Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1 - Questions
Uploaded by
Sok SinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1 - Questions
Uploaded by
Sok SinCopyright:
Available Formats
KXEX1110: Basic Materials Science
Lecturer: Dr. Wong Yew Hoong
Semester II, 2013/2014
Tutorial 1: Atomic Structure and Bonding
1. What is the mass in grams of one atom of gold? How many atoms are there in 1 g of gold?
2. A gold wire is 0.70 mm in diameter and 8.0 cm in length. How many atoms does it
contain? The density of gold is 19.3 g/cm3.
3. A solder alloy contains 52 wt% tin and 48 wt% lead. What are the atomic percentages of
Sn and Pb in the solder?
4. An intermetallic compound has the chemical formula MgxAly, where x and y are simple
integers, and consists of 15.68 wt% magnesium and 84.32 wt% aluminum. What is the
empirical formula of this intermetallic compound?
5. A hydrogen atom exists with its electron in the n = 4 state. The electron undergoes a
transition to the n = 3 state. Calculate (a) the energy of the photon emitted, (b) its
frequency, (c) its wavelength in nanometers (nm).
6. In a commercial X-ray generator, a stable metal such as tungsten (W) is exposed to an
intense beam of high energy electrons. These electrons cause ionization events in the
metal atoms. When the metal atoms regain their ground state, they emit X-rays of
characteristic energy and wavelength. For example, a tungsten atom struck by a high
energy electron may lose one of its K shell electrons. When this happens, another electron,
probably from the tungsten L shell will fall into the vacant site in the K shell. If such a 2p
1s transition occurs in tungsten, a tungsten
K
x-ray is emitted. A tungsten
x-ray
has a wavelength of 0.2138 nm. What is its energy? What is its frequency?
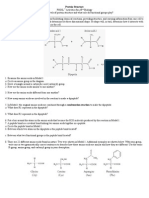
7. Write the electron configuration of the following ions using the spdf notations:
(a) Cr2+, Cr3+, Cr6+ ; (b) Mo3+, Mo4+, Mo6+ ; (c) Se4+, Se6+, Se28. If the attractive force between a pair of Sr 2+ and O2- ions is 1.29 10-8 N and the ionic
radius of the O2- ions is 0.132 nm, calculate the ionic radius of the Sr2+ ion in nanometers.
9. (a) How can the high electrical and thermal conductivities of metals be explained by the
electron gas model of metallic bonding? (b) How can the ductility of metals be
explained by the electron gas model of metallic bonding?
1
KXEX1110: Basic Materials Science
Lecturer: Dr. Wong Yew Hoong
Semester II, 2013/2014
10. What is Paulings equation for determining the percentage ionic character in a mixed
ionic-covalently bonded compound?
11. For each of the following compounds, state wheter the bonding is essentially metallic,
covalent, ionic, van der walls or hydrogen: (a) Ni, (b) ZrO 2, (c) graphite, (d) solid Kr, (e)
Si, (f) BN, (g) SiC, (h) Fe2O3, (i) MgO, (j) W, (k) H2O within the molecules, (l) H2O
between the molecules. If ionic and covalent bonding is involved in the bonding of any of
the compounds listed, calculate the percentage ionic character in the compound.
