Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brilliant Computer Education 2D Manual: Autocad
Uploaded by
Gudapati PrasadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brilliant Computer Education 2D Manual: Autocad
Uploaded by
Gudapati PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
AutoCAD
Introduction:AutoCAD is a commercial software application for 2D and 3D computer-aided design
(CAD) and drafting available since 1982 as a desktop application and since 2010 as
a mobile web- and cloud-based app marketed as AutoCAD 360.
Co-ordinate Systems of AutoCAD:RelativeCoordinates
After first points entered, your next points can be entered by specifying the next
coordinate compare/relative from the first points. The relative coordinate started with
symbol @ tell AutoCAD it was a relative coordinates. Using relative coordinate, points
entered by typing @x,y [Enter]
PolarCoordinates
Polar coordinates used when you need to draw the next points at specify angle. Polar
coordinates system in AutoCAD specifies distance length at which angle. Using polar
coordinate, points entered by typing @distance<angle [Enter]
Selections of AutoCAD
Single Entity:You can pick single object when AutoCAD ask you to select objects.
Window Selection:You can define a window selection by clicking at two points. Click first point on the left
side, and 2nd point on the right side. This will select all elements inside the window.
Cross Selection:Basically if your window selection defined from right to left, then it will be cross
window selection. It will select all elements inside and touching the window.
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Window Polygon:-
This option behaves as window selection, but you can define unlimited points for that
window. Just type WP then [enter] to activate it. All elements inside the window will be
selected.
Cross Polygon:This option behaves as cross selection, but you can define unlimited points for that
cross. Just type CP then [enter] to activate it. All elements inside the window will be
selected.
Fence:You can select drawing elements by defining a fence that touched objects you wanted.
Just type F then [enter] to activate it. After you finish defining your fence, press [enter]
to select.
ALL:Select all [Ctrl+A]
Qselect:With this tool you can select all objects having a property that you specify, and the
options for specifying that property are practically endless. Quick Select works on all
objects of the entire drawing, or on a pre-selected set of objects. The number of
objects chosen by Quick Select can be one, a thousand, or any number at all, with
no extra effort on your part.
Qselect[Enter]
Select the object type
Select the properties of object
Check the operator
Give the value
ok
Oject Snap(for On/Off need to press F3):Object snaps (Osnaps) are one of the handiest tools in AutoCAD. Without them, you
would have a lot of trouble doing even the simplest dimension accurately. Before
discussing how they are used, first think about what they are. Their name, "object
snaps" means that they snap to objects, or more precisely, they snap to specific parts
of an object. A line for example has 3 points that you can snap to: a midpoint
and two endpoints. A circle has 5 points: a center and 4 quadrants.
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Running Object Snap: -
Shift + Right Click
To change the Object Snap settings:Ds [enter]
Click on object snap
Click on select all
Click on ok
END
ENDPOINT
MID
MIDPOINT
EXT
EXTENTION
CEN
CENTER
NOD
NODE
QUA
QUADRANT
INT
INTERSECTION
INS
INSERTION POINT
PER
PERPENDICULAR
TAN
TANGENT
NEA
NEAREST
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
APP
APPARENT
INTERSECTION
Commands
Draw Commands:- The draw commands can be used to create new objects such as
lines and circles
Modify Commands:- The modify commands can be used to modify objects that you
create with draw commands. Such as Copy & Move.
View Commands:- The view commands are playing important role in AutoCAD, After
drawing you should use the view commands to show dimension of plan
Ex: Dimlinear, DimDia.
Enquiry Commands:- This commands are used for knowing
information of your
drawing
Ex: Id, Dist, List, Area.
Command Rules:
The cases are not sensitive
The command doesnt allow spaces
If you enter into the command need to be press Enter or Space bar
If you want to select previous command press Enter or Space bar
If you get out of the command then press ESC
If you want to see the history of drawing then press F2
If you select recent commands then press arrow keys(Up/Down arrows)
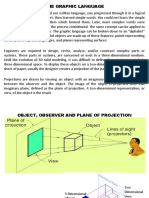
Projections
1. Parallel Projection:Parallel projections have lines of projection that are parallel both in reality and in the
projection plane. Parallel projection corresponds to a perspective projection with an
infinite focal length (the distance from the image plane to the projection point), or
"zoom".
2. Perspective Projection:-
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
It is the projection of a 3D object onto a plane by a set of parallel rays orthogonal to
the image plane. - Parallel lines project to parallel lines. - Size does not change with
distance from the camera.
3. Orthographic Projection:Orthographic projection (or orthogonal projection) is a means of representing a threedimensional object in two dimensions.
The orthographical projection is divided into 3types
1st Angle Projection
2nd Angle Projection
3rd Angle Projection
1st Angle Projection:Here your seen object in one view but drawn into the other view
3rd Angle Projection:Here your seen object in one view drawn into the same view
How to open the AutoCAD application?
Double Click on AutoCAD icon on desktop
AutoCAD User Interface
Status Bar:1. Drawing Co-ordinates (Ctrl +I)
Always shows the current co-ordinate value at the cursor point. Watch the coordinate values change as the cursor moves across the drawing area.
2. Infer Constraints(Ctrl+shift+i)
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Enabling Infer Constraints mode automatically applies constraints between the
object you are creating or editing, and the object or points associated with
object snaps.
3. Snap (F9)
Snap mode takes AutoCAD one step further than the drawing board. With Snap
mode turned on AutoCAD only allows you to pick points which lie on a regular
grid.
4. Grid (F7)
The drawing grid is a regular pattern of dots displayed on the screen which acts
as a visual aid, it is the equivalent of having a sheet of graph paper behind your
drawing on a drawing board.
5. Ortho(F8)
Ortho is short for orthogonal, which means either vertical or horizontal.
6. Polar Tracking(F10)
Polar tracking restricts cursor movement to specified angles. PolarSnap restricts
cursor movement to specified increments along a polar angle.
