Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multi-Site Network Model Management: Power Transmission & Distribution, Inc
Uploaded by
s_banerjeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multi-Site Network Model Management: Power Transmission & Distribution, Inc
Uploaded by
s_banerjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Multi-site Network Model Management
Power Transmission &
Distribution, Inc.
Kurt Hunter
27 June 2007
Multi-site Network Model Management
Topics
Background on Model Management
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
Model Management Implementation
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 2
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
What is Network Model Management?
Maintenance of an equipment and topology model
to support network applications such as power
flow, state estimation and contingency analysis.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 3
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Network Model Management requires:
On-going maintenance of the node/breaker model
of the portion of the electrical network that your
organization operates or oversees as well as
neighboring areas that affect operation of your
network.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 4
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Neighbor B
Network
Neighbor A
Network
External Model
My Network
Neighbor C
Network
Internal Model
Neighbor D
Network
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 5
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Internal Model
Updated frequently
Verified by State Estimator solution
Highly accurate
External Model
Infrequently updated
Requires input from external organizations
Accuracy depends on frequency of update
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 6
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
External Model Update
Requires exchanging network model data with closest
neighbors
Usually done as a wholesale replace of all data within
your network model for a given company
Usually requires conversion between data formats
Requires stitching the new data into the existing data
(primarily updating connectivity references for tie lines)
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 7
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Model Exchange
and Merge
My Network
Model
Network Model Merge
Neighbor A
Neighbor B
PSS/E File
IEEE File
Neighbor C
Proprietary Format
File
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 8
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Model Exchange and Merge
Data received from multiple sources in multiple formats with
multiple unique issues
Usually received as bus/branch (PSS/E, PSLF or IEEE)
Occasionally received as node/breaker, if neighbor used the same
EMS vendor
Semi-automated process at best
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 9
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Model Exchange and Merge
Labor intensive effort
Difficult to automate
Expensive
Performed infrequently
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 10
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Model Exchange and Merge
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 11
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Multi-site Management and Merge
Introduction of ISOs and RTOs made it necessary to construct
large scale detailed network models.
No longer just peer to peer
Member models not necessarily synchronized
Model Exchange from Coordinator to members to improve
synchronization
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 12
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Background on Model Management
Multi-site Management and Merge
Combined Model
el
Member B Model
od
M
be
rA
ed
bin
m
l
de
Mo
M
em
Co
rC
be
Member A
m
Me
Co
M
mb
od
ine
el
dM
od
el
Cordinator
(ISO/RTO)
Member C
Member B
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 13
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
The reality is
CIM will not solve
all your problems.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 14
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
Based on Common Information Model (IEC 61970-301)
Standardizing a profile for node/breaker model exchange
for network applications (IEC 61970-452)
Standardizing an XML based method for data exchange,
including incremental changes (IEC 61970-552-4)
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 15
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
CIM XML Based Model Exchange - Principals
Each modeled object identified by a globally unique, persistent master
resource ID (MRID)
Identification independent of naming
Model exchanged in greatest detail available (and reduced or
equivalenced as necessary by the consumer)
Unique identification independent of data owner (Modeling Authority)
(Unique ID remains constant even if data owner changes)
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 16
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
CIM XML Based Model Exchange Sample XML
<cim:ACLineSegment rdf:ID="_1c0789232f24da7a7c8751ccccf2b38">
<cim:IdentifiedObject.name>N12-N260</cim:IdentifiedObject.name>
<cim:Equipment.MemberOf_EquipmentContainer
rdf:resource="#_e55503e162de464b9d17dfe57f936574"/>
<cim:ConductingEquipment.BaseVoltage
rdf:resource="#_216f3106be824bca99dd83a9af6681b6"/>
<cim:Conductor.bch>0.0010609418</cim:Conductor.bch>
<cim:Conductor.r>0.80864</cim:Conductor.r>
<cim:Conductor.x>13.8624</cim:Conductor.x>
</cim:ACLineSegment>
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 17
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
CIM XML Based Model Exchange - History
Nine Interoperability Tests have been executed
Verified completeness of data exchanged
Verified common understanding of data exchanged
