Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Haematinics PDF
Uploaded by
Keserovic AdmirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Haematinics PDF
Uploaded by
Keserovic AdmirCopyright:
Available Formats
jslum.
com | Medicine
Haematinics
Iron Deficiency Anaemia (IDA) (=Sideropenic anaemia)
Sources
Low
Medium
High
Fruits
Red meats
Organ tissues
Vegetables
Chicken
Fish
Fats
Eggs
Green
Whole wheat
vegetables
flour
Tomatoes
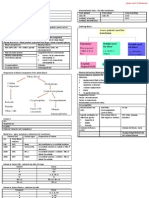
Iron Metabolism
Absorption in Duodenum & Jejunum (proximal)
Absorption when
Iron stores
Iron requirements
Absorbed better in Ferrous (Fe2+) via active transport
Stored in
Ferritin (mucosa)
Transferrin (plasma)
Haemosiderin (alternative storage) = Ferritin + extra
Iron
Iron loss 1mg/ day
Urine
Faeces
Shed cells
Menstruation 20mg/ month
RBCs are destroyed by RES (reticuloendothelial system)
after 120 days iron returned to Transferrin & Ferittin
Hypochromic
Microcytic
Folic Acid
Functions
Production of RBCs in bone marrow
Neural tube formation
Sources
Leafy green vegetables
Fish, Meat, Poultry
Whole grains
Pharmacokinetics
Absorbed in small intestine (primarily Proximal)
Appears in plasma approx. 15-30 mins
Metabolised in liver
(7,8-dihydroFolic acid then to 5,6,7,8-tetrahydroFolic acid)
TetrahydroFolic acid derivates distributed to all body
tissues (primarily stored in Liver)
Excreted in urine (small amounts in feces )
Excreted in milk of lactating mothers
Children
Nutrition diet
Clinical
Tissue hypoxaemia easy fatiguability
Cardiopulmonary compe nsation palpitation,
dyspnoea
Metaboolic consequences O2 dissociation curve
change
Glossitis, Angular stomatitis, Brittle nails, Dysphagia
Pica (crave to eat non-food)
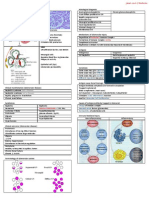
Erythropoietin
Function (hormone )
Controls RBC production
Absorption & Distribution
Intrinsic Factor (IF) produced by cell in stomach
IF + B12
Form IF-B12 comple x, absorbed in intestines
Production
Deficiency of IF
Cause abnormal formation of erythrocytes
(failure of B12 absorption)
Endogenous erythropoietin produced by kidney
(response to anaemia, hypoxia)
Signal BM to produce more RBC
Megaloblastic
anaemia
Large,
abnormal,
immature
erythrocytes
Causes
Excessive blood loss
Inadequate intake of iron
Women
Men
Menstruation
Blood loss
Pregnancy
Gastric ulcer
Neoplasm
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Functions
Normal functioning of Brain & Nervous system
Formation of blood
Deficiency Causes
Folate need (pregnancy, lactation)
Intake (poor diet, alcoholics)
Malabsorption syndromes
Treatment with drugs DHF (dihydrofolate)
reductase inhibitors (eg. Trimethoprim)
Renal dialysis (Folate removed during dialysis)
Liver disease (diminished hepatic storage Folate)
Cancer, Leukaemia, Myeloproliferative disorders
Clinical
Mild jaundice
Glossitis
Angular stomatitis
Pernicious Anaemia
(lack of gastric IF)
(autoimmune disease )
Abnormally large RBC
(macrocytes)
Abnormal WBC
(abnormal nuclei)
Deficiency Causes
Failure of IF secretion
Absense of IF intestinal receptors
Gastrectomy (achlorhydria, lack of IF)
Malabsorption syndrome
Lack of B12 binding protein in plasma
(transcobalaimin II, , globulin)
stomach acidity (inability to remove B12 from meat)
Liver disorders (interfere with storage of B12)
Failure to respond to erythropoietin
Concurrent iron deficiency (corrected with oral iron)
jslum.com | Medicine
Iron Deficiency Anaemia (IDA) (=Sideropenic anaemia)
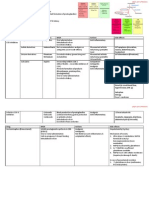
Iron Preparation
Oral
Parenteral (IV, IM)
Corrects IDA as rapidly
Given only when oral
as parenteral
therapy failed
Should not be used
Cannot take oral drugs
(affe ct absorption)
Experience GIT
SR (sustained release)
intolerance to oral
EC (enteric-coated)
Types
Types
Ferrous sulfate
Iron Dextran (IM, IV)
Ferrous gluconate
Dextriferron (IV)
Ferrous fumarate
Saccharated iron oxide (IV)
Side Effects
Side Effects
Black stools
Local pain, tissue staining
Nausea
Headache
Epigastric pain
Diarrhea, Nausea, Vomiting
Constipation
Bronchos pasm
Diarrhoea
Anaphylaxis (*test dose)
Death
Side effects are dose
Z track injection
dependent.