To create new angles
Ds enter
Choose polar tracking
Click on new
Give angle
Click on apply and ok
7. Object Snap(F3)
The Object Snaps (Osnaps for short) are drawing aids which are used in
conjunction with other commands to help you draw accurately. Osnaps allow
you to snap onto a specific object location when you are picking a point. For
example, using Osnaps you can accurately pick the end point of a line or the
center of a circle. Osnaps in AutoCAD are so important that you cannot draw
accurately without them.
8. 3d Object Snap(F4)
Turns 3D object snaps on and off. The 3D object snaps selected under 3D
Object Snap Modes are active while object snap is on. (3DOSMODE system
variable)
9. Object Snap Tracking(F11)
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
The Object Snap Tracking feature allows you to cycle through all valid snap
points within the aperture area, until you find the one you want. This feature
only works when running object snaps are turned on.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Dynamic UCS(F6)
It will be use full in 3d drawings
Dynamic Input(F12)
If it is on then we are not seen command information below of cursor
Show/Hide Line weight
You can seen line weight if it is on otherwise doesnt
Quick Properties(Ctrl+Shift+p)
You can see the properties of selected objects
Selection Cycling(Ctrl+W)
If you have objects that are overlapping and you want to select one of
them, your only option was to hold SHIFT and hit the spacebar while
hovering over the stacked objects. You can still do this method but there
is this (SC) toggle that will come in handy.
Commands
Workspace Current:- Creates, modifies, and saves workspaces and makes a
workspace current.
Wscurrent enter
Enter the new Value of Wscurrent (for Example 3d modeling)
ID:- Displays the UCS coordinate values of a specified location
Id enter
Specify the point
Distance:- In general, the DIST command reports 3D distances in model space and
2D distances on a layout in paper space.
Dist enter
Specify the 1st point
Specify the 2nd point
List:- LIST (Command) You can use LIST to display and then copy the properties of
selected objects to a text file.
List enter
Select the object enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Units: Controls the displayed precision and format for coordinates and angels. The
format, precision, and other conventions to be used in displaying coordinates,
distance, and angles are set and saved in drawing template files. These settings can
also be changed in the current drawing file.
Un Enter
Change the insertion scale
Limits : By using of this command you can set the limits of your Drawing
Limits enter
Specify the lower left corner point
Specify the upper right corner point
Limcheck:- You can control the limits area
Limcheck enter
Enter the new value for limcheck
Note: The integer should be 0 or 1
0 = its allowing to make the object outside of limits
1 = its doesnt allow to make the object outside of limits
Alias Edit:Lunches an editor for aliases stored in the acad.pgp file. With these you can edit
command and add commands
Aliasedit enter
Click on Add
Give the name of the command
Select your command to need to be apply
Ex : For Circle need to be apply the Brilliant
Click on apply
Click on yes
Workspace Current:- Set the current workspace to my workspace
Wscurrent enter
Enter the new value of WsCurrent
UCS Icon( User Co-ordinate System):
Ucsicon enter
Off enter(Ucs icon doesnt show)
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
On enter (ucs icon shows)
Or enter(It will snap with origin)
Noo enter(it will doesnt snap with origin)
Pan: Moves the view in the current viewport position the cursor at the start location
and press the mouse button down. Drag the cursor to the new location. You can also
press the mouse scroll wheel or middle button down and drag the cursor to pan.
P enter
Cursorsize:- You can increase the size of Cursor
Cursorsize enter
Enter the new value for cursor size
Note:- When command is asking specify point then we are seen only cursor
Pickbox: You can increase the size of Pick box
Pickbox enter
Enter the new value for pick box
Note: When command is asking select objects then we are seen only pickbox
Grip Size:- You can increase the Grip size
Gripsize enter
Enter the new value of gripsize
Grip Color:- You can change the color of Grip
Grip color enter
Enter the new value of Grip color
Zoom:-Zooms to increase or de crease the apparent size of objects in the current
viewport.
Z enter
A enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Zoom with object:Z enter
O enter
Select the object to zoom
Zoom with window:Z enter
W enter
Specify first corner point
Specify second corner point
Id: Displays the UCS coordinate values of a specified location. ID lists the X,Y and Z
value of the specified point and stores the coordinate of the specified point as the last
point.
Id enter
Specify first point
Distance: To know distance between one point other point
Dist enter
Specify first point
Specify Second point
List: Displays property data for selected objects. You can use List to display and then
copy the properties of selected object to a text file
List enter
Select the object enter
Area:- With the help this command you can calculate the area and perimeter of an
object
Area enter
Specify first corner point
Specify next point
Specify next point.
How to change background color?
Ans: Op enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Choose display
Click on color
Change the color of drawing area
Click on apply and close
Click on apply and ok
How to change crosshair color?
Ans: Op enter
Choose display
Click on color
Change the color of cross hair
Click on apply and close
Click on apply and ok
To reset all settings:Op enter
Choose display
Click on color
Click on restore all contexts
Click on restore
Click apply& close click on ok
Windowareacolor:- with these command you can change the color window selection
Windowareacolor enter
Enter the new value of window area color
Crossingareacolor:- With these command you can change the color crossing selection
Crossingareacolor enter
Enter the new value of crossing area color
Line:
Creates straight line segments, with line, you can create a series of contiguous line
segments. Each segment is a line object that can be edited separately
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
L enter
Specify First point
Specify Second Point
Circle: Creating a circle using a center point and radius
C enter
Specify center point
Specify Radius of Circle
Circle with Diameter:-
C enter
Specify center point
D enter
Specify Diameter of circle
2P Circle:C enter
2p enter
Specify first point of circle
Specify second point of circle
3p Circle:Specify first point of circle
Specify second point of circle
Specify 3rd point f circle
TTR circle (Tan Tan Radius):C enter
T enter
Specify first tangent of circle
Specify Second tangent of circle
Specify Radius of circle
Trim: you can trim the object to meet the objects of other objects
Tr enter enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Select the objects to trim
Copy:Copies objects a specified distance in a specified direction with the Copymode system
variable, you can control whether multiple copies are created automatically.
