Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phy130 Tutorial 5 Student
Uploaded by
Shuhaila Hanis RosliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy130 Tutorial 5 Student
Uploaded by
Shuhaila Hanis RosliCopyright:
Available Formats
AS120/ PHY130 / TUTORIAL 5 / MAC18-JULY18 / NSZ
TUTORIAL 5
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
1. State the two factors that influence the kinetic energy of a body.
2. An object of mass 0.50 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velociy of 0.8
ms-1. The maximum height by the object is 2.5 m. Compute the work done
against air resistance?(Ans: W= 12.26 J)
3. A boy pulls a 10.0 kg book rack at rest on a smooth floor with a constant
horizontal force of 1.2 N starting from rest.( Ans:i) KE= 6 J; Vf= 1.0954 ms-1)
i. Compute the change in kinetic energy of the box after the boy has pulled it
a distance of 5.0 m.
ii. Compute the final velocity of the box after the boy has pulled it a distance
of 5.0 m.
4. A 5.0 g apple is thrown straight upward with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s at a
point of 1.5 m height from ground. Ignoring air friction. (Ans:i) ET= 1.074 J; ii) PE=
1.07 J)
i. Calculate the total mechanical energy of the apple at initial position.
ii. Calculate the potential energy of the apple at maximum position.
5. State the two factors that influence the kinetic energy of a body.
6.
Figure 1
A tractor is used to pull a sled loaded with a firewood through a distance of 20 m
along level ground. The total weight of the sled with the load is 14700 N. The
tractor pulls the sled and load at a constant force F of magnitude 5000 N at an
angle of 36.9° above the horizontal as shown in Figure 1. The ground exerts a
friction force Ff of magnitude 3500 N on the sled. Calculate: (Ans: i)WF= 80 kJ,
ii)WFf=-70 kJ)
i. The work done by constant force F.
ii. The work dobe by frictional force Ff.
7.
Figure 2
“The real secret of succes is enthusiasm” Page 1
AS120/ PHY130 / TUTORIAL 5 / MAC18-JULY18 / NSZ
A 4.0 kg bead slides on a curved wire, starting from rest at point A as shown in
Figure 2. The wire is frictionless between points A and B. Determine the kinetic
energy of the bead at B. (Ans: Ek= 11.77 J)
8. State work-energy theorem.
9. Explain the Coservation of Energy
10.
Figure 3
Figure 3 shows a worker pushing a wheelbarrow of mass 40 kg with a constant
velocity along a horizontal surface whose coefficient of friction is 0.5. (Ans:
F=318.5 N; b.W= 2758.3 J)
i. What is the force P exerted by the worker if the θ = 30°?
ii. What is the work done by the worker when the wheelbarrow is pushed
through a distance of 10 m?
11. A person pushes a 10 kg cart a distance of 20 m by exerting a 60 N horizontal
force. The frictional resistance force is 50 N. (Ans: WF = 1200 J, Wf = -1000 J;b.
KE= 200 J)
i. How much work is done by each force acting on the cart?
ii. How much kinetic energy does the cart have at the end of the 20 m if it
started from the rest?
12.
Figure 4
What is the increase in potential energy of a 1 kg body when lifted from the floor
to table 1m high as shown in Figure 4? (Ans: Ep= 9.81 J)
13. A constant force of 15 N is applied to an object of mass 5.0 kg at an angle of 35°
with the horizontal. What is the work done by this force on the object if it causes a
displacement of 1.5 m along the horizontal direction?(Ans: W= 18.43 J)
14.
Figure 5
“The real secret of succes is enthusiasm” Page 2
AS120/ PHY130 / TUTORIAL 5 / MAC18-JULY18 / NSZ
Figure 5 shows a skater travelling at 15 m/s at the foot of a 20° inclined plane
continues to skate up 12.8 m up the slope before coming to a stop. Find the
coefficient of friction between the plane with the skater. (Ans: µ = 0.55 )
15. A 490 N sled is dragged for 12 s along a horizontal path with a constant speed of
1.8 m/s by a rope inclined 35° above the horizontal. Given that the tension in the
rope is 280 N, calculate
i. The distance travelled by the sled [Ans: s = 21.6 m]
ii. The work done by the rope on the sled [Ans: a= 1.67 ms-2]
16. A 155 g baseball is thrown up with a speed of 28 m/s. Find the work done on the
baseball against gravity to reach its maximum height.(Ans: W= -60.76J)
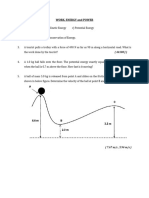
17.
