Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscles of The Back
Uploaded by
jsdlzj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageTrapezius medial superior nuchal line and external protuberance of occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, and spinous process of vertebrae C7-T12 lateral clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula. Trapezius and rhomboid muscles pull scapular upward and medially.
Original Description:
Original Title
Muscles of the back.xlsx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTrapezius medial superior nuchal line and external protuberance of occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, and spinous process of vertebrae C7-T12 lateral clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula. Trapezius and rhomboid muscles pull scapular upward and medially.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageMuscles of The Back
Uploaded by
jsdlzjTrapezius medial superior nuchal line and external protuberance of occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, and spinous process of vertebrae C7-T12 lateral clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula. Trapezius and rhomboid muscles pull scapular upward and medially.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
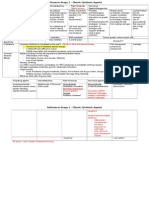
name
proximal attachments/origin
distal attachments/insertion
movement
nerve to muscle and spinal
segment
Trapezius
medial superior nuchal line & external
protuberance of occipital bone,
ligamentum nuchae, & spinous process of
C7-T12
lateral clavicle, acromion and
spine of scapula
Upper fibers: elevate and upwardly
rotate scapula; extend neck Middle
fibers: adduct (retract) scapula Lower
fibers: depress and help upper fibers
upwardly rotate scapula
C3, C4 & accesssory cranial
nerve (XI, 11)
Latissimus dorsi
spines of lower six thoracic vertebrae,
lumbar vertebrae, iliac crest via
thoracolumbar fascia, sacrum, lower three
or four ribs, and inferior angle of scapula
floor of intertubercular (bicipital)
groove of humerus
adducts, medially rotates, and extends
arm at shoulder
thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
Rhomboid major
spinous process of T2-T5 vertebrae
medial border of scapula inferior
to spine
retracts and elevates the medial border of
scapula while it downwardly rotates the
lateral angle
dorsal scapular nerve (C5)
Rhomboid minor
spinous process of C7-T1 vertebrae
medial border of scapula superior
to spine
retracts and elevates the medial border of
scapula while it downardly rotates the
lateral angle
dorsal scapular nerve (C5)
Levator scapulae
transverse processes of the C1-C4
medial border of scapula between
spine and superior angle
Elevates medial border of scapula while
downwardly roating lateral angle; helps
trapezius and rhomboid muscles pull
scapula upward and medially; bends neck
laterally
dorsal scapular nerve (C5) and
ventral primary rami of C3 and
C4
Serratus posterior superior
nuchal ligament and the spinous
processes of vertebrae C7 to T3
elevate second to fifth ribs, aids deep
inspiration
intercostal nerves T2 through T5
Serratus posterior inferior
spinous processes of vertebrae T11 to L2
depress lower ribs, aids expiration
intercostal nerves T9 through T12
Splenius capitis
inferior half of ligamentum nuchae/nuchal
ligament and spinous processes of C7T3/T4
superior nuchal line of occipital
bone and mastoid process of
temporal bone
Splenius cervicis
spinous process of T3-T6
transverse processes of C1-C3/C4
Semispinalis capitis
transverse processes of C7-T6 and
articular process of C4-C6
between superior and inferior
nuchal lines of occipital bone
inferior attachment: ilium (iliac crest)
superior attachments: angle of
ribs
Longissimus of erector spinae
(intermediate column)
inferior attachment: sacrum (and
transverse processes?)
