Professional Documents
Culture Documents
20 Valores Extremos F (X, Y) 1condicion
Uploaded by
Charlie Aguero PorrasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
20 Valores Extremos F (X, Y) 1condicion
Uploaded by
Charlie Aguero PorrasCopyright:
Available Formats
05/10/2014
CLCULO VECTORIAL
CAPTULO II
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
SESIN 21
VALORES EXTREMOS CON
UNA CONDICIN
MTODO DE LAGRANGE
f (P) = g ( P)
g (P) = 0
1736 -1813
Rosa ique Alvarez
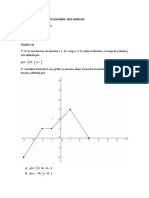
Funcin objetivo: f (x, y) = 9 - x2 - y2 (Paraboloide)
Condicin: x + y = 3 (segmento recto)
MXIMO ABSOLUTO Y MXIMO CON UNA
CONDICIN
Determine geomtricamente si la funcin
f (x, y) = 9 - x2 - y2 tiene un valor
extremo cuando las variables x e y estn
restringidas a x + y = 3
Funcin objetivo: f (x, y) = 9 - x2 - y2
Condicin: x + y = 3
(Paraboloide)
(segmento recto)
Rosa ique Alvarez
TEOREMA DE LAGRANGE
Rosa ique Alvarez
Determinar los valores extremos de una funcin z = f (x, y)
sujeta a una restriccin dada por g(x, y) = 0
Supongamos que la funcin z = f (x, y) tiene un
extremo en el punto P sobre la grfica de la
ecuacin restriccin g(x, y) = 0. Si f y g tienen
primeras derivadas parciales continuas en un
conjunto abierto que contiene la grfica de la
ecuacin restriccin y
, entonces
g (P ) 0
existe un nmero real (multiplicador de
Lagrange) tal que
f ( P ) = g ( P )
Rosa ique Alvarez
Rosa ique Alvarez
1
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
INTERPRETACIN GEOMTRICA
Determinar los valores extremos de una funcin z = f (x, y)
sujeta a una restriccin dada por g(x, y) = 0
MTODO DE LAGRANGE
Sea S la superficie definida por z = f (x, y)
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c ,
c = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11.
Condicin g (x, y) = 0
Curva de nivel g(x, y) = 0 de la superficie w =g(x, y)
Rosa ique Alvarez
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c , c = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11.
Rosa ique Alvarez
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c , c = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11.
f (P0 )
g(P0 )
Rosa ique Alvarez
VALORES EXTREMOS CON UNA CONDICIN
10
INTERPRETACIN GEOMTRICA
MTODO DE LAGRANGE
MTODO DE LAGRANGE
f (P) = g (P)
Rosa ique Alvarez
Sea S la superficie definida por z = f (x, y)
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c
g (P) = 0
1
424
3
CONDICION
c = 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700
Condicin g (x, y) = 0
Curva de nivel g(x, y) = 0
Rosa ique Alvarez
11
Rosa ique Alvarez
12
2
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
INTERPRETACIN GEOMTRICA
VALORES EXTREMOS CON UNA CONDICIN
MTODO DE LAGRANGE
f ( P0 ) = 0 g ( P0 )
f ( P1 ) = 1 g ( P1 )
Rosa ique Alvarez
13
MTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES
DE LAGRANGE (una condicin)
14
MTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES
DE LAGRANGE (una condicin)
Si f tiene un valor extremo con condicin en el punto
P, entonces
Si f tiene un valor extremo con condicin en el punto
P, entonces
f (P) = g (P)
g ( P ) = 0 condicin o restricci n
Rosa ique Alvarez
Rosa ique Alvarez
SISTEMA DE
ECUACIONES
f
g
( P) =
( P)
x
x
f
g
( P) =
( P)
y
y
g ( P) = 0
15
condicin o restriccin
Rosa ique Alvarez
EJEMPLO 1
SOLUCIN
Cul es el rea mxima que puede tener un
rectngulo si la longitud de su diagonal es 2?
