Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IEA Presentation TERM 4 - Spring 2014 - Joe Kim
Uploaded by
jamesjaanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IEA Presentation TERM 4 - Spring 2014 - Joe Kim
Uploaded by
jamesjaanCopyright:
Available Formats
Surviving 4
th
Term
Joe Kim
Grand Marshal
Iota Epsilon Alpha
www.ieasgu.org
This is a compilation from several IEA
members
Everyone has their own opinions
Therefore, take advice with a grain of salt
Adapt it to your own style
Disclaimer!
Helpful Hint
Biggest mistake:
Overloading with resources
Stick with a maximum of 2-3 things
When in doubt, GO BACK TO LECTURE
SLIDES!
Virtually everything they tested was in
the lecture slides!
Pathology What to Study
Lecture notes - #1 priority
Morphology, etiology and pathogenesis 3 most
important
Epidemiology ages for select diseases
Complications
Most commons
Similarities between diseases
Stages of diseases lobar pneumonia, MI, etc.
TNM Staging for Gen Path ONLY!!!
Lab slides:
Images virtually EVERY image on the exam was from lab!
Images from lecture were NOT on our test
Pathoma or Goljian are very helpful
Robbins for clarification
Path Complete for Gen Path
Harry Potter Slides (good for Path Lab)
Rajs Slides:
Very well organized
Combination of lecture slides, lab images, and
Robbins
A LOT of information
Pathology What to Study
Pathology Practice Questions
Robbins Review:
Great vignettes but easier questions
WebPath by Utahs Med School:
Similar to Robbins Review
UWorld and USMLERx questions:
Great vignettes and Step 1 prep
Do after Gen Path
Do not know many people who used Pre-Test or BRS
Pathology Lab
Slides
Use Lecture notes / Robbins
Harry Potter is a good resource here!
If you dont put something important in, the tutor will let
you know
Use the brown boxes in Robbins for your morphology
Dont go crazy on epidemiology, treatment or course of
disease
Dont spend too much time preparing slides
< 30 min per slide
KNOW THESE IMAGES FOR THE EXAMS
Pathology - Extra Work
Concept Maps
Just get something in: no need for a masterpiece
Draw it by hand, and spend no more than 15 minutes
If its not good enough, they will allow you to redo it
CPCs
Dont let these bog you down
Doesnt need to be much greater than a page long
Dont spend too much time on them.
Just try to be able to contribute to the group discussion
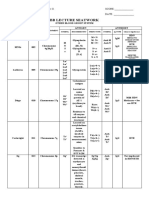
Identify
Peripheral blood smear
Morphology
RBCs: Spherical shape, lack central zone of pallor
Leukocyte
Platelet
Disease
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Etiology
Inherited defect in RBC cytoskeleton proteins
Commonly autosomal dominant trait, 25% have more serious autosomal recessive form
Lack of membrane stability allows loss of membrane fragments while retaining volume,
becomes spherical
Pathogenesis
Limited deformability in spheroid shape
Sequestration and destruction in spleen, congestion of cords of bilroth = splenomegaly
Increased RBC destruction leads to anemia
Hyperplasia of marrow red cell progenitors, increase in RBC production, reticulocytosis
Structural
Changes
Abnormality in proteins that make up mesh like suportive structure.
Autosomal dominant: defect in ankyrin
Autosomal recessive: defect in spectrin
Other Sites
& Diseases
Hemolytic anemias, sickle cell anemia
Signs and
Symptoms
Anemia, splenomegaly, jaundice
Investigation
RBCs show increased osmotic fragility in hypotonic salt solution
Peripheral blood smear
Course
Risk of aplastic crisis, B19 Parvovirus infection
Hemosiderosis
Highlights
Hereditary disease affecting mesh like supportive skeleton
Spherical shape and corresponding loss of flexibility, increased destruction and anemia
See Robbins: Pg _424
Module Heme Slide 4 Group 34 Not Revised March 2014 Joemama
Vignette: Disco Steve presents to the clinic
saying he has Disco in his blood, but he has
been getting tired more frequently. After a
blood smear you agree that he has disco in his
blood, but the disco balls aren't a good thing.
Q1. What is the cause of pathogenesis?
