Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Biostatistics - Research Etymology: Notes From The Lecture & Orientations
Uploaded by
Angelo Bautista0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesLecture trans
Original Title
Introduction to Biostatistics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLecture trans
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesIntroduction To Biostatistics - Research Etymology: Notes From The Lecture & Orientations
Uploaded by
Angelo BautistaLecture trans
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
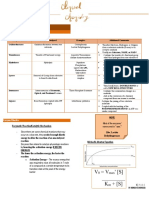
Introduction to Biostatistics | Research o Methods for testing hypotheses:
Notes from the lecture & orientations For comparison hypothesis
Etymology Searching for any
difference between the
bio life
data given
statistic collection, organization,
For relationship hypothesis
analyzation, interpretation of numerical data
Searching for any
Meaning
possible association
Application of statistical methods to the
between the data given
health setting
Constant
Public Health Statistics
A value which remains the same from
Two types:
person-to-person
o Vital statistics
Example:
For vital events
o A week has seven (7) days
Number of births
o A dozen has twelve (12) units
Number of deaths
o or pi is always 3.14159265359
Number of marriages
Variable
Number of divorces (in other
countries) A value which cannot be predicted with
o Health statistics certainty
Morbidity Example:
Mortality o Weight may vary from time-to-time
Hospital and clinical statistics o Blood sugar may change
Service statistics The phenomenon of variation is what makes
Annual physical exams statistics important as it aims to make sense
Immunization of the uncertainty
Regulations for submission of statistics: Types of variables
o 1-month window for submission of o Qualitative
birth data One whose categories are
o 48-hour window for the registration of simply used as labels to
the dead with accompanying distinguish one group from
certificate by a physician another
o 3-month window before marriage for Example:
the registration of matrimony Gender
Branches of Statistics Place of residence
Descriptive statistics o Quantitative
o Summarizes and present the data Measure & ordered per
collected in manner which is easier quantity or amount
for analysis & interpretation Example:
o Example: Height
Bar graph Birth weight
Pie graph Types of Quantitative Variables
Pictograph Discrete variables
o Easier to interpret than raw data o Assumes only integral values or
Inferential statistics whole numbers
o Methods for making generalization o Example:
and conclusions on a target Number of eggs
population based on results from a Number of songs
sample Number of letters
o Types of parameter estimations: Cannot be or
Point estimate Continuous variables
Exact estimated o Variables which can attain any value
average is given including fractions or decimals
Interval estimate o Example:
An estimate is denoted Exact weight contains
as being between two decimals
given numbers Exact height
Scales of Measurement
Nominal
o Label or categories
o Example:
Gender (male or female)
Ordinal
o Ranked or ordered
o Types of ordinality:
Qualitative
Few, moderate, many
Quantitative
1st, 2nd and 3rd
Interval
o Exact distance between two
categories wherein zero is arbitrary
o Example:
Temperature in Celsius
Ratio
o Zero is fixed and no values go below
o Example:
Weight in kilogram
Height in centimeters
Application of Biostatistics
Information-based tool in decision-making
processes
For clinical trials & evaluation of research
activities
Problem identification
AngeloBautista
You might also like
- Introduction to Biostatistics ConceptsDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Biostatistics ConceptsAileen JaymeNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Introduction To BiostatisticsDocument18 pagesLecture1 Introduction To BiostatisticsIdiAmadouNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Syllabus (Final)Document2 pagesBiostatistics Syllabus (Final)sababuttNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To BiostatisticsDocument52 pages1 Introduction To Biostatisticskriss WongNo ratings yet
