Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)
Uploaded by
Chris LauOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)
Uploaded by
Chris LauCopyright:
Available Formats
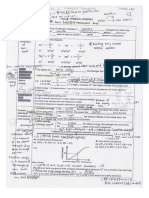
Topic 14: Carbon Chemistry SMK SACRED HEART, SIBU
Tetravalent
1. Carbon forms organic compound Small Size HCH3 is 1oC
Catenate RCH3 is 1oC
Empirical Formula % by mass , Mass of CO2 and H2O R2CH2 is 2oC
2. Chemical formula Molecular Formula Empirical F, Combustion analysis R3CH is 3oC
Structural Formula Displayed , Condensed , Skeletal R4C is 4oC
C and C
+ Stability: 3 > 2 > 1 > CH3
o o o R
3. Carbon species E+ = Lewis acid
C Stability: 3 < 2 < 1 < CH3
o o o Nu = Lewis base
Chain Change in Carbon skeleton
Structural Position Change in position of functional group
Functional Group (a) Alkene & Cycloalkane
(b) Alcohol & Ether
(c) Aldehyde & Ketone
(d) Carbocylic acid & Ester
trans cis
4. Isomerism
Geometrical
Higher m/p Higher b/p
Closely pack More polar
Stereoisomerism Symmertical
VDWF
Optical
Positive EWG increases acid strength / decreases pKa
Inductive Eg: Phenyl group, Hydroxyl group, Nitro- group
effect
when no. of EDG / Size of alkyl group / Distance
Negative EDG decreases acid strength / decreases pKb
Eg: alkyl group and cycloalkyl group
when no. of EWG / Electronegativity / Distance
5. Acid/Base Formation of more stable RCOO - , C6H5O - , C6H5NH2
Resonance
Strength effect Eg: RCOOH + H2O RCOO + H3O+ Equilibrium shift to right
Increasing acid strength : ROH < H2O < phenol < RCOOH < Benzoic acid
Attached to benzene ring Resonance Electron from O delocalises
6. EDG/EWG
(-OH is EDG) into benzene ring
eg: -OH
Not attached to benzene ring Inductive Increases acid strength
(-OH is EWG) effect
You might also like
- STPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (2)
- Carbonyl Compounds: Properties, Reactions and TestsDocument32 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Properties, Reactions and TestsYuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- MPM Table of Reaction For Chemistry Sem 3Document4 pagesMPM Table of Reaction For Chemistry Sem 3STPMBAHARUNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Document2 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Chris LauNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 3Document39 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 3Yuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: (Group 14: C, Si, Ge, SN, PB)Document83 pagesChapter 18: (Group 14: C, Si, Ge, SN, PB)SIVANESVARAN100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Document27 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Raj Nittiya SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 1Document47 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 1Yuzamrah Awang Noh50% (2)
- Thermochemistry Chapter 1Document69 pagesThermochemistry Chapter 1Febian HenryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Chap 03 NewDocument92 pagesChemistry Form 6 Chap 03 Newbrandam0% (1)
- Group 14 ElementsDocument20 pagesGroup 14 Elementshernaniabdullah0% (1)
- Appendix - Chemical Test, Routes of SynthesisDocument11 pagesAppendix - Chemical Test, Routes of Synthesisgoi_pin100% (4)
- STPM ChemistryDocument19 pagesSTPM ChemistryAng chong beng50% (2)
- Complex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Document4 pagesComplex Ions Naming Chemistry STPM Sem 2Chong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2Document7 pagesChemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2kumutha83% (6)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 5Document51 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 5Yuzamrah Awang Noh100% (1)
- Chemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre-Trial QuestionDocument6 pagesChemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre-Trial QuestionKenneth Chan43% (7)
- WWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Document15 pagesWWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Nur AmaleenaNo ratings yet
- STPM Sem 3 Chemistry Note - Chapter AlkanesDocument21 pagesSTPM Sem 3 Chemistry Note - Chapter AlkanesSTPMBAHARU100% (3)
- STPM Chemistry Form 6Document5 pagesSTPM Chemistry Form 6BabasChong100% (1)
- Taklimat Kerja KursusDocument33 pagesTaklimat Kerja KursusUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 03Document39 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 03Ng Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Exp List SPMDocument2 pagesExp List SPMAcyl Chloride Hariprem100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 6 STPMDocument5 pagesChemistry Form 6 STPMChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Elements Sem 2 ChemistryDocument12 pagesGroup 2 Elements Sem 2 ChemistryChong Yin Ping100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 5 CHEMICAL BONDSDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 5 CHEMICAL BONDSJay Bee88% (8)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 2Document52 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 2Yuzamrah Awang NohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Helene_mbbt100% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013Document151 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013Cikgu Faizal100% (15)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Document5 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- Form 4 Chemistry Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Exam Questionsryder1man643367% (6)
- Electrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMPavithiranNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument80 pagesSPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsManisha Sekaran MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 41Document4 pagesLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Suriati Bt A Rashid100% (2)
- Chapter 5 HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Hydrocarbonmeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Groups 1, 17 and 18 ElementsDocument5 pagesPhysical Properties of Groups 1, 17 and 18 ElementslenovosubaNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERDocument31 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERChris Lau75% (4)
- Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry (STPM + Matriculation)Document14 pagesAtoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry (STPM + Matriculation)AlexTanYun-Kai100% (4)
- Carboxylic AcidDocument28 pagesCarboxylic AcidManthan HaritashNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compound PDFDocument52 pagesCarbonyl Compound PDFShubham ChandwaniNo ratings yet
- CARBOXYLIC ACID CHEMISTRYDocument65 pagesCARBOXYLIC ACID CHEMISTRYChin Bao ErNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature Organic Chemistry SummaryDocument5 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature Organic Chemistry SummaryJoanna MalizaNo ratings yet
- Alkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFDocument45 pagesAlkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFPrasad Yarra100% (1)
- Suffix: - Oic AcidDocument18 pagesSuffix: - Oic AcidUsama WaleedNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Chemistry: Department of Chemistry Opch 101 NOV 2020Document5 pagesCarbonyl Chemistry: Department of Chemistry Opch 101 NOV 2020Mlamuli MlarhNo ratings yet
- 02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Document12 pages02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- DSE Chem Last MinuteDocument61 pagesDSE Chem Last Minute何卓函No ratings yet
- PJC Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument18 pagesPJC Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Alkenes: Structure, Properties and ReactionsDocument22 pagesThe Chemistry of Alkenes: Structure, Properties and ReactionsWacka FlockaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument1 pageAlcohols Phenols and EthersNitisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and AlkenesDocument22 pagesCarbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and Alkenesdr lailaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons One Shot BouncebackDocument172 pagesHydrocarbons One Shot BouncebackHarishNo ratings yet
- L5 Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument20 pagesL5 Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Summary SheetDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry Summary SheetLeah BertaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document72 pagesChapter 9Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesSTPM Physics Chapter 17 Electromagnetic InductionChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsChris Lau100% (3)
- STPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current CircuitsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Document2 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 16 Haloalkanes (Short Notes)Chris LauNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentChris LauNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6B Acid Base EquilibriumDocument25 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6B Acid Base EquilibriumChris Lau100% (5)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6C Solubility EquilibriumDocument6 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6C Solubility EquilibriumChris Lau100% (2)
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 6D PHASE EQUILIBRIUM PDFDocument14 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 6D PHASE EQUILIBRIUM PDFChris Lau100% (4)
- STPM Chemistry Past Year Objectives Question (1999-2015)Document28 pagesSTPM Chemistry Past Year Objectives Question (1999-2015)Chris Lau60% (10)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumDocument23 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 6A Chemical EquilibriumChris Lau100% (7)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 3 Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 3 Chemical BondingChris Lau100% (5)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsDocument22 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 5 Reaction KineticsChris Lau100% (12)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERDocument31 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 TOPIC 4 MATTERChris Lau75% (4)
- STPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 1 Atoms Molecule and Stoichiometry (Physical Chemistry)Document15 pagesSTPM Chemistry Term 1 Topic 1 Atoms Molecule and Stoichiometry (Physical Chemistry)Chris Lau88% (17)
- STPM Chemistry Topic 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument18 pagesSTPM Chemistry Topic 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsChris Lau67% (3)
- Mercury Vapor in Paramaribo Suriname EnvironmentDocument2 pagesMercury Vapor in Paramaribo Suriname EnvironmentDaelVanTonderNo ratings yet
- Building Macromolecules - Teacher Notes and Review Questions Answer Key - Updated 2020Document3 pagesBuilding Macromolecules - Teacher Notes and Review Questions Answer Key - Updated 2020Jean Filet ScipioniNo ratings yet
- CDC's Appendix B-Pink Book - Vaccines - Ingredient ListDocument4 pagesCDC's Appendix B-Pink Book - Vaccines - Ingredient ListmickelleNo ratings yet
- 2016 HYDROXY COMPOUNDS (ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS) SUMMARYDocument12 pages2016 HYDROXY COMPOUNDS (ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS) SUMMARYCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- Some Chemicals Present in Industrial and Consumer Products, Food and Drinking-WaterDocument15 pagesSome Chemicals Present in Industrial and Consumer Products, Food and Drinking-WaterJihan Aulia K. SNo ratings yet
- Anti-Aging Clear Skin SerumDocument144 pagesAnti-Aging Clear Skin SerumPDP channelNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Assessment Form - EmptyDocument3 pagesJob Safety Assessment Form - EmptyNurnadia Saliza100% (1)
- Chapter 9 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 9 NotesAndrew RosenNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Katherine Mann - DNA Knotting: Occurences, Consequences and ResolutionDocument181 pagesJennifer Katherine Mann - DNA Knotting: Occurences, Consequences and ResolutionUylrikkNo ratings yet
- Azo Sep - Company Selling Pervap Technique PDFDocument31 pagesAzo Sep - Company Selling Pervap Technique PDFAkhil AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Bactericidal Trigger Spray Surface CleanerDocument1 pageBactericidal Trigger Spray Surface CleanerFrancisco Gustavo Castillo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- MOSH y MOAH Opinion CientificaDocument185 pagesMOSH y MOAH Opinion CientificaDANIEL ZORRONo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in P Block ElementsDocument15 pagesReasoning Questions in P Block ElementsAbhi WaliaNo ratings yet
- Ultraform BrochureDocument40 pagesUltraform BrochurekocakpolimerNo ratings yet
- Polymeric Materials - Part IIDocument49 pagesPolymeric Materials - Part IIRidhwan HaliqNo ratings yet
- Msds Caustic Soda Liquid 48%Document5 pagesMsds Caustic Soda Liquid 48%taufiq hidayatNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangeDocument3 pagesEnergy ChangeAiden YioNo ratings yet
- Din 2403Document9 pagesDin 2403Leonel PazNo ratings yet
- Group For: A Contribution Method Second Virial CoefficientsDocument9 pagesGroup For: A Contribution Method Second Virial CoefficientsSandraColoradoNo ratings yet
- Forage Sample Submission Form 20210901 EFDocument4 pagesForage Sample Submission Form 20210901 EFLyseth ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- BioRes 11 2 5452 Review EspinozaAcosta TRLM Antioxidant Antimicrobial Tech Lignins Appln 8447 PDFDocument30 pagesBioRes 11 2 5452 Review EspinozaAcosta TRLM Antioxidant Antimicrobial Tech Lignins Appln 8447 PDFStelyca MihalutiNo ratings yet
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument36 pagesThin Layer ChromatographyRahul Bajaj100% (4)
- Research FinalDocument53 pagesResearch FinalJhon Paul MonesNo ratings yet
- Fisher Scientific - New Price Book 2013-14Document57 pagesFisher Scientific - New Price Book 2013-14irfanNo ratings yet
- Rotary Evaporator JournalDocument4 pagesRotary Evaporator JournalAditya Dian TjokroatmodjoNo ratings yet
- Controlled Polymerization in Flow Microreactor SystemsDocument56 pagesControlled Polymerization in Flow Microreactor SystemsLuis DiazNo ratings yet
- M.sc. Chemistry Compiled SyllabusDocument48 pagesM.sc. Chemistry Compiled SyllabusSadiaMaryamNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Accidents (Emergency Planning, Preparedness, and Response) Rules, 1996Document43 pagesThe Chemical Accidents (Emergency Planning, Preparedness, and Response) Rules, 1996Mahesh MenonNo ratings yet
- WS4. Lewis Bronsted-Lowry Acids Worksheet (HL)Document4 pagesWS4. Lewis Bronsted-Lowry Acids Worksheet (HL)Yuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Food Additives, E-NUMBERS PDFDocument12 pagesFood Additives, E-NUMBERS PDFjiatrou6350No ratings yet