1)Macrocytic RBC
2)Hypochromic RBC
3)Loss of pliability and flexibility
4)Lack of oxygen transport
The Exams
Virtually all of the information is from lecture slides!!
Exam 1: General Pathology + 2 Systems
General Path: Easier with more 1
st
order questions
They tell you the diagnosis / disease!
DO WELL ON THIS EXAM
Exam 2: Systemic
Probably the most difficult exam I took at SGU
They curved it a LOT, so dont freak out like I did afterwards
They do NOT tell you the diagnosis / disease!
Lots of questions on: etiology, complications, pathogenesis
3
rd
/4
th
+ order questions
Microbiology
Lecture notes - #1 priority
Gram staining and morphology
Gram positive and negative flow charts in First Aid
Enzymes, virulence factors and agars
Epidemiology for pneumonia, meningitis, and STIs
Foods and fomites
Virus classes and morphology (naked vs. enveloped)
Most commons
Keywords and specific differentiating factors
Know the first 2 weeks material very well
Student-made Tables / Charts
Make sure to cross-reference with lecture slides!
Picmonic:
I used it for a couple of bugs.
Some people loved it!
First Aid:
Very organized and has good charts
What not to study:
Specific treatment for specific microbes (but know them for Gen micro)
If they only mention the bug once and dont give specifics about it, dont spend
time memorizing it.
Microbiology
Article quizzes:
Read through the article twice making highlights of what you
think is testable, then study your highlights
Reading comprehension test
Small Groups:
Prepare so you can discuss
Is luck on your side?
10 points was full credit.
15 points if the tutor was impressed.
It really depended on the tutor
Be warned... they might change it(?)
Microbiology
It is possible to get an A
CPD
CPD
Do NOT underestimate this class.
Written test:
Random facts (not even the bolded facts) from
the lab manual and lecture slides
Start reading the lab manual, or else youll end
up cramming hundred of pages of information
Practical / OSCE:
Ashleys Amazing Notes annotate it!
Practice!!
If your brain is fried, find a partner, go to upper Taylor and
practice!
Inspection is deceivingly difficult
Time yourself for:
History taking! (half your OSCE grade!)
Vitals! (Its harder than it looks!)
WIIPEEPS takes at least 30-40 seconds!
CPD
Quizlet'ers:
http://quizlet.com/misunderkicked
Other resources:
1) Pre- Read POCKET for your weeks chapter Sunday Night (its short guys)
2) Attend Lecture - pay attention annotating up RAJ slides OR taking notes on slides given
3) Go disease by disease getting info from a searchable BIG Robbins - skip diseases not covered in
objectives. Read info in entire section of disease including the most important 'boxes' (Ie search
Sarcoidosis - read that whole section)
4) Use Harry Potter in lab while people are talking - better yet mandate people in your group USE
IT when they make their slides so you dont miss something...HP is a crap shoot some good stuff +
some wtfs
5) Pathoma is 4-5 pages per chapter - why the hell wouldnt you just read the chapter? I did for
some systems, others I didnt....its up to you. Did it help? I felt RAJ + Robbins was better for THIS
class.
6) Saturday should be Review day ... the day you actually learn the material. You got a gist during
the week now you memorize. Id do some Robbins Review and talk over RAJ slides with friends.
Sunday Id hit up Micro and go through any Path questions I could find and again RAJ slides
7) Before EXAM re-read your Pocket Chapters it takes like 3hrs to read for an entire exams worth
of material (dont do the general path chapters just systemic)
An Upper Termer s Advice:
Kick some ass!
Any Questions?
