Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 3 Useful Chemical Building Blocks
Uploaded by
griggans100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
198 views1 pageYou should be able to: define an element, compound and mixture. Match up symbols and names of elements. Classify materials as elements, compounds or mixtures using information provided.
Original Description:
Original Title
2 3 useful chemical building blocks
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentYou should be able to: define an element, compound and mixture. Match up symbols and names of elements. Classify materials as elements, compounds or mixtures using information provided.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
198 views1 page2 3 Useful Chemical Building Blocks
Uploaded by
griggansYou should be able to: define an element, compound and mixture. Match up symbols and names of elements. Classify materials as elements, compounds or mixtures using information provided.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
2.
3 Useful Chemicals (Building Key Points Key terms
blocks)
Syllabus Summary (H) = higher only Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Element
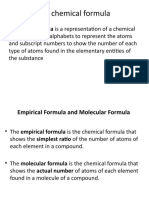
You should be able to: • Elements contain only 1 type of atom, compounds contain at least 2 different atoms Product
Compound Balanced
• define an element, compound and mixture; joined together
Mixture Formula
• match up symbols and names of elements • Compounds are very difficult to separate into their elements
Atom Organic
• recall some chemical symbols • Mixtures are two substances that are not chemically combined
Nucleus Inorganic
• classify materials as elements, compounds • Mixtures are easy to separate
Proton
or mixtures using information provided
Neutron
• State that all matter is made up of atoms
Electron
• recall the structure of the atom
Reactant
• recall that all of the atoms that make up an
element have the same number of protons
and electrons in their atoms.
• Match up formulae and names of some
compounds
• Recognise reactants and products in a Element Compound Mixture
symbol equation
• name the some compounds listed given The Atom
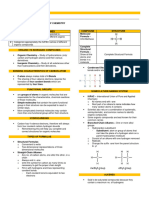
• Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are
their formulae;
found in the nucleus, electrons orbit the nucleus in shells. The first shell can hold a
• write word and symbol equations to show
max of 2 electrons, the second and third shells hold a max of 8
how atoms are rearranged in the chemical
• Protons are positive and have a mass of 1, neutrons are neutral and have a mass of 1
reactions
and electrons are negative and have a mass of 0
• recall and use the formulae of some
compounds l to write balanced symbol Chemical Symbols and Formulae
equations (H)
• Most element symbols are the first letter of the name e.g. Carbon = C
• state that scientists sort out chemicals into C2H7N
• Some are the first two letters of the name e.g. Cobalt = Co
two groups, those that contain carbon and
those that do not; • A few are the first letter and another letter from the name e.g. Magnesium = Mg
• state that living things all contain the • Some are the first letter or letters of the latin name e.g. Sodium = Natrium = Na
element carbon and non-living usually don’t • The formula of a compound tells us which atoms and how many it contains e.g.
• recall the names of some chemicals that do CO2 = 1 x carbon atom and 2 x oxygen atoms
not contain the element carbon
• recognise inorganic and organic Equations
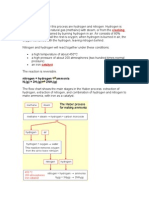
substances; • An equation can be written in words or symbols
• use the words organic and inorganic
correctly and explain the words origin E.G. Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide
• use chemical formulae to recognise a 2 Mg + O2 → 2MgO (must be balanced)
substance as organic or inorganic
(reactants) → (products)
• recall that there are many useful
substances that contain carbon atoms
Organic compounds
• explain why fossil fuels are a source of
• Organic compounds contain carbon, inorganic compound don’t
organic substances;
• Livings things all contain the element carbon
• state that organic chemicals are very • Many useful substances contain carbon e.g. plastics, petrol, products from oil
important in our lives and most are derived
from crude oil.
