Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NDT Report Check List Updated 2013
Uploaded by
pitichai_pCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NDT Report Check List Updated 2013
Uploaded by
pitichai_pCopyright:
Available Formats
TWI Middle East 03-11-12
AUDIT of NDT Reports
Concise Reports Check List
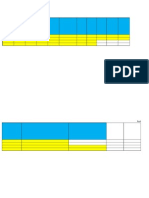
UT
Ultrasonic Testing
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
12)
13)
14)
15)
16)
17)
18)
19)
20)
21)
22)
Material Type (Larger grain = lower Hz) 1)
Time/Stage of inspection
2)
Place of inspection
3)
Equipment/Set Type and Scanning method 4)
Shear/Comp Probe (Single/Twin MAP?) 5)
Probe Size (Usually 10 mm) & Type
6)
Probe Frequency (4-5 MHz < 3 for Cu/SS) 7)
Probe Angle <10 =70 /10-15 = 60-70 >15 = 45 -60 8)
Calibration Block ( & Depth Hole used) 9)
Calibration Range
10)
Scanning method/procedure
11)
Surface condition/finish
12)
Type of couplant
13)
Type of equipment
14)
Scanning Sensitivity
15)
Recording Level
16)
Joint configuration and area of weld tested 17)
All Defects Identified, Sized and Located 18)
NDT Technicians Qualifications & Name 19)
Report is signed stamped and dated
20)
BS Method BS 3923
21)
Now replaced by BS EN 585 & BS EN 1714 22)
MT Magnetic Particle Testing
RT
PT
Radiographic Testing
Material Type (All types)
Time/Stage of inspection
Place of inspection
Procedure/Standard number given
Radiographic Technique (DWDI etc)
Screens front & back (type & thickness)
Gamma/X-ray (Source or Focal Spot Size?)
Type/Strength of source or kva
SFD/OFD
Type and range of IQI
Speed of film (Characteristic Curve)
Sensitivity as % (< 3%)
Density range (2-3)
Focal Spot Size
Geometric Un-sharpness (g) (<0.25mm)
Exposure Time
Development method and time
All Defects Identified, Sized and Located
NDT Technicians Qualifications & Name
Report is signed stamped and dated
BS Method BS 2910 (pipe) BS 2600 (Plate)
Now replaced by BS EN 444
Penetrant Testing
1)
Material Type (Ferritic Steels Only)
1)
Material Type (Non Porous Only)
2)
Time/Stage of inspection
2)
Time/Stage of inspection
3)
Place of inspection
3)
Place of inspection
4)
Procedure/Standard number given
4)
Procedure/Standard number given
5)
Method (Wet/Dry Fluorescent/Contrast etc.) 5)
Method (Colour Contrast/Fluorescent)
6)
Method & standard of surface preparation 6)
Method & standard of surface preparation
7)
Equipment type (Prod/Yolk/Magnet/Bench) 7)
Surface finish is critical (EB as welded??)
8)
Method of Mag (+ DC or AC for Prods) 8)
Shelf Life of Chemicals (Normally 1 Year)
9)
Prod spacing amperage (7.5 amp/mm)
9)
Penetrant Application Method (Spray/Tank)
10)
Use of Correct Terms Prods or Poles etc
10)
Penetrant Dwell time (5 60 minutes)
11)
Contrast Paint (Type and application)11)
Method of Penetrant Removal
12)
Test sequence (2 x directions @ 90 )
12)
Type and application of developer
13)
Sub Surface imperfections (2mm Max)
13)
Evaluation time (10- 30 minutes)
14)
Black light 20 lux or 1000W/cm2
14)
Black Light (20 lux or 1000W/cm2)
15)
Contrast Light (Minimum 500 lux)
15)
Contrast Light (Minimum 500 lux)
16)
Flux measurement Strips/kg Force etc.
16)
Operating Temperature range (5-50C)
17)
> 50C dry powder inks are used
17)
Surface breaking only imperfections
18)
All Defects Identified, Sized and Located 18)
All Defects Identified, Sized and Located
19)
NDT Technicians Qualifications & Name 19)
NDT Technicians Qualifications & Name
20)
Report is signed stamped and dated
20)
Report is signed stamped and dated
21)
BS Method BS 6072 (Inks BS 4069 Paint 5044) 21)
BS Method BS 6443
22)
Now replaced by BS EN 9934 Parts 1-3/ BS EN 1290 22)
Now replaced by BS EN 571 Part 1
Correct Terminology shall be used on all NDT reports and identification and reporting of imperfections.
