Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.6 Voltage Protection: Rate of Change of Frequency (81R)
Uploaded by
riddler_007Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.6 Voltage Protection: Rate of Change of Frequency (81R)
Uploaded by
riddler_007Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1) 7SR158 Description of Operation
3.6
Voltage Protection: Rate of Change of Frequency (81R)
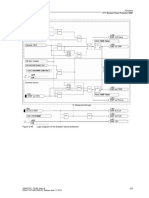
Rate of Change of Frequency (ROCOF) is used to detect islanding or loss of connection between a generator
and the main utility supply.
Six elements are provided 81R-1, 81R-2, 81R-3, 81R-4, 81R-5 & 81R-6.
All ROCOF elements have a common ROCOF Input Mode setting defining whether phase to phase (Ph-Ph) or
phase to neutral (Ph-N) voltages are used. The frequency calculation is based on the highest input voltage
derived from the voltage selection algorithm. The frequency of all VT inputs is monitored continually, switching
between reference voltages is instantaneous.
All elements will be blocked if all voltages fall below the 81R U/V Guard setting.
81R-n Setting sets the pick-up frequency change for the element.
The direction of frequency change, Positive (increasing frequency), Negative (decreasing frequency) or Both,
being looked for by the element is set by the 81R-n Direction setting.
An output is given after elapse of the 81R-n Delay setting.
Operation of the voltage vector shift elements can be inhibited from:
Inhibit 81R-n
A binary or virtual input.
81R U/V Guard
Under voltage guard element.
User Inhibit
Reylogic (graphical logic)
Figure 3-6 Logic Diagram: Rate of Change of Frequency (81R)
2014 Siemens Protection Devices Limited
Chapter 1) Page 27 of 38
7SR158 Technical Manual
Section 4: Control & Logic Functions
4.1
Manual CB Control
Functionality is provided to allow a Relay to manually Open and Close its associated Circuit-Breaker (CB).
A Manual Open Command can be initiated in one of three ways: via a Open CB binary input, via the data
communication Channel(s) or from the relay CONTROL MODE menu. It causes an instantaneous operation via
the Open CB binary output.
It should be noted that a CB Open initiated in this way is fundamentally different from a CB Trip initiated by a
protection function. A CB Trip will initiate functionality such as fault data storage and operation counter.
A Manual Close Command can be initiated in one of three ways: via a Close CB binary input, via the data
communication Channel(s) or from the relay CONTROL MODE menu. It causes an instantaneous operation via
the Close CB binary output.
Repeated Manual Closes are avoided by checking for Positive edge triggers. Even if the Manual Close input is
constantly energised the relay will only attempt one close.
Close CB Delay
Operation of the Close CB binary output can be delayed by the Close CB Delay setting. The status of this delay
is displayed on the relay fascia as it decrements towards zero. Only when the delay reaches zero will the close
command be issued and related functionality initiated.
Blocked Close Delay
The close command may be delayed for the duration that a Block Close CB signal is applied to a binary input.
This can be used, for example, to delay CB closure until the CB energy has reached an acceptable level. The
output Close CB Blocked indicates this condition.
Open CB Delay
Operation of the Open CB binary output can be delayed by the Open CB Delay setting. The status of this delay
is displayed on the relay fascia as it decrements towards zero. Only when the delay reaches zero will the close
command be issued and related functionality initiated.
CB Controls Latched
CB controls for manually closing and tripping can be latched for extra security.
With Reset operation, the control resets when the binary input drops off. This can lead to multiple control restarts
due to bounce on the binary input signal.
With Latch operation, the close or trip sequence always continues to completion (or sequence failure) and bounce
on the binary input is ignored.
Reset operation can be useful, however, as it allows a close or trip sequence to be aborted by dropping off the
binary input signal.