Verified exchange of incremental changes
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 18
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
CIM XML Based Model Exchange
CIM XML Based Model Exchange - History
Interoperability Tests have not:
Verified persistence of master resource IDs (MRIDs)
Verified global uniqueness of MRIDs
Tested data ownership or model merge
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 19
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
Network Model Management Implementation
CIM Model has been expanded to support:
Identification of data ownership
Ease of model merge
A clear methodology has been defined,
But we wont all get there at the same time.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 20
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
Network Model Management Implementation Issues
1. Not everyone has CIM XML capability (particularly outside the
U.S. and in Texas)
2. Not everyone is generating persistent IDs
3. Not everyone is generating globally unique IDs
4. Agreements need to be reached on persistent IDs for boundary
objects
5. Security is necessary around data ownership
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 21
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
1) Not everyone has CIM XML capability (particularly outside
the U.S. and in Texas)
CIM XML is gaining support in Europe and Asia, but is not as widely
used as other data exchange formats.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 22
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
1) Not everyone has CIM XML capability (particularly outside
the U.S. and in Texas)
Resolution Allow remote editing of coordinators combined network
model by members
Members without CIM XML capability piggyback on capabilities of the
coordinators system
Also requires implementation of security based on data ownership
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 23
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
2) Not everyone is generating persistent IDs
Example Internal index based MRIDs such as Substation_174 may
change when equipment is added or deleted.
Persistence has not been tested in interoperability tests
Persistent MRIDs are required for real world model management
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 24
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
2) Not everyone is generating persistent IDs
Resolution Coordinator system generates and assigns a truly globally
unique and persistent ID and maps it to the member maintained
persistent, locally unique ID.
Usually locally unique identification tied to naming, so naming must be
persistent or renaming must be handled as a special case
Usually unique naming is a combination of parameters (Substation
Name, Equipment Name, Equipment Type, etc.)
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 25
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
3) Not everyone is generating globally unique IDs
Example Both Company A and Company B may have a substation
identified as Substation_17845.
First impulse to add company name for uniqueness such as
Company_A.Substation_17845 and Company_B.Subatstion_17845.
Problem arises when Company A buys Company B.
Globally unique IDs cant be tied to data owner.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 26
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
3) Not everyone is generating globally unique IDs
Resolution - Coordinator system generates and assigns a truly globally
unique and persistent ID and maps it to the member maintained
persistent, locally unique ID.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 27
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
Name Registry versus Unique ID Mapping
Name Registry
Maps a single globally unique identifier to multiple names used in
different contexts (names used by different companies, names used
by different applications, etc.)
Unique ID Mapping
Maps a globally unique identifier to the locally unique identifier of
the current data owner
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 28
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
4) Agreements need to be reached on persistent IDs for
boundary objects
Agreement must be reached on the globally unique identification of
any object referenced in more than one model.
For example, the connectivity node in Company A where a tie line
from Company B connects must have an ID that does not change
without agreement from both Company A and Company B.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 29
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
4) Agreements need to be reached on persistent IDs for
boundary objects
Resolution Requires interested parties to:
Agree on common modeling of shared objects
Agree on a primary owner of all shared objects
Agree on globally unique and persistent IDs for shared objects
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 30
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
5) Security is necessary around data ownership
Any single object in the coordinators combined network model can have
only one entity (Modeling Authority) responsible for that data.
Changes to that data, either by direct editing or through import of
incremental change files, must be restricted to only the responsible
Modeling Authority.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 31
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Model Management Implementation
5) Security is necessary around data ownership
Resolution Software tools for Model Management must support the
capability to control who can edit and in some cases view individual
data objects.
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 32
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
Multi-site Network Model Management
Questions?
