Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Form 5 Lesson 25 Structure
Uploaded by
alvin2282Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 5 Lesson 25 Structure
Uploaded by
alvin2282Copyright:
Available Formats
OMEGA TUITION CENTRE
Students name : ____________________________________ Teachers Name : Mr Chew Chin Kuen
Subject : Chemistry Form 5 Class Attend : 5 Chemistry 7
Chapter 3 : oxidation & reduction lesson 26 (26 june 2010) 4.45 6.45 pm
Chemical energy to electrical energy
Chemical / Daniel / Voltaic cell
Chemical energy to electrical energy
Oxidation
Zn Zn
2+
+ 2 e
Silver electrode. As it has a lower position than zinc in electrochemical series
Silvery solid is deposited at silver electrode
Zn + 2 Ag
+
Zn
2+
+ 2 Ag
Barium chloride, when mixed with silver nitrate, will form white precipitate
(g) Write an overall equation for the reaction above
.
[1 mark]
2.
Oxidizing agent
+ 4 0
oxidation
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e-
Using potassium hexacyanoferrate (II). Form a deep blue solution /
Using potassium hexacyanoferrate (III). Form a red blood solution
Green solution turns brown
Yellow precipitate formed
4 Fe
2+
+ SO
2
+ 4 H
+
4 Fe
3+
+ 2 H
2
O + S
Acidified potassium manganate (VII) / acidified potassium dichromate (VI) / bromine water
3.
The presence of hydroxide ion, OH
-
.
The presence of iron (II) ion, Fe
2+
Fe Fe
2+
+ 2 e-
Chemical energy to electrical energy
To prevent excess amount of water in the nail
Metal Y is corroded first before iron nail
Metal Y is more electropositive than iron
Metal Y corroded
X : lead / copper / tin Y : magnesium / aluminium
Q : anodisation R : sacrificial
[3 marks]
4.
Potassium chlorate mixed with manganese (IV) oxide
oxidation
Metal will be oxidized to form metal oxide
Zinc
A , C , B
B is the most electropositive metal
Element B O
Mass 4.8 g 3.2 g
Mol 4.8 / 24 = 0.2 mol 3.2 / 16 = 0.2
Ratio 0.2 / 0.2 = 1 0.2 / 0.2 = 1
Empirical formula = BO
5.
Zinc
Carbon rod I
Dark purplish solid is gathered at anode
2 I
-
I
2
+ 2 e-
Electrode B must have higher position in electrochemical series than A
Metal A is deposited at electrode A
Electrode B is corroded
2 B + A
2+
2 B
+
+ A
A : copper / lead / zinc etc. B : sodium / potassium
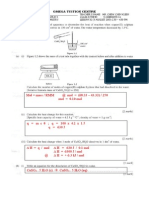
6. Four strips of metals (manganese, cobalt, tin and zinc) are taken and each is dipped into separate
beakers containing aqueous solution of 1 mol dm
Two of the metals, M
A
and M
B
, together with their respective solutions of ions are connected as shown in
Figure 2. The voltmeter reading is noted. The experiment is repeated using different combinations of
metals and ion solutions. The results obtained are shown below.
Experiment M
A
M
B
1 Tin manganese
2 Cobalt Zinc
3 Cobalt manganese
4 Tin Cobalt
(a) (i) What is the function of the salt bridge?
.
(ii) Name a suitable substance for use in the salt bridge.
(b) State the main energy change that take place in the above experiments.
....
(c) Given that tin is the most unreactive metal, arrange the four metals in order of
reactivity.
(d) i. Write oxidation reaction in experiment 2
....
(e) Experiment 3 is repeated without the voltmeter, i.e. the two metals are connected directly by a
piece of wire. In which direction is the electron flow in the connecting wire in
(f) Calculate the e.m.f. value in Experiment 4.
To complete the chemical cell and to separate between the 2 electrolytes.
Potassium chloride / sodium chloride
Chemical energy to electrical energy
Tin, cobalt , zinc , manganese
Zn Zn
2+
+ 2 e
-
From manganese to cobalt
Tin / cobalt = Tin / manganese
= 1.05 0.45
= 0.60 V
Four strips of metals (manganese, cobalt, tin and zinc) are taken and each is dipped into separate
beakers containing aqueous solution of 1 mol dm
-3
divalent ions of their respective metal.
, together with their respective solutions of ions are connected as shown in
Figure 2. The voltmeter reading is noted. The experiment is repeated using different combinations of
metals and ion solutions. The results obtained are shown below.
Voltmeter reading (V) Negative terminal
manganese 1.05 Manganese
0.55 Zinc
manganese 0.45 manganese
obalt Cobalt
What is the function of the salt bridge?
.
Name a suitable substance for use in the salt bridge.
State the main energy change that take place in the above experiments.
....
Given that tin is the most unreactive metal, arrange the four metals in order of
rite oxidation reaction in experiment 2
....
