Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essential Questions
Uploaded by
api-356808706Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Essential Questions
Uploaded by
api-356808706Copyright:
Available Formats
Working With Special Groups
COURSE: Early Childhood Education II UNIT C of Children and Child Care
Issues
ESSENTIAL Understand issues affecting development of
7.00 B2 10%
STANDARD: children.
Understand nutrition issues that affect
OBJECTIVE: 7.01 B2 5%
development of children.
Essential Questions:
What nutrition issues affect the development of children?
How can children’s special nutritional needs and other food-related issues be managed?
How can appropriate menus for children be planned and provided?
UNPACKED CONTENT
Balanced nutrition for children
Nutrition resources
Reliability of sources
My Pyramid for Preschoolers/My Pyramid for Kids
° Need a variety of foods from five food groups
Grain group
Vegetable group
Fruit group
Milk group
Meat and beans group
° Oils not a food group, but need some for good health
° Each child’s age, gender, and physical activity level are used to develop individual
eating plans and determine calories needed
NC Child Care Handbook
° Suggestions for Encouraging Favorable Food Attitudes & Good Eating Habits
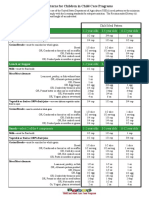
° Meal Patterns for Children in Child Care Programs
° Menu Planning Form
Special nutritional needs---types, causes and effects, prevention and treatment
Under nutrition and malnutrition
Overeating and obesity
Diabetes
Food allergies
Food Restrictions Form
Other food-related issues
Other dietary restrictions
Food preferences
Appreciation for multicultural foods
Special Nutritional Prevention and
Needs Meaning Typical Causes Typical Results Treatment
1. undernutrition Not eating Poverty Growth is slowed or Support programs to reduce
enough food to
maintain a Food likes and dislikes stopped poverty
healthy body and Nutrient deficiencies lead Use appealing variety of
normal activities Unbalanced diet to: foods and food textures,
-Irritability flavors, colors, forms, and
Poor food choices
-Bowed legs temperatures
2. malnutrition Long-term lack Body’s inability to use -Sunken eyes Honor children’s
of proper nutrients -Teeth decay
preferences if possible
nutrients -Fatigue
Teach healthy food choices
3. overeating Eating more than Large supply of food Emotional problems Scale serving sizes to
body needs to
function Trend toward snacking Obesity children’s appetites
Other health problems
Provide small servings
4. obesity Body is more Overeating Lack of self-esteem Change behaviors of parents
than 20%
overweight Poor food choices Poor treatment by peers and children
Inherited tendency to be Hypertension
Help with food choices
overweight; a family Diabetes
Teach foods low in fat and
disorder calories
Family stress
Heart disease
Teach portion control
Physical inactivity
Hardening of the arteries
Provide exercise
Overweight adults
Build self-esteem
Serve healthy. low-fat
foods
5. diabetes Body does not Obesity Feel sick when sugar is Varied diet with fruits,
produce insulin
high or low vegetables, and grains
and is unable to
manage blood Minimize saturated fat and
sugar cholesterol
Moderate sugars, salt
Balanced foods and portion
sizes
Eat at regular intervals
Ask parents for personalized
meal plan
6. food allergy Body reacts Wheat, soy, fish, Sniffles, pain, diarrhea, Provide restricted diet
negatively to
some foods
peanuts, tree nuts, nausea, swelling, rashes, Offer safe substitutes
shellfish, eggs, and milk congestion
cause 90% of food Eliminate food and smells
allergies Anaphylactic shock from classroom
(can be fatal) Obtain information from
parents
Read product labels
You might also like
- Nourishing Your Child: A Guide to Overcoming Eating Problems: Health, #11From EverandNourishing Your Child: A Guide to Overcoming Eating Problems: Health, #11No ratings yet
- 7 01notesweeblyDocument3 pages7 01notesweeblyapi-316565036No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument2 pagesEssential Questionsapi-357231993No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument2 pagesEssential Questionsapi-356809003No ratings yet
- 7 01notesweeblyDocument2 pages7 01notesweeblyapi-298512509No ratings yet
- Compliance ONSDocument30 pagesCompliance ONStioNo ratings yet
