Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QWL-Tamilnadu (Garment) PDF
Uploaded by
Anil Kumar SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QWL-Tamilnadu (Garment) PDF
Uploaded by
Anil Kumar SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
QUALITY OF WORK LIFE AMONG WOMEN EMPLOYEES WORKING IN
GARMENT FACTORIES IN COIMBATORE DISTRICT
S.Subhashini1, Dr.C.S.Ramani Gopal2
Research Scholar1, Prof and Head2, Faculty of Management Studies,
Vinayaka missions University, Salem
ABSTRACT
Many factors determine the meaning of Quality of Work Life (QWL), one of which is work
environment. Quality of Work Life has been defined as "the quality of relationship between
employees and the total working environment". The study focused on the factor influencing
QWL of employees, level of satisfaction of employees on present level of QWL .This study
attempts to evaluate the quality of work life of women employees working in selected
garment factories in Coimbatore district of Tamilnadu and analyze the relationship between
the productivity and quality of work life. Data were collected through questionnaire from a
sample of 100 women employees. The results of the study revealed areas where the factories
need to concentrate to bring about better quality of work life and thereby satisfied women
work force.
KEYWORDS: Working environment, quality of work life, satisfaction, productivity.
INTRODUCTION
Human resource plays an important role in the success of any organization, because most of
the problems in organizations are human and social rather than physical or technical. A good
quality of work life not only attracts new talent but also retain the existing talent. Quality of
work life involves job security, good working conditions, adequate and fair compensation
and equal employment opportunity all together. QWL aims to meet the twin goals of
enhanced effectiveness of organization and improved quality of life at work for employees.
But todays employee would not believe in such values of work. Employees work for salary,
and continue to work, if the conditions of work are encouraging and pleasant and terms of
Page | 22
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
employment are favorable to him. Women are considered as the major working group the
textile and Garment Industries of the country. These industries are more labor intensive and
require finest output at the end. QWL consists of opportunities for active involvement in
group working arrangements or problem solving that are of mutual benefit to employees or
employers, based on labor management cooperation.
WHAT IS QWL?
Quality of work life refers to the relationship between employees and their total
working environment. It considers people as an asset to the organization rather than cost.
This approach believes that people can perform to their best if they are given enough
autonomy in managing their work and make decision. And, so quality of work life is viewed
as an alternative to the control approach of managing people. Warret al. (1979) defined
quality of working life as indicative of variety of apparently relevant factors, including work
involvement, intrinsic job motivation, higher order need strength, perceived intrinsic job
characteristics, job satisfaction, life satisfaction, happiness, and self-rated anxiety. Direct
participation of employees in problem solving and decision making particularly in areas
related to their work is considered to be necessary condition for providing greater autonomy
and opportunity for self direction and self control. This will result in upgrading the QWL. In
todays work environment, organizations need to be flexible, and adopt a strategy to improve
the employees 'Quality of Work Life' to satisfy both the organizational objectives and
employee needs. Effective quality of work life practices in organizations makes its impact
on employee performance and the overall organizations performance.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Taghi Shahr Ashoob (2006) concluded that there is a positive and significant relationship
between quality of work life and organizational commitment.
Ali Najafi (2006) concluded that there's a positive and significant correlation between
quality of work life and managers' profiting. This means that as the quality of work life
increases, the profits of the organization will also improve.
Michael (1992) studied the impact of quality of work life on organizational commitment,
and concluded that after providing quality of work life, changes also take place in
commitment.
Davoodi (1998) in a research entitled "Study of The Impact of Quality of Work Life on Job
Satisfaction among Operational Staff of Mobarakeh Steel Complex" concluded that
involvement in decision making related to work and work conditions has a significant
relationship with job satisfaction, and this relationship is direct moderate.
Maryam Fallah (2006) in a dissertation entitled "Study and Analysis of The Relationship
between Quality of Work Life and Performance of Kosar Economical Organization Staff"
concluded that there's a significant relationship between quality of work life and
performance of staff.