Experiment 3 is repeated without the voltmeter, i.e. the two metals are connected directly by a
piece of wire. In which direction is the electron flow in the connecting wire in Experiment 3?
Calculate the e.m.f. value in Experiment 4.
To complete the chemical cell and to separate between the 2 electrolytes.
Potassium chloride / sodium chloride
ectrical energy
/ manganese cobalt / manganese
Four strips of metals (manganese, cobalt, tin and zinc) are taken and each is dipped into separate
divalent ions of their respective metal.
, together with their respective solutions of ions are connected as shown in
Figure 2. The voltmeter reading is noted. The experiment is repeated using different combinations of
Negative terminal
Manganese
Zinc
manganese
Cobalt
.
....
decreasing order of
....
Experiment 3 is repeated without the voltmeter, i.e. the two metals are connected directly by a
Experiment 3?
7. Figure 1 shows the set-up of apparatus for investigating the reactivity of metals X, Y and Z with
oxygen. Metals X, Y and Z are heated first before heating the mixture of potassium chlorate and
manganese dioxide. The observations are recorded in table 1.
Metal Observation
X (brown powder) Glows and forms a black powder
Y (grey powder) Burns vigorously.
Residue is yellow when hot and white when cold.
Z (grey powder) Glows brightly and forms a dark brown powder.
Table 1
(a) What is the function of manganese dioxide?
(b) Name a compound that can be used to replace the mixture of potassium chlorate and manganese
dioxide.
(c) State one factor that can affect the results obtained in this experiment.
(d) (i) By using the information in Table 1, arrange the three metals in order of decreasing reactivity.
(ii) Name metal X and metal Y.
(e) 3.36 g of metal Z reacts with oxygen to produce 4.46 g of an oxide of Z. Calculate the empirical
formula of the oxide formed. [Relative atomic mass : Z, 56; O, 16]
(f) Z oxide can be reduced to metal Z by hydrogen. Draw the set-up of apparatus to carry out this
reduction in the laboratory.
To provide oxygen form metal to oxidize
Potassium manganate (VII)
Size of metal / temperature
X , Z , Y
X is copper ; Y is zinc
Element Z O
Mass 3.36 1.12
Mol 3.36 / 56 = 0.06 1.12 / 16 = 0.09
Ratio 0.06 / 0.06 = 1 0.09 / 0.06 = 1.5
Empirical formula = Z
2
O
3
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawDocument2 pages2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' LawHorro8480100% (1)
- Module 5-Grammar Exercises AnswersDocument38 pagesModule 5-Grammar Exercises Answersalvin2282100% (1)
- Everything Maths Grade 11 Trig GraphsDocument3 pagesEverything Maths Grade 11 Trig GraphsAmyNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Kimia K1 K2 K3 Dan Skema (SCAN)Document78 pagesTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Kimia K1 K2 K3 Dan Skema (SCAN)Cikgu Faizal67% (3)
- Quality Audit Checklist FOR ISO 9001:2000Document10 pagesQuality Audit Checklist FOR ISO 9001:2000MAdrianRumayarNo ratings yet
- Definition Series PRE SeminarDocument3 pagesDefinition Series PRE Seminaralvin2282No ratings yet
- Carbon Compound QuizDocument2 pagesCarbon Compound Quizalvin2282No ratings yet
- Revision B - SPM 2014: Time (S) 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 Volume of Oxygen (CM) 0 7 14.5 20.5 26.2 30.5 30.5 30.5Document2 pagesRevision B - SPM 2014: Time (S) 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 Volume of Oxygen (CM) 0 7 14.5 20.5 26.2 30.5 30.5 30.5alvin2282No ratings yet
- Revision Calculation Chemical EqDocument2 pagesRevision Calculation Chemical Eqalvin2282No ratings yet
- Form 5 Lesson 33 Structure Chap 4Document7 pagesForm 5 Lesson 33 Structure Chap 4alvin2282No ratings yet
- Revision e Physis f5Document2 pagesRevision e Physis f5alvin2282No ratings yet
- Revision B - SPM 2014: Time (S) 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 Volume of Oxygen (CM) 0 7 14.5 20.5 26.2 30.5 30.5 30.5Document2 pagesRevision B - SPM 2014: Time (S) 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 Volume of Oxygen (CM) 0 7 14.5 20.5 26.2 30.5 30.5 30.5alvin2282No ratings yet
- SPM 2010 Chemistry Common MistakeDocument4 pagesSPM 2010 Chemistry Common Mistakealvin2282No ratings yet
- English PBSMR Lesson 1Document13 pagesEnglish PBSMR Lesson 1alvin2282No ratings yet
- QUIZ 9-AnsDocument7 pagesQUIZ 9-Ansalvin2282No ratings yet
- English PBSMR Lesson 1Document8 pagesEnglish PBSMR Lesson 1alvin2282No ratings yet
- Quiz DDocument2 pagesQuiz Dalvin2282No ratings yet
