Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Report Accessory Great Saphenous Vein
Uploaded by
Editor IJTSRDCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Report Accessory Great Saphenous Vein
Uploaded by
Editor IJTSRDCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)
International Open Access Journal | www.ijtsrd.com
ISSN No: 2456 - 6470 | Volume - 2 | Issue – 6 | Sep – Oct 2018
Case Report: Accessory Great Saphenous Vein
Santoshkumar Singarapu1, Akashata. B. K1, Jeevankumar Giri1,
Krishnan. K1, Shobha. G2, Uma. B. Gopal3
Manu Krishnan
1
Scholars, 2Assistant Professor, 3Professor
PG Scholars
Department of Rachana Shareera, SDM College of Ayurveda and Hospital, Hassan,
Hassan Karnataka, India
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
The anterior accessory great saphenous vein (AASV) The venous system has frequent anatomical
is a common pathway for both primary and recurrent variations, so it is more variable compared to the
symptomatic varices, which is often inadequately arterial system. A good understanding of the venous
recognized by those unfamiliar with venous anatomy. anatomy is very important and proper evaluation of
Varicose veins are a common disorder. Extensive the venous system is crucial to the appropriate
ultrasound
sound (US) mapping of lower extremity chronic treatment of venous disorders. Greater saphenous vein
venous valvular insufficiency includes the great (GSV), also known as the vena saphena magna is the
saphenous vein (GSV), anterior accessory saphenous longest vein in the body.
vein (AASV) and thigh posterior tributary to GSV
such as the posterior accessory saphenous vein The accessory saphenous vein is linked to the greater
(PTSV, PASV)(1-3) 3) Anatomically, the AASV vessel saphenous vein, which runs parallel to it, and is
rests within the same layer of the limb as the GSV, located in the leg and thigh. The greater saphenous
lying just superficial to the deep venous system over vein is a large superficial (near the skin’s surface)
the proximal anterior thigh. It has been shown that vein that originates where the foot's dorsal
dorsa venous
both the refluxing GSV and AASV patterns adversely arch merges with the big toe's dorsal vein. It travels
affect patient-perceived
perceived quality of life measures.4,5 up the leg's medial side (closer to the middle) after
Despite the common finding of AASV reflux, the passing anteriorly to the medial malleolus, a bony
majority of governing bodies focus on few vein projection on the inside of each ankle. The accessory
patterns, namely the great saphenous and small saphenous vein joins it immediately
immediate before it drains
saphenous veins.6Conclusion: Patterns of reflux from into the femoral vein. When the accessory saphenous
the saphenofemoral junction
nction to either the anterior vein reaches the knee, it travels posteriorly along the
accessory saphenous vein or great saphenous vein inner parts of the knee and thigh and finally across the
possess similar disease severity and commonly suffer posterior border of the femur bone's medial
complications of venous stasis. The lateral accessory epicondyle, a rounded bony projection at the lower
saphenous vein is the commonest cause of recurrence (distal) end of the femur where it connects to the
in the groin of varicose
icose veins. It should be looked for knee. The accessory saphenous vein then travels to
specifically during pre-operative
operative assessment duplex the thigh's front surface before entering the saphenous
scanning and at primary surgery. If identified at hiatus, an oval-shaped
shaped opening in the fascia lata of the
operation, we believe it should be either stripped or thigh. The fascia lata is a layer of fibrous connective
avulsed to reduce the risk of recurrence. tissue that envelops the thigh muscles. The vein then
attaches to the femoral vein in the sapheno femoral
Keyword: The great saphenous veinin (GSV), Anterior junction of the femoral triangle. The femoral triangle
accessory saphenous vein (AASV) posterior tributary is a depression in the upper part of the inner thigh that
tha
saphenous vein, posterior accessory saphenous vein contains the femoral nerve, artery, and veins as well
(PTSV, PASV) as lymph nodes and vessels. The greater accessory
saphenous vein branches out into smaller veins that
are made of elastic fiber. These veins have diminished
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 6 | Sep-Oct
Oct 2018 Page: 1188
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) ISSN: 2456-6470
2456
muscle cells and thin walls. They are often the cause superficial epigastric vein (SEV), the external
of varicose veins, which develop when they dilate. pudendal vein (EPV), the superficial circumflex iliac
vein (SCIV), the medial accessory saphenous vein
Case Report: (MASV) and the lateral accessory
acces saphenous vein
During the routine classes of the cadaver dissection of (LASV) . GSV is not only used in i coronary bypass
the lower limb in dissection hall of Department of the surgery but also in the treatment of cerebrovascular
Rachana Sharira (Anatomy) SDM College Of diseases and as grafts in peripheric
ipheric vascular surgery.