1
TWI Middle East 03-11-08
Advantages and Disadvantages of the 4 basic NDT Methods
Penetrant Testing
Advantages
Disadvantages
1) Low operator skill level
1) High surface preparation
2) Non magnetic materials
2) Surface flaws only
3) Low cost method
Magnetic Particle Testing
Advantages
Disadvantages
1) Cleaning not as high as DPI 1) Fe Magnetic alloys only
2) Some near surface flaws
2) De-magnetize after use
3) Not for porous materials
3) Relatively low cost
3) Can cause arc strikes #
4) Relatively simple
4) No permanent record
4) Simple equipment
4) No permanent record
5) Very portable
5) Hazardous chemicals
5) Used through thin coatings
5) Test in 2 directions (90)
# When using the straight current prod technique
Ultrasonic Testing
Advantages
Radiographic Testing
Disadvantages
Advantages
Disadvantages
1) Can find lack of fusion
1) High operator skill
1) A permanent record ?
1) High interpretation skill
2) Most materials
2) Difficult to interpret
2) Most materials tested
2) Access to both sides
3) No safety requirements
3) Requires calibration
3) Detects internal flaws
3) Sensitive to orientation
4) Portable/instant results
4) Lower Hz for Cu. S/S etc.
4) Direct image of flaws
4) High health hazard
5) Can measure thickness
5) Restricted to job geometry
5) Fluoroscopy real time image 5) High capitol cost
You might also like
- Book 5Document3 pagesBook 5pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Cer of Two Safety ValveDocument4 pagesCer of Two Safety Valvepitichai_pNo ratings yet
- AAStorage Tank Data Rev 4 (7.1.15)Document3 pagesAAStorage Tank Data Rev 4 (7.1.15)pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- AA Offstream Tank InspectionDocument1 pageAA Offstream Tank Inspectionpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Ddd-Annual Training Plan 2015Document2 pagesDdd-Annual Training Plan 2015pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Level III Preparatory Schedule For September 2015Document1 pageLevel III Preparatory Schedule For September 2015pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Project CoordinatorDocument1 pageProject Coordinatorpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Compass Reference Settlement and Tilt MeasurementsDocument3 pagesCompass Reference Settlement and Tilt Measurementspitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Severity LevelDocument2 pagesSeverity Levelpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- 48 Page Document SummaryDocument48 pages48 Page Document Summarypitichai_pNo ratings yet
- FR-05 Enrollment Form Rev.01Document1 pageFR-05 Enrollment Form Rev.01pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- TP176 CaseStudiesofPECDocument17 pagesTP176 CaseStudiesofPECpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Asnt 2015 Exam SchduleDocument3 pagesAsnt 2015 Exam Schdulepitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Project CoordinatorrrrDocument1 pageProject Coordinatorrrrpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Asnt 2015 Exam SchduleDocument3 pagesAsnt 2015 Exam Schdulepitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Report Sending Log: Sent Date Report No. Customer Received byDocument2 pagesReport Sending Log: Sent Date Report No. Customer Received bypitichai_pNo ratings yet
- AANDT Course Schedule-2015 RevDocument1 pageAANDT Course Schedule-2015 Revpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Bureau Veritas (Thailand) Ltd. Plant NDT Inspection Services EMI-14-0004 Technical ProposalDocument2 pagesBureau Veritas (Thailand) Ltd. Plant NDT Inspection Services EMI-14-0004 Technical Proposalpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- How To Fill ReportDocument1 pageHow To Fill Reportpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- HSECT LiteratureDocument1 pageHSECT Literaturepitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Bureau Veritas (Thailand) Ltd. Plant NDT Inspection Services EMI-14-0004 Technical ProposalDocument2 pagesBureau Veritas (Thailand) Ltd. Plant NDT Inspection Services EMI-14-0004 Technical Proposalpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Bureau Veritas (Thailand) Ltd. Plant NDT Inspection Services EMI-14-0004 Technical ProposalDocument4 pagesBureau Veritas (Thailand) Ltd. Plant NDT Inspection Services EMI-14-0004 Technical Proposalpitichai_pNo ratings yet
- DDDAnnual Training Plan 2015Document2 pagesDDDAnnual Training Plan 2015pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- How To Fill Report Format1Document1 pageHow To Fill Report Format1pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- RT General Pg1-2Document1 pageRT General Pg1-2pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Requisition Equipment Format Rev.01Document1 pageRequisition Equipment Format Rev.01pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- API 653 SummaryDocument27 pagesAPI 653 Summarypitichai_p100% (1)