Energy Management & Automation Division
Page 33
April 06
2006 Siemens Power Transmissions & Distribution, Inc. All rights reserved
You might also like
- Green Communications: Principles, Concepts and PracticeFrom EverandGreen Communications: Principles, Concepts and PracticeKonstantinos SamdanisNo ratings yet
- IBM Alstom OperationsandMaintenanceOptimizationDocument11 pagesIBM Alstom OperationsandMaintenanceOptimizationalexanderNo ratings yet
- 2008 11 CYMExpress EnglishDocument2 pages2008 11 CYMExpress EnglishPraveen KapoorNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel-Based Tool Kit for Planning Hybrid Energy Systems: A User GuideFrom EverandMicrosoft Excel-Based Tool Kit for Planning Hybrid Energy Systems: A User GuideNo ratings yet
- CIM in Smart Grid ImplementationDocument9 pagesCIM in Smart Grid ImplementationEngineeringNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Traffic Structure on Application and Network PerformanceFrom EverandThe Effects of Traffic Structure on Application and Network PerformanceNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To CIM October 2010Document118 pages01 Introduction To CIM October 2010sahil4INDNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Hybrid Vehicle System Modeling and ControlFrom EverandIntroduction to Hybrid Vehicle System Modeling and ControlRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- XML For Cim Model Exchange: A. Devos, Member Ieee S.E. Widergren, Sr. Member, Ieee J. Zhu, Member IeeeDocument7 pagesXML For Cim Model Exchange: A. Devos, Member Ieee S.E. Widergren, Sr. Member, Ieee J. Zhu, Member Ieeeintiw_23No ratings yet
- Smart Grid IBMDocument19 pagesSmart Grid IBMmakmohit6037No ratings yet
- Extended and Integrated Database Implementation in Korean EMSDocument4 pagesExtended and Integrated Database Implementation in Korean EMSasimasim123No ratings yet
- Information Storage and Management: Storing, Managing, and Protecting Digital Information in Classic, Virtualized, and Cloud EnvironmentsFrom EverandInformation Storage and Management: Storing, Managing, and Protecting Digital Information in Classic, Virtualized, and Cloud EnvironmentsEMC Education ServicesNo ratings yet
- Essential Power System Requirements For Next Generation Data CentersDocument11 pagesEssential Power System Requirements For Next Generation Data CentersMichael Calizo PacisNo ratings yet
- 14 00 Hs Sptius - Pssev32 - Part1Document55 pages14 00 Hs Sptius - Pssev32 - Part1hizbi7No ratings yet
- CIMApplicationsDocument8 pagesCIMApplicationsrahul.srivastavaNo ratings yet
- IEC 61850 TutorialDocument177 pagesIEC 61850 TutorialPradeep Maurya80% (10)
- Symmetrix V-Max MaintenanceDocument108 pagesSymmetrix V-Max MaintenanceSuman Reddy T100% (3)
- Intelligent Management of Electrical Systems in IndustriesDocument29 pagesIntelligent Management of Electrical Systems in IndustriesMAHUMMED SUFYANNo ratings yet
- 6.current Status of ICCP-TASE.2, Secure ICCP, and Other IEC StandardsDocument35 pages6.current Status of ICCP-TASE.2, Secure ICCP, and Other IEC StandardsJuanillo GranCanaritoNo ratings yet
- BRKOPT-2114 Ethernet Operations, Administration and Maintenance (E-OAM) Technical OverviewDocument45 pagesBRKOPT-2114 Ethernet Operations, Administration and Maintenance (E-OAM) Technical Overviewccie123456No ratings yet
- Intelligent Buildings - Meter Reading and Energy ManagementDocument32 pagesIntelligent Buildings - Meter Reading and Energy ManagementManishaDhimanNo ratings yet
- Centera Faststart 2008 - Ps VersionDocument98 pagesCentera Faststart 2008 - Ps Versionqsef007No ratings yet
- Rackliffe Pserc Smart Grid Forum Mar09Document8 pagesRackliffe Pserc Smart Grid Forum Mar09thavaselvanNo ratings yet
- Data Center InfrastructureDocument74 pagesData Center Infrastructureprofericardo71100% (1)
- Vehicle ElectrificationDocument30 pagesVehicle ElectrificationSteve B. SalongaNo ratings yet
- Symmetrix Foundations Student Resource GuideDocument50 pagesSymmetrix Foundations Student Resource GuideJames PeterNo ratings yet