Chapter 1) Page 28 of 38
2014 Siemens Protection Devices Limited
You might also like
- Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (Acsr) : Characteristics of A1/S1 B Conductors As Per IEC 1089/91 TYPE A1/S1 BDocument12 pagesAluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (Acsr) : Characteristics of A1/S1 B Conductors As Per IEC 1089/91 TYPE A1/S1 Briddler_007No ratings yet
- Additional Standards: PrefaceDocument1 pageAdditional Standards: Prefaceriddler_007No ratings yet
- Aaac Conductor PDFDocument18 pagesAaac Conductor PDFJerin LeenusNo ratings yet
- Functions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFDocument1 pageFunctions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFriddler_007No ratings yet
- Additional Standards: PrefaceDocument1 pageAdditional Standards: Prefaceriddler_007No ratings yet
- Device conventions guideDocument1 pageDevice conventions guideriddler_007No ratings yet
- Device conventions guideDocument1 pageDevice conventions guideriddler_007No ratings yet
- Overview of DIGSI 5 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5?Document1 pageOverview of DIGSI 5 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5?riddler_007No ratings yet
- Eg 4Document1 pageEg 4riddler_007No ratings yet
- Monitoring of The Circuit Breaker Auxiliary Contacts: Functions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFDocument1 pageMonitoring of The Circuit Breaker Auxiliary Contacts: Functions 2.17 Breaker Failure Protection 50BFriddler_007No ratings yet
- Eg 5Document1 pageEg 5riddler_007No ratings yet
- Eg 8Document1 pageEg 8riddler_007No ratings yet
- 1 Overview of DIGSI 5: 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5? 12 1.2 Engineering Philosophy and Terms 13 1.3 User Interface 23Document1 page1 Overview of DIGSI 5: 1.1 What Is DIGSI 5? 12 1.2 Engineering Philosophy and Terms 13 1.3 User Interface 23riddler_007No ratings yet
- Eg 7Document1 pageEg 7riddler_007No ratings yet
- Symmetrical ComponentsDocument2 pagesSymmetrical ComponentsHamayoun Murtaza100% (1)
- Eg 6Document1 pageEg 6riddler_007No ratings yet
- Preface: SIPROTEC 5 Engineering Guide, Manual C53000-G5040-C004-1, Release 02.2013 3Document1 pagePreface: SIPROTEC 5 Engineering Guide, Manual C53000-G5040-C004-1, Release 02.2013 3riddler_007No ratings yet
- Siprotec: Preface Functions Mounting and Commissioning Technical Data Appendix Literature Glossary IndexDocument1 pageSiprotec: Preface Functions Mounting and Commissioning Technical Data Appendix Literature Glossary Indexriddler_007No ratings yet
- Note For Your Own Safety, Please Observe The Warnings and Safety Instructions Contained in This ManualDocument1 pageNote For Your Own Safety, Please Observe The Warnings and Safety Instructions Contained in This Manualriddler_007No ratings yet
- Siprotec 5 Engineering Guide DIGSI 5Document1 pageSiprotec 5 Engineering Guide DIGSI 5riddler_007No ratings yet
- 1.3 Setting ModeDocument2 pages1.3 Setting Moderiddler_007No ratings yet
- Symmetrical components calculation balanced unbalanced systemsDocument1 pageSymmetrical components calculation balanced unbalanced systemsriddler_007No ratings yet
- Charging Current in Long Lines and HV CablesDocument1 pageCharging Current in Long Lines and HV Cablesriddler_007No ratings yet
- 7SR158 Argus ContentsDocument1 page7SR158 Argus Contentsriddler_007No ratings yet
- Preface: Purpose of This ManualDocument2 pagesPreface: Purpose of This Manualriddler_007No ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Measurands: FW# FUN INF Description Asdu COTDocument2 pages3.4.2 Measurands: FW# FUN INF Description Asdu COTriddler_007No ratings yet