You might also like
- Chapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument103 pagesChapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and IonsSyahir HamidonNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Periodic Table Lesson 1Document20 pagesGRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Periodic Table Lesson 1dodoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Atomic StructureDocument36 pagesTopic 3 Atomic StructureKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- BMED 105 Basic Chemistry of Life (NOTES)Document4 pagesBMED 105 Basic Chemistry of Life (NOTES)Jobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Essentials Pearson 2016Document253 pagesEssentials Pearson 2016Devansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument24 pagesElements Compounds and MixturesMegan SarahNo ratings yet
- 1 Lec - ChemDocument6 pages1 Lec - ChemAllen Rivera ReyesNo ratings yet
- CHM 092 CHAPTER 1 - Matter &stoichiometryDocument128 pagesCHM 092 CHAPTER 1 - Matter &stoichiometryAisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Complete Lecture 4x4Document17 pagesChapter 2 Complete Lecture 4x4michaelaNo ratings yet
- Non Metalic Substances and Covalent BondingDocument47 pagesNon Metalic Substances and Covalent Bonding42h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Matter, molecules and periodic tableDocument40 pagesLecture 3 - Matter, molecules and periodic tableNaff WariNo ratings yet
- Study Guides 2.1-2.3Document8 pagesStudy Guides 2.1-2.3MA. ASUNCION BeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical FoundationDocument50 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Foundation杨致远No ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry: Course Code: 211502 Course NameDocument17 pagesEngineering Chemistry: Course Code: 211502 Course NameSalama NaumanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Material Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument33 pagesChapter 2 - Material Structure and Interatomic BondingamraqstnaNo ratings yet
- Intro Matter 2 PHDocument27 pagesIntro Matter 2 PHCheick SANOUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Atoms and MoleculesDocument62 pagesChapter 2 - Atoms and MoleculesRoselyn CastilloNo ratings yet
- BioM I Lectures 1 - 3 (SB) 2014Document69 pagesBioM I Lectures 1 - 3 (SB) 2014nonhle nosiphoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Workbook 1Document10 pagesChemistry Workbook 1Dean KimNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesDocument32 pagesAtoms, Elements and Molecules & Compounds and MixturesTshanna RobertsNo ratings yet
- Lecture #9 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesLecture #9 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Organic ChemistryG8 ODL Mary Angeline M. GalmanNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument62 pagesAtoms and Molecules: Larry Brown Tom Holmemuhammad ali shakeelNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRYSAN JOSE, KRIZZIA FAYE U.No ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument39 pagesNaming CompoundsgallosaaronmatthewNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 3Document11 pagesOrg Chem 3Bertille Marie ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 2Document12 pagesOrg Chem 2Bertille Marie ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 5Document12 pagesOrg Chem 5Bertille Marie ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Elements, Atoms, and The Atomic Theory: Type of AtomDocument7 pagesElements, Atoms, and The Atomic Theory: Type of AtomSasikumar MadhavanNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM CHEMICAL FORMULA and NAMING OF COMPOUNDSDocument35 pagesGEN CHEM CHEMICAL FORMULA and NAMING OF COMPOUNDSKC KayeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument11 pagesChemistry of LifeNadiyah KarriemNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Module 2 Elements and CompoundsDocument30 pagesQuarter 1 Module 2 Elements and CompoundsJeline MacallaNo ratings yet
- Science 9: The Variety of Carbon CompoundsDocument10 pagesScience 9: The Variety of Carbon Compoundsrussel castilloNo ratings yet
- Principles of BiochemistryDocument68 pagesPrinciples of Biochemistryblackss copsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Chemistry: Lesson 2: Atoms and MoleculesDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Fundamentals of Chemistry: Lesson 2: Atoms and MoleculesKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- Typeselements CompoundsDocument27 pagesTypeselements CompoundsEverrome AsicoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Chemistry of Life EditedDocument68 pages2.1 The Chemistry of Life EditedPatricia Jayshree Samuel Jacob100% (1)
- Campbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeDocument42 pagesCampbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeSophia Andrei VillalunaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 - ChemistryDocument38 pagesCLASS 10 - ChemistryKavyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between A Compound and A MixtureDocument27 pagesThe Differences Between A Compound and A Mixturearies triwidajatiNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, Ions and Chemical FormulasDocument22 pagesAtoms, Molecules, Ions and Chemical FormulasHIEP PHAM HOANGNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry IntroductionDocument39 pagesBasic Chemistry IntroductionMitch EspinasNo ratings yet
- Atoms PresentationDocument10 pagesAtoms PresentationSu AlghNo ratings yet
- M1 Lec - HandoutDocument5 pagesM1 Lec - HandoutAngel Fiona GañaNo ratings yet
- Study Questions Introduction To ChemistryDocument5 pagesStudy Questions Introduction To ChemistryMsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Functional Groups LECTUREDocument34 pagesChemistry Functional Groups LECTUREkassy jayNo ratings yet
- Quarter1.Week2.Elements and CompoundDocument47 pagesQuarter1.Week2.Elements and CompoundEvelyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Elements and AtomsDocument28 pagesElements and AtomsJulien Kristi HernandezNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Chemical FormulaDocument18 pages3.3 Chemical FormulaLIM CHEE BOON MoeNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Functional GroupsDocument4 pages2.1 Functional GroupsBasti SantiagoNo ratings yet
- ReactivityDocument42 pagesReactivityDarryl WHDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-CarbonDocument23 pagesChapter 4-Carbonjanardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 General Chemistry 1Document16 pagesLesson 4 General Chemistry 1Genevee Ryeleen DelfinNo ratings yet
- Chap 03Document22 pagesChap 03AmandaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS Chemistry Note 1 Definitions of The TermsDocument3 pagesEdexcel AS Chemistry Note 1 Definitions of The TermsSajaniNo ratings yet
- BASIC CHEMISTRY Lect 1Document23 pagesBASIC CHEMISTRY Lect 1briosojoshua0No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 and 3 ChemDocument3 pagesLesson 2 and 3 ChemJazmine Lei PalomoNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Exam-QuestionsQUADRATS AND TRANSECTSDocument8 pagesExam-QuestionsQUADRATS AND TRANSECTSgriggansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry c1 Core PracticalsDocument18 pagesChemistry c1 Core PracticalsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Biology FieldworkqsDocument9 pagesBiology FieldworkqsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms and FoodDocument4 pagesMicroorganisms and FoodgriggansNo ratings yet
- Heart Gcse Qs OnlyDocument6 pagesHeart Gcse Qs OnlygriggansNo ratings yet
- Physics p1 Core PracticalsDocument19 pagesPhysics p1 Core PracticalsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Biology b1 Core Practical QuestionsDocument17 pagesBiology b1 Core Practical Questionsgriggans0% (1)
- Paying 4 ElectricityDocument1 pagePaying 4 ElectricitygriggansNo ratings yet
- How To Reference - Student GuideDocument1 pageHow To Reference - Student GuidegriggansNo ratings yet
- BTEC Science UNIT 5 NervesDocument4 pagesBTEC Science UNIT 5 NervesgriggansNo ratings yet
- The Haber ProcessDocument1 pageThe Haber ProcessgriggansNo ratings yet
- Extract LeadDocument2 pagesExtract LeadgriggansNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Part of Homeostasis and ControlDocument7 pagesHormones: Part of Homeostasis and ControlgriggansNo ratings yet
- BTEC Science UNIT 5 HomeostasisDocument5 pagesBTEC Science UNIT 5 Homeostasisgriggans100% (4)
- Balanced ForcesDocument17 pagesBalanced ForcesgriggansNo ratings yet
- As RevisionDocument4 pagesAs RevisiongriggansNo ratings yet
- Bending LightDocument24 pagesBending Lightgriggans100% (2)
- GSK AssignmentDocument4 pagesGSK Assignmentgriggans100% (4)
- Chromatography StarterDocument1 pageChromatography StartergriggansNo ratings yet
- Revision Class NotesDocument7 pagesRevision Class NotesgriggansNo ratings yet
- Metals in AirDocument1 pageMetals in AirgriggansNo ratings yet
- Task and Mark Sheet 1)Document6 pagesTask and Mark Sheet 1)griggans100% (1)