Page | 23
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
Lokanadha Reddy. M Mohan Reddy.P (2010) said many factors determine the meaning of
Quality of Work Life (QWL), one of which is work environment. QWL consists of
opportunities for active involvement in group working arrangements or problem solving that
are of mutual benefit to employees or employers, based on labor management cooperation.
Jeyarathnam.M, Malarvizhi .V.R (2011) inferred the intensity of working conditions and
the behavioral aspects of the employees in the study area. It concludes that the basic
strategy for improving the quality of work life is to identify employees important needs and to satisfy
those needs. The study also indicated that dissatisfaction might happen due to lack of
recognition, tedious work, unhealthy peer relations, poor working conditions, low selfesteem, occupational stress, heavy work load, monotony, fatigue, time pressures, job
insecurity, instability of job.
Indumathy.R, Kamalraj.S (2012), found that the major factors that influence and decide the
Quality of Work Life are attitude, environment, opportunities, nature of job, people, stress
level, career prospects, challenges, growth and development and risk involved in the work
and rewards.
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
QWL is significant in relation to job satisfaction and overall performance in the
organization. But now-a-days employees are dissatisfied with the several functions of the job
and dealing with social relationship in the organization consequent upon the mechanization
and automation of the industry. Additionally disregard by others and less utilization of skills
caused stress and disappointment among the workforce. They experience alienation, which
may result from poor design of socio-technical systems. Poor quality of work life may lead
to increased absenteeism, stress and ultimately job dissatisfaction. Therefore, organizations
are required to adopt a strategy to improve the employees 'quality of work life'(QWL) to
satisfy both the organizational objectives and employee needs.
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
1. To assess the quality of work life among women employees.
2. To analyze the association between the total work experience of the women employees
and their participation in decision making.
3. To suggest methods for improving QWL by highlighting employees expectations and
required changes.
METHODOLOGY
The research design chosen is Descriptive in nature. The universe of the study comprises of
Women employees working in Garment factories in Coimbatore district of Tamilnadu .A
sample of 100 employees from various departments was selected as respondents on the basis
of purposive sampling. In this study, the primary data was collected through questionnaire
which consists of both open ended and close ended questions. The secondary data was
collected from journals and websites. To evaluate the quality of work life among the
Page | 24
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
employees the opinion of respondents was put under 5-point scales varying from Highly
Satisfied to Highly Dissatisfied as well as Strongly Agree to Strongly Disagree. Before
beginning the main survey, a pilot study was performed with 30 selected respondents to
check the reliability and validity of questionnaire instrument. The respondents were asked to
define the most important issues affecting the overall quality of work life.
DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
PROFILE OF THE RESPONDENTS
This section deals with the findings related to classification of respondents on the basis of
their age, monthly family income, qualification, experience and marital status for their
responses regarding quality of work life.
Table 1 classifies the respondents on the basis of their age, educational qualification, income
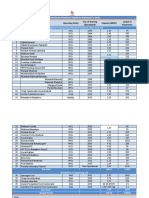
per month and marital status. Table 1 highlights that, out of 100 respondents, 30%
respondents belonged to the age group of below 25 years, 33% respondents belonged to 2535 years age group, 22% respondents belonged to 36-45 years age group, 10% respondents
belonged to 46-50 years age group and 5% respondents belonged to the age group of above
50 years. It is also clear from the table that only 13% of the respondents had experience less
than one year, 49% had experience between 1-3 years, 27% of the respondents had 3-5 years
of experience ,9% of the respondents had 5-7 years of respondents and only 2% hold more
than 7 years of experience. The table also indicates that 18% of the respondents were
uneducated, 32% of the respondents had school level education, 17.8% were ITI holders,
20% were diploma holders, 25% were graduates and 5% were post graduates.
Only 10 % of the respondents had monthly income of below Rs.5000, 57% were in the
income category of Rs.5001-10000, 20% were in the income category of Rs.10001-15000,
15% were in the income category of Rs.15001-20000 and 3% were in the income category
of above Rs.20000. From the table 1, it is clear that 63% of the respondents were married
and remaining 37% was unmarried.
