Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nandihar Hydropower Project
Uploaded by
Ali Nawaz KhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nandihar Hydropower Project
Uploaded by
Ali Nawaz KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
BACKGROUND
Ghorband and Nandihar Hydropower Projects were identified by Pakhtunkhwa Hydel
Development Organisation (PHYDO) [the then SHYDO], Peshawar, Pakistan and Deutsche
GesellschaftfuerTechnischeZusammenarbeit GmbH (GTZ), Eschborn, Germany through a
report titled Hydropower Development in Mountainous areas of NWFP: 1992. The details
for these Projects are given in Vol. III Chapter5 of Regional Development Study Indus
Swat / Mansehra West through an inventory of hydropower potential for Indus Swat and
Mansehra area. Only small portion of hydropower potential (about 15%) has since been
developed. A large portion of the same is yet to be harnessed.
Afterwards PHYDO had planned to develop stepwise several of these identified schemes
with selective alternatives. Out of these Ghorband Hydropower Project was identified as
SCHEME No. 2 / Alternative 1 SeraiKarora on Ghorband / Shin River (18 MW) now
called as Ghorband Hydropower Project [GHPP] and Scheme No. 7/ Alternative 1 Thakot
on Nandihar River (10.3 MW) now called as Nandihar Hydropower Project [NHPP] and are
entrusted to Ghorband Nandihar Hydropower Consultants [GNHPC] for present Feasibility
Stage Study.
Accordingly, Consultancy Agreement for Feasibility Studies of both Ghorband and Nandihar
Hydropower Projects was signed on 22 June, 2012 between Joint Venture of Consultants
comprising of NDC, BAK and Hydro-Techin association with LI and KEC(GNHPC)by
Pakhtunkhwa HYDEL Development Organization (PHYDO) Peshawar (Client) at a total
cost of Rs. 65,864,464/- breakup of which is tabulated below:
Sr. No.
Description
Amount (Rs.)
Salary Cost/Remunerations
34,058,067
Direct (Non Salary) Cost Projection Office
14,362,589
Direct Cost Field Office
3,103,808
Field Survey and Investigations Cost
14,340,000
Grand Total: 65,864,464
(Rupees Sixty Five Million Eight Hundred&Sixty Four Thousand Four Hundred and Sixty
Four only)
Note: Later, on the request of the Consultants an Addendum No. 01 was issued in Nov 2012
wherein Consultants were allowed to adjust/reallocate funds within various Direct Costs
Heads and for new items of Costs as warranted for completion of services. Consultants were
also allowed to adjust Salary Costs within the provisions earlier made.
As a part of Services, the Consultants prepared a combined Inception Reportfor both the
Hydropower Projects which was submitted to the Client in Oct 2012, whereas, combined Mid
Term Report was submitted in Jul 2013.
S-1
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
In this Report only Nandihar Hydropower Project is discussed.
INTRODUCTION
Nandihar Hydropower Project (GHPP) was proposed as runoff the river (Diurnal peaking
Project) on NandiharKhwar River in Battagram District of KPK. After thorough deliberations
in different meetings and discussions with the Client, finally it was decided that a Power
Tunnel (from Batle to the site of the Powerhouse inbetween Bar Goriar and KuzGoriar
Villages) is to be constructed. This option was approved by PHYDO and the Consultants
were allowed to carry out additional topographic surveys, Geotechnical studies etc for
conducting the Feasibility Studies of this option.The proposed Hydropower Station, as per
TOR, will have no huge reservoir. However, it would include Weir, Tunnel, Penstock and
Powerhouse etc. These components may have some impact on the environments,
temporary or permanent.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE PROJECT
The Project is based on the concept of divertinga partial flow of Nandihar River by means of
a diversion weir and further through a 5.9 Km power tunnel to the Power House where water
discharges to the Indus River some 12 Km further downstream.