Co (or) Cp enters
Select the objects enter
Specify the base point
Specify the displacement point
Copy with Distance:Co enter
Select the object to copy
Specify the base point
@ X distance, Y Distance
Copym:- copies objects multiple times with option to repeat, divide measure, and
array
Copym enter
Select objects
Specify Base point
Specify Second point
@ X distance, y distance
Move:Moves objects a specified distance in a specified direction. Use coordinates, grid snaps,
object snaps, and other tools to move objects with precision.
Move with Distance:M enter
Select the object to move
Specify the base point
@ X distance, Y Distance
Mirror:-
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Creates a mirrored copy of selected objects. You can create object that represent half of
a drawing, select them, and mirror them across a specified line to create the other
half.
Mi enter
Select objects to mirror
Specify first point of mirror line
Specify second point of mirror line
Erase source object (Yes/No) No enter
Rotate:Rotates objects around a base point. You can rotate selected objects around a
base point to an absolute angle.
Ro enter
Select objects enter
Spaceify base point
Spaceify Rotation angle
Offset:Creates concentric circles, parallel and curves. You can offset an object at a specified
distance or through point.
O enter
Specify offset distance
Select object to offset
Specify a point on side of offset
Offset with multiple:O enter
Specify offset distance
Select object to offset
M enter
Specify a point on side to offset
Time:- Displays the date and time statistics of a drawing. The total Editing time
cannot be rest of stopped. Plotting time is not included in the total edition time, nor is
the viewing time if the drawing is not saved
Time enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Save Time:- You can set the time of save (auto recovery information)
Savetime enter
Enter new value for save time
Ellipse:-Creates a ellipse using center point
El enter
Specify axis endpoint
Specify other endpoint of axis
Specify distance to other axis
TCASE:Tcase enter
Select the object
Choose your case of your text
Arctext :Creates text following a selected arc
Arctext enter
Select your arc
Type your text
Ok
Explode :Breaks a compound object into its component objects. Explodes a compound
object when you want to modify its components separately. Object that can be
exploded includes blocks, polylines and regions among others.
X enter
Select the objects enter
Text Explode:Explode text into polyline
Txtexp enter
Select objects enter
Scale:-
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Enlarges or reduces seleted objects, keeping the proportions of the object the
same after scaling.
Sc enter
Select the obejct to scale enter
Spaceify base point
Spaceify the scale factor
Break:
Breaks the selected object between two points. You can create a gap between
two specified points on an objet, breaking it into two objects.
Br enter
Select the object to break
F enter
Specify the frist Break point
Specify the 2nd Break point
Break with specified distance
Br enter
Select the object to break
F enter
Specify the frist break point
@x distance ,y distance.
Join:joins similar objects to form a single, unbroken object . Combines a series of finite
linear and open curved objects at their commaon endpoints to create a single 2D or
3D object. The type of object that results depends on the types of objects selected, the
type of object seleted first, and whether the objects are coplanar.
Join enter
Select the object to join enter
Extend :
Extend object to meet the edges of other objects. To extend objects, first select the
boundaries. Then press enter and select the object that you want to extend.
Ex enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Select the all object enter
Select the objects to extend
Extend with Fence:Ex enter
Select the all object enter
F enter
Specify the first point
Specify the next point.
Rectangle :
Creates a rectangular polyline. With this command, you can specify the rectangle
parameters(length, width, rotation) and control the type of corners(fillet,chamfer, or
square)
Rec
enter
Specify the first corner point
Specify the 2nd corner point
Rectangel with fillet:Rec
enter
F enter
Enter the fillet radius for rectangle
Specify the first corner point
Specify the 2nd corner point
Rectangle with Chamfer:Rec enter
Cha enter
Enter the first chamfer distance for rectangle
Enter the 2nd chamfer distance for rectangle.
Specify the first corner point
Specify the 2nd corner point
Rectangle with Dimension:Rec
enter
Specify 1st corner point
D enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Specify the length of rectangle
Specify the width of rectangle
Specify the other corner point
Note: Once we are used any mode to rectangle that will continue to other rectangles
Polygon:- Creates an equilateral closed polyline.
You can specify the different
parameters of the polygon including the number of sides. The difference between the
inscribed and circumscribed
Inscribed: The polygon is makes inside of circle
Circumscribed :- The polygon is makes outside of circle
Pol enter
Enter no.of sides
Centre of Polygon
Enter an option (Inscribed, circumscribed)
Give the radius of circle.
Lengthen: Changes the length of objects and the included angle of arcs. You can
specify changes as a percentage, an increment, or as a final length or angle.
Lengthen enter
Select the object enter
T enter
Specify the total length
Select object to change
Fillet:- Rounds and fillets the edges of objects.
F enter
R enter
Specify fillet radius
Select 1st object
Select 2nd object
Chamfer:- Bevels the edges of objects
Cha enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
D enter
Specify 1st chamfer distance
Specify 2nd Chamfer distance
Select 1st object
Select 2nd object
Hyperlink:Attaches a hyperlink to an object or modifies an existing hyperlik. Hyperlinks in
a drawing provide jumps to associated files.
Hyperlink enter
Select the object enter
Click on file
Select your file
Click on open
Click on ok
To open hyperlink press Ctrl+Click on Object
Browser:- Launches the default web browser defined in your systems registry
Browser
enter
Enter the web location
Explore:- You can open the my computer
Explore enter
JPGout:- you can save the drawing as a jpg format
Jpgout
enter
Write the file name
Choose your location
Click on save
Select the object to save
Array:-
creates multiple copies of objects in a
pattern. You can create copies of
objects in a regularly spaced rectangular, polar or path array
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Rectangle Array:-
The Rectangle Array is mostly depending on Row, columns and
distance between them
-ar
enter
Select the objects in array enter
R
enter
Enter number of rows
Enter number of columns
Enter distance between rows
Enter distane between columns
Polar array:- The Polar array is mostly depending on center point, number of objects
in array and angle to fill
-ar enter
Select the object in array enter
Po enter
Specify the center point
Enter number of items
Specify angle to fill
Rotate arrayed objects (y/n) y enter
Path Array:- Evenly distributes object copies along a path or a portion of a path. The
path can be a line , polyline, 3d polyline, spline, helix,arc circle or ellipse.