Figure 7
Figure 7 shows a bead slidings on a wire. If friction forces are negligible and the
bead has a velocity of 300 cm/s at A, compute its speed at [Ans:i. VB = 4.768 ms-
1 ; ii. V = 3.311 ms-1
c
i. point B
ii. point C
18. Calculate the average horsepower required to raise a 150 kg drum to a height of
20 m in a time of 1.0 minute. [Ans:P= 490.5 Watt]
19. An engine expends 29.828 kW in propelling a car along a level track at 15.0 ms -1.
Compute the total retarding force acting on the car. [Ans: F= 1.99 kN]
20. A 900 kg car whose motor delivers maximum power of 40.0 h.p to its wheels can
maintain a steady speed of 130 km/h on a horizontal roadway. How large is the
friction force that impedes its motion a this speed? [Ans:Ff= 826 N]
“The real secret of succes is enthusiasm” Page 3
You might also like
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDocument12 pagesWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- ZF Servocomà ® RAS Rear Axle Steering System - ZF LenksystemeDocument2 pagesZF Servocomà ® RAS Rear Axle Steering System - ZF Lenksystemewurtukuk50% (2)
- Work and Energy: Key Concepts ExplainedDocument124 pagesWork and Energy: Key Concepts Explainedjack100% (1)
- F0358 CMM 010Document164 pagesF0358 CMM 010MJI EUWNo ratings yet
- Form I Integrated Science End of Year ExamDocument10 pagesForm I Integrated Science End of Year ExamMiss Rambaran100% (2)
- Unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions v2 2016 AnswersDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions v2 2016 AnswersJane CongaoNo ratings yet
- Parker Substrate 4250-InTRAFLOW Dec 2003Document12 pagesParker Substrate 4250-InTRAFLOW Dec 2003Laurence MalanumNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Review Problems NewDocument6 pagesCh8 Review Problems NewVic VanceNo ratings yet
- Measure Moments with MomentsDocument10 pagesMeasure Moments with MomentsVarshLok100% (2)
- Work, Energy and Power Cambridge OLDocument14 pagesWork, Energy and Power Cambridge OLSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter7 PDFDocument24 pagesTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lechler Brochure Tank Equipment Cleaning enDocument84 pagesLechler Brochure Tank Equipment Cleaning enAnonymous lswzqloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Das14103 - Chapter 6Document4 pagesTutorial Das14103 - Chapter 6Najiha SufianNo ratings yet
- Absolute Dependent Motion Analysis of Two ParticlesDocument57 pagesAbsolute Dependent Motion Analysis of Two ParticlesFrancis Philippe Cruzana CariñoNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Document2 pagesWork Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Amarch BahiluNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Force and MotionDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 Force and MotionNadhirah Kaspol AnuarNo ratings yet
- Uploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFDocument6 pagesUploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFRolando TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Work, Energy and PowerDocument4 pagesChapter 5: Work, Energy and PowerPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Wpe ExercisesDocument11 pagesWpe ExercisesjoeNo ratings yet
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- PHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionDocument8 pagesPHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionAli MaarajNo ratings yet
- Three Identical BallsDocument5 pagesThree Identical BallsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- CH 8 - Energy & WorkDocument23 pagesCH 8 - Energy & WorkJonni Maruli Tua SitorusNo ratings yet
- 6B Physics - WPEDocument3 pages6B Physics - WPEDanielle MullingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Work, Energy UpdatedDocument43 pagesChapter 7-Work, Energy UpdatedNoor BlNo ratings yet
- Phys10 Chap6 Work&KineticEnergyDocument5 pagesPhys10 Chap6 Work&KineticEnergyEngelbert Bicoy Antod100% (1)
- WORKDocument43 pagesWORKmailforprinting101No ratings yet
- At The End of This Session, Students Will Be Able To 1. Understand Kinetics of Rigid Body. 2.relate Between Force, Mass & Acceleration. 3.solve Relevant ProblemsDocument22 pagesAt The End of This Session, Students Will Be Able To 1. Understand Kinetics of Rigid Body. 2.relate Between Force, Mass & Acceleration. 3.solve Relevant ProblemsrajeswariNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstDocument34 pagesPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Two Laws of Motion and Energy ProblemsDocument24 pagesSheet Two Laws of Motion and Energy ProblemsTony AtefNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Worksheet PacketDocument14 pagesWork Energy Worksheet PacketSara Afzal0% (1)