superior attachments: transverse
processes of vertebra and rib
tubercles. (Its most superior
portion, the longissimus capitis
muscle, attaches to the mastoid
process of the temporal bone)
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Spinalis of erector spinae
(medial column)
inferior attachments: spinous processes
superior attachments: spinous
processes (spinalis muscle is
present at lumbar, thoracic, and
cervical vertebrae levels)
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
iliocostalis of erector spinae
(lateral column)
superior borders of ribs 2 to 5,
lateral to their angles
inferior borders of ribs 9 to 12,
lateral to their angles
antagonist
bilateral action: extends head and neck
dorsal (= posterior) rami of spinal
unilateral actions: laterally flexes and
nerves C2-C6
rotates head and neck to same side
bilateral action: extends and
hyperextends head and neck unilateral
actions: laterally flexes and rotates head
and neck to same side
dorsal rami of middle and lower
cervical spinal nerves
bilateral action: extends and
hyperextends head and neck unilateral dorsal rami of middle and lower
actions: rotates head and neck to opposite
cervical spinal nerves
side
All three columns of the erector spinae
muscle extend the vertebral column when
both sides work together. If only one side
is active, it bends the VC laterally toward
the side that is active.
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
rectus
abdominis
muscle
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Second StripeDocument1 pageSecond StripejsdlzjNo ratings yet
- FibroidsDocument4 pagesFibroidsjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Management As An InternDocument2 pagesIV Fluid Management As An InternjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Analgesia For InternsDocument4 pagesAnalgesia For InternsjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Perinatal Depression From Adolescence and Before Conception (VIHCS) : 20-Year Prospective Cohort StudyDocument9 pagesPrediction of Perinatal Depression From Adolescence and Before Conception (VIHCS) : 20-Year Prospective Cohort StudyjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- AMSA Rural Health SurveyDocument3 pagesAMSA Rural Health SurveyjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument5 pagesOsteoporosisjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- VMAT Protocol - Victorian Medical Assistance TeamDocument27 pagesVMAT Protocol - Victorian Medical Assistance TeamjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Signs, Causes and TreatmentDocument3 pagesDKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Signs, Causes and TreatmentjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- INTERN Referee Process and Sample FormDocument2 pagesINTERN Referee Process and Sample FormjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Uni of Melb 2005 Mcqs EditedjrDocument19 pagesUni of Melb 2005 Mcqs EditedjrjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Explanation StationDocument4 pagesExplanation StationjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateDocument3 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StatejsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Mock Peg Stem: Zhengjie Lim 2018Document7 pagesMock Peg Stem: Zhengjie Lim 2018jsdlzjNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- CHARGE SyndromeDocument1 pageCHARGE SyndromejsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Articular System and Joints OverviewDocument9 pagesArticular System and Joints OverviewjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- MED1022 Study Guide 2014Document213 pagesMED1022 Study Guide 2014jsdlzj100% (1)
- AAFP - Evaluation of Acute Abdomen in AdultsDocument8 pagesAAFP - Evaluation of Acute Abdomen in AdultsTe HineahuoneNo ratings yet
- Acute InflammationDocument38 pagesAcute InflammationjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- PolypsDocument2 pagesPolypsjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesArrhythmiasjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology Summary - Weeks 1 To 6Document2 pagesEpidemiology Summary - Weeks 1 To 6jsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Social Determinants of Health and Health PromotionDocument1 pageSocial Determinants of Health and Health PromotionjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Back PDFDocument4 pagesMuscles of The Back PDFjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Overview of neuromuscular blocking agents and their mechanisms of actionDocument2 pagesOverview of neuromuscular blocking agents and their mechanisms of actionjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Own Notes-Anticancer 2Document2 pagesOwn Notes-Anticancer 2jsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Zee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesDocument2 pagesZee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Own Notes-Anticancer 1Document2 pagesOwn Notes-Anticancer 1jsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Grow 6 Inches Taller in 90 DaysDocument90 pagesGrow 6 Inches Taller in 90 Daysyankev100% (6)