Ar enter
Select the objects in array enter
Pa enter
Select the path curve
Enter the no of items in array
Specify the distance between them
As enter (Associative)
Off enter
Note:- Associative mode On = when you click on one others automatically select
Associative mode Off = When you click on one only that object is select
Design C enter:Manages and inserts content such as blocks, xrefs, and hatch patterns. Use the tree
view on the left side to browse sources of content and to display content in the content
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
area. Use the content area on the right side to add items to a drawing or to a tool
palette.
Dc enter
Line Type :- We can load the different types of lines
Lt enter
Click on load
Select your line type
Click on ok
Applying the line to objects:Double click on object
Change the line type
Line type scale:- We can change scale of line type
LTS enter
Enter the new value for line type
Line weight:- By using of this command you can able to give thickness to the selected
objects
Lineweight
enter
Select your lineweight
Click on ok
Note:- After applying the lineweight you need to be on the show lineweight
How to apply the line weight to objects?
Ch(properties) enter
Select object you need
Change lineweight
Properties:Controls properties of existing objects. When more than one o bject is selecte, only
those properties common to all selected objects are displayed. When no objects are
selected, only the current settings of general properties are displayed.
Ch enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Select the objects
Now change the properties of selected objects.
Table:- creates an empty table object. A table is a compound object that contains
data in rows and columns. It can be created from an empty table or a table style. A
table can also be linked to data in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Table enter
Give the number columns and Rows
Click on ok
Specify intersection point.
Blend: Creates a tangent or smooth spline between the endpoints of two open curves
Blend enter
Select first object
Select second object
Properties:- Controls properties of existing objects. When more than one object is
selected, only those properties common to all selected objects are displayed. When no
objects are selected, only the current settings of general properties are displayed.
Ch enter
Select object to change
Change your settings
Redraw:- You can refresh the view ports
R enter
Stretch:Stretches objects crossed by a selection window or polygon. Objects that are partially
enclosed by a crossing window are stretched. Objects that are completely enclosed
within the crossing window, or that are selected individually, are moved rather than
stretched. Several objects such as circles, ellipses, and blocks, cannot be stretched.
S enter
Select (with the help of cross selection ) objects to stretch enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Specify base point
Specify 2nd point
Image Attach: - when you attach an image file, you link that referenced file to the
current drawing. Any changes to the reference file are displayed in the current drawing
when it is opened or reloaded.
Imageattach enter
Select your image from system
Click on open
Specify insertion point
Specify scale factor
Export PDF:- You can save the drawing as PDF format
Exportpdf enter
Write name of file
Set the location to save
Click on save
Boundary :- creates a region or a polyline from an enclosed area. Each point that you
specify identifies the surrounding objects and creates a separate region or polyline.
Bo enter
Click on ok
Pick internal point
Match Properties: Applies the properties of a selected object to other objects. The
types of properties that can be applied include color, layer, line type, linetype scale,
lineweight, plot style, transparency, and other specified properties.
Ma enter
Select the source object
Select the destination object
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Polyline:- Creates a 2D polyline A 2D polyline is a connected sequence of segments
created as a single planar object. You can create straight line segments, arc segments,
or a combination of the two.
Pl enter
Specify start point
Specify next point.
Polyline with Arc:Pl enter
Specify start point
Arc enter
Specify end of arc
Donut:- creates a filled circle or a wide ring. A donut consists of two arc polylines that
are joined end to-end to create a circular shape. The width of the polylines is
determined by the specified inside and outside diameters. To create solid-filled circles,
specify an inside diameter of zero.
Do enter
Specify inside diameter
Specify outside diameter
Wipeout :- Creates a polygonal area that masks underlying objects with the current
background color. The wipeout area is bounded by a frame that you can turn on for
edition and turn off for plotting
Wipeout
enter
Specify the start point
Specify next point
To hide frame of wipeout:Wipeout
F enter
Off enter
enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Dimensioning
Dimensioning is the process of adding measurement annotation to a drawing.
AutoCAD 2013 provides many ways to dimension objects and many ways to format
dimensions.
Dimensions show the measurement of objects, the distances or angles between
objects, or the distance of a feature from an origin you specify. AutoCAD 2013 provides
three basic types of dimensioning: Liner, radial, and angular. Dimensions can be
horizontal, vertical, aligned, rotated, ordinate, baseline, or continued. You can create
dimension styles to format dimensions quickly and ensure that dimensions in your
drawing conform to industry or project standards.
Dimlinear: By using this command you can measure the linear objects
Dimlinear
Specify the first extension line origin
Specify the second extension line origin
Specify the dimension line locations
Dimaligned: creates a linear dimension that is aligned with the origin points of the
extension lines
Dimaligned
Specify the first extension line origin
Specify the 2nd extension line origin
Specify the dimension line location
DimAngular:- measures the angle between selected objects or 3 points. Objects that
can be selected includes arcs, Circles and lines, among others.
Dimangular
Specify the first extension line origin
Specify the 2nd extension line origin
Specify the arc line location
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Dimradius :- Creates a radius dimension for a circle or an arc. Measures the radius of
selected circle or arc and displays the dimension text with a radius symbol in front of
it. You can use grips to reposition the resulting radius dimension easily
Dimradius
Select the arc
Specify the arc line location
DimDiameter: Creates a diameter dimension for a circle or an arc.
Measures the
diameter of a selected circle or arc, and displays the dimension text with a diameter
symbol in front of it. You can use grips to easily reposition the resulting diameter
dimensions
Dimdia
Select the arc
Specify the arc line location
Dim Continue :- Creates a dimension that starts from an extension line of a previously
created dimension Automatically continues creating additional dimensions form the
last linear, angular, or ordinate dimension created, or from a selected extension line.
The dimension lines are lined up automatically.
Dimcontinue
Specify next point
Specify next point
Dim jogged:- Creates jogged dimensions for circles and arcs. Creates jogged radius
dimension when the center of an arc or circle is located off the layout and cannot be
displayed in its true location. The origin point of the dimension can be specified at a
more convenient location called the center location override.