- Chapter 2) 7SR158 Technical ManualDocument2 pagesChapter 2) 7SR158 Technical Manualriddler_007No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Greenhouse Gas Reduction Strategy 2020 2022Document2 pagesGreenhouse Gas Reduction Strategy 2020 2022te fannyNo ratings yet
- Compressor Anti SurgeDocument4 pagesCompressor Anti SurgeAboaliNo ratings yet
- Colorful Convection CurrentsDocument2 pagesColorful Convection CurrentsJustin LoredoNo ratings yet
- 2018-2020 - Yamaha - mt-07 CAP1Document104 pages2018-2020 - Yamaha - mt-07 CAP1Ernesto Capdepon CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Barometric LegsDocument25 pagesRethinking Barometric LegsLeomar Pcheco100% (1)
- Green SkillsDocument5 pagesGreen Skillsnaina premrajka0% (1)
- RCC RESO 20 06 - (Central - Scheduling) PDFDocument57 pagesRCC RESO 20 06 - (Central - Scheduling) PDFSherwin SabandoNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Hose Winch For Pile Driving Hammer (Menck) PDFDocument1 pageLeaflet Hose Winch For Pile Driving Hammer (Menck) PDFGhyd ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Compressibility of Natural GasDocument20 pagesCompressibility of Natural GasIman AkbariNo ratings yet
- Cyberview SB Corporate PresentationDocument11 pagesCyberview SB Corporate PresentationVaniesa EdwardNo ratings yet
- Differential Relay MiCOM P632Document7 pagesDifferential Relay MiCOM P632gjkjai0% (1)
- Weymouth and Panhandle Equations For Gas PipelinesDocument4 pagesWeymouth and Panhandle Equations For Gas PipelinessgrsthNo ratings yet
- Csa Type Teck 90: Csa Teck90 Armoured Power, Multi-Conductor, 5000V, UnshieldedDocument2 pagesCsa Type Teck 90: Csa Teck90 Armoured Power, Multi-Conductor, 5000V, Unshieldedjoseodelgado17No ratings yet
- 1ai) Tender Design Technical AppraisalDocument32 pages1ai) Tender Design Technical AppraisalSathishNo ratings yet
- Jobs in Rural vs Urban AreasDocument10 pagesJobs in Rural vs Urban AreasAnoshKhanNo ratings yet
- Fisherpaykel 4517554260 dh9060p 428210c Heat Pump Clothes Dryer User GuideDocument40 pagesFisherpaykel 4517554260 dh9060p 428210c Heat Pump Clothes Dryer User Guidemember1000No ratings yet
- Specifications and RequirementsDocument22 pagesSpecifications and RequirementsMohammed AnasNo ratings yet
- SMART1000LCDDocument2 pagesSMART1000LCDcarlos tNo ratings yet
- 1 - Designing Ultrasonic Flow MetersDocument183 pages1 - Designing Ultrasonic Flow Metersmunzii100% (1)
- Particle Physics NotesDocument378 pagesParticle Physics Notesewanmc189No ratings yet
- Operator Manual FurunoDocument40 pagesOperator Manual FurunoJan JbaNo ratings yet
- Optimization Studies in Sulfuric Acid Production: 1. AbstractDocument6 pagesOptimization Studies in Sulfuric Acid Production: 1. Abstractdiegotorete1994No ratings yet
- Filipinnovation Publication v02Document15 pagesFilipinnovation Publication v02ajesgNo ratings yet
- Improving Wash Fastness of Reactive Dyed CottonDocument2 pagesImproving Wash Fastness of Reactive Dyed CottonRezaul Karim TutulNo ratings yet
- GE MARC Projector Lamp Bulletin 1978Document2 pagesGE MARC Projector Lamp Bulletin 1978Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Specifying Windows and Doors Using Performance StandardsDocument78 pagesSpecifying Windows and Doors Using Performance StandardsghadasaudiNo ratings yet
- Major Environmental Issues of Pakistan Prevention and SolutionsDocument29 pagesMajor Environmental Issues of Pakistan Prevention and SolutionssaadNo ratings yet
- Transmission Poles/Towers Audit Form: Electrical Power Transmission (EE-352)Document7 pagesTransmission Poles/Towers Audit Form: Electrical Power Transmission (EE-352)akif amirNo ratings yet
- OLSS & EOLSS Valves - S&F - A3 SizeDocument4 pagesOLSS & EOLSS Valves - S&F - A3 Sizeprem sagar100% (3)