- English PBSMR Lesson 1Document13 pagesEnglish PBSMR Lesson 1alvin2282No ratings yet
- Biology Module For Excellence CoverDocument15 pagesBiology Module For Excellence Coveralvin2282No ratings yet
- Grammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms ExplainedDocument3 pagesGrammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms Explainedalvin2282No ratings yet
- English PBSMR Lesson 1Document8 pagesEnglish PBSMR Lesson 1alvin2282No ratings yet
- Grammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms ExplainedDocument3 pagesGrammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms Explainedalvin2282No ratings yet
- QP2 CH 7 ADocument5 pagesQP2 CH 7 Aalvin2282No ratings yet
- English Teaching MatrixDocument1 pageEnglish Teaching Matrixalvin2282No ratings yet
- Grammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms ExplainedDocument3 pagesGrammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms Explainedalvin2282No ratings yet
- Latihan Matematik Tingkatan 2 Chap02 Square, Square Root, Cube and Cube RootDocument3 pagesLatihan Matematik Tingkatan 2 Chap02 Square, Square Root, Cube and Cube RootEzra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Cos MyanmarDocument6 pagesCos Myanmaralvin2282No ratings yet
- HCM-PP TourDocument1 pageHCM-PP Touralvin2282No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andummahputeriNo ratings yet
- Science f5c3Document2 pagesScience f5c3alvin2282No ratings yet
- Lesoon PHI 20188 Lesson NotesDocument77 pagesLesoon PHI 20188 Lesson NotesGlennNo ratings yet
- Las 1-Earth Sci and LifeDocument4 pagesLas 1-Earth Sci and LifeAlria CabugNo ratings yet
- Manual 3322006Document46 pagesManual 3322006mallikapathakNo ratings yet
- Car crushing hydraulic circuit analysisDocument22 pagesCar crushing hydraulic circuit analysisphankhoa83100% (1)
- Table A. Equivalent Length, (L/D) of Valves and Pipe FittingsDocument7 pagesTable A. Equivalent Length, (L/D) of Valves and Pipe Fittingst_i_f_anoNo ratings yet
- Earthing CalculationDocument4 pagesEarthing Calculationanandpurush100% (1)
- GulfSea Diesel GE 40 PDFDocument2 pagesGulfSea Diesel GE 40 PDFObydur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Stage Separation Dynamic Analysis of Upper State PDFDocument18 pagesStage Separation Dynamic Analysis of Upper State PDFandradesosNo ratings yet
- Bidwell 2005Document6 pagesBidwell 2005Arturo GBNo ratings yet
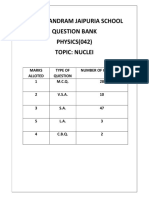
- Nuclei QB XiiDocument23 pagesNuclei QB XiiToshani GuptaNo ratings yet
- ST Johns School QuestionsDocument3 pagesST Johns School QuestionsGOOGLE NETNo ratings yet
- Rabin CryptosystemDocument41 pagesRabin CryptosystemArkadev GhoshNo ratings yet
- Gating System Design GuideDocument11 pagesGating System Design GuideAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- Design and Implementation of Solar Tracking SystemDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Solar Tracking SystemerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Abhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- Mercury Project OverviewDocument18 pagesMercury Project OverviewKageyamaNo ratings yet
- Passive Flow Separation Control Over NACA 63018Document1 pagePassive Flow Separation Control Over NACA 63018miladrakhshaNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem Mech Diploma OdishaDocument14 pages5th Sem Mech Diploma OdishaBIBEKANANDA SAHOONo ratings yet
- Int - Ph.D. Math - SCDocument11 pagesInt - Ph.D. Math - SCapi-26401608No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Heating PDFDocument19 pagesThermodynamics of Heating PDFMatias MuñozNo ratings yet
- BEMO Roof Brochure en 2019Document27 pagesBEMO Roof Brochure en 2019Anonymous wzuyBcNo ratings yet
- AAnalyst 800 Detection Limits-Chromium DataDocument2 pagesAAnalyst 800 Detection Limits-Chromium DataЂорђе РадојичићNo ratings yet
- 4709 Outline f15Document2 pages4709 Outline f15ricedragonNo ratings yet
- Therm6.3 10211 ValidationDocument7 pagesTherm6.3 10211 ValidationJavierNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument39 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterSilhouette DreamNo ratings yet
- Accessible Design LightingDocument8 pagesAccessible Design LightingArch AmiNo ratings yet
- Community Radio User GuideDocument285 pagesCommunity Radio User GuideHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- IAST Lect23 SlidesDocument30 pagesIAST Lect23 SlideskyleNo ratings yet
- EmiDocument6 pagesEmivmktptNo ratings yet