Funcin Objetivo
16
:f (x, y) = x y
Funcin rea
(Superficie)
(x , y)
Condicin
: g(x, y) = x2 + y2 4 = 0
Longitud diagonal
Rosa ique Alvarez
17
Rosa ique Alvarez
18
3
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
Funcin rea
f(x,y)=xy
x = 2 cos t
C : y = 2 sent t [0, / 2]
z = 4 cos t sent
Rosa ique Alvarez
19
Rosa ique Alvarez
20
SOLUCIN
SOLUCIN
f (x, y) = x y, funcin rea
g(x, y) = x2 + y2 4 = 0, condicin
MTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES DE LAGRANGE
f ( x, y) = g ( x, y )
g ( x, y) = 0
MTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES DE LAGRANGE
f ( x, y) = g ( x, y )
g ( x, y) = 0
Rosa ique Alvarez
y = (2 x )
x = ( 2 y)
x 2 + y 2 = 4 condicin
SISTEMA DE
ECUACIONES
Rosa ique Alvarez
21
22
Interpretacin Geomtrica del Ejemplo 1
Resolviend o el sistema
x = y = 2 ; = 1/ 2
Area = 2
Curvas de Nivel de la funcion Area: f(x, y)=xy
3
3.5
El rectngulo de mxima rea con
diagonal 2 es el cuadrado cuyos lados
miden 2. Su rea es 2.
14
16
(sqrt(2) ,sqrt(2))
2.5
12
Curva Condicin
Curva de Nivel
Maximo
1.5
k=4
k=3
k=2
2
0.5
k=1
0
0
Rosa ique Alvarez
23
0.5
1.5
2
X
2.5
Rosa ique Alvarez
3.5
24
4
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
MTODO DE LAGRANGE PARA TRES
VARIABLES INDEPENDIENTES
w = f (x, y, z)
g(x, y, z) = 0
f
g
=
x
x
f
g
=
y
y
f
g
=
z
z
g ( x, y , z ) = 0 condicin o restricci n
Rosa ique Alvarez
25
5
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
You might also like
- Campo Escalar GuiaDocument29 pagesCampo Escalar GuiaAida AcostaNo ratings yet
- Derivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresDocument112 pagesDerivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresMario CastroNo ratings yet
- Calculo Vectorial Extremos de FuncionesDocument26 pagesCalculo Vectorial Extremos de FuncionesCésar PilarNo ratings yet
- Calculo Vectorial Extremos de FuncionesDocument39 pagesCalculo Vectorial Extremos de Funcionesayanez22No ratings yet
- Tema22 Funciones Pares e Impares, Algebra de FuncionesDocument4 pagesTema22 Funciones Pares e Impares, Algebra de FuncionesSEBAS OLARTENo ratings yet
- 22valores Extremos Condicionados Metodo de LagrangeDocument10 pages22valores Extremos Condicionados Metodo de LagrangeJesus Ernesto Peralta HuasasquicheNo ratings yet
- Primera Fase Ejercicios CalDocument19 pagesPrimera Fase Ejercicios CalFernando Ovalle BlancoNo ratings yet
- 22 - Algebra de Funciones y Funcion InversaDocument8 pages22 - Algebra de Funciones y Funcion InversaCamilaNo ratings yet
- Acetatos Unidad 2 Calculo AvanzadoDocument54 pagesAcetatos Unidad 2 Calculo AvanzadoJ EnriQue AlcNo ratings yet
- AMIII Trabajo Practico N2Document4 pagesAMIII Trabajo Practico N2cordobezaldana29No ratings yet
- Trabajo 4a FuncionesDocument2 pagesTrabajo 4a FuncionesArielCusipumaOrtegaNo ratings yet
- GUIA N° 5 ALGEBRA DE FUNCIONESDocument7 pagesGUIA N° 5 ALGEBRA DE FUNCIONESRaúl edgardo Cardona lafaurieNo ratings yet
- VALORES EXTREMOS F (X, Y) 1CONDICIODocument6 pagesVALORES EXTREMOS F (X, Y) 1CONDICIOJordan ZavaletaNo ratings yet
- Composicion: DE FuncionesDocument17 pagesComposicion: DE FuncionesPaul Anderson Bardales MilianNo ratings yet
- Practica Grupo 5Document20 pagesPractica Grupo 5Wily Quispe CopariNo ratings yet
- Taller10 2015Document2 pagesTaller10 2015hernan estradaNo ratings yet
- Briozzo-Calculo Difer y OptimizacionDocument25 pagesBriozzo-Calculo Difer y OptimizacionLuis AlvearNo ratings yet
- Calculo - Funciones de Varias VariablesDocument6 pagesCalculo - Funciones de Varias VariablesSergio Cerda SabugoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos de FuncionesDocument10 pagesEjercicios Resueltos de FuncionesFabián Sánchez Parrines100% (1)
- Extremos RestringidosDocument12 pagesExtremos RestringidosjemmyjimenezNo ratings yet
