Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharynx, Oesophagus, Stomach
Uploaded by
Julia IshakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharynx, Oesophagus, Stomach
Uploaded by
Julia IshakCopyright:
Available Formats
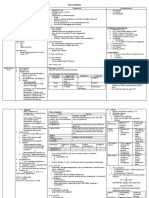
GIT
Pharynx,Oesophagus & Stomach
PHARYNX
NASAL ORAL LARYNGEAL
LOCATION Lies above soft palate Lies behind oral Behind opening of
cavity larynx
STRUCTURES INSIDE (1)pharyngeal tonsil -palatine tonsil - most of foreign
Lymphatic tissues - a lot of lymphatic bodies stick to
are well developed tissues (under piriform
in baby and children tongue) fossa( depression
due to immature - to ring the alarm, in mucus
immune in them. lymphatic tissue membrane) esp.
When increasing in enlarge in size fish bone
age, become less in
size and function
enlargement of it
cause partial
obstruction of nasal
pharynx(Adenoid)
(2) opening of auditory
tube
(3) tubal elevation-
superior of the auditory
tube
NERVE SUPPLY
Motor - supply muscles
(sup.,middle,inferior
constrictor) supplied by
pharyngeal plexus EXCEPT
stylopharyngeal –by
glossopharyngeal n.
Sensory maxillary n. Glossopharyngeal n. Interval laryngeal
n.(br. of vagus
nerve)
ARTERIAL SUPPLY - ascending pharyngeal a.(br. of external carotid a.) *internal carotid a. Gives no
supply to neck but BRAIN
- tonsilar branches of facial a.
- br. of maxillary n lingual a.
LYMPH DRAINAGE deep cervical lymph nodes(along interjugular vein)
ESOPHAGUS
Tube join laryngeal part of pharynxat C6 n join stomach at abdomen
25 cm long = ureter
Greater part – within thorax
lesser(abdominal) part - in abdomen
- 1.25 cm
# At level of T10,
-it passes through the diaphragm n join into stomach
- 3 anatomical n physiological constriction (narrowing of lumen) occur
1) pharynx → esophagus
2) esophagus come into contact with aorta
3) esophagus → stomach
+++ no anatomical sphincter btwn lower part of eso n stomach
+++ in most of cancer, tumors occur in constriction
+++ oesophageal reflux= ascending of content of stomach to lower part of eso
PARTS OF ESOPHAGUS
UPPER MIDDLE LOWER
BLOOD SUPPLY
Artery Inferior thyroid a. Esophageal branches Lt. Gastric a
(fr subclavian a.) of descending aorta
Vein Inferior thyroid v. Azygos v. Lt. Gastric v.
(fr subclavian v.)
NERVE SUPPLY Parasympathetic
LYMPHATIC Deep cervical lymph Sup & post Lymph nodes along
DRAINAGE nodes mediastinal nodes Lt. Gastric blood
vessels that drin into
celiac nodes
STOMACH
- Dilatable portion
- Capacity : 1500ml/cc
- Fixed at ends (cardiac & pyloris), mobile in btwn
- Location: upper part of abdomen, behind Lt. Costal margin, epigastric & umbilical region
- J- shaped
- Has : 2 openings----cardiac & pylorus
: 2 curvatures---- lesser & greater
: 2 surfaces------ anterior & posterior
It is ÷ into 4 PARTS:
FUNDUS BODY ANTRUM PYLORUS
-normally full with - start fr. Cardiac Incisura angularis Tubular part
gas orifice → incisura →pylorus Has: - pylorus
- gas bubble present angularis sphincter
as black spot during - pyloric
X-ray canal
-Dome- shaped
Relations
Anteriorly: anterior abdominal wall, left costal margin, left pleura & lung, the diaphragm, the
left lobe of liver
Posteriorly: lesser sac, diaphragm, spleen, left suprarenal gland, upper part of left kidney,
splenic artery, pancreas, transverse mesocolon & treansverse colon
PERITONEAL FOLDS
Lesser omentum- connect lesser curvature of stomach to liver
Greater ometum- connect lower part of greater curvature to tranverse colon
- ‘policeman’ of the abdomen= localize any infection in body
Gastrosplenic omentum – connect upper part of greater curvature to spleen
ARTERY VEIN LYMPHATIC NERVE
-Lt. gastric a. Drain into portal Lymph vessels follow Sympathetic fibres
- Rt. gastric a. circulation: arteries into: fr. Celiac plexus
-Short gastric a. -Lt. % Rt. gastric v. LT. & Rt.gastric nodes. Parasympathetic fr.