- WorkDocument5 pagesWorkRoriel Hernandez BenamirNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power Class Notes and Example ProblemsDocument10 pagesWork Energy Power Class Notes and Example ProblemsMikiyo bestNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise SolutionsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise SolutionsLorenzo YapNo ratings yet
- UiTM PULAU PINANG SEMESTER JULAI – OKT 2010 PHY130 – FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS I WORK AND ENERGY (15chDocument6 pagesUiTM PULAU PINANG SEMESTER JULAI – OKT 2010 PHY130 – FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS I WORK AND ENERGY (15chHisyammudin RoslanNo ratings yet
- Additional Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesAdditional Sample ProblemsMarifer CavintaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Unit1Document4 pagesWorksheet Unit1RajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy WorksheetDocument5 pagesWork and Energy WorksheetTheOnesNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions: Energy (Grade 11 Level)Document11 pagesExam Questions: Energy (Grade 11 Level)Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- WEP Energy Question BankDocument2 pagesWEP Energy Question BankAJ SkybornNo ratings yet
- Work, Power Energy Q&ADocument93 pagesWork, Power Energy Q&ADebalina DassNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet on Work, Energy and PowerDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet on Work, Energy and PowerGaming baseNo ratings yet
- Adv Work Energy Practice ProblemsDocument11 pagesAdv Work Energy Practice ProblemsZanduarNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power ExplainedDocument34 pagesWork, Energy and Power ExplainedncmzcnmzzNo ratings yet
- (Physics) AnswersDocument15 pages(Physics) AnswersLoraine Rose EstivaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Work, Energy and PowerDocument5 pagesTutorial Work, Energy and PowerAimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Moments 1Document5 pagesUnit 11 Moments 1Kesha DilworthNo ratings yet
- Ch6. Work and Energy Work Done by A Constant ForceDocument93 pagesCh6. Work and Energy Work Done by A Constant ForceKtel R MacarioNo ratings yet
- Energy Questions 2Document2 pagesEnergy Questions 2Unidentified PersonNo ratings yet
- Example Sheet 2 QuestionsDocument2 pagesExample Sheet 2 QuestionsTrevor LewisNo ratings yet
- Padilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMDocument25 pagesPadilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMKurt Allen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument9 pagesWork Power EnergySanmati Jain100% (1)
- Physics 122 Problem SetDocument86 pagesPhysics 122 Problem SetCarmen DraghiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Work, Energy, Power & EfficiencyDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Work, Energy, Power & EfficiencyEric MitchellNo ratings yet
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordDocument40 pagesRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter5Document18 pagesTB Chapter5Jerry HuntNo ratings yet
- Level - 0: CPP - WpeDocument15 pagesLevel - 0: CPP - Wpechaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- UP HW CH 7 SDocument4 pagesUP HW CH 7 SVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- The tension in each string will be the sameDocument7 pagesThe tension in each string will be the sameRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Ridge National Laboratory: Thermal Properties of Wood Panel Products Buildings Wood and For Use inDocument57 pagesRidge National Laboratory: Thermal Properties of Wood Panel Products Buildings Wood and For Use inShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- BotaniName PDFDocument17 pagesBotaniName PDFShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- PHY130 Fundamentals of Physics Lab Report TemplateDocument1 pagePHY130 Fundamentals of Physics Lab Report TemplateShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Bio103 - Biology TEST 1 (30 Marks)Document1 pageBio103 - Biology TEST 1 (30 Marks)Shuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Phy130 Tutorial 9Document3 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 9Shuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial Problems and AnswersDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial Problems and AnswersShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Phy130 