- Funciones: definición, dominio y rangoDocument9 pagesFunciones: definición, dominio y rangoJosseling Huamán EncoNo ratings yet
- Cálculo III Ejercicios Funciones DiferenciablesDocument2 pagesCálculo III Ejercicios Funciones DiferenciablesMarco Cuevas SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Derivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresDocument106 pagesDerivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresBercho PérezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de FuncionesDocument1 pageEjercicios de Funciones130 Rodriguez Mendoza Herlan NelsonNo ratings yet
- Calculo Vectorial Unidad 4 (Completo)Document38 pagesCalculo Vectorial Unidad 4 (Completo)AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Practica 5 C 32020Document1 pagePractica 5 C 32020Marcelo SalazarNo ratings yet
- FuncionesDocument7 pagesFuncionesDora Anita Mamani ChuraNo ratings yet
- Funciones Parte3 UvirtualDocument14 pagesFunciones Parte3 UvirtualepmelsNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Propuestos Funcion Compuesta, Inversa, ImplicitaDocument3 pagesEjercicios Propuestos Funcion Compuesta, Inversa, ImplicitaJulio MayaudonNo ratings yet
- Funciones PDFDocument30 pagesFunciones PDFSara GomezNo ratings yet
- Facultad de Ciencias Fisicas Y MatematicasDocument11 pagesFacultad de Ciencias Fisicas Y MatematicasBenjamin FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Sesion 3Document15 pagesSesion 3ErickRojasNo ratings yet
- ListaDeEjercicios4Respuestas 23 2Document8 pagesListaDeEjercicios4Respuestas 23 2Vico HuacchaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios 1CAVDocument8 pagesEjercicios 1CAVRafael AntonioNo ratings yet
- La Integral DefinidaDocument13 pagesLa Integral DefinidaMario Orlando Suárez IbujésNo ratings yet
- Unidad 1.3 Calculo DiferencialDocument3 pagesUnidad 1.3 Calculo DiferenciallauraNo ratings yet
- Guía - HT - Sem 14Document7 pagesGuía - HT - Sem 14MiguelNo ratings yet
- Funciones LaTeXDocument3 pagesFunciones LaTeXMarcelo CruzNo ratings yet
- 7 Analisis Vectorial PDFDocument41 pages7 Analisis Vectorial PDFR16QNo ratings yet
- Funciones matemáticas y sus aplicacionesDocument3 pagesFunciones matemáticas y sus aplicacionesYxjjk.01No ratings yet
- Tema 7 Funciones Notables y Operaciones Con FuncionesDocument14 pagesTema 7 Funciones Notables y Operaciones Con FuncionesAlexandra Zevallos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Condición de segundo orden mínimo globalDocument18 pagesCondición de segundo orden mínimo globalJuan Carlos Giron RojasNo ratings yet
- TP7 DiferenciabilidadDocument3 pagesTP7 DiferenciabilidadmarianelaNo ratings yet
- FuncionesDocument51 pagesFuncionesZurianis RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Metodo de Lagrange UbDocument6 pagesMetodo de Lagrange UbChristian PatiñoNo ratings yet
- EntregableDocument5 pagesEntregableDenissNo ratings yet
- Algebra de FuncionesDocument4 pagesAlgebra de FuncionesCesar Gallardo BrionesNo ratings yet
- Unid - Ii.funciones Varias Variables 2018Document79 pagesUnid - Ii.funciones Varias Variables 2018Raul Victor Velasquez JaqueNo ratings yet
- Estudio de Las Estudiode Las Funciones RealesDocument8 pagesEstudio de Las Estudiode Las Funciones RealesLeny LauraNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de FuncionesDocument3 pagesEjercicios de FuncionesRonald Quispe TiconaNo ratings yet
- Semana 5Document10 pagesSemana 5ronnner quispeNo ratings yet
- Parte4 PDFDocument4 pagesParte4 PDFjorgeNo ratings yet
- Taller de Ejercicios 09Document3 pagesTaller de Ejercicios 09Camila Valeria Ruiz RamirezNo ratings yet
- Practica de FuncionesDocument3 pagesPractica de FuncionesCHOQUE MAMANI DANIELA ESTHERNo ratings yet