Ayurveda , Hassan , Karnataka. Observation was There are many anatomical variations of the GSV at
made: the level of the thigh, calf and knee. Studies of SFJ
1. The lower extremity dissection carried out, the left began at the turn of the 19th century and were
GSV drained into the superficial femoral vein dominated by surgeons who stripped the GSV during
(SFV) instead of the CVF. surgical treatment of varicose veins. In 1916 Homans
2. There was a short and blind ending vascular was the first to ligate all the tributaries of GSV near
structure at the medial aspect of the CFV at the the SFJ. This mode of operation, including many
level of the SFJ (fig 01). different modifications, remains
emains a principal
princi surgical
3. The diameter of the GSV was 6.3 mm above and procedure today. Familiarity with the anatomy of this
3.0 mm below the knee and nd GSV was insufficient tributary network, termed by Bruska and a Hilty
in both locations. theconfluensvenosussubinguinalis,
inguinalis, is therefore very
4. There were varicose venous structures up to 9 mm important in the radical surgery of the GSV. The
connecting with GSV both below and above the confluensvenosussubinguinalis lis is formed by 5 main
knee. veins: GSV, EPV, SEV common truncus, SCIV, and
5. Perforating veins were detected extending the LASV. The connections between them are, however,
incision till below the knee i.e head of the tibia, variable according to Orsini,, who distinguished 135
and fallowed till the tip of the great toe i.e course anatomical variants of the GSV, although without
of the greatat sephanous vein, the erect position classifying them into general groups
group as Kocon and
between both the GSV and crural veins in the Zebrowski’s study. Konrad identified 5 types of
crural region and small saphenous vein and crural draining pattern of the GSV according to the number
veins in the crural region. of its direct tributaries. Type 1, with 3 direct
collaterals of the GSV, is the most frequently
encountered (47.8%). The common trunk, which
drains into the GSV, is formed by the conjunction of 2
or 3 collaterals. It is most often formed by 2
tributaries, SEV and SCIV [8]. In our case GSV did
not end in the CFV but drained in to the SFV. To our
knowledge, no similar case of SFJ anatomical
variation
tion has been defined. There have been
revolutionary developments in the diagnosis and
treatment of chronic venous insufficiency
in in recent
years. The treatment options for varicose veins
include conservative approach, sclerotherapy,
ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy,
rotherapy, and junction ligation
with orr without vein stripping.
stripping Although expertise in
venous anatomy and variations may not be necessary
in conservative approach, interventional treatment
Discussion: modalities may necessitate expertise. Hence, if
The GSV is still the most popular vein graft in important anatomicall variations are not recognized,
coronary artery bypass surgery even
ven though synthetic surgical or lesser invasive procedures might result in
grafts and arteriamammariainterna are becoming used incomplete SFJ surgery.. Consequently the knowledge
more frequently.. It plays an important role in the and identification of anatomical variations play an
venous return of the lower extremity because it has a important role in increasing the success and efficacy
lot of branches along its course and it has re
relations of surgical treatments and in decreasing the
with deeper veins. The main tributaries are the recurrence rates.
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 6 | Sep-Oct
Oct 2018 Page: 1189
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) ISSN: 2456-6470
2456
From descriptions and from the histology of the veins saphenous vein in the upper er thigh or directly into a
in the saphenous compartment as compared with deep vein in the groin. The proximal part runs inside
tributaries, it may be concluded that only veins which the compartment of the great saphenous vein where it
course through the saphenous compartment really is often separated by a layer of connective tissue. In
correspond to the great saphenous vein. Duplication healthy veins, its course along the thigh is only visible
of the great saphenous vein is therefore only present on ultrasound
sound from the groin to where it leaves the
when both vessels course through the compartment. fascia or slightly distal of that point. If the vein is
This is in contrast to the considerably higher figures refluxive
fluxive it can be seen varicose directly beneath the
published previously for duplication (27 %, K Kubik skin in several places along its length. As with the
1985 in Appendix 2). thigh tributaries, the exact anatomical course of this
Conclusion: vein is superfluous,
fluous, as it forms part of a venous
The great saphenous vein (v. saphena magna; internal network. If the anterior accessory saphenous vein is
or long saphenous vein), the longest vein in the refluxive,
fluxive, it is easily identified because of its
body, begins in the medial marginal vein of the superficial location. In the middle third of the thigh, a
dorsum of the foot and ends in the femoral vein about connecting vein is often found between the anterior
3 cm. below thee inguinal ligament. It ascends in front accessory saphenous vein and the great saphenous
of the tibial malleolus and along the medial side of the vein. If one of these veins becomes incompetent, the
leg in relation with the saphenous nerve. It runs other may become overloaded with reflux re from this
upward behind the medial condyles of the tibia and vein. A good understanding of the venous anatomy is
femur and along the medial side of the thigh and, very important and proper evaluation of the venous
passing through the fossa ovalis, ends in the femoral system is crucial to the appropriate treatment of
vein. venous disorders.