By this concept some 215m head can be obtained for Power Generation which permits a
maximum available capacity ex-generator of 12.3 MW and a mean annual energy generation
of 69.84GWh at a base cost of US $ 40.078 million. Salient features of the project are as
follows;
Salient features of Nandihar Hydropower Project
Description
Design Discharge
Environmental Flows
No. & Type of Units
Design Discharge (single unit)
Net Head
Turbine Efficiency at QD
Symbol Value
Qd
6.5
Qe
0.2
2
Qunit
3.25
Hn
214.37
T
92
Generator Efficiency
98%
Transformer Efficiency
Tr
99.5%
Annual Shutdown
Results
Gross Power
Annual Energy
Plant Factor
TAS
20
days
PG
EA
PF
12.3
69.84
64.7
MW
GWh
%
S-2
Unit
m3/sec
m3/sec
Pelton
m3/sec
m
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
General Information
Total Cost of the
Project
Unit
Cost
of
Generation
EIRR (compared to
CCGT)
Period
of
Construction
PKR.5039.41 M (US
$ 47.097 M)
Penstock length
Rs. 3.935/-
Penstock Dia
Penstock)
13.46%
No. of Turbine
2 Pelton Units
36 Months
Rated Power
12.3 MW
Left
Bank
of
NandiharKhwar
KuzGandur Village
Annual
Energy
Annual Shutdown
20 Days
Catchment Area
Powerhouse location
Weir & reservoir
Weir Height
Free board
Normal
Reservoir
level
Minimum reservoir
level
Reservoir Capacity
@743
Weir Top Level
Tail water level
Length of the Weir
crest
Desander
TYPE
463 km2
Goriar Village
64.7%
12.8 m
1.8 m
Plant Factor
Spillways details
Main Upper Spillway
Gated/Ungated
Height of the Spillway
743 m a.s.l
Width of the Spillway
3.5 m
738 m a.s.l
No. of Bays
4 No.
No. of Chambers
2 No.
Total Length
76.5 m
Project Layout
Weir Location
400.0 m
(Steel
Estimated
1.3 m
69.84 GWh
Radial Gated
2.5 m
744.8 m a.s.l
512 m a.s.l
Discharge capacity at
261 Cumecs
Max. RWL
Bottom Outlets
Gated/Ungated
Vertical Lift Gate
92 m
Height of the Spillway
1.5 m
Width of the Spillway
No. of Bays
Discharge capacity at
Max. RWL
Total
Discharge
Capacity
1.5 m
3 No.
0.1 MCM
Surface
Total Width of 2.
9.73 m
Chambers
Gross Head
224.5
Surge Shaft Dia
4.0 m
22.0 m
10.2
Surge Shaft Height
Net Head
214.37
Power house
Power & energy
Type
6.5 Cumecs
Intake
(Lateral
Intake) at Left
Headrace
tunnel
(HRT) Length
HRT
Diameter
(Horse Shoe)
Single Intake
Trashrack
334.0 Cumecs
Surge shaft
Total Head loss
Design Discharge
73 Cumecs
Surface
House
Power
Main Dimensions (W x L
43.5 x 14 x 17
xH)
with
Tailrace Channel
5968.0 m
Type
Trapezoidal
2.3 m
Total length
18 m
S-3
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
SCOPE OF SERVICES
Scope of services of the Consultants was elaborated in the Terms of Reference (TOR)
issued by the PHYDO, which comprises the following tasks:
- TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEY
- HYDROLOGY AND SEDIMENTATION
- ENGINEERING GEOLOGY & EVALUATION OF SEISMICITY
- ASSESMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL IMPACTS
- DESIGN AND LAY OUT OF STRUCTURES
- DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTRUCTIN PLAN
- TRANSMISSION OF POWER
- UNIT PRICE
- BENEFITS OF THE PROJECT
- ECONOMIC PARAMETERS
- SENSITIVITY ANALYSES
- OPERATONATIONAL COST ESTIMATE
- SERVICES AND REPORTING BY THE CONSULTANTS
- PC-I
All the aforementioned tasks are described in detail in the succeeding chapters, however,
the status of each task is briefly given here under:
Topographic Survey
Topographic Survey of Nandihar HPP Area was commenced during the month of Jan 2013.
