Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Appendix C Modified Iowa Formula: Inspecting Pipeline Installation
Uploaded by
gacm98Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendix C Modified Iowa Formula: Inspecting Pipeline Installation
Uploaded by
gacm98Copyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from ascelibrary.org by 181.14.205.243 on 07/30/15. Copyright ASCE. For personal use only; all rights reserved.
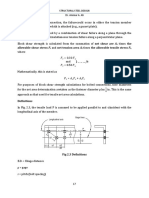
APPENDIX C
MODIFIED IOWA FORMULA
The primary formula used for predicting horizontal deection for ex-
ible pipe is the Modied Iowa Formula. It establishes the relationship
between the load on the pipe (DlKsWcr3), the pipe support (EI) and the soil
support (0.061Er3) and demonstrates the importance of the soil interac-
tion with the pipe.
The equation is:
Dl K sWc r 3
x =
(EI + 0.061E r 3 )
where:
x = horizontal increase in diameter, in.
Dl = deection lag factor
Ks = bedding factor; generally assumed to be 0.1 (0.083 to 0.110 depend-
ing on the bedding angle)
Wc = PD = load on pipe per unit length of pipe, lb/linear in.
r = radius of pipe (assumed equal to D/2 in the derivation of the Iowa
Formula), in.
t = pipe wall thickness, in.
E = modulus of elasticity of the pipe material, psi
I = Moment of Inertia of the pipe wall cross-section, in.4 per linear
inch = in.3
E = horizontal modulus of soil reaction, psi
P = vertical soil pressure on top of the pipe, psi
D = diameter of the pipe, in.
261
Inspecting Pipeline Installation
262 INSPECTING PIPELINE INSTALLATION
Interestingly, the Modied Iowa Formula was never meant to design
pipe, just to predict deection. Vertical deection is a much more impor-
tant value. Vertical deection of a exible pipe is essentially equal to the
vertical deection of the side-ll soil (that soil on the immediate side of
the pipe from the top of the pipe to the bottom of the pipe).
Downloaded from ascelibrary.org by 181.14.205.243 on 07/30/15. Copyright ASCE. For personal use only; all rights reserved.
It should be recognized that the shape of the pipe should take the form
of an ellipse rather than a series of eccentric curves or, worse yet, an inver-
sion. Notice that r in the formula is assumed to be one-half the diameter.
A substantial variation in the curvature of the pipe would impact the
results of the formula. Forms other than relatively uniform ellipses can
lead to the premature failure of the pipe due to buckling. Such detrimental
pipe deections occur when the soil is improperly compacted and can
become accentuated with exible pipe having low levels of pipe stiffness
(EI/r3).
The horizontal modulus of soil reaction, E, is a function of the type of
soil, the compaction of the soil, the diameter of the pipe, and the height
of cover over the pipe. Tables have been prepared based on experience,
but it should be recognized that E is an imprecise value that can not be
determined through basic soil mechanics.