TABLE 1: Demographic factors of the respondents
Demographic factors
Below 25 years
25-35 years
36-45 years
46-55 years
Above 55 years
No. of Respondents
Age
Percentage (%)
30
33
22
10
5
30%
33%
22%
10%
5%
Page | 25
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
Educational Qualification
Not educated
School level
Diploma
Graduate
Post Graduate
Less than a year
1 year 3 years
3 years -5 Years
5 years -7Years
More than 7 years
Below Rs.5000
Rs.5001-10000
Rs.10001-15000
Rs.15001-20000
Above Rs.20000
Married
Unmarried
18
32
20
25
5
Experience
13
49
27
9
2
Income(per month)
10
57
20
10
3
Marital Status
65
35
18%
32%
20%
25%
5%
13%
49%
27%
9%
2%
10%
57%
20%
10%
3%
65%
35%
PERCEPTION OF RESPONDENTS TOWARDS VARIOUS FACTORS
INFLUENCING QUALITY OF WORK LIFE
Garment units being intensively labor oriented have got to first measure the women
employees perception about their working atmosphere. It is essential to identify what the
employees are expecting and which factors are most important to them. Respondents were
influenced by a variety of factors regarding quality of work life. The respondents were asked
to rate various parameters like relationship with co-worker, workload, leave facilities,
training programs, occupational stress, career growth, respect at workplace and opportunities
for utilizing skills and abilities etc. on five point Likert scales.
Page | 26
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
TABLE 2: Perception of respondents towards various parameters regarding Quality of
Work Life
S.No
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Factors(Highly Satisfied to Highly Dissatisfied)
Relationship with co-worker
Opinion about workload
Health and safety measures
Satisfaction about feedback given
Opinion about working hours
Training programs given by the organization
Opinion about Respect at workplace
Grievance handling procedure
Mean Score
3.13
2.95
2.15
3.19
3.20
3.58
3.00
4.02
Table 2 shows the responses towards critical Parameters regarding quality of work life. The
mean scores infer that the women employees of Garment units opined that their satisfaction
on Grievance handling (4.02) was good and were dissatisfied with the Health and Safety
measures (2.15) and Grievance handling procedure (4.51)
SIGNIFICANT RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TOTAL WORK EXPERIENCE AND
PARTICIPATION IN DECISION MAKING
This section deals with the findings related to relationship between total work experience of
the workers and their participation in decision making using Chi-Square analysis.
Null Hypothesis
There is no significant relationship between the total work experience of the women
employees and their participation in decision making.
Alternate Hypothesis
There is a significant relationship between the total work experience of the women
employees and their participation in decision making.
TABLE 3: Association between the total work experience of the women employees and
their participation in decision making.
Total Work Experience
Less than a year
1 year 3 years
3 years 5 years
5 year 7 years
More than 7 years
TOTAL
yes
0
11
11
7
2
31
No. of Respondents
No
13
38
16
2
0
69
Total
13
49
27
9
2
100
Page | 27
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
TABLE 3 (a): Calculated Chi-Square value and Table Value.
Sl.No
1.
Factor
Calculated
X2 Value
Work Experience &
Employees
participation in
Decision Making
12.343
Degree of
Freedom
4
Table
Value
9.48
Remarks
Calculated X2 value
is more than the
Table value.
Table 3 & Table 3(a) shows the calculated value (12.343) is more than the table value (9.48)
at 5% level of significance. So the null hypothesis is rejected. Hence there is a significant
relationship between the total work experience of the women employees and their
participation in decision making
MEASURES TO BE ADOPTED BY THE ORGANIZATION TO IMPROVE THE
QUALITY OF WORK LIFE
TABLE 4: Satisfactory ranks given by the women employees regarding the QWL
factors of the garment factories
Factors
HS S
Salary
Health & Safety
Job Security
Work
Atmosphere
Permitted Leave
5
2
23
43
10
12
30
22
20
16
15
10
10
12 20
DS HDS Weighted
Average
30 35
220
30 40
206
22 10
334
15 20
383
Weighted
Score
14.67
13.73
22.26
25.53
Rank
23
15.93
35
239
4
5
2
1
Table: 4 shows the Measures to be adopted by the organization to improve the quality of
work life. It proves that the women workers of the organization are most satisfied with the
Work atmosphere and job security measures of the factory. And the workers are not much
satisfied about the permitted leave that could be availed and they are least satisfied with the
Salary and Health and Safety provided by the company.