- Assigment (ANKIDocument22 pagesAssigment (ANKIBapan RoyNo ratings yet
- Nutri Finals ReviewerDocument13 pagesNutri Finals ReviewerRaemalyn SaludNo ratings yet
- Childhood Obesity NewsletterDocument2 pagesChildhood Obesity Newsletterapi-357111605No ratings yet
- Doh Programs First 1000 Days Ni BabyDocument65 pagesDoh Programs First 1000 Days Ni BabyjpnachorNo ratings yet
- FNCP Week 3 (Pastor)Document5 pagesFNCP Week 3 (Pastor)Charisma PastorNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Essentials for Medical StudentsDocument53 pagesNutrition Essentials for Medical StudentsJerahmeel Sombilon GenillaNo ratings yet
- Desordenes Alimentarios en PreadolescentesDocument5 pagesDesordenes Alimentarios en PreadolescentesPucca HontasNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Ms. Shesly P. Jose Ii Yr MSC NursingDocument94 pagesWelcome: Ms. Shesly P. Jose Ii Yr MSC NursingShesly PhilominaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition (PPT 1 2 3 4) ReviewerDocument12 pagesNutrition (PPT 1 2 3 4) ReviewerOscar CruzNo ratings yet
- Eating Feeding DisorderDocument8 pagesEating Feeding DisorderRichielle Gwyneth OmayaoNo ratings yet
- Eating DisorderDocument18 pagesEating DisorderHoney Bee S. PlatolonNo ratings yet
- VIJUNGCO Eating DisordersDocument3 pagesVIJUNGCO Eating DisordersCHS FLORENCE NIGHTINGALE CLUBNo ratings yet
- Improving Family Health Through EducationDocument4 pagesImproving Family Health Through EducationJOHN ROIENo ratings yet
- SEVERE MALNUTRITION AND MICRO NUTRIENT DEFICIENCYDocument65 pagesSEVERE MALNUTRITION AND MICRO NUTRIENT DEFICIENCYbayuNo ratings yet
- Ating Isorders AND Iabetes: W S F O G C & H E G T WDocument25 pagesAting Isorders AND Iabetes: W S F O G C & H E G T WAnonymous QOCn5dNo ratings yet
- infographicDocument1 pageinfographicapi-739298057No ratings yet
- Indonesia's Triple Burden of MalnutritionDocument25 pagesIndonesia's Triple Burden of MalnutritionnadhiraafifaNo ratings yet
- Adhd Nutrition Considerations ChecklistDocument1 pageAdhd Nutrition Considerations Checklistapi-235820714No ratings yet
- What Causes Failure To Thrive in A Child?Document1 pageWhat Causes Failure To Thrive in A Child?Bhie BhieNo ratings yet
- Eating DisordersDocument4 pagesEating DisordersCarina ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Gizi Normal, Atlit, Dan Pasien: Yoseph Samodra FK Ukdw September 2018Document70 pagesGizi Normal, Atlit, Dan Pasien: Yoseph Samodra FK Ukdw September 2018Siti AnjelinNo ratings yet
- Feeding Problems:: Pediatrician's RoleDocument40 pagesFeeding Problems:: Pediatrician's RoleTimothy Eduard A. SupitNo ratings yet
- Why Teens Develop Eating DisordersDocument1 pageWhy Teens Develop Eating DisordersShan Mosses AmadorNo ratings yet
- 1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument7 pages1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFMAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- 1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument7 pages1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFMAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- Guia DesordensalimentaresDocument15 pagesGuia DesordensalimentaresZélia TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Malnutrition: DR. Dr. Luh Putu Ratna Sundari Physiology Department Universitas UdayanaDocument62 pagesPhysiology of Malnutrition: DR. Dr. Luh Putu Ratna Sundari Physiology Department Universitas UdayanaDinda Amalia SNo ratings yet
- Signs & Symptoms of An Eating DisorderDocument2 pagesSigns & Symptoms of An Eating DisorderWrendell BrecioNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Health Q2 M4 Nov. 21 2023Document10 pagesGrade 7 Health Q2 M4 Nov. 21 2023hayafaypNo ratings yet
- Food Selectivity DR Titis SpAKDocument16 pagesFood Selectivity DR Titis SpAKMuhammad HerryNo ratings yet
- Rise of Anorexia in ChildrenDocument9 pagesRise of Anorexia in ChildrenlvohNo ratings yet
- Types of Childhood Eating ProblemsDocument7 pagesTypes of Childhood Eating ProblemsRachma Normalita DewiNo ratings yet
- AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Identificando e Tratando Transtornos Alimentares InglesDocument10 pagesAMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Identificando e Tratando Transtornos Alimentares InglesMarcelo Viana PsiquiatraNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan Chapter VIDocument3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan Chapter VIBi B BelleNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorder PresentationDocument25 pagesEating Disorder Presentationbyfaith137No ratings yet