Inspecting Pipeline Installation
You might also like
- Introduction To Art Therapy Research (By Lynn Kapitan)Document104 pagesIntroduction To Art Therapy Research (By Lynn Kapitan)td100% (1)
- Engineers' Survival Handbook (2022)Document46 pagesEngineers' Survival Handbook (2022)Luis Jose DuranNo ratings yet
- Duolingo Essay TemplateDocument53 pagesDuolingo Essay TemplateJay PatilNo ratings yet
- Swagelok Pipe FittingsDocument24 pagesSwagelok Pipe Fittingsgacm98100% (1)
- She BrochureDocument9 pagesShe Brochuregacm98No ratings yet
- Calculation of Fault Rates of Overhead Power Distribution Lines Due Lightning-Induced Voltages Including The Effect of Ground ConductivityDocument8 pagesCalculation of Fault Rates of Overhead Power Distribution Lines Due Lightning-Induced Voltages Including The Effect of Ground ConductivityDragonsitoNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics of Buried PipesDocument6 pagesStructural Mechanics of Buried PipesobricenoNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument7 pagesUnit IiVishwajeet VermaNo ratings yet
- Mms MMHL FinalDocument4 pagesMms MMHL Finalapi-436858496No ratings yet
- Chapter III Torsion 3.3Document3 pagesChapter III Torsion 3.3Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Application of The Ruling Span Concept For Overhead Lines in Mountainous Terrain.Document6 pagesApplication of The Ruling Span Concept For Overhead Lines in Mountainous Terrain.diux96No ratings yet
- Vano Regulador en Terreno Inclinado - 00714512Document6 pagesVano Regulador en Terreno Inclinado - 00714512rloayzamariacaNo ratings yet
- Analisa Tanggapan Tegangan Dan Arus Terhadap Perubahan Parameter Saluran TransmisiDocument7 pagesAnalisa Tanggapan Tegangan Dan Arus Terhadap Perubahan Parameter Saluran TransmisiWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- I. Introduction To Wave Propagation: July, 2003 © 2003 by H.L. Bertoni 1Document71 pagesI. Introduction To Wave Propagation: July, 2003 © 2003 by H.L. Bertoni 1DrShashikant DargarNo ratings yet
- Design of 3000mm MS Pipe for Sewerage NetworkDocument9 pagesDesign of 3000mm MS Pipe for Sewerage Networknavneet3bawaNo ratings yet
- Tubesheet PDFDocument8 pagesTubesheet PDFRitesh VishambhariNo ratings yet
- Equations For Flooding Rate in Packed Towers 1960Document1 pageEquations For Flooding Rate in Packed Towers 1960Victor VazquezNo ratings yet
- Helv Phys Acta V70 p813 821 (1997)Document9 pagesHelv Phys Acta V70 p813 821 (1997)Lucian BaltesNo ratings yet
- Concrete Crack Width MeasurementDocument6 pagesConcrete Crack Width MeasurementcedaserdnaNo ratings yet
- The TransmissionLine Equations for Multiconductor LinesDocument21 pagesThe TransmissionLine Equations for Multiconductor Linesdooman2012No ratings yet
- Webb, Eckert - 1972 - Application of Rough Surfaces To Heat ExchangerDocument12 pagesWebb, Eckert - 1972 - Application of Rough Surfaces To Heat ExchangerKau Carlos XavierNo ratings yet
- TOCIEJ-11-748 - Shape FactorDocument9 pagesTOCIEJ-11-748 - Shape FactorharishduttNo ratings yet
- HDDCrossingReport - 3.doc 10 12Document3 pagesHDDCrossingReport - 3.doc 10 12Yoga ArviansyahNo ratings yet
- Parameters of Single and Three Phase Lines With Single and Double CIRCUITSDocument13 pagesParameters of Single and Three Phase Lines With Single and Double CIRCUITSperiyasamiaadhithanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Theory Energy LossesDocument6 pagesFluid Flow Theory Energy LossesAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics of Drip irrigation System Pipe NetworkDocument22 pagesHydraulics of Drip irrigation System Pipe NetworkSurekha DabhadeNo ratings yet
- Annual: MeetingDocument8 pagesAnnual: MeetingyohannesNo ratings yet