-Lt. gastroepiploic drain directly into -Lt. & Rt. gastroepiploic Rt. & Lt. vagus
a. portal v. nodes nerve
-Rt. -Short gastric v. & Lt. -Short gastric nodes
gastroepiploic a. gastroepiploic v. Join All lymph fr. Stomach
the splenic vein eventually passes to
- Rt. gastroepiploic v. the celiac nodes
join s the sup. located around the root
mesenteric v. of celiac artery on the
post. abdominal wall
You might also like
- Spinal CordDocument3 pagesSpinal CordJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument3 pagesBrain StemJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides LadscapeDocument2 pagesAminoglycosides LadscapeJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Dna Gyrase InhibitorDocument2 pagesDna Gyrase InhibitorJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Except in Viruses - May Be RNADocument6 pagesExcept in Viruses - May Be RNAJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- HistamineDocument2 pagesHistamineJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Venum OrgDocument3 pagesVenum OrgJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Anti FungalsDocument4 pagesAnti FungalsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption N Routes of Drug Transmission Systemic NonDocument3 pagesDrug Absorption N Routes of Drug Transmission Systemic NonJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- ArthropodsDocument2 pagesArthropodsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- AminoglycosidesDocument2 pagesAminoglycosidesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Antifolate DrugsDocument2 pagesAntifolate DrugsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Gp5 X-Entero PassDocument2 pagesMB Gp5 X-Entero PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Rickettsiaceae PassDocument2 pagesMB Rickettsiaceae PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Herpes VirusesDocument4 pagesHerpes VirusesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- ClostridiumDocument1 pageClostridiumJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Aureus C. Diphteriae (Man) : Classification Based On HaemolysisDocument4 pagesAureus C. Diphteriae (Man) : Classification Based On HaemolysisJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Spirochaete PassDocument2 pagesMB Spirochaete PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Bacterial Growth, Nutrition & CultureDocument1 pageMB Bacterial Growth, Nutrition & CultureJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Mycobacterium PassDocument2 pagesMB Mycobacterium PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Gp2 PassDocument1 pageMB Gp2 PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Rickettsiaceae PassDocument2 pagesMB Rickettsiaceae PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB GP 5 Entero PassDocument4 pagesMB GP 5 Entero PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB Bacterial ClassificationDocument1 pageMB Bacterial ClassificationJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB GP 4 CB PassDocument2 pagesMB GP 4 CB PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MorphologyDocument2 pagesBacterial MorphologyJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- MB GP 4 B& C PassDocument3 pagesMB GP 4 B& C PassJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Systemic MycosesDocument2 pagesSystemic MycosesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Virulence FactorsDocument2 pagesBacterial Virulence FactorsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument1 pageSubcutaneous MycosesJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Snell AbdomenDocument43 pagesSnell AbdomenBenNo ratings yet
- Revised Anat 4.1 Abdomen in General - ZuluetaDocument8 pagesRevised Anat 4.1 Abdomen in General - Zuluetalovelots1234No ratings yet
- The Pancreas: Anatomy and Clinical ConsiderationsDocument40 pagesThe Pancreas: Anatomy and Clinical ConsiderationsMuthannah MarawanNo ratings yet