Contact me: jo3kim@gmail.com
Visit: www.ieasgu.org to download
this presentation
You might also like
- OBGYN Student Study GuideDocument39 pagesOBGYN Student Study GuideGoffo13100% (4)
- NBME Sample Questions 2Document4 pagesNBME Sample Questions 2Melissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- NBME Sample Questions 2Document4 pagesNBME Sample Questions 2Melissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Shelf ReviewDocument77 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Shelf ReviewDuke71% (7)
- Installation InstructionsDocument1 pageInstallation InstructionsjamesjaanNo ratings yet
- NBME Sample Questions 2Document4 pagesNBME Sample Questions 2Melissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument6 pagesPulmonary PathologyjamesjaanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument6 pagesPulmonary PathologyjamesjaanNo ratings yet
- Booklists For Fall 2012Document80 pagesBooklists For Fall 2012jamesjaanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Biochemistry of MuscleDocument68 pagesBiochemistry of MuscleWisnu KuncoroNo ratings yet
- Other Blood Group System AssignmentDocument5 pagesOther Blood Group System AssignmentMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 14.2Document6 pagesInheritance 14.2YashodhaNo ratings yet
- Art and DesignDocument3 pagesArt and DesignGabriela SaNo ratings yet
- GOLOBOFF - Refining Phylogenetic AnalysesDocument312 pagesGOLOBOFF - Refining Phylogenetic Analyseskatarine n. norbertinoNo ratings yet
- Chromocult Coliform PDFDocument4 pagesChromocult Coliform PDFAndres GalárragaNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Corn LabDocument25 pagesGenetics of Corn LabScience House100% (2)
- Plants Part 1Document28 pagesPlants Part 1Puneet TatranNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Dry Eye Lactoferrin and Lactobionic Acid: Mini ReviewDocument6 pagesAge-Related Dry Eye Lactoferrin and Lactobionic Acid: Mini ReviewldNo ratings yet
- SedulousDocument2 pagesSedulousZoe RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes: Basis of Causes and Away of PreventionDocument11 pagesType 1 Diabetes: Basis of Causes and Away of PreventionOpenaccess Research paperNo ratings yet
- Lehne's Pharmacology for Nursing Care Test Bank Chapter 1Document3 pagesLehne's Pharmacology for Nursing Care Test Bank Chapter 1Angel Beaudoin-AlfordNo ratings yet
- Integrative AcarologyDocument492 pagesIntegrative AcarologyVasilii90No ratings yet
- BioremediationDocument23 pagesBioremediationDeepak ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- G10 Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesG10 Protein SynthesisChinsyn FeiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Plant Kingdom Through AlgaeDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Plant Kingdom Through AlgaeDivyansha Sharma100% (1)
- Cytogenetic AbnormalitiesDocument48 pagesCytogenetic AbnormalitiesGlomelyn Rose Ortiz TañedoNo ratings yet
- 3 2+chromosomesDocument1 page3 2+chromosomesCryzZNo ratings yet
- Anemia of Chronic Disease PDFDocument14 pagesAnemia of Chronic Disease PDFSuci PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Wesam Mohammed EmharibDocument8 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Wesam Mohammed Emharibنسيم حامدNo ratings yet
- COST 843 Quality Enhancement of Plant Production Through Tissue CultureDocument48 pagesCOST 843 Quality Enhancement of Plant Production Through Tissue CultureAriana ChimiNo ratings yet
- Traditional Knowledge of Botany and Agriculture Revealed in The Vēda Sa Hitās, Brāhma Ās, Ara Yakās and Upani AdsDocument15 pagesTraditional Knowledge of Botany and Agriculture Revealed in The Vēda Sa Hitās, Brāhma Ās, Ara Yakās and Upani AdsManeesh MisraNo ratings yet
- Honeycutt 2009 Chap 76Document6 pagesHoneycutt 2009 Chap 76Michelle Alejandra BrionesNo ratings yet
- D-37/1, TTC MIDC, Turbhe, Navi Mumbai-400 703: ThyrocareDocument3 pagesD-37/1, TTC MIDC, Turbhe, Navi Mumbai-400 703: ThyrocareSahil VaishyaNo ratings yet
- MLT Entry Test PaperDocument7 pagesMLT Entry Test PaperMuhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cephalotoxins: A Hotspot For Marine Bioprospecting?: Cátia Gonçalves and Pedro M. CostaDocument7 pagesCephalotoxins: A Hotspot For Marine Bioprospecting?: Cátia Gonçalves and Pedro M. CostaJordy ChandiaryNo ratings yet
- 02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-MergedDocument14 pages02 Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Text-Mergedsurya narayanaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- NehaDocument91 pagesNehaPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsDocument28 pagesTopic 5 - Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsMorapeli Real MJNo ratings yet