- Igneous RocksDocument4 pagesIgneous RocksgriggansNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument20 pagesReflectiongriggansNo ratings yet
- SlimeDocument5 pagesSlimegriggansNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument7 pagesClassificationgriggansNo ratings yet
- ReactionsandparticlesDocument4 pagesReactionsandparticlesgriggansNo ratings yet
- Waves and Radiation Front SheetDocument3 pagesWaves and Radiation Front Sheetgriggans100% (5)
- BTEC First Diploma in Applied Science Student Tracking SheetsDocument6 pagesBTEC First Diploma in Applied Science Student Tracking Sheetsgriggans100% (6)
- Tomatosphere AssignmentDocument2 pagesTomatosphere AssignmentgriggansNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pour CardDocument1 pageConcrete Pour Cardegirijesh50% (2)
- Lead Glass: A Historical Overview of its Composition, Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsDocument13 pagesLead Glass: A Historical Overview of its Composition, Manufacturing, Properties and ApplicationsAnas SiddNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Academic Science (SNC 1D1) Unit 2: Chemistry: Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Academic Science (SNC 1D1) Unit 2: Chemistry: Classification of Matterzia mooreNo ratings yet
- Tentative Final NotesDocument13 pagesTentative Final NotesRockNo ratings yet
- P Nagar, Near Ordnance Factory: 0t, R111 KOTA / S T. / CAIDocument2 pagesP Nagar, Near Ordnance Factory: 0t, R111 KOTA / S T. / CAISupradeep GoudNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Various Cement GA and Their Impact On Grindability and Cement PerformanceDocument6 pagesCharacterization of Various Cement GA and Their Impact On Grindability and Cement PerformanceNam HuynhNo ratings yet
- Hydrochloric Acid GuideDocument4 pagesHydrochloric Acid GuideEazy DigitalNo ratings yet
- Class A1A2Document8 pagesClass A1A2luisfer811No ratings yet
- Sept E: Bleaching Agent Containing ChlorineDocument3 pagesSept E: Bleaching Agent Containing ChlorinemayNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - 1st Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesScience 7 - 1st Quarter Examjoan marie Pelias89% (95)
- 9701 s15 QP 22 PDFDocument8 pages9701 s15 QP 22 PDFAl BeruniNo ratings yet
- How To Solder: Captain Matt Audette Jan 2017Document24 pagesHow To Solder: Captain Matt Audette Jan 2017DK SinghNo ratings yet
- The Plastic Piping Industry in North AmericaDocument20 pagesThe Plastic Piping Industry in North AmericaBembotas BembaNo ratings yet
- SCC 5Document1 pageSCC 5TasmanijskaNemaNo ratings yet
- Ampco 18.23: Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageAmpco 18.23: Technical Data SheetdedosimoesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: How The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 3: How The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructurePineda, Sean AlfredNo ratings yet
- CICO Thermoseal XLDocument2 pagesCICO Thermoseal XLsanjayNo ratings yet
- Carbon Regeneration KilnsDocument3 pagesCarbon Regeneration KilnsLuis LabradorNo ratings yet
- Potential Damage PKTDocument7 pagesPotential Damage PKTFebri Ramdani NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions for Non-Electric Pressure Steam Sterilizers Models 1915X, 1925X, 1941XDocument24 pagesOperating Instructions for Non-Electric Pressure Steam Sterilizers Models 1915X, 1925X, 1941Xwilmerrr100% (1)
- Analysis of a Simple Salt- Lead NitrateDocument1 pageAnalysis of a Simple Salt- Lead NitrateShreeNo ratings yet
- Complexes, Ligands and ChelatesDocument21 pagesComplexes, Ligands and Chelatesraisul razaNo ratings yet
- Getting Start of Dispensing-180713Document33 pagesGetting Start of Dispensing-180713Tuyên VũNo ratings yet
- Effect of Ripe and Unripe Plantain Peel Ash On Concrete Compressive StrengthDocument4 pagesEffect of Ripe and Unripe Plantain Peel Ash On Concrete Compressive StrengthOluwaseun AdetayoNo ratings yet
- DIY Wood Acrylic Color Changing LED LampDocument13 pagesDIY Wood Acrylic Color Changing LED Lampsachin0307No ratings yet
- Gaugeable Tube Fittings Andadapter FittingsDocument56 pagesGaugeable Tube Fittings Andadapter FittingsDiegoNo ratings yet
- Biaxial Geogrid : Product PropertiesDocument1 pageBiaxial Geogrid : Product PropertiesINARQ1979No ratings yet
- SS Catalog DigitalDocument83 pagesSS Catalog DigitalAnonymous VevcFXASNo ratings yet
- Titratievoorbeelden Assay MethodsDocument13 pagesTitratievoorbeelden Assay MethodsGBL 22No ratings yet
- Concrete TypesDocument19 pagesConcrete Typesraj100% (1)