Findings of the study
The findings are presented on the basis of different tools of analysis such as Simple
Percentage analysis, Chi-Square Analysis and Weighted average.
It is observed that that the women employees of the garment factory are satisfied with on
Grievance handling procedures followed by the factory and were dissatisfied with the Health
and Safety measures provided and having more of Occupational stress.
There is a significant relationship between the total work experience of the women
employees and their participation in decision making. That means only experienced workers
are included in taking critical decision making situations.
Page | 28
Asia Pacific Journal of Research
Vol: I Issue XII, December 2013
ISSN: 2320-5504, E-ISSN-2347-4793
Women workers of the organization are most satisfied with the Work atmosphere and job
security measures of the factory and are not much satisfied about the permitted leave that
could be availed. They are least satisfied with the Salary and Health and Safety provided by
the company.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
In todays Industrial World, Workers are considered as the most important assets of the
organization. An assured good quality of work life not only attracts young and new talent
but also retain the existing experienced talent. The study indicated that increase in quality of
work life results in increase in productivity. The study recommended that an attractive pay
scale can be offered and permissible leave limits can be extended. Grievance handling
procedures can be made at a satisfactory level. It is further recommended that all the workers
could be included in critical decision making situations.
REFERENCE
1. Arya, P.P (1984), Work Satisfaction and its Correlates, Indian journal of
IndustrialRelations, Vol. 20, 89-100.
2. Ashoob, Taghi, 2006. "Study of The Relationship between Quality of Work Life and
Organizational Commitment of The High Schools of Gonbad-e- Kavus City".
3. Camman, C., (1984), Productivity of Management Through QWL Programs, In
Frombun, Editor, Strategic Human Resource Management, New York: Wiley.
4. Davoodi, Seyed Mohammadreza, 1998. "Study of The Impact of Quality of Work Life on
Job Satisfaction among The Staff of Mobarakeh Steel Complex".
5. Eaton, A.E., Gordon, M.E., and Keefe, J.H., (1992), The impact of quality of worklife
programs and grievances system effectiveness on union commitment, International
and Labor Relations Review, Vol. 45, No. 3
6. Fallah, Maryam, 2006. "Study and Analysis of The Relationship between Quality of
Work Life and Performance of Kosar Economical Organization Staff".
7. Guna Seelan Rethinam, Maimunah Ismail (2008 ) Constructs of Quality of Work Life:
A Perspective of Information and Technology Professionals - European Journal of Social
Sciences Volume 7, Number 1 (2008)
8. Indumathy.R, Kamalraj.S (2012), A Study On Quality Of Work Life Among Workers
With Special Reference To Textile Industry In Tirupur District A Textile Hub - Zenith
International Journal Of Multidisciplinary Research Vol.2 Issue 4, April 2012
9. Jeyarathnam.M, Malarvizhi .V.R (2011) , Quality Of Work Life Among Sugar Mill
Employees A Study In Tamilnadu - Zenith International Journal of Business Economics
& Management Research Vol.1 Issue 3, December 2011
10. Lokanadha Reddy. M , Mohan Reddy.P (2010) Quality of work life of employees:
Emerging Dimensions - Asian Journal Of Management Research,Vol.1,Jun 2010
11. Kothari.C.R.,Research Methodology,Vikas Publication House, New Delhi, 1967
12. www.chrmglobal.com/article/183/Quality of Work Life
13. www.citehr.com
Page | 29
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Placement Information SystemDocument51 pagesPlacement Information SystemAnil Kumar Singh67% (3)
- Technical SpecificationsDocument24 pagesTechnical SpecificationsAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Labor Law 2015 ChanDocument133 pagesLabor Law 2015 ChanIris Torrente100% (9)