Avoid local tissue staining
Overcome by
(brown discoloration)
Prevent escape of solution
Daily dose
from mus cle tissue
Taking after/ with
meals
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to drug
Hemochromatosis/ Hemolytic anaemia
Anaphylatic-type reaction (parenteral)
Interactions
(form insol uble complex, absorption)
Tetracycline (antibiotic)
Methyldopa
Levodopa
Bisphosphonates
Quinolones
Calcium (food)
Absorption (Better at pH) Decreased when taking
Antacids, Phosphates, Tannins (from tea)
Toxicity
Acute (children common)
Chronic
Necrotising gastroenteritis = Haemosiderosis
Nausea, Vomiting,
= Haemochromatosis
Diarrhoea
Acidosis, Cyanosis,
Excess deposits in Heart,
Circulatory collapse
Liver, Pancreas
(organ failure)
Gastric scarring
Pyloric stenosis
Treatment
Treatment
Induce vomiting, lavage
Intermittent phelebotomy
(phosphate, carbonates)
Desferrioxamine
Hasten evacuation
(if involve iron overload
(catharsis/ purging)
ocular haemosiderosis,
Sodium bicarbonate
haemochromatosis)
Desferrioxamine/
deferoxamine
Folic Acid
Oral supplements
Megaloblastic anaemia
Folic acid deficiency
1mg dose sufficient to
Remove megaloblastic anaemia
Restore normal serum folate levels
Replenish body stores of folate
Side Effects
Allergic hypersensitivity (parenteral)
Vitamin B12
Cyanocobalamin (synthetic form of B12 )
Oral
Pernicious anaemia can be
treated entirely
(1000 ug/ day)
Parenteral
Cyanocobalamin
Hydroxocobalamin
( protein-bound)
(remain longer in blood)
Side Effects
Itching, Rash
Mild diarrhoea
Peripheral vascular thrombosis, RBC production
Contraindications
Pernicious anaemia
Aneamis which B12 is deficient
Side Effects
Rapid Haematocrit & Hb
Hypertension, Thrombotic compli cations
Influenza-like symptoms
(can be reduced if IV injection given over 5 mins)
Allergic reaction (infrequent, mild)
Darbepoetin alfa
(long acting, synthetic form of erythropoietin)
Treatment of
Chronic renal failure (IV, subcutaneous injection)
Anaemia in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy
Interactions
Phenytoin (antagonize anticonvulsant action)
Epilepsy patient require dose of Phenytoin if Folic Acid
given
Folinic Acid (Not the same as Folic Acid)
(= leucovorin)(Calcium folinate/ Leucovorin calcium)
Treat folate deficiency megaloblastic anaemia
Adjuvant cancer chemotherapy (involve
Methotrexate) (rescue/ reverse toxic effects of
methotrexate)
Used synergistically with 5-fluorouracil
(chemotherapy agent)
Erythropoietin
Therapeutic uses (Treating anaemia)
Chronic Kidney Disease & Myelodysplasia
Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy & radiation
Critical illness (heart failure)
AIDS patient receiving zidovudine (AZT)
1 Bone Marrow
Supplements
Supplement in processed foods
Vitamin pill form (multi-vitamins)
Mode
Liquid
Transdermal patch
Nasal spray
Injection
Risks of use
Cardiovascular problems
Cardiac arrest
Arrhythmia
Hypertension
Hypertensive encephalopathy
Congestive heart failure
Vascular thrombosis/ ischemia
Myocardial infarction
Edema
You might also like
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- (MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyDocument6 pages(MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyHenryboi CañasNo ratings yet
- Acute Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: DiseaseDocument3 pagesAcute Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: DiseaseHades Luciferos PallonesNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Document18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Ars MoriendiNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Thrombosis: OutlineDocument11 pagesHemostasis and Thrombosis: OutlineManila MedNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chapter7Document43 pagesMidterm Chapter7Frances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Haematology-Summary My NotesDocument24 pagesHaematology-Summary My NotesToria053No ratings yet
- Systemic Pathology Study NotesDocument33 pagesSystemic Pathology Study NotesLaura BourqueNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument3 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- 18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDocument9 pages18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- Pathology Finals Reviewer on WBCs, Lymph Nodes, Spleen & ThymusDocument5 pagesPathology Finals Reviewer on WBCs, Lymph Nodes, Spleen & Thymusangel_sagun_1No ratings yet
- Anemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDocument15 pagesAnemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine Lesions Comparison ChartDocument9 pagesSmall Intestine Lesions Comparison ChartfadoNo ratings yet
- IKD9 - Radiological Evaluation of Renal CystsDocument26 pagesIKD9 - Radiological Evaluation of Renal CystsRenal Association MauritiusNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Key NotesDocument12 pagesMicrobiology Key NotesHarini Rajeev LaxminarayanNo ratings yet
- Kidney Physiology (Q & A)Document28 pagesKidney Physiology (Q & A)ramadan100% (1)