Tutorial 8Document3 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 8Shuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Rotational motion tutorialDocument2 pagesRotational motion tutorialShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Rotational motion tutorialDocument2 pagesRotational motion tutorialShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial Problems and AnswersDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial Problems and AnswersShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Phy130 Tutorial 8Document3 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 8Shuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Phy130 Tutorial 4Document6 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 4Shuhaila Hanis Rosli100% (1)
- Phy130 Tutorial 4Document6 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 4Shuhaila Hanis Rosli100% (1)
- Phy130 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 1Shuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Phy130 Tutorial 8Document3 pagesPhy130 Tutorial 8Shuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Schaums Outline of - College Physics, 9th EditionDocument1 pageSchaums Outline of - College Physics, 9th EditionShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- Protection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDocument44 pagesProtection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDerouich2019No ratings yet
- An Impedance Source Multi-Level Three Phase Inverter With Common Mode Voltage Elimination and Dead Time CompensationDocument18 pagesAn Impedance Source Multi-Level Three Phase Inverter With Common Mode Voltage Elimination and Dead Time CompensationRadu GodinaNo ratings yet
- Waste Materials Storage and Disposition Written Test 1Document4 pagesWaste Materials Storage and Disposition Written Test 1GENEBEI FAITH SAJOLANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Work Energy and PowerDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Work Energy and PowerKenny Jay LabianoNo ratings yet
- Speader Valves Hk66b102Document12 pagesSpeader Valves Hk66b102seaqu3stNo ratings yet
- Engineering Laboratory (En19003) Experiment No. 4 (Ee2) : Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test of Single Phase TransformerDocument4 pagesEngineering Laboratory (En19003) Experiment No. 4 (Ee2) : Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test of Single Phase TransformerEvan JoshyNo ratings yet
- Huawei PI OverviewDocument15 pagesHuawei PI OverviewHdz EdilNo ratings yet
- Transient Stability Improvement of Power System Using UpfcDocument18 pagesTransient Stability Improvement of Power System Using UpfcMuhammadWaqarNo ratings yet
- BHELDocument38 pagesBHELSharath Chandra100% (1)
- Pump QuotationsDocument3 pagesPump Quotationsdibyendu65No ratings yet
- Protect8.31-20kVA - 26476-00 - REV1Document12 pagesProtect8.31-20kVA - 26476-00 - REV1Dodi HarzetyaNo ratings yet
- Mi 3210 Teraohmxa 10Kv: Professional Insulation Testing With Powerful Diagnostic ToolsDocument2 pagesMi 3210 Teraohmxa 10Kv: Professional Insulation Testing With Powerful Diagnostic ToolsTuan Anh Le CongNo ratings yet
- Pocket Mechanic Manual (Petrol Version)Document177 pagesPocket Mechanic Manual (Petrol Version)Bill jonesNo ratings yet
- ασκήσεις υδραυλικων λαδιουDocument160 pagesασκήσεις υδραυλικων λαδιουchristodoulos charalambousNo ratings yet
- Fcu Pressure Drop PDFDocument18 pagesFcu Pressure Drop PDFvishalNo ratings yet
- IV Report 1-1Document11 pagesIV Report 1-1sree lekshmiNo ratings yet
- Is SP 72 2010Document25 pagesIs SP 72 2010mkannanofficialNo ratings yet
- Bottom-Up Cost Evaluation of SOEC Systems (10-100MW)Document14 pagesBottom-Up Cost Evaluation of SOEC Systems (10-100MW)Roy JudeNo ratings yet
- Hyundai XG350 3.5L V6 Specs & TolerancesDocument185 pagesHyundai XG350 3.5L V6 Specs & TolerancesAngie Bravo CangasNo ratings yet
- OZM-Katalog 2016Document23 pagesOZM-Katalog 2016Chonk LeeNo ratings yet
- Ato and Nuclear LongDocument74 pagesAto and Nuclear LongtitancryNo ratings yet
- Routage GR.I 251-441 - GBDocument6 pagesRoutage GR.I 251-441 - GBAhmad MohammadNo ratings yet
- Pratt & Whitney Canada: Maintenance Manual MANUAL PART NO. 3034342Document18 pagesPratt & Whitney Canada: Maintenance Manual MANUAL PART NO. 3034342EstebanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Steam CycleDocument35 pagesBoiler Steam CycleMichał KisielewskiNo ratings yet
- DC Generator: Construction and WorkingDocument7 pagesDC Generator: Construction and WorkingGlen Howell PanesNo ratings yet