You might also like
- Tutorial 1: Atomic Structure and BondingDocument1 pageTutorial 1: Atomic Structure and BondingAbood AtiyatNo ratings yet
- Solution Tuto 1Document4 pagesSolution Tuto 1Abood AtiyatNo ratings yet
- KENYANG TECH UNI INTRO TO MATERIALS FOR ELECTRONICS TUTORIALDocument8 pagesKENYANG TECH UNI INTRO TO MATERIALS FOR ELECTRONICS TUTORIALlolaNo ratings yet
- Keep502 PDFDocument13 pagesKeep502 PDFB DamNo ratings yet
- CH 110 Tutorial On Atomic Structure and PeriodicityDocument2 pagesCH 110 Tutorial On Atomic Structure and PeriodicityBonaventure MasekoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom - Subatomic Particles and Developments Leading to Bohr's ModelDocument13 pagesStructure of Atom - Subatomic Particles and Developments Leading to Bohr's ModelNandini Classes,City Light ,Surat. Cell (9429090525No ratings yet
- Question BankeemcDocument8 pagesQuestion BankeemcapurvaNo ratings yet
- Indian School Muscat: Class - Xi Chemistry Worksheet - 01 Structure of AtomDocument2 pagesIndian School Muscat: Class - Xi Chemistry Worksheet - 01 Structure of AtomPriya Satheesh100% (1)
- WorksheetDocument2 pagesWorksheetNimisha KaushikNo ratings yet
- Solid State DPPDocument10 pagesSolid State DPPHarsha vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Sample PapersDocument3 pagesClass Xi Sample PapersAastha ThakurNo ratings yet
- ENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer)Document9 pagesENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer)Hữu Danh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank...Document7 pagesChemistry Question Bank...Vansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation Atoms and NucleiDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation Atoms and Nucleishanugamer0042No ratings yet
- Introduction to Materials Science Homework on Magnetic and Optical PropertiesDocument1 pageIntroduction to Materials Science Homework on Magnetic and Optical PropertiesHimanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Numericals 11Document73 pagesNumericals 11vamshicloud14No ratings yet
- Problems For Practice - Dual NatutreDocument2 pagesProblems For Practice - Dual NatutreSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- BPUT Question Bank For Material ScienceDocument4 pagesBPUT Question Bank For Material ScienceMr.S UpenderNo ratings yet
- As Wet-1Document8 pagesAs Wet-1Rsrao JNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Photoelectric Effect WorksheetDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Photoelectric Effect Worksheetkartavya VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - I - 1, 2, 4,11,12Document78 pagesChemistry - I - 1, 2, 4,11,12SubhanNo ratings yet
- Absorption in One-Dimensional Metallic-Dielectric Photonic CrystalsDocument7 pagesAbsorption in One-Dimensional Metallic-Dielectric Photonic CrystalsDana PopescuNo ratings yet
- Materials Characterisation ExercisesDocument4 pagesMaterials Characterisation Exercisesyaswanth1992No ratings yet
- Work Sheet - Structure of AtomDocument2 pagesWork Sheet - Structure of AtomAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Testpaper-5 Atomic Structure MARKS:45 Choose The Correct Answer: 5 1 5Document1 pageTestpaper-5 Atomic Structure MARKS:45 Choose The Correct Answer: 5 1 5Uma Maheshwari GNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry II: Crystal Field Theory and Ligand Field TheoryDocument77 pagesCoordination Chemistry II: Crystal Field Theory and Ligand Field TheorySOLeeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Atomic Structure+2022 23Document2 pagesTutorial 3 Atomic Structure+2022 23Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- AD302 GRB Electronic MAGNET Last13yrsDocument4 pagesAD302 GRB Electronic MAGNET Last13yrsonrabiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Physics - Ii Regulation 2013Document10 pagesQuestion Bank For Physics - Ii Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJINo ratings yet
- Phy June 10 PDFDocument3 pagesPhy June 10 PDFNivedh VijayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- One Mark QuestionsDocument4 pagesOne Mark Questionshari95No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument2 pagesStructure of Atommirthika .RNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04 EEE307Document1 pageAssignment 04 EEE307Masudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 1.solid StateDocument4 pages1.solid StateChemGuru 4 U0% (1)
- Assignment EL3004Document5 pagesAssignment EL3004altharunNo ratings yet
- Second Semester PH2161 - ENGINEERING Physics-II Important 2 - Mark Questions Unit Wise - 2013 EditionDocument3 pagesSecond Semester PH2161 - ENGINEERING Physics-II Important 2 - Mark Questions Unit Wise - 2013 EditionaeroherozNo ratings yet