- (6-7) PATH - Colonic Polyps and CarcinomaDocument11 pages(6-7) PATH - Colonic Polyps and Carcinomaaaron mbindyoNo ratings yet
- UROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasDocument33 pagesUROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Pathology 2 PDFDocument69 pagesBone Marrow Pathology 2 PDFJorge VenturaNo ratings yet
- Major Bacterial Genera TableDocument12 pagesMajor Bacterial Genera TablemojdaNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Pediatric Diseases Chapter SummaryDocument16 pagesGenetic and Pediatric Diseases Chapter SummaryJustine HungNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written II TablesDocument10 pagesNeuro Written II TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Superficial and Cutaneous Mycoses: 2. Disease CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesSuperficial and Cutaneous Mycoses: 2. Disease CharacteristicsMA. ANGELI DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1Maryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmDocument1 pageAcute Myeloproliferative Acute Lymphoproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Chronic Lymphoproliferative Plasma Cell NeoplasmAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Renal BiopsyDocument53 pagesRenal Biopsybusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDocument5 pagesDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPENo ratings yet
- Actinic Keratosis: (Aka Bowen's Disease)Document5 pagesActinic Keratosis: (Aka Bowen's Disease)fadoNo ratings yet
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDocument4 pages4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Document9 pagesWeek 7. Renal Pathology Continued.Amber LeJeuneNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written III TablesDocument5 pagesNeuro Written III TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Aiims Discussion 2015Document115 pagesAiims Discussion 2015langhalilafaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesDocument3 pagesHeart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (3)
- Pitfalls in Diagnosis of HsilDocument1 pagePitfalls in Diagnosis of HsilMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Sources of Parasitic InfectionDocument74 pagesSources of Parasitic InfectionCristy Jean100% (1)
- Dermatology Resident Roundup Histologic BodiesDocument2 pagesDermatology Resident Roundup Histologic BodiesAreg JosephsNo ratings yet
- FRCPath+picture-based+questions (1)Document39 pagesFRCPath+picture-based+questions (1)Marvi UmairNo ratings yet
- Non-Pathogenic Intestinal Amoebae Cyst MorphologyDocument2 pagesNon-Pathogenic Intestinal Amoebae Cyst MorphologyCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Screening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisDocument2 pagesScreening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisBianca ANo ratings yet
- Reedsternberg CellDocument2 pagesReedsternberg CellYakan AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- 1.05 Qualitative 0 Quantitative Platelet DisordersDocument9 pages1.05 Qualitative 0 Quantitative Platelet DisordersShiena ArchividoNo ratings yet
- Manage Stab Wound BleedingDocument7 pagesManage Stab Wound BleedingJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Diseases of ImmunityDocument13 pagesDiseases of ImmunityRose AnnNo ratings yet
- WBC Lymph Node SpleenDocument12 pagesWBC Lymph Node Spleendr brijesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Para Compre 2Document17 pagesPara Compre 2serainie maiNo ratings yet
- Serological TestsDocument2 pagesSerological TestsKimberly EspaldonNo ratings yet
- Leukemia and Lymphoma OverviewDocument2 pagesLeukemia and Lymphoma OverviewAyeshaArifNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Anemia: Anemia Is A Laboratory DiagnosisDocument3 pagesRed Blood Cell Disorders Anemia: Anemia Is A Laboratory DiagnosisAnonymous 8hJAATBNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY WebpathDocument35 pagesENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY Webpathapi-3766657No ratings yet
- Iron Metabolism: DR Mukhtiar BaigDocument58 pagesIron Metabolism: DR Mukhtiar BaigdrmukhtiarbaigNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument9 pagesAnemiaMila Canoza HerreraNo ratings yet
- Pathology - Chapter 14Document14 pagesPathology - Chapter 14Cory GrayNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromsDocument4 pagesNephrotic Nephritic SyndromsKimiwari100% (2)
- RBC DisordersDocument19 pagesRBC DisordersAbhiram KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests Diagnostic GuideDocument2 pagesLiver Function Tests Diagnostic GuideostarburstoNo ratings yet
- Final Cyto Presentation BaruuuuDocument1 pageFinal Cyto Presentation BaruuuuMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Skin Structure and Function GuideDocument10 pagesSkin Structure and Function GuideyassrmarwaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDocument1 pagePosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDocument1 pageVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDocument4 pagesPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument6 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- ThrombophiliaDocument3 pagesThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDocument2 pagesRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390No ratings yet