- Two WiresDocument3 pagesTwo WiresaumoghNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines With: Exponential TaperDocument7 pagesTransmission Lines With: Exponential Taperreza mirzakhaniNo ratings yet
- Speed of Sound EquationDocument8 pagesSpeed of Sound Equationr3dbloodNo ratings yet
- Shunt Admittance of Overhead LinesDocument14 pagesShunt Admittance of Overhead LinesChristopher StanleyNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of steady flow profiles in packed beds by a variational methodDocument9 pagesEvaluation of steady flow profiles in packed beds by a variational methodAkarsha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Symphatetic Inrush Kumbhar2007Document6 pagesSymphatetic Inrush Kumbhar2007Anonymous BBX2E87aHNo ratings yet
- Determinación Campo D KDocument4 pagesDeterminación Campo D KJose Antonio MendezNo ratings yet
- تقرير تحليلاتDocument6 pagesتقرير تحليلاتAreej AdeebNo ratings yet
- 2008 Yh Ieee ApDocument20 pages2008 Yh Ieee Apzied houanebNo ratings yet
- Wind LoadDocument3 pagesWind Loadvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- Packed TowersDocument6 pagesPacked TowersVictor VazquezNo ratings yet
- AD-1key MLRITDocument22 pagesAD-1key MLRITSaiAerrogantNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF SIMULTANEOUS GROUND AND PHASE FAULTS ONDocument7 pagesANALYSIS OF SIMULTANEOUS GROUND AND PHASE FAULTS ONsoumenNo ratings yet
- oluwade_posterDocument1 pageoluwade_postermohamedbelhajm540No ratings yet
- Instrumentation File MaterialDocument14 pagesInstrumentation File MaterialkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Kra Emer 1955Document9 pagesKra Emer 1955Youcef FermiNo ratings yet
- 5.current ElectricitytheoryDocument28 pages5.current ElectricitytheorySuman SainiNo ratings yet
- Una Nueva Fórmula Explícita de Factor de Fricción para Flujos Laminares, de Transición y Turbulentos en Tuberías Lisas y RugosasDocument6 pagesUna Nueva Fórmula Explícita de Factor de Fricción para Flujos Laminares, de Transición y Turbulentos en Tuberías Lisas y Rugosasdaniel quispe mezaNo ratings yet
- ASME PTC 30-1991 Air Cooled Heat ExchangersDocument19 pagesASME PTC 30-1991 Air Cooled Heat ExchangersShanNo ratings yet
- B.Tech 6th Semester Antenna & Wave Propagation NotesDocument20 pagesB.Tech 6th Semester Antenna & Wave Propagation NotesThe LoggerNo ratings yet
- Kelm110 PDFDocument35 pagesKelm110 PDFDeepak pandeyNo ratings yet
- Rigid conduit for fluid flow in two-phase fluid systems - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国Document6 pagesRigid conduit for fluid flow in two-phase fluid systems - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国944062528qqNo ratings yet
- Laminar Entrance F L o W in Curved Annular Ducts: and Seung O. ParktDocument9 pagesLaminar Entrance F L o W in Curved Annular Ducts: and Seung O. ParktPrabal AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Measure ground impedance accounting for coupling effectDocument10 pagesMeasure ground impedance accounting for coupling effectSueja MalligwadNo ratings yet
- Agua en El SueloDocument6 pagesAgua en El SueloAlejandra AcostaNo ratings yet
- Allowable Shear Stress F: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AliDocument1 pageAllowable Shear Stress F: Structural Steel Design Dr. Ammar A. AlisereNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 2004Document13 pagesLec 2 2004Swati SatyendraNo ratings yet
- EEE209 Online2Document28 pagesEEE209 Online2MeowNo ratings yet
- Induction Heating of Ferromagnetic PlatesDocument10 pagesInduction Heating of Ferromagnetic Plateshercules_vidalNo ratings yet
- Gate-Induced Drain Leakage Current in MOS DevicesDocument3 pagesGate-Induced Drain Leakage Current in MOS Devicessusovan56No ratings yet
- ENERGY ANALYSIS OF PIPESDocument29 pagesENERGY ANALYSIS OF PIPESBonifacioNo ratings yet
