Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pro 4
Uploaded by
Rubban Kuna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagespoyto
Original Title
Pro4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpoyto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesPro 4
Uploaded by
Rubban Kunapoyto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Transcription:
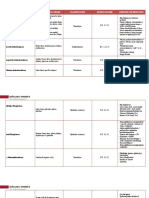
Takes place in nucleus
A complementary copy of the gene is made using RNA
1. Gene opens up. Hydrogen bonds break between bases
2. RNA nucleotides attracted to complementary bases and form
hydrogen bonds.
3. RNA nucleotides joined together by enzyme RNA Polymerase.
4. Complementary RNA copy of gene now made. It is called mRNA
(messenger RNA)
5. Single stranded mRNA molecule diffuses out of gene
6. mRNA molecule leaves nucleus through nuclear pore (large holes
in nuclear envelope)
7. Many mRNA strands are made before gene closes.
MRNA is complementary, not a copy!
DNA
TAC GAA TCT GAG CAC GGC TAT ATC
mRNA.
AUG CUU AGA CUC GUG CCG AUA UAG
Translation:
Takes place in cytoplasm
MRNA code read by ribosome and amino acids assembled in
correct order to make protein
1. mRNA strand binds to cleft in ribosome. Start AUG codon fits
into bottom of P site
2. tRNA diffuses into P site and recognises the mRNA codon using
its specific anticodon
Edexcel AS Biology Revision Notes
Written by Tim Filtness
3. A second tRNA diffuses into the A site and recognises the
mRNA codon there.
4. The amino acids between the two tRNAs join together forming a
peptide bond
5. The tRNA in the P site diffuses into the cytoplasm and binds to
another specific amino acid.
6. The ribosome moves one codon down the mRNA chain so that the
P site is filled with the tRNA from the A site and the A site is
empty
7. When the ribosome reaches the stop codon it releases the
mRNA and the amino acid chain.
Most ribosomes translate whilst attached to the rER. The
completed primary protein is inserted into the rER, where enzymes
fold it into its secondary and tertiary shape.
Many ribosomes can translate the same piece of mRNA at the same
time. A polysome forms
You might also like
- Topic Inheritence2Document6 pagesTopic Inheritence2Rubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 122Document10 pagesLecture 122Rubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity of The Coffee-Cup Calorimeter UsedDocument1 pageHeat Capacity of The Coffee-Cup Calorimeter UsedRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Groby Community College 1Document5 pagesGroby Community College 1Rubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Immunity Unit 4 Topic 6 WorksheetDocument17 pagesImmunity Unit 4 Topic 6 WorksheetAysha MohideenNo ratings yet
- Name The Following Ionic CompoundsDocument6 pagesName The Following Ionic CompoundsEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- HTTP://WWW - Forexreviews.info: The Engulfing TraderDocument1 pageHTTP://WWW - Forexreviews.info: The Engulfing TraderRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- How seed banks and zoos help preserve biodiversityDocument4 pagesHow seed banks and zoos help preserve biodiversityRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Top Forex Candlestick Patterns GuideDocument1 pageTop Forex Candlestick Patterns GuideRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- AICE Biology Guided Reading: Enzymes CH 3Document1 pageAICE Biology Guided Reading: Enzymes CH 3Rubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Multicellular PlantsDocument2 pagesTransport in Multicellular PlantsRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Groby Community College 1Document5 pagesGroby Community College 1Rubban KunaNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesHydrocarbonsRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Microscopy Techniques for Bacteria and AmoebaeDocument2 pagesCell Structure: Microscopy Techniques for Bacteria and AmoebaeRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases & ImmunityDocument2 pagesInfectious Diseases & ImmunityRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- PostureDocument1 pagePostureRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chni Nutrition Review 2000Document11 pagesChni Nutrition Review 2000liggiedy100% (1)