The delay in commencement of this very important task can be attributed to the absence of
Project Manager for about three months and late fielding of Survey Parties. In order to
achieve a much suitable result, the Topographic Survey was repeated time and again with
the help of TOS and Satellite Images etc. The survey was finally completedto the satisfaction
of all concerned in the month of July 2013.
Hydrology and Sedimentation
The hydrological studies for Nandihar HPP were required to determine probable runoff of the
project catchment and the discharges available for power generation in its magnitude and
seasonal variations as well as quantum of sediments flow. These studies included
Installation of Gauge Station and fielding of suitable Hydrographer, Gauge/Sediments
observers etc. All the Hydrological and Sedimentation studies were carried out according to
TOR provided by the Client and completed in Oct 2013, however, gauge
observation/sediment measurement continued till end Dec 2013.
Engineering Geology & Evaluation of Seismicity
Geological and Geotechnical Engineering was conducted satisfactory, however, it was a little
bit delayed because of late fielding of Chief Geologist. Simultaneously, construction material
survey was carried out as a parallel activity. Similarly, Seismic Hazard Evaluation was also
carried out by a relevant expert. All these activities were successfully completed by Oct 2013
and reports by concerned experts were submitted in Nov 2013.
S-4
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
Project Layout and Hydraulic Design
The information provided in PHYDO/GTZ report is of very basic level. The revised estimated
power is 10.3 MW. Several layouts were studied for this project. In planning,these layouts
and recommendations of the GTZ report were kept in view. However, several significant
changes were found necessary in the light of latest available topographic, hydrological and
environmental data.
The hydraulic design studies of Nandihar Hydropower Project include design of weir, intake,
sand trap, power tunnel, surge shaft, penstock, powerhouse and tailrace.
Seismic Hazards
Seismic Hazard Evaluation for the Nandihar Hydropower Project has been carried out using
both Deterministic as well as Probabilistic Approaches. In this regard all the earthquakes
recorded/ reported from 1973 till April 2013 were studied and all the tectonic features that
can pose seismic hazard for the project were taken care of. Acceleration attenuation
relationships used in this risk assessment were also tested against the Strong Motion data
recorded at Abbottabad and Tarbela Observatories. Project volume and electric-power
generation as well as water storage capacity along with possible human-life/ property
hazard, in case of its failure, were also kept in mind while suggesting design parameters
related to the Peak Ground Accelerations, both for a Maximum Credible Earthquake and an
Operating Basis Earthquake
Structural Design Studies
Structure design of the project has been done ensuring the stability and safety of structures
against encountered forces/loads including hydrostatic pressure, earth pressure, imposed
live, uplift, seismic and other design loads etc using guidelines of established manuals and
code of practices. Reinforcement Design is based on ACI Ultimate Strength Design (USD)
method. Grade 60 bars are used. Load factors for components other than power tunnel, are
based on ACI 318-01. Factors for power tunnel are adopted from US Army Corps of
Engineers EM 1110-2-2901 Tunnels and Shaft in Rock. Design strength of structural
members has been taken as a product of nominal strength and strength reduction factor.
Allowable stresses are according to ACI 318. Design considerations for all individual Project
Components are elaborated in the relevant Sections of the report.
Mechanical Equipment
Mechanical equipment includes turbines, governors, inlet valves, gates, stop-logs, trashracks and cranes etc. For the operating net head range of 210.57m to 214.37m a Francis
type of turbine could be considered for Nandihar power plant. However for the range of
discharges available, from 27.54 m3/s (maximum) to 0.94 m3/s (minimum), a Pelton turbine
is considered more appropriate, as it has a better efficiency over the whole range of
discharges. From the comparative study of various turbine sizes and combinations, two
turbines each with 4.25 m3/sec flow have been selected. Considering turbine efficiency of
92% and the head range of 210.57m to 214.37m and design flow of 4.25m3/s, the power will
be 6.15 MW for each unit considering generator efficiency as 98%. For determining
appropriate unit capacity, both technical as well as economic aspects have been examined
in a comparative study taking into account equipment dimensions, transport limitations,
S-5
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
power and energy benefits, manufacturing experience, power system regulation, and cost
estimates etc.