- Evaluación y operaciones con funciones matemáticasDocument5 pagesEvaluación y operaciones con funciones matemáticasSeg JulsNo ratings yet
- 7-Análisis VectorialDocument49 pages7-Análisis VectorialLuis Miguel Mendoza GarciaNo ratings yet
- Clase 1 (8 05 23)Document10 pagesClase 1 (8 05 23)Gladys MontillaNo ratings yet
- Teoría de cuerpos y teoría de GaloisFrom EverandTeoría de cuerpos y teoría de GaloisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Plan de TrabajoDocument10 pagesPlan de TrabajoCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Informe de Motores 2.0Document20 pagesInforme de Motores 2.0Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Francobordo PT1Document7 pagesFrancobordo PT1Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Di 00016735 010 001Document2 pagesDi 00016735 010 001Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- La Ejecución Del Proyecto Tuvo Un 31Document1 pageLa Ejecución Del Proyecto Tuvo Un 31Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Informe 4 Maquinas CCDocument29 pagesInforme 4 Maquinas CCAbdigal Gabriel Camargo BarraNo ratings yet
- Comunicación IIDocument86 pagesComunicación IIRenzo Salas Motta100% (1)
- Ingenieria Economica Problema de Balanece Empresa StrongDocument2 pagesIngenieria Economica Problema de Balanece Empresa StrongCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Rodrigo Huasupoma Malca 3 PCDocument12 pagesRodrigo Huasupoma Malca 3 PCCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Sistema de fondeo embarcaciónDocument25 pagesSistema de fondeo embarcaciónCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Temas y Nombres ActualizadosDocument3 pagesTemas y Nombres ActualizadosCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Rodrigo Huasupoma Malca 3 PCDocument12 pagesRodrigo Huasupoma Malca 3 PCCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Acreditación APEINDocument80 pagesAcreditación APEINCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Tubo de Reynolds Labo 3Document4 pagesTubo de Reynolds Labo 3Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- TransfeDocument6 pagesTransfeCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Cronograma Máquinas Eléctricas 2017-1Document2 pagesCronograma Máquinas Eléctricas 2017-1Jordan CLNo ratings yet
- Segunda ClaseDocument2 pagesSegunda ClaseCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- TESIS - Analisis de Esfuerzos en El Alargamiento de Un BuqueDocument82 pagesTESIS - Analisis de Esfuerzos en El Alargamiento de Un BuquePercy Andia SernaNo ratings yet
- Semana NavalDocument1 pageSemana NavalCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- 5ta PCDocument2 pages5ta PCCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Tubo de Reynolds Labo 3Document4 pagesTubo de Reynolds Labo 3Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Guia de Horario 2019-Ii - Preliminar: Bef01: Ética Y Filosofía Política Bfi03: Física IiiDocument10 pagesGuia de Horario 2019-Ii - Preliminar: Bef01: Ética Y Filosofía Política Bfi03: Física IiiCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Corte Por OxigenoDocument27 pagesCorte Por OxigenoCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Programas 2Document2 pagesProgramas 2Charlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Como Estructurar Un Informe TecnicoDocument2 pagesComo Estructurar Un Informe TecnicoRückseiteA.MatosNo ratings yet