- EPRI CIM and 61850 Harmonization 061610Document29 pagesEPRI CIM and 61850 Harmonization 061610Jaime A. SánchezNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Management of Electrical Systems in IndustriesDocument30 pagesIntelligent Management of Electrical Systems in Industriesshubham6300100% (26)
- Gmail - glossary document with IT termsDocument7 pagesGmail - glossary document with IT termsJoson ChanNo ratings yet
- 02 IK IESYS e Introduction To Industrial EthernetDocument32 pages02 IK IESYS e Introduction To Industrial EthernetHernando AlborNo ratings yet
- Siemens AutomationDocument13 pagesSiemens AutomationHamadou TeteNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Fundamentals - Multisim Power Components - National Instruments PDFDocument5 pagesPower Electronics Fundamentals - Multisim Power Components - National Instruments PDFRajshNo ratings yet
- White Paper Nmea 2000Document25 pagesWhite Paper Nmea 2000Guille AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Austin Energy - ADMS ImplementationDocument21 pagesAustin Energy - ADMS Implementationsistemcba100% (1)
- Multidisciplinary Design Optimization Methods - Gang - LeiDocument251 pagesMultidisciplinary Design Optimization Methods - Gang - LeiKerr HoNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Power 3 Release3.9Document2 pagesSpectrum Power 3 Release3.9Yane HdezNo ratings yet
- In Vehicle NetworkingDocument5 pagesIn Vehicle NetworkingRana PrataapNo ratings yet
- Ethernet: Introduction To NetworksDocument62 pagesEthernet: Introduction To NetworksAdie Madi AsmadiNo ratings yet
- 02 IK IESYS e Introduction To Industrial EthernetDocument32 pages02 IK IESYS e Introduction To Industrial Ethernetsergio_lindau892No ratings yet
- The Past Present and Future of PowerdrivesDocument20 pagesThe Past Present and Future of PowerdrivesHarshaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of EV HEV PDFDocument17 pagesModeling and Simulation of EV HEV PDFshawn liNo ratings yet
- Integrated Aeronautical Information DatabaseDocument21 pagesIntegrated Aeronautical Information DatabaseDaniel Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- SWE2003 - Requirements Engineering and ManagementDocument12 pagesSWE2003 - Requirements Engineering and ManagementDhanwanth JPNo ratings yet
- Deploying AMI SolutionsDocument6 pagesDeploying AMI SolutionsPithoon UngnaparatNo ratings yet
- Master's in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Design and AnalysisDocument10 pagesMaster's in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Design and AnalysisGopiNo ratings yet
- Generative Design For Ev Electrical Systems: Doug Burcicki, Director Automotive - Mentor, A Siemens BusinessDocument6 pagesGenerative Design For Ev Electrical Systems: Doug Burcicki, Director Automotive - Mentor, A Siemens BusinesszacNo ratings yet
- Cisco Datacenter Disaster RecoveryDocument63 pagesCisco Datacenter Disaster Recoverybreinerq100% (1)
- Flaps Simulation: H. Guelzau, TUHH T. Krueger, AIRBUSDocument12 pagesFlaps Simulation: H. Guelzau, TUHH T. Krueger, AIRBUSPrasad KaneNo ratings yet
- SIMOTICS MotorsDocument26 pagesSIMOTICS MotorsJeimy Rafael Zacarias RodriguezNo ratings yet
- What'S New With Emc Controlcenter V6.0Document30 pagesWhat'S New With Emc Controlcenter V6.0Nalla MaheshNo ratings yet
- 03c - IEC 61850 - 20130111-En - SagarDocument38 pages03c - IEC 61850 - 20130111-En - SagarVishwanath TodurkarNo ratings yet
- Tute CCADM PDFDocument5 pagesTute CCADM PDFamanNo ratings yet
- V8: Net-Ing A Greener Data CenterDocument24 pagesV8: Net-Ing A Greener Data CenterAnonymous kbmKQLe0JNo ratings yet
- PTC12 Opt Wkshop Todd BundyDocument39 pagesPTC12 Opt Wkshop Todd Bundy7kkhsNo ratings yet
- ZSM Scenarios and Key Requirements - Farni BotenDocument11 pagesZSM Scenarios and Key Requirements - Farni BotenManoj ChandNo ratings yet
- Mktlit Uib PiDocument4 pagesMktlit Uib PisinanovicismarNo ratings yet
