Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TMC AdustableSpeedDrive WP PDF
Uploaded by
Tandin WangChukOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TMC AdustableSpeedDrive WP PDF
Uploaded by
Tandin WangChukCopyright:
Available Formats
APPLICATION EDGE VOLUME 1, ISSUE 2
AC VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVE SYSTEMS FOR
INDUCED-DRAFT AND FORCED-DRAFT FANS
Applying Variable Frequency Drives to Boiler Fans Fans with constant-speed motors require mechanical
Large AC variable frequency drives (VFDs) provide flow control equipment that introduce significant
significant benefits when applied to induced-draft losses to the system. Devices commonly used to
fans (IDFs) and forced-draft fans (FDFs) at fossil- control flow and pressure are dampers, inlet guide
fueled electric generating stations. By avoiding the vanes, and slip couplings such as fluid couplings.
use of mechanical flow dampers or louvers, which The losses introduced include throttling losses for
introduce air pressure drops, significant energy dampers and guide vanes, and slip losses for fluid
savings can be achieved. couplings. These mechanical losses are much greater
than the corresponding electrical losses of solid-state
IDFs and FDFs can be applied to two types of fossil- electrical VFDs, which typically operate at efficiencies
fuel-fired boilers: pressurized boilers using FDFs, exceeding 95 percent. Elimination of the mechanical
and balanced draft boilers using both FDFs and IDFs. losses is usually the most compelling and easily
Application of VFDs to both types of fans usually quantified reason for applying VFDs.
results in the most significant energy and capacity
benefits for generating station applications. Reduced Starting Duty for Drive Motors
By applying VFDs, the starting duty for the motors
can be greatly reduced, as compared to conventional
across-the-line starting. When operating on a VFD,
only running load current levels are required for
acceleration. This negates the extra heat load in the
Air motor and voltage sag conditions that can occur
during an across-the-line start. This is important
I.D. Fan because boiler fan motors usually experience the
most severe starting duty of any generating station
motor due to the high inertia of the fans. Boiler
fan motors are also often the largest motors in the
auxiliary power system, which can translate to the
largest voltage dips when starting across the line,
further increasing the severity of the starting duty.
Application of VFDs virtually eliminates starting
voltage dip.
Boiler Elimination of Repetitive Starting Restrictions
F.D. Fan There are often severe repetitive starting restrictions
placed on fan motors due to the heat generated by
Figure 1. Balanced Draft Boilers
the large inrush currents during an across-the-line
start. These restrictions allow the motors to cool
The benefits of applying a VFD are a function of the between starts but can cause significant delays at
fan capability margins that usually exist for IDFs the plant. For example: during plant startup and
and FDFs. These margins result from conservative following maintenance shutdowns, fans may require
design and application practices that allow for balancing. During the balancing procedure the motor
boiler operation at rated continuous capacity and fan are usually started several times, and the
when operating changes occur. Typical operating repetitive starting restrictions can frequently cause
contingencies include fouling in the boiler resulting extended delays in completing the balancing. As
from soot and ash, increased excess air due to mentioned above, application of VFDs to the fans
variations in fuel quality, and provisions for additional eliminates both the starting restrictions and delays
pressure drop in anticipation of the addition of air when starting the motor.
quality control equipment.
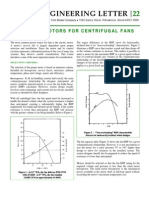
Lower Short-circuit Current Fan Characteristics
During faults in the auxiliary power system, VFDs 2.5
contribute significantly lower short-circuit current
levels than constant-speed motors. Since the boiler
fan motors are often the largest at the plant, the 2.0
reduction in fault duty for switchgear and other
system components can be significant. The net
% OF SPEED
1.5
result of these savings is an increase in the total
motor load that can be applied to a single switchgear
bus or (for existing systems) a reduction in motor- 1.0 % FLOW
starting voltage dips and short-circuit duties.
Reduction in Risk of Boiler Implosion 0.5
IDFs are located on the exhaust gas side of a balanced % PRESSURE
draft boiler and are usually controlled to maintain
a slightly negative pressure in the boiler. If a flame 0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
collapse occurs in the boiler, or if there is a sudden
% OF TOTAL
loss of air entering the boiler, the IDFs will evacuate
the gas from the boiler and create a vacuum. If the Figure 2. Fan Characteristics
fans have sufficient capability, a boiler implosion
might occur.
Application of VFDs to IDFs can reduce the risk of The result of this reduced pressure is that less vacuum
implosion during one of these events. The ability of is applied to the boiler initially. In addition, many
an IDF to create a vacuum in a boiler depends on the large VFDs are capable of regenerative braking. VFDs
pressure the fan develops when the boiler has been with regenerative braking are the only control system
evacuated and the flow is low or nonexistent. Until normally applied to fans that can provide powered
the mechanical guide vanes or dampers are closed, deceleration. This enables much faster deceleration
IDFs with constant-speed motors continue to pull a than is possible with de-energized coastdown. The
vacuum with the pressure associated with full speed. result is to further reduce the risk of implosion.