- ChanDocument2 pagesChankenny stefanusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Stomach Gastroepiploic Artery: Go ToDocument7 pagesAnatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Stomach Gastroepiploic Artery: Go ToNicoletaStanNo ratings yet
- 4.abdomen and Pelvis Gross SpottersDocument122 pages4.abdomen and Pelvis Gross Spottersmatt medmedmedicNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum Omenta Inner HerniasDocument54 pagesPeritoneum Omenta Inner HerniasCatalin SavinNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesOverview of The Digestive SystemTarun Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Stomach: David A. Mahvi, David M. MahviDocument44 pagesStomach: David A. Mahvi, David M. MahviXuân SơnNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 11 e 11th Edition Elaine N Marieb Susan J Mitchell Lori A SmithDocument7 pagesSolution Manual For Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 11 e 11th Edition Elaine N Marieb Susan J Mitchell Lori A SmithMelissa DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Cavity Anatomy in CT PeritoneographyDocument24 pagesPeritoneal Cavity Anatomy in CT PeritoneographyHugo Alberto C FNo ratings yet
- SpleenDocument69 pagesSpleenprabowoaji12No ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQS: Abdomen: 1 BC 2 D 3 CD 4 B 5 D 6 A 7 C 8 D 9 E 10 BCD 11 CDE 12 BC 13 BCDDocument37 pagesAnatomy MCQS: Abdomen: 1 BC 2 D 3 CD 4 B 5 D 6 A 7 C 8 D 9 E 10 BCD 11 CDE 12 BC 13 BCDPeter BoatengNo ratings yet
- Chloe's Story - The Risks of Weight Loss SurgeryDocument58 pagesChloe's Story - The Risks of Weight Loss SurgerySyarafina AzzahraaNo ratings yet
- Splanchnology: Anatomy of Internal OrgansDocument29 pagesSplanchnology: Anatomy of Internal OrgansEugene Osei AmoakoNo ratings yet
- The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R Medical University: Dissertation Submitted ToDocument129 pagesThe Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R Medical University: Dissertation Submitted ToAmmar AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- 14 StomachDocument24 pages14 Stomachafzal sulemaniNo ratings yet
- 9 Regions of The Abdominal CavityDocument1 page9 Regions of The Abdominal CavityBBCherriNo ratings yet
- Тесты На Руб.3к ОМ ПЕД АнглDocument25 pagesТесты На Руб.3к ОМ ПЕД АнглСымбат КулдасоваNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-1 PDFDocument50 pagesAnatomy-1 PDFSaransh Ghimire100% (1)
- Surgical Diseases of The Pancreas and Biliary Tree (PDFDrive)Document484 pagesSurgical Diseases of The Pancreas and Biliary Tree (PDFDrive)anovi_sky100% (1)
- MPMSU MBBS 1st Year Previous Year Questions (2015-2023)Document83 pagesMPMSU MBBS 1st Year Previous Year Questions (2015-2023)Koshtubh Pratap Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- Partial Gastrectomy and Gastrointestinal Reconstruction - UpToDateDocument59 pagesPartial Gastrectomy and Gastrointestinal Reconstruction - UpToDatebo gum parkNo ratings yet
- Topographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery of The StomachDocument57 pagesTopographic Anatomy and Operative Surgery of The StomachEl Raai El Saleh HospitalNo ratings yet
- Large Blood Vessels of The GutDocument61 pagesLarge Blood Vessels of The GutpoojaNo ratings yet
- Serial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoDocument41 pagesSerial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Pattern (Anatomy 2021Document115 pagesQuestion Paper Pattern (Anatomy 2021Aranya BhandaryNo ratings yet
- 1166 Stomach Dr.-RaviDocument38 pages1166 Stomach Dr.-RaviKubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2022-04-21 في 11.10.40 صDocument55 pagesلقطة شاشة 2022-04-21 في 11.10.40 صEngi KazangyNo ratings yet
- GI Anatomy Golden!Document39 pagesGI Anatomy Golden!Ayodeji SotimehinNo ratings yet