- PCI Intl Registration Form-1Document4 pagesPCI Intl Registration Form-1pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- INS - Phased Array Flange Face InspectionDocument2 pagesINS - Phased Array Flange Face Inspectionpitichai_p100% (1)
- Acousticemissiontesting 140603033903 Phpapp01Document40 pagesAcousticemissiontesting 140603033903 Phpapp01pitichai_pNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Food Process Engineering Lab 3. BOILER OPERATIONDocument22 pagesFood Process Engineering Lab 3. BOILER OPERATIONMuhyiddin Noor AfandiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Statics and Manometers OutlineDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Statics and Manometers OutlineVerin VericuetoNo ratings yet
- HAZOP Training290620Document93 pagesHAZOP Training290620NasrulNo ratings yet
- Wolkite University Museum Technique Group AssignmentDocument23 pagesWolkite University Museum Technique Group AssignmentNatnael SisayNo ratings yet
- SemiconDocument9 pagesSemiconRealyn PugayNo ratings yet
- 6 - Cortés (2022) - Synthesis of Nanostructured BaTiO3 Films by Hydrothermal Modification of Ti Surfaces Using Ba (OH) 2 and Oleic AcidDocument6 pages6 - Cortés (2022) - Synthesis of Nanostructured BaTiO3 Films by Hydrothermal Modification of Ti Surfaces Using Ba (OH) 2 and Oleic Acidmaria cortesNo ratings yet
- EDXRF Analysis of Polymer Films Thickness and CompositionDocument2 pagesEDXRF Analysis of Polymer Films Thickness and CompositionnadiarhNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report OnDocument1 pageA Seminar Report Onu10ch019No ratings yet
- Efficient Synthesis of 3-Hydroxy-1,4-Benzodiazepines Oxazepam and Lorazepam by New Acetoxylation Reaction of 3-Position of 1,4-Benzodiazepine Ring - Organic Process Research & DevelopmentDocument12 pagesEfficient Synthesis of 3-Hydroxy-1,4-Benzodiazepines Oxazepam and Lorazepam by New Acetoxylation Reaction of 3-Position of 1,4-Benzodiazepine Ring - Organic Process Research & DevelopmentSimon GeschwindNo ratings yet
- Parent Consent Petition Tutorialclass PDC 2Document8 pagesParent Consent Petition Tutorialclass PDC 2John Bryan AldovinoNo ratings yet
- Chap 8 Ques - AnsDocument11 pagesChap 8 Ques - AnsHaley WillhelmNo ratings yet
- Saranya IJPSRDocument8 pagesSaranya IJPSRBhavana GangurdeNo ratings yet
- Mep 1 1Document58 pagesMep 1 1Amisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- OLEDreport PDFDocument26 pagesOLEDreport PDFStanimir YordanovNo ratings yet
- T50 300 Xl092grexbDocument3 pagesT50 300 Xl092grexbSykat ZamanNo ratings yet
- Will Silver Bromide PrecipitateDocument14 pagesWill Silver Bromide PrecipitateLeonidasNo ratings yet
- Manual Screen Changer For Extrusion Processes: Your Benefi TsDocument2 pagesManual Screen Changer For Extrusion Processes: Your Benefi Tsneuro4761No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Method For CompositesDocument41 pagesManufacturing Method For CompositestpmendozaNo ratings yet
- 14 CH242 Conjugated & UVDocument72 pages14 CH242 Conjugated & UVrizqiaNo ratings yet
- Canadian Coast Guard Welding SpecificationDocument39 pagesCanadian Coast Guard Welding Specificationalvin dueyNo ratings yet
- FCC Monograph PDFDocument4 pagesFCC Monograph PDFWilsonNo ratings yet
- KEY Macromolecules Chart 2015Document4 pagesKEY Macromolecules Chart 2015Joshua BernilNo ratings yet
- A Certain Light Bulb Containing Argon Has A Pressure of 1Document1 pageA Certain Light Bulb Containing Argon Has A Pressure of 1Bill Christian Villamor CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Nust ChemistryDocument137 pagesNust Chemistryahmed ilyasNo ratings yet
- Material TechnologyDocument46 pagesMaterial TechnologyVarunNo ratings yet
- Effects of CN Ratios and Turning Frequencies On The Composting Process of Food Waste and Dry LeavesDocument8 pagesEffects of CN Ratios and Turning Frequencies On The Composting Process of Food Waste and Dry LeavesJonathan SotoNo ratings yet
- RHOPLEX™ EC-3000: 100% Acrylic Polymer For The Roof Coatings MarketDocument4 pagesRHOPLEX™ EC-3000: 100% Acrylic Polymer For The Roof Coatings MarketLong An DoNo ratings yet
- Brittany L. Hayes - Recent Advances in Microwave - Assisted SynthesisDocument11 pagesBrittany L. Hayes - Recent Advances in Microwave - Assisted SynthesisnnnnjwNo ratings yet
- Puresilk Salt ChlorinatorDocument10 pagesPuresilk Salt Chlorinatornike_y2kNo ratings yet