When minimizing the risk of boiler implosion, there Another benefit to operating at a reduced speed is
are two significant advantages to VFDs: normal that it decreases erosion and wear to fan impellers,
operating speeds are usually lower compared to tips, and other surfaces. The impinging speed of
constant-speed motors and a VFDs control response particulates in flue gas is reduced, improving the life
is much faster. The pressure developed by the fan is of induced-draft fan impellers. Additionally, fan noise
proportional to the square of the speed (see Figure 2). levels are lower at the reduced speeds.
Since fan motors powered by VFDs normally operate
at less than full speed, this is a significant benefit.
With typical fan application margins, IDFs operate at
less than full speed even when the generating unit
is operating at full load. Consequently, the pressure
developed by the fan during a potential implosion
condition is less when operating on a VFD.
+1-540-283-2300 www.tmeic.com
2060 Cook Drive • Salem, VA 24153 USA
AE-081216
© TMEIC Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- Introduction to Fly-by-Wire Flight Control Systems: The professional pilot’s guide to understanding modern aircraft controlsFrom EverandIntroduction to Fly-by-Wire Flight Control Systems: The professional pilot’s guide to understanding modern aircraft controlsNo ratings yet
- 32.37.20.10 Instrument Signal LinesDocument36 pages32.37.20.10 Instrument Signal LinesJohn Rangel50% (2)
- RMC Plant Manufacturing Project ReportDocument84 pagesRMC Plant Manufacturing Project ReportHarshada Hikare100% (1)
- Holiday Inspection Testing CoatingsDocument5 pagesHoliday Inspection Testing CoatingsharmlesdragonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Hydro GeneratorDocument32 pagesChapter 9 Hydro GeneratorDivyansh Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- To VFD or To FCVDocument7 pagesTo VFD or To FCVAmit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Why Use Bypass in Variable Frequency Drive SystemDocument6 pagesWhy Use Bypass in Variable Frequency Drive Systemmani_208eeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 Hydro Generator Characteristics and Performance PDFDocument32 pagesChapter-9 Hydro Generator Characteristics and Performance PDFVerruumm AmineNo ratings yet
- Overview of Design Aids For Structural Steel FFDocument42 pagesOverview of Design Aids For Structural Steel FFjohn100% (1)
- Full Paper P-031Document9 pagesFull Paper P-031SUBRATA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Online System, Functions, and PlatformsDocument28 pagesOnline System, Functions, and PlatformsJules Gajes80% (5)
- Application of VFD in Power PlantDocument62 pagesApplication of VFD in Power PlantSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper On Design of Machine ToolsDocument8 pagesExam Paper On Design of Machine ToolsCharles Ondieki100% (1)
- Voltage Regulator Catalog enDocument16 pagesVoltage Regulator Catalog ensunny_2502No ratings yet
- Siemens VFD HandbookDocument4 pagesSiemens VFD Handbookshanks263No ratings yet
- Iveco Magirus DLK 55 CsDocument6 pagesIveco Magirus DLK 55 CsRicardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- EC Motors Harmonic StudyDocument6 pagesEC Motors Harmonic StudyRamaiah Kumar100% (1)
- Nammiaca 000036Document435 pagesNammiaca 000036gangadhark196No ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DrivesDocument46 pagesVariable Frequency DrivesCubix AutomationNo ratings yet
- Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesFrom EverandGas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesNo ratings yet
- PV On Buildings and Fire Safety: Recommendation For DRRG Solar PV SystemsDocument17 pagesPV On Buildings and Fire Safety: Recommendation For DRRG Solar PV SystemsAbhinav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Protection of Generators, Transformers, Generator-Transformer Units andDocument38 pagesProtection of Generators, Transformers, Generator-Transformer Units andkarsakkNo ratings yet
- Value Stream MapDocument42 pagesValue Stream MapultratangoNo ratings yet
- Smart BoomDocument10 pagesSmart BoomKevine Khaled100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management: Author: B. Mahadevan Operations Management: Theory and Practice, 3eDocument31 pagesSupply Chain Management: Author: B. Mahadevan Operations Management: Theory and Practice, 3eAjmal sNo ratings yet
