Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical Assignment - Chemicals of Life (2014-15 Stream)
Uploaded by
Hazo FemberaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Assignment - Chemicals of Life (2014-15 Stream)
Uploaded by
Hazo FemberaiCopyright:
Available Formats
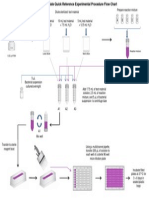
Practical Assignment 1: Biomacromolecules [50 Marks]
You are provided with 8 unknown liquid samples A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H and test tubes. These
samples were equally treated in the following experiments.
Experiment 1:
Procedure:
1) Take 5 ml of each sample and put in 8 separate test tube s
2) Using a grease pencil, number the tubes A1, B1, C1 etc.
3) Add one drop of Lugols reagent solution to all test tubes.
*Samples B, C and D had blue-black color; others have the brown color of Lugols reagent.
4) Repeat steps 1 to 2 and add 4 5 drops of saliva collected from the volunteer student
5) Set the tubes in a water bath @ 37C for hour or more.
6) Remove the tubes from the water bath and test contents by adding one drop of Lugols reagent.
*You note all have the same brown color.
Experiment 2:
Procedure:
1) Place 5 ml of Reagent X into 8 test tubes and label as in experiment 1 above.
2) Add four to five drops of each of the 8 samples.
3) Place tubes in a beaker water-bath over a Bunsen burner; boil for 2 minutes.
4) Remove the tubes and let cool slowly in a test tube rack.
*Samples A, B and F develop an orange color with an orange-red precipitate
5) Repeat steps 1 to 2 (replacing Reagent X with Barfoeds reagent) and heat the test tubes for 15-20
min, followed by cooling.
Experiment 3:
Procedure:
1) Into each of the 8 test-tubes containing the samples, add 5 ml of Seliwanoffs reagent.
2) Place the test tubes into a beaker water-bath over a Bunsen burner; boil for 1 minute.
3) Note any color change.
*A deep cherry red color was observed in Samples G and F, while sample A gave a slight or faint
pink color. Sample B gave a colour which was somewhat closer to cherry red.
Experiment 4:
Procedure:
1) Add 5 ml of 5% sample G to each of two test tubes; label these Tube 1 and Tube 2.
2) To Tube 1, add 5 mL of Reagent X and bring to a boil in the beaker water bath.
3) Remove Tube 1 from heat immediately.
4) To Tube 2, add two drops of 1M HCl and boil in the beaker water bath for 1 minute.
5) Remove Tube 2 from heat and neutralize with two drops of 1M NaOH.
6) Test the contents of Tube 2 with 5 mL of Reagent X.
*Tube 1 remained blue while Tube 2 turned orange with an orange-red precipitate.
Experiment 5:
Procedure:
1) Add 3 ml of 10% NaOH and one drop of 1% CuSO
4
to 5mL of the 8 samples in test tubes and mix
well.
2) Add additional drops of CuSO
4
until a color change is seen.
*A mauve (deep-purple or violet) color is observed in Samples B and D.
Experiment 6:
Procedure:
1) Mix 2 mL of 1% alcohol 3 mL of each of the 8 samples
2) Add 0.5 ml of 0.1% freshly prepared Ninhydrin to the 5 mL alcoholic mixture prepared above
3) Heat in a water bath and note color formation.
*A deep blue/purple color was observed in samples B and E.
4) Repeat steps 1 to 2 using 5 mL of 1% albumin solution.
5) Heat to boiling the albumin to which Ninhydrin was added.
*No deep blue/purple was observed
Experiment 7:
Procedure:
To 2 ml of each of the 8 samples, 3mL of 70% ethanol was added, followed by vigorous mixing. After
10 min observations were noted. A milky emulsion was observed only in Samples B and E.
Experiment 8:
You are provided with additional samples I and J. To 5 mL of each of these samples, 3 mL Bial's
reagent was added, followed by gentle heating in a Bunsen Burner or hot water bath.
Sample I gave a blue-green color while sample J gave a muddy-brown colour.
Questions
1. Use the results in all the 7 experiments to investigate the identities of chemicals in samples 1 to
7. State the name of the test, and present your results in tabular form, explaining the
mechanism(s) behind any colour development (e.g.).
Sample Constituent chemicals [10] Explanations and deductions [15]
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
1. Explain why B, C and D failed to produce the blue-black color after Step 4 of experiment 1. [2]
2 Identify Reagent X used in experiments 2 and 4. [2]
3. State and explain the results expected in step 5 of experiment 2, explaining the difference between
Reagent X and Barfoeds reagent. [4]
4. Explain the difference (in principle) between experiments 2 and 3. [2]
5. (a) In experiment 4, explain why Tube 2, gave an orange-red precipitate after acid treatment.
Hence state the name of the reaction of Sample G constituent with HCL. [5]
(b) Explain why this is important to neutralize HCl with NaOH, prior to addition of Reagent. [2]
6. Explain the difference between test in experiments 5 and 6. [2]
7. Explain why 1% albumin solution in Experiment 6 failed to give the positive Ninhydrin test. [2]
8. Explain, giving names, difference between samples B and H. [2]
9. Explain the mechanism(s) behind formation of blue-green and muddy-brown colours in Exp.8 [2]
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Dubbel-Handbook of Mechanical EngineeringDocument918 pagesDubbel-Handbook of Mechanical EngineeringJuan Manuel Domínguez93% (27)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering, SI Edition 9th Edition by Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan Solution ManualDocument14 pagesPrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering, SI Edition 9th Edition by Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan Solution ManualJehan Pahlevi100% (1)
- Science 6 1st Quarter TestDocument4 pagesScience 6 1st Quarter TestkentNo ratings yet
- SBC Detailed ReportDocument36 pagesSBC Detailed ReportPraneeth Kumar100% (1)
- Erico System 3000Document12 pagesErico System 3000Juan E Torres M67% (3)
- The Elements of A Research ProposalDocument10 pagesThe Elements of A Research ProposalHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- ITP - For Gas Turbine & AuxilliariesDocument12 pagesITP - For Gas Turbine & AuxilliariesAmmar1111186% (7)
- Subsea PLEM & PLET - Theory & Application PDFDocument127 pagesSubsea PLEM & PLET - Theory & Application PDFPaolo BertolliNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions For 16-17 of 2019 - BioScienceDocument14 pagesInterview Questions For 16-17 of 2019 - BioScienceHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Obesity Prevalence SSADocument9 pagesObesity Prevalence SSAHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ChecklistDocument13 pagesBiodiversity ChecklistHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- CHAP04 Probability and The Binomial Theorem PDFDocument10 pagesCHAP04 Probability and The Binomial Theorem PDFHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Dna GuideDocument43 pagesDna GuideHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics ManualDocument117 pagesBioinformatics ManualHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Tissue CultureDocument25 pagesTissue CultureHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- 1.chemistry of HormonesDocument9 pages1.chemistry of HormonesHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Ames Test Reference ChartDocument1 pageAmes Test Reference ChartHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- DNA RepairDocument68 pagesDNA RepairHazo FemberaiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Motion On Packing EfficiencyDocument14 pagesEffect of Motion On Packing EfficiencydonkosarevNo ratings yet
- Study BG 462 9 Beams On Elastic FoundationDocument15 pagesStudy BG 462 9 Beams On Elastic Foundationmanish mehtaNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Steel Under TensionDocument6 pagesBehavior of Steel Under TensionAshNo ratings yet
- Questions On Concepts Q5.1) : and andDocument23 pagesQuestions On Concepts Q5.1) : and andAlejandra Fajardo ApoloNo ratings yet
- Critical Chloride Content in ConcreteDocument8 pagesCritical Chloride Content in ConcreteChatchai ManathamsombatNo ratings yet
- NPL Testing Demonstrates The Flir Gf320 Meets Epa Ooooa StandardsDocument2 pagesNPL Testing Demonstrates The Flir Gf320 Meets Epa Ooooa StandardsjimmymorelosNo ratings yet
- Soal-Soal Kel 4Document4 pagesSoal-Soal Kel 4Sayyidati ZuhrohNo ratings yet
- DKD Guidance - Calibration of Liquid WaterDocument14 pagesDKD Guidance - Calibration of Liquid WatergustavoesanchezNo ratings yet
- Rh35v-Zik DC 1R 113466Document3 pagesRh35v-Zik DC 1R 113466José Hildo PereiraNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFDocument6 pagesSolutions To Mathematics 17 Exercises On Systems of Equations PDFMichael Christian BaysauliNo ratings yet
- Spe 80945 MSDocument10 pagesSpe 80945 MSLuciano FucelloNo ratings yet
- Coefficient Estimation in The Dynamic Equations of Motion of An AUVDocument4 pagesCoefficient Estimation in The Dynamic Equations of Motion of An AUVanitapinkyNo ratings yet
- Roses Amend 12Document477 pagesRoses Amend 12Koert OosterhuisNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Interaction Effects On The System Period and The System Damping Due To Foundation Embedment and Layer Depth - IMPORTANTEDocument17 pagesEvaluation of Interaction Effects On The System Period and The System Damping Due To Foundation Embedment and Layer Depth - IMPORTANTEAlejandro PérezNo ratings yet
- GraphIsotherm Linear STTN - A - 20150226 - 1 30C - 0,5MM - 3 JamDocument1 pageGraphIsotherm Linear STTN - A - 20150226 - 1 30C - 0,5MM - 3 JamYunus HidayatNo ratings yet
- EPFL Lectures On Conformal Field Theory in D 3 DimensionsDocument68 pagesEPFL Lectures On Conformal Field Theory in D 3 DimensionsMojeime Igor NowakNo ratings yet
- Tribology International: Rongping Yun, Peter Filip, Yafei LuDocument10 pagesTribology International: Rongping Yun, Peter Filip, Yafei LuRajiv Gandhi Rajiv GandhiNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolutionDocument12 pagesHW 1 SolutionESTUDIANTE JOSE DAVID MARTINEZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Design of Storm Water Drains for Bangaluru Campus ZonesDocument4 pagesDesign of Storm Water Drains for Bangaluru Campus Zonessalmaan mastanNo ratings yet
- Humanoid RobotsDocument17 pagesHumanoid RobotsPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Estimation of Tannins by HPLC: Der Pharmacia Lettre March 2016Document5 pagesQuantitative Estimation of Tannins by HPLC: Der Pharmacia Lettre March 2016kun antaNo ratings yet
- Analex RPDDocument16 pagesAnalex RPDpeach5100% (1)