Electrical Equipment
Theelectricalequipmentforpowerproductionandtransmission,comprisingallnecessaryauxiliary
suppliesandservices,willbeconstructedtoprovideamaximum
power
outputwiththehighestreliabilityand availability.Theequipmentmainlyconsists of:
Twoverticalshaft generators of 6.15 MW each feeding two 11 kV outgoing feeders,
11kV Switchyard consisting of circuit breakers, Isolators C.Ts, P.Ts, earthing
switches, measuring devices etc.each connected via 11 kV single core cables to the
respective generator circuit breaker.
Two 11KV outgoing feedersforinterconnectionofthepowerplantwithtwooutgoing
transmissionlinecircuit either feeding radial load or synchronized with local 11 kV
distribution line(132 kV Grid is available at Thakotabout 3km away).
AuxiliarysupplyforallelectricalpowerneedsoftheNANDIHARbuildingsandtheintake
area.
Measuring, controlandprotectiondevicesforallfunctionsoftheplantincluding the control
Room.
Environmental and Social Assessment (IEE & SIA)
A series of meetings were held by the GNHPC Environmentalist/Social Expert with local
population, elites of the area, public representatives, district administration, revenue, forest,
agriculture, irrigation & other departments for consultation, information sharing and obtaining
their views about the proposed project. Lands in Nandihar Project area comprise cultivated,
waste lands and settlements. Fruits and thick forest lies in the Project area, which will have
to be removed during construction stage of this Project.
It is concluded that the Project activities will have some adverse environmental impacts of
medium to high level in some (identified) areas. The overall environmental impact will be
from low to medium. There should be trained staff at the project site for environmental
management and monitoring.
Cost Estimates
The total project construction cost of civil works has been estimated on the basis of current
market. Appropriate escalation factor has also been applied to meet with current market
prices. In case of cost of E&M Equipment, due consideration has been given to the current
recession in the market. Equipment which can be manufactured locally has also been
appropriately utilized. The estimate is based on current price level and in converting US
dollars to Pak Rupees, the prevailing exchange rate as in January -2014 has been adopted
viz US$ 1 = Rs. 107.00.
Base cost of the project has been estimated as PKR 4288 million (40.078 million $) and the
investment cost as PKR 5039 million including price escalation, custom duties and interest
during construction.
S-6
Nandihar Hydropower Project Feasibility Report
Executive Summary
Based on these cost estimates for the project, economic and financial analyses of the project
have been carried-out.
Economic Analysis
To demonstrate economic feasibility of Nandihar Hydropower Project, equivalent thermal
power cost approach has been used. The life cycle cost of Nandihar HPP has been
compared with the life cycle of cost of alternative equivalent thermal plant i.e. Steam
Generation Plant using Furnace Oil (FO Plant) and a Combined Cycle Gas Turbine (CCGT).
Above analysis reveal that;
Nandihar Hydropower Project (NHPP) is an economical and feasible Project on River
Nandihar. Its installed capacity, as estimated through different studies, comes to
12.3MW. The Project will generate 69.84GWh of annual energy when fully
commissioned, which is anticipated to take 36 months after fulfillment of requisite
formalities like detailed Engineering Design, Tendering and Letter of Commencement
to the Contractor.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Studies have determined the overall impact
rating of the Project activities as low to medium.
It is concluded that the IEE is adequate to justify environmental and social clearance
of the Project. There is no need for further analysis and the environmental and social
assessment of the Project.
Project Economic analysis of the project reveals that the project is economically
viable as the Economic Internal Rate of Return (EIRR) is greater than the opportunity
cost of capital.
EIRRs calculated for the CCGT & Furnace oil Thermal alternatives come to 14.22%
& 24.25% with CDM benefits and 13.46% & 23.87% without CDM Benefits
respectively.
FIRR comes to 11.56% whereas cost of Generation is PKR 3.935 per unit.
The Economic comparison FO plant and CCGT with Hydropower plant indicates CB
ration without CDM as 1.12 & 1.81 and with CDM as 1.15% & 1.84% respectively.