Dimjogged
Select the arc or circle
Specify the jogged dimension location
Dimension Style Manager
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
A Dimension style is a named collection of dimension settings that control the
appearance of dimension. You create dimension styles to specify the format of
dimension quickly, and to ensure that dimensions conform to standards
D
Its open the dimension style manager dialog Box
List:Lists dimension styles in the drawing. The Current style is highlighted. Right-Click in
the list to display a shortcut menu with option to set the current style, rename styles,
and delete styles. You cannot delete a style that is current or in use in the current
drawing. The icon before the style name indicates that the style is annotative
Set Current:Sets the style selected under styles to current. The current style is applied to
dimensions you create
New:
Displays the Create New Dimension Style Dialog box, in which you can define a new
dimension style
Modify:
Displays the Modify Dimension Styles dialog box, in which you can modify dimension
styles. Dialog box options are identical to those in the New Dimension Style dialog box.
Override:
Displays the Override Current Style dialog box, in which you can set temporary
Overrides to dimension styles. Dialog box options are identical to those in the New
Dimension Style dialog box, Overrides are displayed as unsaved changes under the
dimension style in the styles list.
Compare:
You can compare two dimension styles or list all the properties of one dimension style.
Line Tab
Dimension Lines:
Color:- Displays and sets the color for the dimension line. If you click
select color for this you can use the Dimclrd command
Line Type:- Sets the line of the dimension line. Dimltype system
varibale
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Line Weight :- Sets the Weight of line of the dimension line . dimlwd command
for this
Base line Spacing:- Sets the spacing between the dimension lines of a baseline
dimension. a distance. For information about baseline dimension, see
dimbaseline. For this you can use dimdli
Suppress:- Supperesses display of dimension lines. Dim line1 suyppresses the
first dimension line; Dimline 2 suppresses the second dimension line.
(dimsd1and Dimsd2 system variables)
Extension lines
Extend beyond dimline:- Specifies a distance to extend the extension
lines above the dimension line.
Offset from origin:- Sets the distance offset the extension lines from the
points on the drawing that define the dimension
Fixed length extension lines:- this option used for you can set the fixed
length of extension lines
Primary Units Tab
Unit format:-
Sets the current units format for all dimension types except
angular.
Precision :- Displays and sets the number of decimal places in the dimension
text.
Prefix:-
includes a prefix in the dimension text. You can enter text or use
control codes to display special symbols. For example, entering the control code
%%C displays the diameter symbol. When you enter a prefix, it overrides any
default prefixes such as those used in diameter and radius dimensioning.
Suffix:- includes a suffix in the dimension text. You can enter text or use
control codes to display special symbols. For example, entering the text mm
results in dimension text similar to that shown in the illustration. When you
enter a suffix, it overrides any default suffixes
Alternate Units
If you on this you can see the alternate units for primary units
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Unit format :- Sets the current units format for all dimension types except
angular.
Multiplier Alternate Units:- Specifies the multiplier used as the conversion
factor between primary and alternate units. For example, to convert inches to
millimeters, enter 25.4. The value has no effect on angular dimensions, and it
is not applied to the rounding value or the plus or minus tolerance values.
Block
The Block is divided into 4 types
1.
2.
3.
4.
Block
Wblock
Bedit
Attribute Block
Block:- Effective management increases the productivity of your drawing. With
various tools in AutoCAD you can organize and manipulate the shared
drawings more effectively.
Working With Blocks:At times, you many require an object or a group of objects at various places in
your drawing. For example, a mechanical component may need the same
symbol (nuts,bolts) at different drawing location. AutoCAD provides you with a
powerful tool to handle such issues-Block.
A Block is a collection of objects the you can associate together to form a single
object. You can insert, scale, and rotate a block in a drawing. You can explode a
block into its component objects, modify them, and redefine the block.
AutoCAD LT 2013 updates all future instances of that block based on the block
definition.
Block streamline the drawing process. For example, you can use blocks to
Build a standard library of frequently used symbols, components, or
standard parts. You can insert the same block numerous times instead
of recreating the drawing elements each time.
Revise drawings, efficiently by inserting, relocating, and copying blocks
as components rather then individual geometric objects.
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Save disk space by storing all references to the same block as one block
definition in the drawing database.
Each time when a block is inserted, you are creating an instance. When you
insert a block instance, you can assign a scale factor and rotation angle to the
inserted block. You can also scale a block instance using different values in
any coordinate (x,y) direction
Defining Blocks:To define a block
Specify a base point
Select objects to block
Chose one of the selection mode (Retain, Covert to block or Delete )
You can also enter a text description and specify an icon used to identify the
block definition in the AutoCAD design Center
Wblock:- The WBLOCK command is used to write, all or a part of a drawing to
a new file. You can also save a block as a drawing file. WBLOCK command
displays the Write Block dialog box
Dynamic Blocks:
A drawing created in AutoCAD is frequently composed of a series of standard
components or blocks use in various place, whether it is a single drawing or a
complete set of drawings.
These components can represent such diverse items as doors or desks, nuts
and bolt,s and pipe and fittings. In AutoCAD these standard components are
mostly represented by locks. Blocks save time and help to standardize drawings
by eliminating the need to redraw standard components over and over again.
However, they can be difficult to manage and manipulate. Often thousands of
blocks are available to user to help them find, insert and edit according toe
their design
AutoCAD 2013 makes block dynamically. This new concept helps to create or
add a dynamic behavior to your existing block libraries. The main idea is that
you can create one block with many possibilities, so that one block can
represent many. This will help you to reduce the block library size significantly.
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
For example, you can create a dynamic block and insert that into the drawing.
A block can be scaled, rotated, mirrored stretched and insertion point changed
on the fly during the insertion Each component can be move independently
and then arrayed. For a block to be dynamic, it must contain at least one
parameter and one action. That action should be associated with the
parameter.
Parameters:Parameters help to define custom properties for the block reference. For
example, the add Point parameter or any other parameter of the current
dynamic block defines different actions on it.