- Stress ManagementDocument59 pagesStress ManagementAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 03 Literature ReviewDocument5 pages03 Literature ReviewShaini Ekka100% (2)
- Inventory Management in Electric Loco ShedDocument83 pagesInventory Management in Electric Loco ShedAnil Kumar Singh60% (20)
- Company ProfileDocument28 pagesCompany ProfileAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Visa Application Document PDFDocument18 pagesVisa Application Document PDFUsama NaveedNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Instruction and Applied in IndustryDocument269 pagesCatalyst Instruction and Applied in IndustryhamedNo ratings yet
- Study of Manufacturing Process ManagementDocument73 pagesStudy of Manufacturing Process ManagementAnil Kumar Singh0% (1)
- Inventory-Management at IFFCODocument170 pagesInventory-Management at IFFCOAnil Kumar Singh100% (2)
- Cyber Security Technician COADocument302 pagesCyber Security Technician COAkanantaram7197100% (1)
- Managing Human Resources The New Normal (Ingrid L. Potgieter, Nadia Ferreira)Document343 pagesManaging Human Resources The New Normal (Ingrid L. Potgieter, Nadia Ferreira)macarena100% (1)
- Inventory ManagementDocument138 pagesInventory ManagementGoutham Bindiga50% (2)
- Course Title: DISSERTATION Course Code: MSDS600 Credit Units: Seven Level: PGDocument11 pagesCourse Title: DISSERTATION Course Code: MSDS600 Credit Units: Seven Level: PGAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- MB0052 B1699 MQP Descriptive 1Document28 pagesMB0052 B1699 MQP Descriptive 1mrahul29_400215311No ratings yet
- Course Title: DISSERTATION Course Code: MSDS600 Credit Units: Seven Level: PGDocument11 pagesCourse Title: DISSERTATION Course Code: MSDS600 Credit Units: Seven Level: PGAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- UPES Dissertation GuidelinesDocument3 pagesUPES Dissertation GuidelinesAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Guidelines For Non-Doctoral Program - V-3 October 2016 PDFDocument23 pagesDissertation Guidelines For Non-Doctoral Program - V-3 October 2016 PDFAvinash MuralaNo ratings yet
- MB0053 MQPDocument20 pagesMB0053 MQPDeepak ThapaNo ratings yet
- Major Pipelines in IndiaDocument2 pagesMajor Pipelines in IndiaAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Study On Fuel Policy Reforms in India by IEADocument116 pagesStudy On Fuel Policy Reforms in India by IEAAshok PatsamatlaNo ratings yet
- Trends Global Oil ENGDocument64 pagesTrends Global Oil ENGreneroessler2113No ratings yet
- UPES Dissertation GuidelinesDocument3 pagesUPES Dissertation GuidelinesAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Online Training and PlacementDocument158 pagesOnline Training and PlacementAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Bulletin UGC NET July 2018Document20 pagesBulletin UGC NET July 2018Mahesh100% (1)
- Eni World Oil Review 2018 Volume 1Document88 pagesEni World Oil Review 2018 Volume 1Gabriel ColmontNo ratings yet
- 14 Online Job PortalDocument65 pages14 Online Job PortalAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- HRIS - Rationale of The StudyDocument6 pagesHRIS - Rationale of The StudyAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Inventory-Management - Theory & DIDocument102 pagesInventory-Management - Theory & DIAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Everything you wanted to know about insulationDocument4 pagesEverything you wanted to know about insulationsushilk28No ratings yet