Revenue has been estimated on the basis of system sale price of 10.35 PKR/Kwh.
2% auxiliary consumption has been assumed.
Conclusions
From the Study it has been concluded that the project is viable and recommended for
detailed engineering design and execution.
S-7
You might also like
- Retaining Wall DesignDocument5 pagesRetaining Wall DesignAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Request For Expressions of Interest (Consulting Services - Firms Selection)Document2 pagesRequest For Expressions of Interest (Consulting Services - Firms Selection)Ali Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Byelaws Pec For ConsultantsDocument56 pagesByelaws Pec For ConsultantssaifullahbhuttaNo ratings yet
- 96 MW Batakundi HPP Feasibility Report Executive SummaryDocument24 pages96 MW Batakundi HPP Feasibility Report Executive SummaryAli Nawaz Khan100% (1)
- An Intro To Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument21 pagesAn Intro To Computational Fluid DynamicsRorldanNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Magazine ASCEDocument88 pagesCivil Engineering Magazine ASCEAli Nawaz Khan100% (2)
- Kandiah Geodetic Control NetworkDocument8 pagesKandiah Geodetic Control NetworkAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
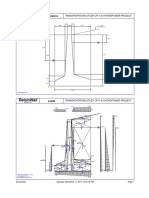
- POWERHOUSE Longintudinal DrawingDocument1 pagePOWERHOUSE Longintudinal DrawingAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation For SeminarDocument43 pagesPresentation For SeminarAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 300 Solved Problems in Geotechnical EngineeringDocument0 pages300 Solved Problems in Geotechnical Engineeringmote3488% (17)
- PPDB AdDocument2 pagesPPDB AdAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Validation of A Hybrid 3D and 2D Numerical Flow Modeling Technique For An Instantaneous Dam Break 56 13Document7 pagesValidation of A Hybrid 3D and 2D Numerical Flow Modeling Technique For An Instantaneous Dam Break 56 13Ali Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Computational Modeling of Flow Over A SpillwayDocument64 pagesComputational Modeling of Flow Over A SpillwayAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Impact of Spillway Crest Levels on Upstream Flows for Marala HPPDocument6 pagesCFD Analysis of Impact of Spillway Crest Levels on Upstream Flows for Marala HPPAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Hydropower Potential and Water ProjectsDocument72 pagesPakistan's Hydropower Potential and Water ProjectsAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Initial Environmental ExaminationDocument46 pagesInitial Environmental ExaminationAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Impact of Spillway Crest Levels on Upstream Flows for Marala HPPDocument6 pagesCFD Analysis of Impact of Spillway Crest Levels on Upstream Flows for Marala HPPAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Marala HPP Environmental StudyDocument37 pagesMarala HPP Environmental StudyAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Kaigah HPP - Executive SummaryDocument27 pagesKaigah HPP - Executive SummaryAli Nawaz Khan100% (1)
- 300MW Balakot HPP Feasibility ReportDocument17 pages300MW Balakot HPP Feasibility ReportAli Nawaz Khan50% (2)
- Thakot BriefDocument2 pagesThakot BriefAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- DRE-12 Ch-1 Dam Introduction 28-8-2012Document48 pagesDRE-12 Ch-1 Dam Introduction 28-8-2012Ali Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Sediment Flushing Analysis of Karot ReservoirDocument31 pagesSediment Flushing Analysis of Karot ReservoirAli Nawaz Khan100% (1)
- Trash RackDocument17 pagesTrash RackAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet: Review of Hydraulic Design of Shamozai Cross Regulator at RD 50+000 of Machai CanalDocument4 pagesCalculation Sheet: Review of Hydraulic Design of Shamozai Cross Regulator at RD 50+000 of Machai CanalAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Integer at Ed OperationDocument84 pagesInteger at Ed OperationAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Integer at Ed OperationDocument84 pagesInteger at Ed OperationAli Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Environmental Engineering (3-0-0) : Objective: This Course Introduces The Students To The Environmental Consequences ofDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Engineering (3-0-0) : Objective: This Course Introduces The Students To The Environmental Consequences ofAbhi MishraNo ratings yet