Dynamic blocks can thus be
modified instantly as per requirement, using the same block
Actions:After association any parameter set to a block action must be defined to the
block. These actions define how the geometry of a dynamic block reference will
move or change when custom properties of a lock reference are manipulated in
a drawing. Types of action are Move, Rotate, Scale, Stretch, Polar Stretch, Array,
Lookup and Flip.
Attributes
An attribute is a label or tag that attaches data to a b-lock. Example of data
that might be contained in an attribute are part numbers, Prices, comments,
and owner name When you insert a block with a variable attribute, AutoCAD
Prompts you to enter the data to be stored with the block. You can extract
attribute information from a drawing and use that information in a spreadsheet
or database to produce items such as a part list or a Bill of Mater. You can
associate more than one attribute with a block, provide that each attribute has
a different tag. Attributes can be invisible with means that the attribute is not
displayed or plotted. However information on the attribute is stored in the
drawing file.
External References:-
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
An external reference is a link between two drawings. The drawing opened by
the user is referred as the current drawing. The current drawing can also be a
new one. The drawing, which is in link with the current drawing, will be called
the referenced drawing or xref. This link provides a feature to view both the
drawings in the drawing editor, but maintains each drawings data in separate
drawing files. The only information in the reference drawing is that it becomes
a permanent part of the current drawing and lists directory path
XREF
Its open the on palate click on dwg select the your reference and ok
Layers
Layer is an organizing tool. Layers are like one, where you can keep various
types of information. Its always a good idea to keep notes and reference
symbols about each element of the drawing as well as drawing dimensions on a
new layer. For example, one of your clients may need a plot representing the
components in full detail, whereas other requests a plot without sections and
detail for the same component. In manual drafting, you would have to redraw
the drawing for each client. With AutoCAD you can turn off all the lawyers that
you dont need and plot a drawing contacting only the required information.
New Layer:- creates a new layer. After you choose new, the list displays a layer
named layer1. You can edit this layer immediately.
Set Current:- Sets the selected layer as the current layer.
Delete Layer:- deletes the selected layers from the drawing file definition. The
following reference layers cannot be deleted. 1. Layers 0 and Defpoints 2. Layers
containing objects 3. Current Layer. 4. X-ref dependent layers
Layer Filter:-by using of this you can create a layer filter based on one or more
properties of the layers. Filter name specifies a name for the saved filter. Layer
name specifies which layers to filter. Filters the specified status of respective
parameters.
Hatching
hatches are shaded patterns which generally represent a cross section of a
mechanical component or any civil representation like roof. Hatching is tedious
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
and time consuming job. Now with AutoCAD the Bhatch command makes this
just as a matter of few picks and clicks away. Follow these steps to hatch with
Bhatch command
H
Its open the hatch Dialog box
Add pick points:- Determines a boundary from existing objects that form an
enclosed area around the specified point.
Add Select Objects:- Determines a boundary from selected object that form an
enclosed area. When you use the select objects option, hatch does not detect
interior objects automatically. You must select the objects within the selected
boundary to hatch or fill those objects according to the current island detection
style.
Type:- Sets the pattern type. These patterns are stored in the ACAD.PAT and
ACADISO.PAT files.
Pattern:- Lists the available predefined patterns. The pattern option is available
only if you set type to predefined
Swatch: Displays a preview of the selected pattern.
Angle And Scale:- Angle specifies an angle for the hatch pattern relative to the
X-Axis of the current UCS. Scale expands or contracts a predefined or custom
pattern. This option is available only if you set type to predefined or custom
H Enter
Click on swatch
Click on predefined
Select your pattern style
Click on add pick points (Hatching apply to boundary area)
Pick internal point
(Or)
Click on Add select objects
Select objects
Give the scale and angle
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
To apply the Gradient :H enter
Click on Gradient
Choose two colors
Click on add pick points
Pick internal point
Enter
Image Attach :Match: - You can match the properties such as linetype,color, line weight,
hatching
Ma
Select the source object
Select the Destination Objects
Measure:Creates point object or blocks at measured intervals along the length or
perimeter of an object
Note:- After using these you should use the DDPTYPE Command
Me
Select the obejct to measure
Specify the length of segment
Measure with Block:Me enter
Select object to measure
B enter
Enter block name
Align block object (Y/N) y enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Specify length of segment
DDPTYPE
Select the point sytle
Divide :- Creates evenly spaced point obejct or blocks aling the length or
perimeter of an object
Div
Select the obejct to divide
Enter the Number of segments
Note 1:- The segments should be in between of 2 to 32767
Note 2:-After using this command you should use DDPTYPE Command
Ddptype enter
Select point style
Ok
Boundary :- Creates a region or a polyline from an enclosed area. Each point that
you specify identifies the surrounding objects and creates a separate region or
polyline.
Bo enter
Click on ok
Pick on internal area
Multiline : Create multiple parallel lines
ML eneter
Specify the first point
Specify the 2nd point
Multiline Style:- Manages styles for multiple parallel lines
Mlstyle enter
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Click on modify
Do your Modifications
Click on ok
Multiline Edit:Mledit enter
Select your edit tool
Select first multiline
Select 2nd multiline
Match :-
applies the properties of a selected object to other objects. The types of
properties that can be applied include color, layer, line type, linetype scale, lineweight,
plot style, transparency, and other specified properties.
Ma enter
Select the source object
Select the destination object
Linetype:- we can load different types of line types in to the drawing
Linetype
enter
Click on load
Select your line type
Click on ok
Click on ok
To apply the line type to the object , double click on object and change the line type
Record:- Starts the Action Recorder. You can create an action macro by recording
most of the commands that you are already familiar with.
Actrecord enter
Now do your drawing
To Stop the Record then use ACTSTOP
Action Stop:-
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Stops the action recorder and provides the option of saving the recorded actions to an
action macro file. You can use this command to stop the recording or playback of an
action macro based on the current state of the action recorder. When the recording of
an action macro is stopped, the recorded actions are saved to an action macro file.
Actstop enter
Give the action name
How to run macro?