- Assignment Phy IIDocument1 pageAssignment Phy IIKhan JanNo ratings yet
- Chem 2Document1 pageChem 2vikicool37No ratings yet
- Lectut-MTN-105-Doc-MT 201A-Tutorial - CH 1 (4 Files Merged)Document9 pagesLectut-MTN-105-Doc-MT 201A-Tutorial - CH 1 (4 Files Merged)Vikhyath KstNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Exercises by ResonanceDocument35 pagesAtomic Structure Exercises by Resonancechiragjn12086% (7)
- Chem Sem4 Unit 1:chapter1Document13 pagesChem Sem4 Unit 1:chapter1Ankit AthreyaNo ratings yet
- Doc-20230304-Wa0000 230704 130512PDF 230704 130544Document33 pagesDoc-20230304-Wa0000 230704 130512PDF 230704 130544Seshakrishna SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Ph2161 Engineering Physics IIDocument3 pagesPh2161 Engineering Physics IIClement RajNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - CPP-2-1Document4 pagesAtomic Structure - CPP-2-1UtsavNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure File1Document3 pagesAtomic Structure File1thirupathi KNo ratings yet
- 1-PhysRevMaterials 7 024417Document10 pages1-PhysRevMaterials 7 024417r ZhNo ratings yet
- 11 HW ChemistryDocument6 pages11 HW ChemistryJ BalanNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. V Semester Physics:: Paper VI (A) Solid State Physics:: Imp QuestionsDocument2 pagesB.Sc. V Semester Physics:: Paper VI (A) Solid State Physics:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument1 pageAtomic StructureLakshya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Metal Lathe Waste As Material For The Absorption of Electromagnetic Radiation Based OrgoniteDocument4 pagesUtilization of Metal Lathe Waste As Material For The Absorption of Electromagnetic Radiation Based OrgoniteStellaEstel100% (1)
- Inorganic Materials Chemistry and Nanomaterials Module SynopsisDocument48 pagesInorganic Materials Chemistry and Nanomaterials Module SynopsisJorge Humberto Flores AvilaNo ratings yet
- LILAVATIBAI PODAR SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL (ISC) ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS questionsDocument3 pagesLILAVATIBAI PODAR SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL (ISC) ELECTRONS AND PHOTONS questionsAnkit BansalNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India.,: Jee-Main - 1 Year Revision - Chemistry - AssignmentsDocument9 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India.,: Jee-Main - 1 Year Revision - Chemistry - AssignmentswanetanishqNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class 11Document8 pagesAssignment Class 11Just a PlaceNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On D and F Block PDFDocument9 pagesResearch Paper On D and F Block PDFVishwa RahulNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument7 pagesRevision QuestionsShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 5Document2 pagesPhysics Assignment 5Anuza PaneruNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Physics (Question Bank) - Dual Natutre of Matter and Radiation (Subj) - 04.02.2022Document4 pagesClass Xii - Physics (Question Bank) - Dual Natutre of Matter and Radiation (Subj) - 04.02.2022Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Research 2Document66 pagesResearch 2a.2005kamalNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Achievements: Selection of Papers Presented at the Birmingham Metallurgical Society's Diamond Jubilee Session, 1963-1964From EverandMetallurgical Achievements: Selection of Papers Presented at the Birmingham Metallurgical Society's Diamond Jubilee Session, 1963-1964W. O. AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Customs Duty CalculatorDocument3 pagesCustoms Duty CalculatorAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 - QuestionsDocument1 pageTutorial 7 - QuestionsSok SinNo ratings yet
- nrcs144p2 042170Document50 pagesnrcs144p2 042170senaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Crack Propagation and Creep Life PredictionDocument4 pagesFatigue Crack Propagation and Creep Life PredictionSok SinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 - QuestionsDocument1 pageTutorial 10 - QuestionsSok SinNo ratings yet
- 11 Cells and BatteriesDocument21 pages11 Cells and BatteriesSok SinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - QuestionsDocument1 pageTutorial 2 - QuestionsSok SinNo ratings yet
- Krieger Princeton 0181D 10531Document156 pagesKrieger Princeton 0181D 10531Sok SinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - QuestionsDocument1 pageTutorial 3 - QuestionsSok SinNo ratings yet