- Art Deco in Mumbai: (Theaters)Document9 pagesArt Deco in Mumbai: (Theaters)abhishekNo ratings yet
- Materials Selection GuideDocument34 pagesMaterials Selection GuideLinh GiangNo ratings yet
- NSR Nab-1000 (Ais Transponder (B) ) User's ManualDocument25 pagesNSR Nab-1000 (Ais Transponder (B) ) User's ManualPalaKhartikeyan50% (4)
- BA Anchor Data SheetDocument17 pagesBA Anchor Data SheetbrodieNo ratings yet
- Captive Motor-Transformer PDFDocument11 pagesCaptive Motor-Transformer PDFAmorn Thumrat100% (1)
- Best VFD Applications For HVAC SystemsDocument4 pagesBest VFD Applications For HVAC SystemsjnikkoNo ratings yet
- Trane Jan2006Document8 pagesTrane Jan2006TomLinNo ratings yet
- Variable-Frequency Drives Upgrade Reactor Circulating PumpsDocument4 pagesVariable-Frequency Drives Upgrade Reactor Circulating PumpsDaniloGarciaMuñozNo ratings yet
- Specifying-VFDs-white-paper (Especificando Inversores)Document8 pagesSpecifying-VFDs-white-paper (Especificando Inversores)Gabriel SilvaNo ratings yet
- Figure No. 1 Variable Frequency DriveDocument38 pagesFigure No. 1 Variable Frequency Drivet_aditya2506No ratings yet
- Figure No. 1 Variable Frequency DriveDocument38 pagesFigure No. 1 Variable Frequency DriveAshutosh SoniNo ratings yet
- Control Valve 1103Document5 pagesControl Valve 1103partho143No ratings yet
- NAMV PaperDocument8 pagesNAMV PaperenginvservNo ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: IntegralmotorsforcentrifugalfansDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: IntegralmotorsforcentrifugalfansjameeloNo ratings yet
- Yonis Hussain ReportDocument9 pagesYonis Hussain ReportENG.YONIS HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Impacto Baja Potencia Generadores DieselDocument4 pagesImpacto Baja Potencia Generadores DieselFrank ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Energy-Saving Project of 5500-HP 13-kV Wound Rotor Induction Motor On A Kiln ID Fan Using A Low-Voltage Slip Power Recovery Drive-A Case StudyDocument5 pagesEnergy-Saving Project of 5500-HP 13-kV Wound Rotor Induction Motor On A Kiln ID Fan Using A Low-Voltage Slip Power Recovery Drive-A Case StudyJulioNo ratings yet
- X Ahorro Energetico Con Variadores de FrecuenciaDocument7 pagesX Ahorro Energetico Con Variadores de FrecuenciaJayson TeoNo ratings yet
- Power Quality: M V S I o V F DDocument5 pagesPower Quality: M V S I o V F DHari Krishna.MNo ratings yet
- Copeland VFDDocument4 pagesCopeland VFDluigi schiavoneNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Forced Draft and Induced Draft FansDocument6 pagesLiterature Review: Forced Draft and Induced Draft FansAlif Nur FirdausNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Control vs. Eddy Current ControlDocument3 pagesVariable Frequency Control vs. Eddy Current ControlA.YOGAGURUNo ratings yet
- Engineering Bulletin: Variable Frequency Drive/ Generator ApplicationDocument2 pagesEngineering Bulletin: Variable Frequency Drive/ Generator ApplicationMustafa A.WNo ratings yet
- Motor CatalogDocument1 pageMotor CatalogKingsley InbasinghNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Electric MotorsDocument61 pagesUnit2 - Electric MotorsNethaji BKNo ratings yet
- Advances in Motor TechnologyDocument8 pagesAdvances in Motor TechnologyWeider SilvaNo ratings yet
- Benefits of VFD Drives in Irrigation PumpingDocument4 pagesBenefits of VFD Drives in Irrigation PumpingFawaaz KhurwolahNo ratings yet
- Motor VFDDocument3 pagesMotor VFDjowdiverNo ratings yet
- VFD For Centrifugal PumpsDocument11 pagesVFD For Centrifugal PumpsChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drive Basics and Benefits for HVAC ApplicationsDocument3 pagesVariable Frequency Drive Basics and Benefits for HVAC ApplicationsRohitash NitharwalNo ratings yet
- Understanding Variable Speed Drives: Basic VFD TheoryDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Variable Speed Drives: Basic VFD TheorynikecerreroNo ratings yet
- Subject: Using Emergency Power With DSD Elevator DrivesDocument4 pagesSubject: Using Emergency Power With DSD Elevator DrivesmehariiNo ratings yet
- Fans, Blowers, and Fluidizers Failure ModesDocument5 pagesFans, Blowers, and Fluidizers Failure Modesingdimitriospino_110No ratings yet