- Resource Efficiency For Textile IndustryDocument19 pagesResource Efficiency For Textile IndustrysulemaanNo ratings yet
- The Manufacturing Progress Report For HRSG Non-Pressure Part & DCSDocument17 pagesThe Manufacturing Progress Report For HRSG Non-Pressure Part & DCSAgustinus SitioNo ratings yet
- Leyeco IiiDocument20 pagesLeyeco IiiShishi LagrosasNo ratings yet
- CV Inghon Update May 21Document6 pagesCV Inghon Update May 21Inghon SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit and Energy SavingDocument21 pagesEnergy Audit and Energy SavingPrafulla Mandlekar100% (2)
- Pestel PresentationDocument11 pagesPestel PresentationJervis Mercado LacatanNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard Time debate over NE statesDocument2 pagesIndian Standard Time debate over NE statesvijaynarayan guptaNo ratings yet
- Sidewalk Labs MIDP Volume 2Document234 pagesSidewalk Labs MIDP Volume 2jillianiles100% (1)
- Ontario's Electricity Distribution System MapDocument1 pageOntario's Electricity Distribution System Mapswell20% (1)
- 2 Earthing Schemes: 2.4 Selection Criteria For The TT, TN and IT SystemsDocument1 page2 Earthing Schemes: 2.4 Selection Criteria For The TT, TN and IT Systemstucurici5740No ratings yet
- Rupp Direct Fired BrochureDocument28 pagesRupp Direct Fired BrochureAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- For The Written Activity The Learner Will Complete The Following Assessment. Total Assessment Length Should Be Between 800 - 1500 WordsDocument13 pagesFor The Written Activity The Learner Will Complete The Following Assessment. Total Assessment Length Should Be Between 800 - 1500 WordsAnmol PoudelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Standards, Certification and Marking: ObjectivesDocument15 pagesUnit 2: Standards, Certification and Marking: ObjectivesHaianh PhamNo ratings yet
- A National Vision Smart Grids KoreaDocument10 pagesA National Vision Smart Grids KoreaAlan Edu RojasNo ratings yet
- What Is A Shell CorporationDocument25 pagesWhat Is A Shell CorporationJames MondeloNo ratings yet
- Nema SM 24 1991 R2002Document93 pagesNema SM 24 1991 R2002surawutwijarn100% (2)
- Xavier S Alumini RecordsDocument8 pagesXavier S Alumini RecordsvivekthotaNo ratings yet
- Catalog 2011 Maharashtra Multi Distributors LTDDocument106 pagesCatalog 2011 Maharashtra Multi Distributors LTDinfo8243100% (1)
- UP6 4-11 KW Oil-Flooded Rotary Screw CompressorsDocument8 pagesUP6 4-11 KW Oil-Flooded Rotary Screw CompressorsMiguel AndresNo ratings yet
- Maple Ridge Pitt Meadows News - June 22, 2011 Online EditionDocument38 pagesMaple Ridge Pitt Meadows News - June 22, 2011 Online EditionmapleridgenewsNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of Proposed Palestinian Electrical NetworkDocument44 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of Proposed Palestinian Electrical NetworkHamada Almasalma0% (1)
- EE Optimization for Power Plants TrainingDocument313 pagesEE Optimization for Power Plants TrainingItilekha DashNo ratings yet
- Esp LVDocument104 pagesEsp LVAbdullaKakkadKarumbilNo ratings yet
- Petsec Energy Research Report 13 June 2017 FinalDocument40 pagesPetsec Energy Research Report 13 June 2017 Finalrasnowmah2012No ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument43 pagesSummer Training ReportVikalp SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift MethodsDocument239 pagesArtificial Lift MethodsEbenezer Amoah-Kyei100% (2)
- India Sugar Sector Report - Oct18Document37 pagesIndia Sugar Sector Report - Oct18VINAYAK AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Final Coal ReportDocument101 pagesFinal Coal Reportvikasgupta2750% (2)
- Training Program Guide 2013Document52 pagesTraining Program Guide 2013yash1239100% (1)