- 0 - Biomechanics of Lumbar SpineDocument25 pages0 - Biomechanics of Lumbar SpineCHAITANYA SAHITHINo ratings yet
- Function of The BrainDocument16 pagesFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy I OsteologyDocument42 pagesGross Anatomy I OsteologySonia FelixNo ratings yet
- Guenon Rene Studies in Hinduism 106p PDFDocument106 pagesGuenon Rene Studies in Hinduism 106p PDFСаша ПаповићNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Traction TractionDocument5 pagesCare of Patients With Traction TractionMOHAMMAD JABBER M. PAUDACJRNo ratings yet
- Main bones and joints of the human skeletal systemDocument2 pagesMain bones and joints of the human skeletal systemTai Hui XinNo ratings yet
- Board Review Axial Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum, Pelvis, Cranial) Touro Burns 2022Document169 pagesBoard Review Axial Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum, Pelvis, Cranial) Touro Burns 2022Sean LeeNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Structure & Function of The Body 14th Edition by Gary A. Thibodeau Kevin T. PattonDocument36 pagesTest Bank Structure & Function of The Body 14th Edition by Gary A. Thibodeau Kevin T. Pattonbachababy83% (6)
- Melo Et Al 2022 Sciadonus AlphacrucisDocument8 pagesMelo Et Al 2022 Sciadonus AlphacrucisMarcelo Roberto Souto de MeloNo ratings yet
- Exogenous Spinal Trauma - Clinical Assessment and Initial ManagementDocument7 pagesExogenous Spinal Trauma - Clinical Assessment and Initial Managementtaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Forces in BodyDocument48 pagesForces in Bodytema_racamaNo ratings yet
- Morphology, Systematics, and Biology of The Spanish MackerelsDocument148 pagesMorphology, Systematics, and Biology of The Spanish MackerelsRio AlmusataNo ratings yet
- Growing Taller ForeverDocument44 pagesGrowing Taller ForeverDr Hector C Sikazwe0% (2)
- SDSG Radiographic Measuremnt ManualDocument120 pagesSDSG Radiographic Measuremnt ManualYuliana Wiralestari100% (2)
- Differential Diagnosis of Low Back Pain: Elizabeth Huntoon, MD, and Marc Huntoon, MDDocument7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Low Back Pain: Elizabeth Huntoon, MD, and Marc Huntoon, MDGangsar DamaiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument11 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyKean GB60% (5)
- 2024 LHC 205Document31 pages2024 LHC 205WaqasSanaNo ratings yet
- Cervical & Lumbar Traction GuideDocument21 pagesCervical & Lumbar Traction Guidevinayman100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injury....Document44 pagesSpinal Cord Injury....PrabhuswamyChowdiah75% (4)
- Spinal Cord Injury Case StudyDocument8 pagesSpinal Cord Injury Case StudyMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- Manual of Osteopathic Technique 1993Document271 pagesManual of Osteopathic Technique 1993kevin0631100% (9)
- Simulation of Lumbar Spine Biomechanics Using AbaqusDocument1 pageSimulation of Lumbar Spine Biomechanics Using AbaqusSIMULIACorpNo ratings yet
- Asia ScaleDocument30 pagesAsia ScaleKavya MittalNo ratings yet
- Osteopathy Principles and Practice v1 (Proby) PDFDocument126 pagesOsteopathy Principles and Practice v1 (Proby) PDFAnonymous 3NmUUDt100% (1)
- Pages 183 Physiological Psychology MCQ 1Document34 pagesPages 183 Physiological Psychology MCQ 1AdsNo ratings yet
- RAMNATH Sciatica Presentation 0812Document57 pagesRAMNATH Sciatica Presentation 0812Nisa SulistiaNo ratings yet
- Part 5 Emergency Response PlanDocument23 pagesPart 5 Emergency Response Planalex.kollosovNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spondylosis Guide: Causes, Symptoms & ExercisesDocument49 pagesLumbar Spondylosis Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Exercisesfreska ayu wardhaniNo ratings yet
- The Prostate Is A Common Site of Carcinoma. It: Abdomen and PelvisDocument62 pagesThe Prostate Is A Common Site of Carcinoma. It: Abdomen and PelvissrisakthiNo ratings yet