- Can't Eat, Won't EatDocument2 pagesCan't Eat, Won't EatMark HayesNo ratings yet
- mhn 23Document18 pagesmhn 23Vaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders and Related ConditionsDocument16 pagesEating Disorders and Related ConditionsBismahNo ratings yet
- Practical - 4: Conducts Nutritional Survey and Assists Nutritional Programmes: Nutrition Surveys: ConceptDocument14 pagesPractical - 4: Conducts Nutritional Survey and Assists Nutritional Programmes: Nutrition Surveys: ConceptSujatha J JayabalNo ratings yet
- MALNUTRITION ENERGY-PROTEIN DOCUMENTDocument67 pagesMALNUTRITION ENERGY-PROTEIN DOCUMENTummu asiriNo ratings yet
- Health7 Q2 W5 6Document8 pagesHealth7 Q2 W5 6Joseph RemolaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Obesity Treatment: A Toolkit For Louisiana Primary Care ProvidersDocument24 pagesChildhood Obesity Treatment: A Toolkit For Louisiana Primary Care ProvidersAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Recognizing Binge Eating Disorder Brochure For NPM 569Document2 pagesUnderstanding and Recognizing Binge Eating Disorder Brochure For NPM 569Ruqayyah Rivera ColinNo ratings yet
- Referat ObesitasDocument20 pagesReferat ObesitasfaisalNo ratings yet
- Health 7-Q2 Week 1-4 Nutrition V2.0Document22 pagesHealth 7-Q2 Week 1-4 Nutrition V2.0Coffee PrinceNo ratings yet
- MalnutritionDocument19 pagesMalnutritionshavonprince97No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Module Eating DisordersDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Module Eating DisordersShaima's VlogsNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nutrition 2020 SGDocument27 pagesPediatric Nutrition 2020 SGHajira GhaniNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument68 pagesREPORTVIVIEN CONSIGNANo ratings yet
- Diet and Dental Caries The Psychological.1Document2 pagesDiet and Dental Caries The Psychological.1Shivani DubeyNo ratings yet
- Assesment1 Task2Document25 pagesAssesment1 Task2anna.koscielska95No ratings yet
- Ch.3 Food, Nutrition, Health & FitnessDocument14 pagesCh.3 Food, Nutrition, Health & FitnessSimar SinghNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Assessment 2Document4 pagesNutrition Assessment 2api-582846016No ratings yet
- 4 01 Notes WeeblyDocument6 pages4 01 Notes Weeblyapi-298512430No ratings yet
- 5.01 ContinuedDocument9 pages5.01 Continuedapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument1 pageCover Letterapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Bianca Collins: ObjectiveDocument1 pageBianca Collins: Objectiveapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Essential Questions: Generate PlanDocument2 pagesEssential Questions: Generate Planapi-298512509No ratings yet
- Meal Patterns DcdeeDocument1 pageMeal Patterns Dcdeeapi-357231993No ratings yet
- 3 02notesweeblyDocument2 pages3 02notesweeblyapi-298512509No ratings yet
- Bianca Collins: ObjectiveDocument1 pageBianca Collins: Objectiveapi-356808706No ratings yet
- 9Document1 page9api-357231993No ratings yet
- Feeding: in A NC DCD EE Licensed Infant ClassroomDocument8 pagesFeeding: in A NC DCD EE Licensed Infant Classroomapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Child AbuseDocument24 pagesChild Abuseapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument3 pagesEssential Questionsapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Polner 8Document32 pagesPolner 8api-357232591No ratings yet
- Healthy Snack LabDocument6 pagesHealthy Snack Labapi-357232591No ratings yet
- Objective 5.01Document7 pagesObjective 5.01api-356808706No ratings yet
- Naptime For An Infant: Objective 5.01 ContinuedDocument4 pagesNaptime For An Infant: Objective 5.01 Continuedapi-357233146No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument2 pagesEssential Questionsapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionDocument2 pagesEssential Questionapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument2 pagesEssential Questionsapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Essential QuestionsDocument2 pagesEssential Questionsapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Daycare Drawing EdwardsDocument1 pageDaycare Drawing Edwardsapi-356808706No ratings yet