- School-Based Assessme NT: Project 2013-2014Document31 pagesSchool-Based Assessme NT: Project 2013-2014Sok SinNo ratings yet
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument8 pagesFalling Head Permeability Testdwivediashish2100% (2)
- Chapter 7 Limits and ContinuityDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Limits and ContinuityHsk Kogilan50% (2)
- 3.5 Practising Helthy LifeDocument9 pages3.5 Practising Helthy LifeSok SinNo ratings yet
- Fin1877 PDFDocument2 pagesFin1877 PDFRizqka PertiwiNo ratings yet
- BI2 Q&A (Kedah)Document12 pagesBI2 Q&A (Kedah)SimPorNo ratings yet
- 3.4 HomeostasisDocument40 pages3.4 HomeostasisSok SinNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pentaksiran Baru STPM The New STPM Assessment System For ChemistryDocument20 pagesSistem Pentaksiran Baru STPM The New STPM Assessment System For ChemistrySok SinNo ratings yet
- MM2 (PHG)Document19 pagesMM2 (PHG)SimPor100% (6)
- 3.1 Coordination and ResponseDocument13 pages3.1 Coordination and ResponseSok SinNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Percubaan Tahun 2008 Tingkatan 3 Penilaian Menengah RendahDocument23 pagesPeperiksaan Percubaan Tahun 2008 Tingkatan 3 Penilaian Menengah RendahSimPor100% (3)
- Eagle Color SeriesDocument2 pagesEagle Color SeriestrumukyNo ratings yet
- Types of Microtomes & PartsDocument7 pagesTypes of Microtomes & PartsWhite WolfNo ratings yet
- 2019 Cre Ii L24-26Document32 pages2019 Cre Ii L24-26Aman PrasadNo ratings yet
- ME 555 Stress Analysis Unit 3Document50 pagesME 555 Stress Analysis Unit 3TheoNo ratings yet
- University of Perpetual Help System DALTA Calamba CampusDocument23 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help System DALTA Calamba CampusJ HNo ratings yet
- Deterministic Performance EstimationDocument36 pagesDeterministic Performance EstimationErwdukNo ratings yet
- 03 Protein StructureDocument5 pages03 Protein StructureIvan TranconNo ratings yet
- NUREG 1123 Revision 2Document446 pagesNUREG 1123 Revision 2Mike CantrellNo ratings yet
- AISC DG11 ExamplesDocument7 pagesAISC DG11 ExamplesMarcel Toruño MendezNo ratings yet
- MDM BeamDocument19 pagesMDM BeamBrian chunguliNo ratings yet
- Metallic ChemistryDocument14 pagesMetallic ChemistryEko Budi PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Pass SurveyingDocument31 pagesPass SurveyingAmit ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Stability in Control SystemsDocument20 pagesStability in Control Systemssamir100% (1)
- AISC RequirementsDocument1 pageAISC Requirementsparag7676No ratings yet
- Submarine Cable Installation ContractorsDocument19 pagesSubmarine Cable Installation Contractorswiji_thukulNo ratings yet
- Effect of Shortening Type On The Rheological Characteristics of Cookie DoughDocument11 pagesEffect of Shortening Type On The Rheological Characteristics of Cookie DoughAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- 4aap Method PhenolDocument5 pages4aap Method PhenolhitessshhhNo ratings yet
- ExamplesCh18 AccessibleDocument34 pagesExamplesCh18 AccessibleSyed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Design For Manufacturing and AssemblyDocument168 pagesDesign For Manufacturing and Assemblygnanasekar100% (2)
- 421 Lab Report 3Document4 pages421 Lab Report 3Christian SawayaNo ratings yet
- Glass production process guideDocument10 pagesGlass production process guideSumbul Ahsum HaleemNo ratings yet
- Spor LanDocument30 pagesSpor LanKumar sssssNo ratings yet
- Physics Linx Class 11 Logarithm ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics Linx Class 11 Logarithm ProblemsPartha PrustyNo ratings yet
- FVM Witch OpenFOAM-MatlabDocument817 pagesFVM Witch OpenFOAM-MatlabDavid Mestanza100% (1)
- Lihardo Rotua Sinaga. Maulidatul Fadhilah. Maria Angel Aftritesia. BilPhys19. Thermodynamics. Mini ResearchDocument14 pagesLihardo Rotua Sinaga. Maulidatul Fadhilah. Maria Angel Aftritesia. BilPhys19. Thermodynamics. Mini ResearchFitri handayaniNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Velocity Steel Pipe Schedule 40 Metric UnitsDocument1 pageFluid Flow Velocity Steel Pipe Schedule 40 Metric UnitsRobert ThanhNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Mobile Robot Motion PlanningDocument151 pagesIntroduction to Mobile Robot Motion Planningvarun_bluejayNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Current is Directly Proportional to VoltageDocument5 pagesOhm's Law: Current is Directly Proportional to VoltageLawrence DecanoNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Unforged Bar Bulb in Engine Valve ManufacturingDocument6 pagesReduction of Unforged Bar Bulb in Engine Valve ManufacturingSurajNo ratings yet
- 8 ChannelDocument39 pages8 ChannelGertjan DuniceriNo ratings yet