- Open-phase Protection for MotorsDocument5 pagesOpen-phase Protection for MotorsAnamarialuzNo ratings yet
- Affinity Laws For Variable Speed Centrifugal PumpsDocument4 pagesAffinity Laws For Variable Speed Centrifugal PumpsSwapnil KadamNo ratings yet
- General Information For Integral Horsepower (Ihp) Motors On Variable Frequency Drives (VFDS)Document3 pagesGeneral Information For Integral Horsepower (Ihp) Motors On Variable Frequency Drives (VFDS)Ibhar Santos MumentheyNo ratings yet
- Compatibility of Motor & VFDDocument3 pagesCompatibility of Motor & VFDorkwfdet sharklasersNo ratings yet
- VFD Versus Control Valve For Pump Flow ControlsDocument6 pagesVFD Versus Control Valve For Pump Flow ControlsCarlos WayNo ratings yet
- DIAGRAMA - IW047 e IW048 - CMG - SGAT SeriesDocument21 pagesDIAGRAMA - IW047 e IW048 - CMG - SGAT Seriesjrgravinaig.com.br PauloNo ratings yet
- BUS Ele Tech Lib Motor Insulation Class Life PDFDocument1 pageBUS Ele Tech Lib Motor Insulation Class Life PDFlimkokchiang809No ratings yet
- NIDECDocument18 pagesNIDECroyert8No ratings yet
- AC Generator Reverse KVAr IssueDocument14 pagesAC Generator Reverse KVAr IssueMURALINo ratings yet
- AC Generator Reverse KVAr IssueDocument14 pagesAC Generator Reverse KVAr IssueMURALINo ratings yet
- What Is Temperature RiseDocument12 pagesWhat Is Temperature RisemajesusNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed Drive - IntroductionDocument6 pagesVariable Speed Drive - Introductionawhk2006No ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DriveDocument4 pagesVariable Frequency Drivearavind_k104No ratings yet
- Toshiba - Service FactorDocument4 pagesToshiba - Service FactorCarlos CamayoNo ratings yet
- Plugging An Induction MotorDocument23 pagesPlugging An Induction MotorEngr Hamza Ali ImranNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- 7 1Document1 page7 1Tandin WangChukNo ratings yet
- PSpice Notes v5.0Document15 pagesPSpice Notes v5.0Lăcătuş DanielNo ratings yet
- Dac 2fadc NotesDocument10 pagesDac 2fadc NotesravindarsinghNo ratings yet
- 21 IM Equivalent CircuitsDocument22 pages21 IM Equivalent CircuitsManan SanghviNo ratings yet
- Fluid ReferenceDocument19 pagesFluid ReferencemarkalvinbonNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Formulae PDFDocument1 pageDifferentiation Formulae PDFTandin WangChukNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Formulae PDFDocument1 pageDifferentiation Formulae PDFTandin WangChukNo ratings yet
- HI-E Dry 195 HI-E DRY 195: - Read and Save These Instructions - Read and Save These InstructionsDocument17 pagesHI-E Dry 195 HI-E DRY 195: - Read and Save These Instructions - Read and Save These Instructionsluis gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Workstation Assembly Instructions PDFDocument1 pageWorkstation Assembly Instructions PDFChris EfstathiouNo ratings yet
- Inspeccion Visual Ta1 Tractor d6r II (B)Document7 pagesInspeccion Visual Ta1 Tractor d6r II (B)RAMON CALDERONNo ratings yet
- Costing FormatDocument9 pagesCosting FormatGopal JetaniNo ratings yet
- L P GDocument11 pagesL P GPhi MacNo ratings yet
- Justin Culver Resume 1Document3 pagesJustin Culver Resume 1Chris CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Non WovenDocument16 pagesNon WovenMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Appendix C.26 D: Single Cell RCC Box Culvert of Size 2 X 3 (U/S & D/S Pitching)Document7 pagesAppendix C.26 D: Single Cell RCC Box Culvert of Size 2 X 3 (U/S & D/S Pitching)Bilal Ahmed Barbhuiya100% (1)
- Analysis of The Filament-Wound Glass Reinforced Rectangular Cross Section Composite Pipes in AnsysDocument1 pageAnalysis of The Filament-Wound Glass Reinforced Rectangular Cross Section Composite Pipes in AnsysIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- TA-250 & TA-300: Installation and ManualDocument26 pagesTA-250 & TA-300: Installation and ManualjodseedNo ratings yet
- Geogrids in Walls and SlopesDocument6 pagesGeogrids in Walls and SlopesYong Cheng Hung100% (1)
- Q-438222 Urban Mining - Phase 2 - REV0 - DNDocument14 pagesQ-438222 Urban Mining - Phase 2 - REV0 - DNnknfiveNo ratings yet
- Wafer Thinning and Through Silicon ViasDocument41 pagesWafer Thinning and Through Silicon ViasJohn RecheNo ratings yet
- Consumer Chemistry (CH 419)Document9 pagesConsumer Chemistry (CH 419)Mihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet