Shona - FSI Basic Course101_languages100% (1)
- Classroom English activities for secondary studentsDocument3 pagesClassroom English activities for secondary students14 Alan Eduardo Gamboa RojasNo ratings yet
- Answer - Unit - 4 - Understanding and Using English Grammar. Teacher's Guide - 2017 5th - 285pDocument1 pageAnswer - Unit - 4 - Understanding and Using English Grammar. Teacher's Guide - 2017 5th - 285pjsantos7012No ratings yet
- Rules and Examples of Spotting ErrorsDocument3 pagesRules and Examples of Spotting ErrorsRohan MishraNo ratings yet
- Grammar Year 6 KSSR ENGLISH 2015Document17 pagesGrammar Year 6 KSSR ENGLISH 2015theTulipBiruNo ratings yet
- 2 Paquete Present SimpleDocument36 pages2 Paquete Present SimpleJHONATAN FRANCO MARULANDANo ratings yet
- Greek: An Intensive CourseDocument5 pagesGreek: An Intensive CourseAdrianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Modality, Scope and Quantification - Word MapDocument1 pageChapter 7 - Modality, Scope and Quantification - Word MapareszNo ratings yet
- Using The Hans-Wehr: For Form I Patterns & Verbal NounsDocument9 pagesUsing The Hans-Wehr: For Form I Patterns & Verbal NounsRipanKOENo ratings yet
- Một Số Cấu Trúc Viết Lại CâuDocument5 pagesMột Số Cấu Trúc Viết Lại CâuAnhThư Cao100% (1)