- Gene Cloning Electroporation Transformation: Submitted To: Mam Dr. Farzana ShahinDocument33 pagesGene Cloning Electroporation Transformation: Submitted To: Mam Dr. Farzana ShahinKazmi TvNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics IntroductionDocument39 pagesBiostatistics IntroductionMohammed Abdela100% (1)
- Introduction To Virology: 1.1 Definition and Scope of VirologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Virology: 1.1 Definition and Scope of VirologyasayeyordanosNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Lecture 1ADocument13 pagesTopic 1 Lecture 1ANG ZI JIANNo ratings yet
- ISBS Newsletter 2018Document31 pagesISBS Newsletter 2018Genieve Yeo100% (1)
- SC 331 Introduction to BiostatisticsDocument6 pagesSC 331 Introduction to BiostatisticsAamir AnwarAliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiostatisticsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To BiostatisticsGarmenkellNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour About PowerDocument13 pagesOrganizational Behaviour About PowerAkshay JadavNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter 8Document4 pagesSummary of Chapter 8Michael JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Molecular Fibroza CisticaDocument15 pagesDiagnostic Molecular Fibroza CisticaLiviu Athos TamasNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology SlidesDocument30 pagesEpidemiology SlidesHongMingNo ratings yet
- Level 3000 and 4000 Module DetailsDocument5 pagesLevel 3000 and 4000 Module DetailsJulia LohNo ratings yet
- Data Collection Release NotesDocument2 pagesData Collection Release NotesPavel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Research Method Unit-1Document19 pagesResearch Method Unit-1gsach11No ratings yet
- 16625.Hsl4207 Microbiology (Parasitology & Mycology) CH 13Document4 pages16625.Hsl4207 Microbiology (Parasitology & Mycology) CH 13Tarun AroraNo ratings yet
- Biomedwet Bachelor PDFDocument506 pagesBiomedwet Bachelor PDFmphil.rameshNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Medical Virology BasicsDocument88 pagesIntroduction to Medical Virology BasicsSutapa PawarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular Biology and GeneticsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Biology and Geneticsasa arangNo ratings yet
- Third Year Research Methodology SyllabusDocument2 pagesThird Year Research Methodology Syllabusfatima kim souNo ratings yet
- Homework - 2 Module: Biostatistics (MPH 521) YEAR-2021: Girls BoysDocument4 pagesHomework - 2 Module: Biostatistics (MPH 521) YEAR-2021: Girls BoysShyam Shrestha100% (2)
- Assignment HypersensitivityDocument3 pagesAssignment HypersensitivityNurzatul syamim busriNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of ManagementDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Practices of ManagementsuramyavNo ratings yet
- ABBAS BAB 2 Innate ImmunityDocument28 pagesABBAS BAB 2 Innate ImmunitydianaNo ratings yet
- FMEA AnalysisDocument8 pagesFMEA AnalysismsabryNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document13 pagesCH 14Manish MalikNo ratings yet
- Molecular DiagnosticsDocument19 pagesMolecular DiagnosticsRAHUL ROYNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal Antibody: Engineering and TherapyDocument39 pagesMonoclonal Antibody: Engineering and TherapyAugusta Rizki AnandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Data Collection MethodsDocument6 pagesChapter 5: Data Collection MethodsRana HaiderNo ratings yet
- MHC Molecules and T Cell ReceptorsDocument39 pagesMHC Molecules and T Cell Receptors16_dev5038100% (1)
- Principles and Practices of Management Question PapersDocument11 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Management Question PapersNagarajan Mani50% (2)
- Basic Molecular Biology & Biotechnology Training ManualDocument23 pagesBasic Molecular Biology & Biotechnology Training Manualsameer420No ratings yet
- Mean, Median & Mode PDFDocument11 pagesMean, Median & Mode PDFwolfretonmaths100% (1)
- Introduction To EpidemiologyDocument87 pagesIntroduction To EpidemiologyMugisha Laurian100% (1)
- Chapter 14 - Managerial ControlDocument49 pagesChapter 14 - Managerial ControlpedoqpopNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Improving Operational Effectiveness in The Clinical Laboratoryat King Fahd Armed Forces Hospital (Kfafh)Document7 pagesStrategies For Improving Operational Effectiveness in The Clinical Laboratoryat King Fahd Armed Forces Hospital (Kfafh)IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Answer Organizational BehaviourDocument9 pagesAnswer Organizational BehaviourBedanta DorshanNo ratings yet
- LN Molecular Biolog Applied Genetics FINALDocument529 pagesLN Molecular Biolog Applied Genetics FINALarivasudeva100% (1)
- CC Partii&III NotesDocument30 pagesCC Partii&III NotesAnielle Mongaya100% (1)
- HypersensitivityDocument44 pagesHypersensitivitymohamed100% (1)
- Hypersensitivity ReactionDocument23 pagesHypersensitivity ReactionJo CanensNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Clinical Case Study 3 Lymphoma FinalDocument27 pagesPortfolio Clinical Case Study 3 Lymphoma Finalapi-277136509No ratings yet
- AKC Histo Drawings PDFDocument130 pagesAKC Histo Drawings PDFDanDeleanuNo ratings yet
- FIN3101 Corporate Finance Practice Questions Topic: Capital BudgetingDocument3 pagesFIN3101 Corporate Finance Practice Questions Topic: Capital BudgetingKelly KohNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VirologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Virologyyezan27No ratings yet
- Understanding EpidemiologyDocument40 pagesUnderstanding EpidemiologyCharityOchiengNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics and Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesBiostatistics and Research MethodologyAnonymous sF8ZuiG100% (1)
- Introduction To EpidemiologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To EpidemiologylagathurcNo ratings yet
- Biostat NotesDocument8 pagesBiostat NotesPam FajardoNo ratings yet
- T Cell Differentiation and ActivationDocument15 pagesT Cell Differentiation and Activationnet_set100% (1)
- Medical TechnologistDocument2 pagesMedical Technologistapi-329932534No ratings yet
- Anatomical Directional TerminologyDocument4 pagesAnatomical Directional TerminologyJZA 66No ratings yet
- Immunology IHC LectureDocument49 pagesImmunology IHC LectureDavid ChristianNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To EpidemiologyDocument22 pages1-Introduction To EpidemiologyANTHONY KHAOYANo ratings yet
- Blood GroupingDocument3 pagesBlood GroupingJalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- The Journal - History of Culture MediaDocument16 pagesThe Journal - History of Culture MediaDholakia100% (4)
- Biostatistics CourseDocument100 pagesBiostatistics CourseAlamgir Hossain100% (1)
- Gross HSB B - Anatomy of The Back & Suboccipital Region PDFDocument2 pagesGross HSB B - Anatomy of The Back & Suboccipital Region PDFAngelo Bautista100% (1)
- NMAT Practice Set Part 1 & Part 2 With Answer KeyDocument64 pagesNMAT Practice Set Part 1 & Part 2 With Answer KeyLucid Lynx100% (1)
- Gross HSB B - Anatomy of The Back & Suboccipital Region PDFDocument2 pagesGross HSB B - Anatomy of The Back & Suboccipital Region PDFAngelo Bautista100% (1)
- Microbiology - Draft 1Document5 pagesMicrobiology - Draft 1Angelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Biochem TestsDocument1 pageGram Positive Cocci Biochem TestsAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- P - Endocrine Disorders - TransDocument4 pagesP - Endocrine Disorders - TransAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- UriSed ClinLab2014Document6 pagesUriSed ClinLab2014Angelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Text SubtextDocument1 pageText SubtextAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Honey & Acetic Acid Research ProposalDocument29 pagesHoney & Acetic Acid Research ProposalAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology Part 2Document10 pagesRenal Physiology Part 2Angelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer: Clinical Lab LawsDocument4 pagesMidterms Reviewer: Clinical Lab LawsAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Oreimo - Volume 1Document275 pagesOreimo - Volume 1Angelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Oreimo - Volume 2Document390 pagesOreimo - Volume 2Angelo Bautista100% (1)
- Road Success EntrepreneurDocument18 pagesRoad Success EntrepreneurHenry Vargas GamboaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The XXV Scientific ConferenceDocument137 pagesProceedings of The XXV Scientific ConferenceAdriana MeloNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology U1 P1 Answers PDFDocument1 pageCAPE Biology U1 P1 Answers PDFKaylia WilsonNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCourse OutlinerabiaNo ratings yet
- Dream It, Do It, Live It: 9 Easy Steps To Making Things Happen For YouDocument23 pagesDream It, Do It, Live It: 9 Easy Steps To Making Things Happen For YouCapstone PublishingNo ratings yet
- Monsters, Madmen and Myths A Critical Review of The Serial Killing Literature by Joshua Stuart-BennettDocument35 pagesMonsters, Madmen and Myths A Critical Review of The Serial Killing Literature by Joshua Stuart-BennettSalvador Murlà AlluéNo ratings yet
- Homework For The Week 6Document9 pagesHomework For The Week 6Leyla AliyevaNo ratings yet
- MGT 105.3 Entrepreneurship CourseDocument1 pageMGT 105.3 Entrepreneurship CourseShishir ModakNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents and Class DescriptionsDocument80 pagesTable of Contents and Class DescriptionsLandrel LoneNo ratings yet
- Task 3: Lesson Plan ReflectionsDocument28 pagesTask 3: Lesson Plan Reflectionsapi-374921761No ratings yet
- Department of Education: 12 Confucius Humanities and Social SciencesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: 12 Confucius Humanities and Social SciencesJesh Manansala-DesavilleNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Interview Professor Safeya Effat: I History Taking 1. Personal DataDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Interview Professor Safeya Effat: I History Taking 1. Personal DataAcha Angel BebexzNo ratings yet
- Ijapa Tiroko Oko YaniboDocument11 pagesIjapa Tiroko Oko Yanibomuyiwa osoNo ratings yet
- 5 Common Mistakes Language Learners MakeDocument2 pages5 Common Mistakes Language Learners MakeQuim EraNo ratings yet
- Rhythm Magazine Advice For DrummersDocument2 pagesRhythm Magazine Advice For DrummersNeil DaviesNo ratings yet
- PMIEF Project Management Kit For Primary School Practice Guide For TutorsDocument55 pagesPMIEF Project Management Kit For Primary School Practice Guide For Tutorslinacio68No ratings yet
- Stormweaver Ii - Chapter 5Document18 pagesStormweaver Ii - Chapter 5Bishwa SilwalNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Teaching StrategiesDocument12 pagesSocial Studies Teaching Strategiesapi-266063796100% (1)
- Assignment Educ 211Document3 pagesAssignment Educ 211Gerald Jem BernandinoNo ratings yet
- Perfect Promo Guide Udemy PDFDocument2 pagesPerfect Promo Guide Udemy PDFSEBASTIAN GARCIA NUNEZNo ratings yet
- Motivation LetterDocument1 pageMotivation Lettercams89100% (3)
- MSC Construction Project Management - Heriot-Watt University 48kDocument5 pagesMSC Construction Project Management - Heriot-Watt University 48kalfrobiwongytNo ratings yet
- Toastmaster FullDocument39 pagesToastmaster Fullmachinel1983No ratings yet
- 04 - 01 - Sample Onsite AgendaDocument1 page04 - 01 - Sample Onsite AgendaJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Keeping The Republic Power and Citizenship in American Politics, 9th Edition, Christine Barbour, Gerald C. WrightDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Keeping The Republic Power and Citizenship in American Politics, 9th Edition, Christine Barbour, Gerald C. Wrighthung.umbrette.h8gdpg100% (20)
- Spiritual Solutions by Deepak Chopra - ExcerptDocument24 pagesSpiritual Solutions by Deepak Chopra - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group89% (9)
- Employee Reprimand Letter for TardinessDocument4 pagesEmployee Reprimand Letter for TardinessMarjoriz Tan Ignacio100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: "Pete The Cat-Rocking in My School Shoes" by Eric Litwin (Document9 pagesLesson Plan: "Pete The Cat-Rocking in My School Shoes" by Eric Litwin (FranciscoDiegoNo ratings yet
- Parental Compliance With Car Seat Usage: A Positive Approach With Long-Term Follow-UpDocument12 pagesParental Compliance With Car Seat Usage: A Positive Approach With Long-Term Follow-UpHaffizi IrfanNo ratings yet
- BIMAS 2 Teacher Standard Form From Tim Simmons WCPSSDocument2 pagesBIMAS 2 Teacher Standard Form From Tim Simmons WCPSSA.P. Dillon50% (2)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseFrom EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (126)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesFrom EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (139)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)