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument3 pagesSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Pituitary DysfunctionDocument2 pagesPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 pagesRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDocument5 pagesPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDocument4 pagesPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Nsaids DrugsDocument2 pagesNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoNo ratings yet
- Obstructive UropathyDocument3 pagesObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Nocturnal EnuresisDocument1 pageNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Nursing Effective Leadership in Career DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNursing Effective Leadership in Career DevelopmentAlan Divine BNo ratings yet
- Abalone Report InfographicDocument1 pageAbalone Report InfographicjanetNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix Commands: Cat - List A FileDocument3 pagesBasic Unix Commands: Cat - List A Filekathir_tkNo ratings yet
- Marcos & Sumulong Highway, Rizal Applicant'S Information Sheet (Non-Academic)Document2 pagesMarcos & Sumulong Highway, Rizal Applicant'S Information Sheet (Non-Academic)dummy testerNo ratings yet
- Bakhtar University: Graduate School of Business AdministrationDocument3 pagesBakhtar University: Graduate School of Business AdministrationIhsanulhaqnooriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System Protection BookDocument2 pagesElectrical Power System Protection BookHimanshu Kumar SagarNo ratings yet
- Lean Foundation TrainingDocument9 pagesLean Foundation TrainingSaja Unķnøwñ ĞirłNo ratings yet
- Burton Gershfield Oral History TranscriptDocument36 pagesBurton Gershfield Oral History TranscriptAnonymous rdyFWm9No ratings yet
- इंटरनेट मानक का उपयोगDocument16 pagesइंटरनेट मानक का उपयोगUdit Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Visual AnalysisDocument4 pagesVisual Analysisapi-35602981850% (2)
- Fundamentals of Analytics in Practice /TITLEDocument43 pagesFundamentals of Analytics in Practice /TITLEAcad ProgrammerNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Summer Vacation PDFDocument4 pagesClass 7 Summer Vacation PDFPrince RajNo ratings yet
- Engaged Listening Worksheet 3 - 24Document3 pagesEngaged Listening Worksheet 3 - 24John BennettNo ratings yet
- Prof 7 - Capital Market SyllabusDocument10 pagesProf 7 - Capital Market SyllabusGo Ivanizerrckc100% (1)
- Lecture Notes - Design of RC Structure - Day 5Document6 pagesLecture Notes - Design of RC Structure - Day 5Tapabrata2013No ratings yet
- Apple Mango Buche'es Business PlanDocument51 pagesApple Mango Buche'es Business PlanTyron MenesesNo ratings yet
- A StarDocument59 pagesA Starshahjaydip19912103No ratings yet
- Eng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionDocument2 pagesEng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionNiña RasonableNo ratings yet
- Maheshwar Handlooms Cluster Diagnostic StudyDocument15 pagesMaheshwar Handlooms Cluster Diagnostic Studyumang31390100% (3)
- IT WorkShop Lab ManualDocument74 pagesIT WorkShop Lab ManualcomputerstudentNo ratings yet
- Insecticide Mode of Action Classification GuideDocument6 pagesInsecticide Mode of Action Classification GuideJose Natividad Flores MayoriNo ratings yet
- WritingSubmission OET20 SUMMARIZE SUBTEST WRITING ASSESSMENT 726787 40065 PDFDocument6 pagesWritingSubmission OET20 SUMMARIZE SUBTEST WRITING ASSESSMENT 726787 40065 PDFLeannaNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper Maths CBSE Class IX - IIIDocument8 pagesModel Test Paper Maths CBSE Class IX - IIIAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Grammar Level 1 2013-2014 Part 2Document54 pagesGrammar Level 1 2013-2014 Part 2Temur SaidkhodjaevNo ratings yet
- The Alkazi Collection of Photography Vis PDFDocument68 pagesThe Alkazi Collection of Photography Vis PDFMochamadRizkyNoorNo ratings yet
- 19-Year-Old Female With Hypokalemia EvaluatedDocument5 pages19-Year-Old Female With Hypokalemia EvaluatedMohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- How to use fireworks displays at Indian weddings to create magical memoriesDocument3 pagesHow to use fireworks displays at Indian weddings to create magical memoriesChitra NarayananNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting - LabourDocument7 pagesCost Accounting - LabourSaad Khan YTNo ratings yet
- Public Relations & Communication Theory. J.C. Skinner-1Document195 pagesPublic Relations & Communication Theory. J.C. Skinner-1Μάτζικα ντε Σπελ50% (2)
- 1995 - Legacy SystemsDocument5 pages1995 - Legacy SystemsJosé MªNo ratings yet