Go to Manage tab(Workspace should be Drafting and Annotations)
Click on Play
OLE Object:- inserts a linked or embedded object
Insertobj enter
Select your application
Click on ok
Section Plane :Create as section object that acts as a cutting plane through 3D objects. Section plane
objects create section of 3D Solids, surfaces, and meshes. Use live sectioning with
section plane objects to analyze a model, and save sections as blocks for use in layouts
Sectionplane enter
D enter
Specify first point
Specify second point. Enter
To Create section:Right click on section choose the generate 2d Section/Elevation
Specify intersection point
Specify x Scale factor
Specify y scale
Specify Angle
Brilliant Computer Education
2D Manual
Flatshot:- Creates a 2D representation of all 3d objects based on the current view. The
edges of all 3d solids, surfaces, and meshes are projected line of sight onto a plane
parallel to the viewing plane.
Flatshot enter
Select Create
Title Block: To create Title Block:Click on layout
To change page setup:Right Click layout choose page setup manger
Click on Modify
Click paper size
Change the paper size and then press ok and close
Now create your Title Block
Save enter
Give the file name
Change save as type (with AutoCAD drawing template)
Click on save
To use Title Block:Click on new
Choose your created template
Now do your model
Plot:Drawing to a plotter, printer, or file.
A drawing file, drawing template file Xref. Or
block definition that was created with or modified by an education version will always
be plotted with the following plot stamp
Plot enter
Select your plot or Printer type
Set paper size
Choose plot area (display,model,layout)
Click on ok
You might also like
- AutoCAD BeginnersDocument26 pagesAutoCAD Beginnerssquirticus100% (2)
- Autocad Training: by MuralidharanDocument20 pagesAutocad Training: by Muralidharanraj4110640No ratings yet
- Autocad PDFDocument35 pagesAutocad PDFHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Autocad Training ManualDocument13 pagesAutocad Training Manualnveman100% (1)
- Theory of ProjectionsDocument33 pagesTheory of Projectionsambika1969in0% (1)
- CAD Drawing Icons and Limits in AutoCADDocument27 pagesCAD Drawing Icons and Limits in AutoCADsomadina ijeomah-DanielNo ratings yet
- Autocad s'13 NittDocument38 pagesAutocad s'13 NittNitin VarmanNo ratings yet
- Tools For 2d Digital ModellingDocument45 pagesTools For 2d Digital ModellingNaGamani KanDanNo ratings yet
- Overview of An Engineering DrawingDocument23 pagesOverview of An Engineering DrawingEslam Mohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Engineering Drawing FundamentalsDocument79 pagesIntroduction to Engineering Drawing FundamentalsSujan NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Contentfile 22842 PDFDocument175 pagesContentfile 22842 PDFSnehaNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D - Roads Design: 2From EverandAutoCAD Civil 3D - Roads Design: 2Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- AutoCAD TutorialDocument9 pagesAutoCAD TutorialSatish Annigeri100% (3)
- AutoCAD Basics for Surveying EngineeringDocument22 pagesAutoCAD Basics for Surveying EngineeringBakhtiyar Q.Khawaja100% (1)
- RAJKIYA ENGINEERING COLLEGE PRESENTATION ON AUTOCADDocument32 pagesRAJKIYA ENGINEERING COLLEGE PRESENTATION ON AUTOCADKshitij MallNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3From EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Pictorial DrawingDocument10 pagesPictorial DrawingJoceme CRISTORIANo ratings yet
- Autocad 2d NotesDocument33 pagesAutocad 2d NotesGudapati PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sakshi Ahire (Inplant Traning)Document26 pagesSakshi Ahire (Inplant Traning)Tejas DeoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: AutocadDocument30 pagesChapter - 1: AutocadRaghava VNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2013 InterfaceDocument7 pagesAutoCAD 2013 InterfaceimgtxNo ratings yet
- Inplant Training ReportDocument19 pagesInplant Training ReportTejas DeoreNo ratings yet
- Presentation on Summer Training in AutoCADDocument74 pagesPresentation on Summer Training in AutoCADAatish kumar0% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Lab1Document8 pagesEngineering Drawing Lab1hasant_4No ratings yet
- Introduction To AUTOCAD (Compatibility Mode)Document71 pagesIntroduction To AUTOCAD (Compatibility Mode)Prajapati KrishiNo ratings yet
- About AutocadDocument10 pagesAbout AutocadGautam GautamNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2000 Class NotesDocument32 pagesAutoCAD 2000 Class Notestelecom_numl8233No ratings yet
- Auto CadDocument4 pagesAuto CadVikesh VemulapalliNo ratings yet
- Get Oriented with AutoCAD Basics in Under 15 MinutesDocument9 pagesGet Oriented with AutoCAD Basics in Under 15 MinutesJasmina PečenkovoćNo ratings yet
- 3D CADD Module1Document17 pages3D CADD Module1Domingo Brioso Gamis IIINo ratings yet
- Auto CadDocument24 pagesAuto Cadkanchan Redas RedasNo ratings yet
- CADDDocument66 pagesCADDusiaf007No ratings yet
- Brief Abstract.: Week Two: Auto Cad. Technologist'S Name: MR - KeterDocument6 pagesBrief Abstract.: Week Two: Auto Cad. Technologist'S Name: MR - Ketervincent rotichNo ratings yet
- Virginia University Online Eucation DocumentDocument42 pagesVirginia University Online Eucation Documentapi-253004596No ratings yet
- Krish CAD NotesDocument102 pagesKrish CAD Notesjagand647No ratings yet
- Presented By:-Rahul SainiDocument18 pagesPresented By:-Rahul SainiashishNo ratings yet
- Erase, Copy, Mirror, Offset, Array, Move, Rotate, Scale, Stretch, Lengthen, Trim, Extend, Break at Point, Break, Chamfer, Fillet, ExplodeDocument18 pagesErase, Copy, Mirror, Offset, Array, Move, Rotate, Scale, Stretch, Lengthen, Trim, Extend, Break at Point, Break, Chamfer, Fillet, ExplodeRida E ZahraNo ratings yet