- Corte Por OxigenoDocument27 pagesCorte Por OxigenoCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- PCDocument15 pagesPCCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Problemas PropuestosDocument4 pagesProblemas PropuestosCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Acuerdos de explotación de naves y modalidades como consorcios y sociedades de gestiónDocument7 pagesAcuerdos de explotación de naves y modalidades como consorcios y sociedades de gestiónCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- San Martín de PorresDocument4 pagesSan Martín de PorresCharlie Aguero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Reporte-Pasion en AccionDocument26 pagesReporte-Pasion en AccionSheila GracidaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledFABIOLA MARICIELO GUTIERREZ LAIZANo ratings yet
- F-Dir-43 Guía de Tarea Integradora II Ing. PbioDocument11 pagesF-Dir-43 Guía de Tarea Integradora II Ing. PbioEdwinHdzNo ratings yet
- Evaluación objetivos proyectosDocument6 pagesEvaluación objetivos proyectosEder LópezNo ratings yet
- Modelo marketing holísticoDocument24 pagesModelo marketing holísticoMaria Fernanda Ortiz GutierrezNo ratings yet
- INFORME MENSUAL AMBIENTAL No 1Document23 pagesINFORME MENSUAL AMBIENTAL No 1Anibal HerronNo ratings yet
- Ensayo CamDocument12 pagesEnsayo CamEr Imperio Latino GrNo ratings yet
- Practica 1Document12 pagesPractica 1Steban LuceroNo ratings yet
- Carrera RadiologoDocument3 pagesCarrera RadiologoAlicia KaragiannisNo ratings yet
- TDR Herramientas Manuales y OtrosDocument3 pagesTDR Herramientas Manuales y OtrosJonathan Garcia CalizayaNo ratings yet
- Micrografia Cuantitativa Ramos, VilcaDocument16 pagesMicrografia Cuantitativa Ramos, VilcaChrist VNo ratings yet
- P12 Determinación de Las Propiedades Termodinámicas de Una Celda GalvánicaDocument4 pagesP12 Determinación de Las Propiedades Termodinámicas de Una Celda GalvánicaAdolfo GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Mall Plaza Food Tienda Menor 2019Document71 pagesMall Plaza Food Tienda Menor 2019carlosNo ratings yet
- Comunicacion LeemosDocument6 pagesComunicacion Leemoselena hernandez aparcanaNo ratings yet
- Candidatos Autoridades Territoriales 2019Document3,062 pagesCandidatos Autoridades Territoriales 2019Nicolas AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Demanda JemDocument6 pagesDemanda JemAlejandro Vitaliano NicolínNo ratings yet
- TermocuplasDocument9 pagesTermocuplasjimmyNo ratings yet
- Estabilización de taludes mediante muro de tablestacas y enrejado vegetadoDocument12 pagesEstabilización de taludes mediante muro de tablestacas y enrejado vegetadoLudger Suarez BurgoaNo ratings yet
- 4 Analisis y Descripcion de PuestosDocument57 pages4 Analisis y Descripcion de PuestosmariaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios. XQueryDocument5 pagesEjercicios. XQueryJuan SánchezNo ratings yet
- Metodo de BiseccionDocument15 pagesMetodo de BiseccionMarlon Maldonado AguirreNo ratings yet
- Daltonismo EjerciciosDocument3 pagesDaltonismo EjerciciosjoseNo ratings yet
- Practica Calificada 01 - A Ms Excel Apl NegDocument6 pagesPractica Calificada 01 - A Ms Excel Apl NegRicardo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Usos Óxidos HidrurosDocument4 pagesUsos Óxidos HidrurosFriida Fernanda'100% (1)
- Diseño y Desarrollo de Proceso de ProducciónDocument6 pagesDiseño y Desarrollo de Proceso de ProducciónMariela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Memorandum Multiple #033-2023/Mdn/Gm: AtentamenteDocument7 pagesMemorandum Multiple #033-2023/Mdn/Gm: AtentamenteWilliam Huayhua MamaniNo ratings yet
- 04 - Institucionalidad Del Saneamiento RuralDocument93 pages04 - Institucionalidad Del Saneamiento RuralBrian Polo BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Solicitud de Entrega de Prestaciones A Un Trabajador Presentado Ante La JuntaDocument2 pagesSolicitud de Entrega de Prestaciones A Un Trabajador Presentado Ante La Juntaclarisk074No ratings yet
- Mapa Mental Figura Juridica AlbaceaDocument1 pageMapa Mental Figura Juridica AlbaceaJHON GANEMNo ratings yet
- Introducción A CSS 3Document18 pagesIntroducción A CSS 3Alfredo MVNo ratings yet