- Engineering Calculation: (This Correlated Heat Transfer Coefficient at Tube Side Condition of Flow)Document3 pagesEngineering Calculation: (This Correlated Heat Transfer Coefficient at Tube Side Condition of Flow)RajdeepsinhNo ratings yet
- Week 11 SeepageDocument31 pagesWeek 11 Seepagedritz tevesNo ratings yet
- Ground Fault in OHLDocument4 pagesGround Fault in OHLInayat HathiariNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Effect of Substrate On Properties of MN PhosphateDocument16 pagesEffect of Substrate On Properties of MN Phosphategacm98No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Control On Phosphating of High Strength Cold-Rolled SteelDocument4 pagesAtmosphere Control On Phosphating of High Strength Cold-Rolled Steelgacm98No ratings yet
- Study On Growth and Corr Resistance of MN Phosphate CoatingsDocument7 pagesStudy On Growth and Corr Resistance of MN Phosphate Coatingsgacm98No ratings yet
- 5 HPHT Ray StawaiszDocument8 pages5 HPHT Ray Stawaiszgacm98No ratings yet
- Rigless Intervention System: Efficiency and Safety Without The RigDocument4 pagesRigless Intervention System: Efficiency and Safety Without The Riggacm98No ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Inconel 625 at Elevated TempDocument13 pagesMechanical Behavior of Inconel 625 at Elevated Tempgacm98No ratings yet
- Modified Manganese Phosphate Conversion CoatingDocument24 pagesModified Manganese Phosphate Conversion Coatinggacm98No ratings yet
- Fittings and Pup JointsDocument8 pagesFittings and Pup JointsWiwyt Narko100% (1)
- Agnew ConocoPhilips Installation Impact of Continuous Surfactant Injection To Remediate Liquid Loading On Gas Wells PDFDocument12 pagesAgnew ConocoPhilips Installation Impact of Continuous Surfactant Injection To Remediate Liquid Loading On Gas Wells PDFgacm98No ratings yet
- EFFECT OF FLOW ON CORROSION OF API PIPELINE STEELS GRADES IN NaCI SOLUTIONS+CO2Document25 pagesEFFECT OF FLOW ON CORROSION OF API PIPELINE STEELS GRADES IN NaCI SOLUTIONS+CO2gacm98No ratings yet
- 17-4 PH Stainless SteelDocument21 pages17-4 PH Stainless Steelmavis16100% (1)
- Fracture Toughness Inconel 625Document10 pagesFracture Toughness Inconel 625gacm98No ratings yet
- Ellectronically Controlled Pressure Relief Valve-BrochureDocument4 pagesEllectronically Controlled Pressure Relief Valve-Brochuregacm98No ratings yet
- Subsurface Safety EquipmentDocument36 pagesSubsurface Safety Equipmentgus_tavo161100% (1)
- Cyclonic Desander: Sand and Solids Handling For All ApplicationsDocument2 pagesCyclonic Desander: Sand and Solids Handling For All Applicationsgacm98No ratings yet
- Belzona Fluid ElastomerDocument2 pagesBelzona Fluid Elastomergacm98No ratings yet
- 3-Digit Counter and DisplayDocument7 pages3-Digit Counter and DisplayEfren Joseph A. PaduaNo ratings yet
- GB-T 1220 Ac Inox STD ChinaDocument15 pagesGB-T 1220 Ac Inox STD Chinagacm98No ratings yet
- Nickel and Its AlloysDocument164 pagesNickel and Its Alloysgacm98100% (2)
- Control Choke GuideDocument16 pagesControl Choke Guidegacm9875% (4)
- Guardian GreaseDocument2 pagesGuardian Greasegacm98No ratings yet
- General Catalog en BS MD07.4Document306 pagesGeneral Catalog en BS MD07.4gacm98No ratings yet
- ISSF The Salt Spray Test and Its Use in Ranking Stainless SteelsDocument20 pagesISSF The Salt Spray Test and Its Use in Ranking Stainless Steelstwinkle_twinkleNo ratings yet
- Hardfacing Solutions For Oil Gas Applications V1Document25 pagesHardfacing Solutions For Oil Gas Applications V1gacm98100% (1)
- GE Gate Valve PDFDocument2 pagesGE Gate Valve PDFgacm98No ratings yet
- Slab Gate Valves Api 6ADocument39 pagesSlab Gate Valves Api 6AJuan Pablo100% (1)
- Thrust Bearing CatalogDocument138 pagesThrust Bearing CatalogAlvaroNo ratings yet
- MagnumDocument16 pagesMagnumgacm98100% (1)
- Dry Air Gas PropertiesDocument25 pagesDry Air Gas Propertiesmshah222No ratings yet
- S10.s4 Bearing-CapacityDocument20 pagesS10.s4 Bearing-CapacityRodolfo Jesus Calle FloresNo ratings yet
- Bitumen With Salt PDFDocument9 pagesBitumen With Salt PDFbkswain2003No ratings yet
- Vernacular Architecture: Sem VDocument42 pagesVernacular Architecture: Sem VPriya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction PaperIvy Jean PalamosNo ratings yet
- 2 ENGLISH Board AKDocument4 pages2 ENGLISH Board AKRoseMay JimenaNo ratings yet
- Volunteering Cures LonelinessDocument2 pagesVolunteering Cures LonelinessRəşad XəlilliNo ratings yet
- 20211004113328615a841821965 Soan Bai Tap Trac Nghiem Tieng Anh 11 Unit 9 Cities of The Future Dap AnDocument17 pages20211004113328615a841821965 Soan Bai Tap Trac Nghiem Tieng Anh 11 Unit 9 Cities of The Future Dap Anthuy dinhNo ratings yet
- ELV (ED Coating)Document2 pagesELV (ED Coating)Mohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Energetics Explained: Exothermic vs Endothermic ReactionsDocument12 pagesEnergetics Explained: Exothermic vs Endothermic ReactionsAliyah HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Tales of The Grotesque and Arabesque - Edgar Allan Poe PDFDocument274 pagesTales of The Grotesque and Arabesque - Edgar Allan Poe PDFCosmin PopaNo ratings yet
- SECTION 21 - MicropilingDocument8 pagesSECTION 21 - MicropilingTony JamesNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Equivalent Resistance and Impedance of The Cylindrical Network Based On Recursion-Transform MethodDocument12 pagesCalculation of The Equivalent Resistance and Impedance of The Cylindrical Network Based On Recursion-Transform Methodmark_990566444No ratings yet
- Ps3 Unit 8 Lesson 1 Period 2Document6 pagesPs3 Unit 8 Lesson 1 Period 2Quách Thi NhungNo ratings yet
- Morphology The Words of LanguageDocument29 pagesMorphology The Words of LanguageErick GalvezNo ratings yet
- Retest Practical Exam Details for 57 SubjectsDocument9 pagesRetest Practical Exam Details for 57 SubjectsWhat WhatNo ratings yet
- Shape Functions in Finite Element AnalysisDocument22 pagesShape Functions in Finite Element AnalysissyampnaiduNo ratings yet
- Permapak Seal Bore Production PackerDocument1 pagePermapak Seal Bore Production PackerPedro GarzónNo ratings yet
- "We Googled You": An Analysis of The CaseDocument7 pages"We Googled You": An Analysis of The CaseMukul MohtaNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4218-15 Contenido NHDocument3 pagesASTM D4218-15 Contenido NHNelson VivancoNo ratings yet
- Composite Shell Lining For Tunnels and Mined StationsDocument7 pagesComposite Shell Lining For Tunnels and Mined StationsDEBASIS BARMANNo ratings yet
- CE 555 Hydraulics Lecture and Tutorial OverviewDocument5 pagesCE 555 Hydraulics Lecture and Tutorial OverviewbakrichodNo ratings yet
- MGT544 Chapter 3 PerceptionDocument14 pagesMGT544 Chapter 3 PerceptionaidaarifahNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method GuideDocument7 pagesScientific Method GuideVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology & Society: Historical Antecedents in Ancient TimesDocument48 pagesScience, Technology & Society: Historical Antecedents in Ancient Timesnatalie clyde matesNo ratings yet
- Errores de FlebotomiaDocument5 pagesErrores de FlebotomiaSandra Amayrane Alcántara Balderas100% (1)
- The Use of 1% Nano-Fe3O4 and 1% Nano-TiO2 As Partial Replacement of Cement To Enhance The Chemical Performance of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument12 pagesThe Use of 1% Nano-Fe3O4 and 1% Nano-TiO2 As Partial Replacement of Cement To Enhance The Chemical Performance of Reinforced Concrete StructuresCamila Marçal GobiNo ratings yet