- Demand Growth in South AsiaDocument10 pagesDemand Growth in South Asias_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- HC - WbsedclDocument1 pageHC - Wbsedcls_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- _ags_0ad6935a-4b17-11ee-b0cd-00155dc84829Document1 page_ags_0ad6935a-4b17-11ee-b0cd-00155dc84829s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cag Report PPSPDocument3 pagesCag Report PPSPs_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum Connectivity Regulations (7th Amendment)Document1 pageCorrigendum Connectivity Regulations (7th Amendment)s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Excitation & Avr SystemDocument32 pagesExcitation & Avr SystemSreeram PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Negative Seq Based Protection IBRDocument7 pagesNegative Seq Based Protection IBRs_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- A Smart Transmission Grid For EuropeDocument8 pagesA Smart Transmission Grid For Europes_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Modelling Storage Operation For Markets Participation Advanced System ServicesDocument4 pagesModelling Storage Operation For Markets Participation Advanced System Servicess_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Excitation & Avr SystemDocument32 pagesExcitation & Avr SystemSreeram PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- OSTI Report Frequency Control Performance MeasurementDocument48 pagesOSTI Report Frequency Control Performance Measurements_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Surajit Kol Goa Boarding Pass 150318Document1 pageSurajit Kol Goa Boarding Pass 150318s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- IBR Impacts On Protection SystemDocument11 pagesIBR Impacts On Protection Systems_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Webinar # 3: Power System Stabilizer (PSS) TuningDocument24 pagesWebinar # 3: Power System Stabilizer (PSS) TuningVigneshwaran KandaswamyNo ratings yet
- All India and Regional Demand Forecast 15-Apr-2019Document19 pagesAll India and Regional Demand Forecast 15-Apr-2019s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Uc PDFDocument33 pagesUc PDFs_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- UFR1Document3 pagesUFR1s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) :: Q1. When We Can Apply For The Scheme?Document3 pagesFrequently Asked Questions (Faqs) :: Q1. When We Can Apply For The Scheme?Made For eachotherNo ratings yet
- PSAT/VSAT/TSAT vs PSSE software for TTC studiesDocument1 pagePSAT/VSAT/TSAT vs PSSE software for TTC studiess_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Security - Vulnerability Power GridsDocument8 pagesSecurity - Vulnerability Power Gridss_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Growth of Solar Energy in IndiaDocument6 pagesGrowth of Solar Energy in Indias_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Summer Trg. 2018Document1 pageSummer Trg. 2018s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- PidDocument18 pagesPidByron Xavier Lima CedilloNo ratings yet
- Psoc Lecture 1Document3 pagesPsoc Lecture 1Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- JUSNL Transmission LinesDocument2 pagesJUSNL Transmission Liness_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Receipt Fund Trannsfer Chirantan 110118Document1 pageReceipt Fund Trannsfer Chirantan 110118s_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Receipt DetailsDocument1 pageBharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Receipt Detailss_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- EI 010 606 L05 Telemetry and Remote ControlDocument1 pageEI 010 606 L05 Telemetry and Remote Controls_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Tech Brief Dual Operator TRNSFR SWTCHDocument3 pagesTech Brief Dual Operator TRNSFR SWTCHkfaliNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Frequency Control in A Power System Lecture 16: Automatic Generation Control (AGC)Document4 pagesModule 3: Frequency Control in A Power System Lecture 16: Automatic Generation Control (AGC)Ashwani RanaNo ratings yet