- Final Synopsis - Pallab (HRIS)Document4 pagesFinal Synopsis - Pallab (HRIS)Anil Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Inventory Management System DriplexDocument104 pagesInventory Management System DriplexAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- The Shoes Story (Positive Thinking, Negative Thinking, Attitude, Perspective, Mindset)Document1 pageThe Shoes Story (Positive Thinking, Negative Thinking, Attitude, Perspective, Mindset)Anil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management Kakatiya OverseasDocument104 pagesInventory Management Kakatiya OverseasAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management System DriplexDocument104 pagesInventory Management System DriplexAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Revitalization Plan Development Process - An ExampleDocument33 pagesRevitalization Plan Development Process - An Examplerrbangolan18No ratings yet
- Aspac HistoryDocument10 pagesAspac HistoryAngelica MiascoNo ratings yet
- Rue Byars 11e PPT Ch01Document31 pagesRue Byars 11e PPT Ch01Mai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Job Redesign and SchedulingDocument16 pagesJob Redesign and Schedulinganooj666666No ratings yet
- Teacher Tunover 2.HILINA ASSEFADocument96 pagesTeacher Tunover 2.HILINA ASSEFATilahun Mikias100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Week 7 UcspDocument134 pagesQuarter 1 Week 7 UcspNameNo ratings yet
- Philippine Government Issues On Unstoppable of NepotismDocument20 pagesPhilippine Government Issues On Unstoppable of NepotismAbdul Fatah M. MacabantogNo ratings yet
- Metrolab Industries, Inc. vs. Roldan-Confesor, G.R. No. 108855, February 28, 1996, 254 SCRA 182Document22 pagesMetrolab Industries, Inc. vs. Roldan-Confesor, G.R. No. 108855, February 28, 1996, 254 SCRA 182jonbelzaNo ratings yet
- Challenges Facing Zimbabwean Pension Funds: July 2019Document5 pagesChallenges Facing Zimbabwean Pension Funds: July 2019madzibaba munengwaNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Occupational Therapy Assistant Interview Questions and AnswersDocument17 pagesTop 10 Occupational Therapy Assistant Interview Questions and Answersakheel ahammedNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Fundamentals of Human Resource Management 13th Edition Susan L Verhulst David A DecenzoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Fundamentals of Human Resource Management 13th Edition Susan L Verhulst David A Decenzoflotageepigee.bp50100% (42)
- Imasen Phil. MFG Corp. Vs Alcon (G.R. No. 194884 October 22, 2014)Document6 pagesImasen Phil. MFG Corp. Vs Alcon (G.R. No. 194884 October 22, 2014)Ann ChanNo ratings yet
- CH 3-Strategic-HrmDocument37 pagesCH 3-Strategic-HrmHussein Sami MakkiNo ratings yet
- MOA-TEMPLATE - CompanyDocument6 pagesMOA-TEMPLATE - CompanyMichael CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Ndian Conomic Evelopment: T C XIDocument211 pagesNdian Conomic Evelopment: T C XIryan kingNo ratings yet
- The Human Impact of Data LiteracyDocument20 pagesThe Human Impact of Data LiteracySd NvNo ratings yet
- Acc 116 - Chap 3Document7 pagesAcc 116 - Chap 3Azlie ArzimiNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Employee Engagement in Mediating The Improvement of Staff Performance at The HospitalDocument12 pagesThe Importance of Employee Engagement in Mediating The Improvement of Staff Performance at The HospitalNadia ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- Emmanuel 101Document7 pagesEmmanuel 101Khen FelicidarioNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Expansion Project ManagementDocument30 pagesWarehouse Expansion Project Managementjey456No ratings yet
- Plot No. 55, 1 Floor, 4 Cross, 3 Main, R.M.V 2 Stage, Dollars Colony, Opp. Lane of Apollo Pharmacy, Bangalore-560094Document12 pagesPlot No. 55, 1 Floor, 4 Cross, 3 Main, R.M.V 2 Stage, Dollars Colony, Opp. Lane of Apollo Pharmacy, Bangalore-560094Anurag SinghNo ratings yet
- Iggy's Bread of The WorldDocument7 pagesIggy's Bread of The WorldSoumya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Upload 2Document27 pagesUpload 2NAGESH PORWALNo ratings yet
- Construction Disputes: Secret (2002)Document5 pagesConstruction Disputes: Secret (2002)acurvz2005No ratings yet