- Clinically Significant EnzymesDocument3 pagesClinically Significant EnzymesNoreen B. BañagadoNo ratings yet
- Indbro - PDF Nutrient LevelDocument2 pagesIndbro - PDF Nutrient LevelvetbcasNo ratings yet
- JURNAL KELOMPOK 3 ABSTRAK SalinanDocument17 pagesJURNAL KELOMPOK 3 ABSTRAK SalinanVikaNo ratings yet
- Zymography Methods For Visualizing Hydrolytic EnzymesDocument11 pagesZymography Methods For Visualizing Hydrolytic EnzymesIonescu AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CHM3270 Ch12.1 Activity3 KEYDocument2 pagesCHM3270 Ch12.1 Activity3 KEYTaiNo ratings yet
- 9 Csomes DNADocument6 pages9 Csomes DNAKenth Roger A. MaquilingNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis, Kreb Cycle Electron TransportDocument19 pagesGlycolysis, Kreb Cycle Electron TransportShahidatul4297100% (2)
- Quiz DnaDocument8 pagesQuiz DnaFriska Aprianti100% (3)
- Drug Metabolism: Dr. Amal BelaidDocument28 pagesDrug Metabolism: Dr. Amal BelaidMustafa RihanNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank. Harmening Chapter 2 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesBlood Bank. Harmening Chapter 2 Review QuestionsMerry GraceNo ratings yet
- DNA-Protein Synthesis: Transcription, Translation & RegulationDocument33 pagesDNA-Protein Synthesis: Transcription, Translation & RegulationSharlene OngNo ratings yet
- RNA InterferenceDocument26 pagesRNA InterferenceAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 05 - Class Notes - Shodh 2.0 Batch For CSIR NET - GATE Life SciencesDocument13 pagesBiochemistry 05 - Class Notes - Shodh 2.0 Batch For CSIR NET - GATE Life SciencesSanjay Kumar RaoNo ratings yet
- S.No MRN Customer Name Client Time Application # Customer Mob # Order Schedule Date Pop LocationDocument10 pagesS.No MRN Customer Name Client Time Application # Customer Mob # Order Schedule Date Pop Locationarindam dasNo ratings yet
- Lipids ReviewDocument62 pagesLipids ReviewApril Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- 300 Micronutrient Sample Report 8 19Document15 pages300 Micronutrient Sample Report 8 19lamNo ratings yet
- Antipurinergic Therapy For Autism-An In-Depth Review.Document15 pagesAntipurinergic Therapy For Autism-An In-Depth Review.Miguel Romero100% (1)
- HW As Cie Biological MoleculesDocument17 pagesHW As Cie Biological Moleculestdmvq7yhggNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lipids PDFDocument55 pagesChapter 3 Lipids PDFVinz TombocNo ratings yet
- PerfectRead DatasheetDocument1 pagePerfectRead DatasheetTenGigaBioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Lippincott BiochemistryDocument53 pagesChapter 21 Lippincott BiochemistryMeysam SajjadiNo ratings yet
- Understanding HemostasisDocument53 pagesUnderstanding HemostasisGirum TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 - Quantitation of Total Proteins, Enzymes and TheirDocument56 pagesLecture6 - Quantitation of Total Proteins, Enzymes and TheirKrisan Mallion LuisNo ratings yet
- BCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20Document31 pagesBCC - DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Lecture 20AmyNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids NotesDocument17 pagesAmino Acids NotesNguyễn SunNo ratings yet
- 09 ASA SK Vit MineralsDocument25 pages09 ASA SK Vit MineralsmarofNo ratings yet
- Preclass Quiz 6 - Fa19 - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (47940) PDFDocument3 pagesPreclass Quiz 6 - Fa19 - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (47940) PDFElizabeth DouglasNo ratings yet
- Sas3 Bio024Document36 pagesSas3 Bio024Merlyn Limbaga CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Lock+and+Key Versus Induced FitDocument3 pagesLock+and+Key Versus Induced FitNandan Gowda NanduNo ratings yet