- Annamalai International Journal of Business Studies and Research AijbsrDocument2 pagesAnnamalai International Journal of Business Studies and Research AijbsrNisha NishaNo ratings yet
- Phys101 CS Mid Sem 16 - 17Document1 pagePhys101 CS Mid Sem 16 - 17Nicole EchezonaNo ratings yet
- Inside Animator PDFDocument484 pagesInside Animator PDFdonkey slapNo ratings yet
- DELcraFT Works CleanEra ProjectDocument31 pagesDELcraFT Works CleanEra Projectenrico_britaiNo ratings yet
- Lankeda 3d Printer Filament Catalogue 2019.02 WGDocument7 pagesLankeda 3d Printer Filament Catalogue 2019.02 WGSamuelNo ratings yet
- Case Study Hotel The OrchidDocument5 pagesCase Study Hotel The Orchidkkarankapoor100% (4)
- Change Management in British AirwaysDocument18 pagesChange Management in British AirwaysFauzan Azhary WachidNo ratings yet
- "Behind The Times: A Look at America's Favorite Crossword," by Helene HovanecDocument5 pages"Behind The Times: A Look at America's Favorite Crossword," by Helene HovanecpspuzzlesNo ratings yet
- AsiaSat 7 at 105Document14 pagesAsiaSat 7 at 105rahman200387No ratings yet
- STAT455 Assignment 1 - Part ADocument2 pagesSTAT455 Assignment 1 - Part AAndyNo ratings yet
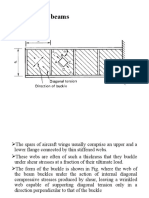
- Tension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisDocument19 pagesTension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisPrajeesh RajNo ratings yet
- Briana SmithDocument3 pagesBriana SmithAbdul Rafay Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- RACI Matrix: Phase 1 - Initiaton/Set UpDocument3 pagesRACI Matrix: Phase 1 - Initiaton/Set UpHarshpreet BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Preventing and Mitigating COVID-19 at Work: Policy Brief 19 May 2021Document21 pagesPreventing and Mitigating COVID-19 at Work: Policy Brief 19 May 2021Desy Fitriani SarahNo ratings yet
- Merchandising Calender: By: Harsha Siddham Sanghamitra Kalita Sayantani SahaDocument29 pagesMerchandising Calender: By: Harsha Siddham Sanghamitra Kalita Sayantani SahaSanghamitra KalitaNo ratings yet
- Whisper Flo XF 3 PhaseDocument16 pagesWhisper Flo XF 3 Phasehargote_2No ratings yet
- Exercises2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesExercises2 Solutionspedroagv08No ratings yet
- April 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesDocument16 pagesApril 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesStrathmore Times100% (1)
- Thin Film Deposition TechniquesDocument20 pagesThin Film Deposition TechniquesShayan Ahmad Khattak, BS Physics Student, UoPNo ratings yet
- QuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1Document12 pagesQuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1subhrajitm47No ratings yet
- Contact and Profile of Anam ShahidDocument1 pageContact and Profile of Anam ShahidSchengen Travel & TourismNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)Document6 pagesInterpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)afalfitraNo ratings yet
- 8dd8 P2 Program Food MFG Final PublicDocument19 pages8dd8 P2 Program Food MFG Final PublicNemanja RadonjicNo ratings yet
- #3011 Luindor PDFDocument38 pages#3011 Luindor PDFcdouglasmartins100% (1)
- Kami Export - BuildingtheTranscontinentalRailroadWEBQUESTUsesQRCodes-1Document3 pagesKami Export - BuildingtheTranscontinentalRailroadWEBQUESTUsesQRCodes-1Anna HattenNo ratings yet
- Game Rules PDFDocument12 pagesGame Rules PDFEric WaddellNo ratings yet
- 4 Wheel ThunderDocument9 pages4 Wheel ThunderOlga Lucia Zapata SavaresseNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification for Pig Farming SkillsDocument7 pagesTable of Specification for Pig Farming SkillsYeng YengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 of David CrystalDocument3 pagesChapter 3 of David CrystalKritika RamchurnNo ratings yet
- Photographing Shadow and Light by Joey L. - ExcerptDocument9 pagesPhotographing Shadow and Light by Joey L. - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group75% (4)