- CAD Lab ManualDocument40 pagesCAD Lab ManualvelavansuNo ratings yet
- English Module 1 Quarter 2Document6 pagesEnglish Module 1 Quarter 2Prince Alexander A. DuarteNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Draftingwps OfficeDocument5 pagesComputer-Aided Draftingwps OfficeMarvin Espenocilla EspeñoNo ratings yet
- Cad-Cam Lab Manual 2022-23manualDocument63 pagesCad-Cam Lab Manual 2022-23manualMvk MvkNo ratings yet
- AutocafDocument61 pagesAutocafAllu ArjunNo ratings yet
- CAD-CAM LAB MANUAL 2021-22manualDocument59 pagesCAD-CAM LAB MANUAL 2021-22manualShashankNo ratings yet
- Autocad Basics Tutorial HandoutDocument12 pagesAutocad Basics Tutorial HandoutJimBeeNo ratings yet
- Short Notes of Autocad... Deepak BoseDocument15 pagesShort Notes of Autocad... Deepak BosePrithviRaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- (Type The Document Title) : CONTACTS, 0710924016. EMAILDocument32 pages(Type The Document Title) : CONTACTS, 0710924016. EMAILAndree GeorgeaNo ratings yet
- Auto CAD Introduction Lec 1Document16 pagesAuto CAD Introduction Lec 1Moaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Name of Institution: Dedan Kimathi University of TechnologyDocument50 pagesName of Institution: Dedan Kimathi University of TechnologyEVANS KIPNGETICHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 3d Drawing UpdatedDocument29 pagesIntroduction To 3d Drawing UpdatedSidrak MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Autocad Lecture UpdatedDocument39 pagesAutocad Lecture UpdatedRuben BalaquiNo ratings yet
- Auto CADDocument61 pagesAuto CADThiru MuruganNo ratings yet
- Rohit - My ReportDocument22 pagesRohit - My ReportNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- BASIC DRAWING AIDS FOR CAD Lesson For TodayDocument7 pagesBASIC DRAWING AIDS FOR CAD Lesson For TodayJoel ManioNo ratings yet
- Autocad Basics Tutorial HandoutDocument13 pagesAutocad Basics Tutorial Handoutdika dikaNo ratings yet
- Learn AutoCAD Basics in 40 StepsDocument57 pagesLearn AutoCAD Basics in 40 StepsgurpreetNo ratings yet
- Circular viewport in AutoCADDocument12 pagesCircular viewport in AutoCADDanny ArimaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Auto CADDocument56 pagesPresentation On Auto CADAll you Need to KnowNo ratings yet
- Autocad Basics Tutorial HandoutDocument12 pagesAutocad Basics Tutorial HandoutKenshin UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Autocad IntroDocument21 pagesAutocad IntroAyush sharma100% (1)
- Final Cad ManualDocument43 pagesFinal Cad ManualdhanabalNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)No ratings yet
- AutoCAD ElectricalDocument2 pagesAutoCAD ElectricalGudapati PrasadNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2012 SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesAutoCAD 2012 SYLLABUSGudapati PrasadNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2012 SYLLABUSDocument1 pageAutoCAD 2012 SYLLABUSGudapati PrasadNo ratings yet
- Tally ProblemsDocument10 pagesTally ProblemsGudapati PrasadNo ratings yet
- PSU Multiview Drawing GuideDocument41 pagesPSU Multiview Drawing GuideRachel Faith GarciaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Drawing: Usman AbdullahDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Drawing: Usman AbdullahAbrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics NotesDocument21 pagesComputer Graphics Noteskunjbhatia1No ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection LessonDocument6 pagesOrthographic Projection LessonJoy OramaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination Spring 2013 CS602-Computer GraphicsDocument18 pagesMidterm Examination Spring 2013 CS602-Computer Graphicsblanooba231100% (1)
- Amity Campus Graphics AssignmentsDocument30 pagesAmity Campus Graphics AssignmentsAmanya AllanNo ratings yet
- ProjectionDocument6 pagesProjectionistiake zahanNo ratings yet
- CS602 Solved MCQs Final Term by JUNAID-1Document39 pagesCS602 Solved MCQs Final Term by JUNAID-1Zee Khan100% (3)
- Theory of Projection PDFDocument52 pagesTheory of Projection PDFSiddhrajsinh Zala100% (2)
- CGM Short Notes PDFDocument54 pagesCGM Short Notes PDFUDxNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 3D Transformation & Viewing: 2160703 Computer GraphicsDocument71 pagesUnit-5 3D Transformation & Viewing: 2160703 Computer GraphicsUzma Rukhayya ShaikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Projection and BasicsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Projection and BasicsMithun SiloriyaNo ratings yet
- CAD GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-4 08052021103022AMDocument20 pagesCAD GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-4 08052021103022AMvivek panchalNo ratings yet
- Computer GraphicsDocument11 pagesComputer GraphicsKasozi BakulumpagiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 02 - Projection TheoryDocument28 pagesLecture - 02 - Projection TheoryMoses KambohNo ratings yet
- Two Marks - Part - 1Document14 pagesTwo Marks - Part - 1sathyaaaaa1No ratings yet
- Line AlgorithmDocument62 pagesLine AlgorithmAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument99 pagesEngineering DrawingBinu ChandranNo ratings yet
- 3 D TransformationDocument53 pages3 D TransformationshubhangiNo ratings yet
- 2D Projections of 3D Objects Using Perspective & Parallel TechniquesDocument21 pages2D Projections of 3D Objects Using Perspective & Parallel TechniquesPalashAhujaNo ratings yet
- RSW 2 - OutlineDocument12 pagesRSW 2 - OutlineJorisNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics & MultimediaDocument9 pagesComputer Graphics & MultimediaMathan NaganNo ratings yet
- 12m NAQSHADAYNTADocument33 pages12m NAQSHADAYNTAAbdi GaboobeNo ratings yet
- Projection Points GuideDocument31 pagesProjection Points GuideANURAG KNSRNo ratings yet
- Upang Cea 2bsme Mae109 P1Document32 pagesUpang Cea 2bsme Mae109 P1Althea ManlaNo ratings yet