- 5 02notesweeblyDocument2 pages5 02notesweeblyapi-298512509No ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureapi-356808706No ratings yet
- Bianca Collins - Wednesday September 20Document2 pagesBianca Collins - Wednesday September 20api-356808706No ratings yet
- Obj 3Document33 pagesObj 3api-356809003No ratings yet
- Eceii3 01vocabDocument3 pagesEceii3 01vocabapi-356434058No ratings yet
- 3Document3 pages3api-356808706No ratings yet
- Ece II 1Document4 pagesEce II 1api-356808706No ratings yet
- Eceii1 01vocabularyDocument2 pagesEceii1 01vocabularyapi-316587271No ratings yet
- Non Deterministic Finite AutomataDocument30 pagesNon Deterministic Finite AutomataAnikNo ratings yet
- Sample of Accident Notification & Investigation ProcedureDocument2 pagesSample of Accident Notification & Investigation Procedurerajendhar100% (1)
- Ir Pc-1: Pre-Check (PC) Design Criteria For Freestanding Signs and Scoreboards: 2019 CBCDocument15 pagesIr Pc-1: Pre-Check (PC) Design Criteria For Freestanding Signs and Scoreboards: 2019 CBCAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- PPM To Percent Conversion Calculator Number ConversionDocument1 pagePPM To Percent Conversion Calculator Number ConversionSata ChaimongkolsupNo ratings yet
- Project Planning and Management Unit 1Document13 pagesProject Planning and Management Unit 1Savant100% (1)
- Modesto Mabunga Vs PP (GR 142039)Document3 pagesModesto Mabunga Vs PP (GR 142039)Ericha Joy GonadanNo ratings yet
- OM - Rieter - UNIMix A76Document321 pagesOM - Rieter - UNIMix A76Phineas FerbNo ratings yet
- Silicone Bonding BrochureDocument4 pagesSilicone Bonding BrochureAmir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Effect of Dust On The Performance of Wind Turbines PDFDocument12 pagesEffect of Dust On The Performance of Wind Turbines PDFJallal ArramachNo ratings yet
- Psalms Magick of The Old Testament PDFDocument129 pagesPsalms Magick of The Old Testament PDFirrrs100% (1)
- Complimentary JournalDocument58 pagesComplimentary JournalMcKey ZoeNo ratings yet
- Template - Time in ManufacturingDocument2 pagesTemplate - Time in ManufacturingVero RoaNo ratings yet
- Surface water drainage infiltration testingDocument8 pagesSurface water drainage infiltration testingRay CooperNo ratings yet
- Writing A Formal Letter To The PresidentDocument1 pageWriting A Formal Letter To The PresidentPiaAnaisNo ratings yet
- History shapes Philippine societyDocument4 pagesHistory shapes Philippine societyMarvin GwapoNo ratings yet
- English For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Lecture 5: Past SimpleDocument11 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Lecture 5: Past Simplealmastar officeNo ratings yet
- Teaching TrigonometryDocument20 pagesTeaching Trigonometryapi-21940065No ratings yet
- Canna DispensariesDocument35 pagesCanna DispensariesWaf Etano100% (1)
- Judges - God's War Against HumanismDocument347 pagesJudges - God's War Against HumanismgypsylanternNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesBahasa InggrisArintaChairaniBanurea33% (3)
- The Daily Tar Heel For September 18, 2012Document8 pagesThe Daily Tar Heel For September 18, 2012The Daily Tar HeelNo ratings yet
- Digital MarketingDocument70 pagesDigital MarketingTarun N. O'Brain Gahlot0% (2)
- XYZ Company Asset Inventory ReportDocument1 pageXYZ Company Asset Inventory ReportNini KitsNo ratings yet
- GBM Auction Versus English Auction A Large-Scale Empirical Study - E. Bessire, K. Elhadji Tchiambou (October 2021)Document18 pagesGBM Auction Versus English Auction A Large-Scale Empirical Study - E. Bessire, K. Elhadji Tchiambou (October 2021)Guillaume GonnaudNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument23 pagesANAPHYYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing & IdentityDocument218 pagesAcademic Writing & IdentityGustavo RegesNo ratings yet
- Serto Up To Date 33Document7 pagesSerto Up To Date 33Teesing BVNo ratings yet
- Moment Influence Line LabsheetDocument12 pagesMoment Influence Line LabsheetZAXNo ratings yet
- Book3 79 111000 0000100120 DAH MPL RPT 000005 - ADocument101 pagesBook3 79 111000 0000100120 DAH MPL RPT 000005 - ANassif Abi AbdallahNo ratings yet
- The Secret Language of AttractionDocument278 pagesThe Secret Language of Attractionsandrojairdhonre89% (93)