Tributaries.—AtAt the ankle it receives branches from Referances:
the sole of the foot through the medial marginal vein; 1. Labropoulos N, Kang SS, Mansour MA, et al.
in the leg it anastomoses freely with the small Primary superficial reflux with competent
saphenous vein, communicates with the anterior aand saphenous trunk. Eur J VascEndovascSurg 1999;
posterior tibial veins and receives many cutaneous 18: 201–206.
veins; in the thigh it communicates with the femoral 2. Garcia-Gimeno M, Rodriguez-Camarero
Rodriguez S,
vein and receives numerous tributaries; those from the TagarroVillalba S, et al. Duplex mapping of 2036
medial and posterior parts of the thigh frequently primary varicose veins.. J VascSurg 2009; 49:
unite to form a large accessory saphenous vvein which 681–689.
joins the main vein at a variable level Near the fossa 3. Rasmussen LH, Bjoern L, Lawaetz M, et al.
ovalis it is joined by the superficial epigastric, Randomised clinical trial comparing endovenous
superficial iliac circumflex, and superficial external laser ablation with stripping of the t great
pudendal veins. A vein, named the saphenous vein: clinical outcome and recurrence
thoracoepigastric, runs along the lateral aspect of the after 2 years. Eur J VascEndovascSurg 2010; 39:
trunk between the superficial epigastric vein below 630–635.
and the lateral thoracic vein above and establishes an 4. Bush RG, Flanagan J, Gueldner T, et al. Factors
important communication between the femoral and associated with recurrence of varicose veins after
axillary veins. thermal ablation: results of the recurrent
recurre veins
after thermal ablation study. Sci World J 2014;
The anterior accessory saphenous veins join the upper Article ID 505843: 7.
section of the great saphenousnous vein in an almost 5. Theivacumar NS, Darwood RJ and Gough MJ.
constant position .The anterior accessory saphenous Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) of the anterior
vein is an axial vein which originates from the lateral accessory great saphenous vein (AAGSV):
part of the calf. Then, it ascends to the posterior knee abolition of sapheno-femoral reflux with
running medially along the thigh to drain into the preservation
eservation of the great saphenous vein. Eur J
great saphenous vein in the groin. The anterior VascEndovascSurg 2009; 37: 477–481.
477
accessory saphenous vein almost always connects 6. Treatment of Varicose Veins. Anthem blueb cross
directly with the great saphenous vein in the blue shield web site,
confluence
fluence of superficial inguinal veins as a sapheno www.anthem.com/medicalpolicies/policies/mp_p
femoral tributary. Rarely, it drains into the great w_a053323.htm (accessed 19 May 2014).
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 6 | Sep-Oct
Oct 2018 Page: 1190
You might also like
- Vena Saphena Magna Peculiarities of Origin Trajectory and DrainageDocument6 pagesVena Saphena Magna Peculiarities of Origin Trajectory and DrainageLatescu ConstantinNo ratings yet
- PE Varicose VeinDocument38 pagesPE Varicose VeinDumora FatmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Superficial Venous SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The Superficial Venous SystemRokeshwar Hari DassNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Venous System of the Lower LimbDocument13 pagesAnatomy of the Venous System of the Lower Limbyunie0959No ratings yet
- Venous anatomy and pathophysiologyDocument4 pagesVenous anatomy and pathophysiologyAn'umillah Arini ZidnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomia VenelorDocument4 pagesAnatomia Venelorflorentyna78No ratings yet
- Vascular Perforator AnatomyDocument6 pagesVascular Perforator AnatomyGoFishGoNo ratings yet
- Persist SCIAT VEIN and ART-MB-Parry 2002Document5 pagesPersist SCIAT VEIN and ART-MB-Parry 2002residentes dxiNo ratings yet
- 2865 5436 1 PBDocument6 pages2865 5436 1 PBhaykal achmadNo ratings yet
- Positioning On Surgical Table: Claudio Schonauer Antonio Bocchetti Giuseppe Barbagallo Vincenzo Albanese Aldo MoraciDocument6 pagesPositioning On Surgical Table: Claudio Schonauer Antonio Bocchetti Giuseppe Barbagallo Vincenzo Albanese Aldo MoraciMonika ThakurNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Dialysis Vascular Access: Tushar J. Vachharajani, MD, FASN, FACPDocument75 pagesAtlas of Dialysis Vascular Access: Tushar J. Vachharajani, MD, FASN, FACPEileen del RosarioNo ratings yet
- AVF NewDocument81 pagesAVF NewBasit AliNo ratings yet
- 549-2. Article Text - Manuscript-2768-1-10-20151106Document5 pages549-2. Article Text - Manuscript-2768-1-10-20151106Estanislao MartinNo ratings yet
- 2023 Vein AnatomyDocument6 pages2023 Vein AnatomyKarenNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonography of The Lower Extremity Veins: Anatomy and Basic ApproachDocument11 pagesUltrasonography of The Lower Extremity Veins: Anatomy and Basic ApproachSelçuk PervazNo ratings yet
- Varicose VeinsDocument37 pagesVaricose VeinsJavier SaadNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Nerves 1948Document4 pagesBlood Supply of Nerves 1948ChadiIbrahimNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Endovascular Management of Fusiform Aneurysms in The Posterior Circulation - The Era of Flow DiversionDocument7 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Endovascular Management of Fusiform Aneurysms in The Posterior Circulation - The Era of Flow DiversionCharles MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Increasing Versatility of Reverse-Flow Sural Flap in Distal Leg and Foot ReconstructionDocument0 pagesIncreasing Versatility of Reverse-Flow Sural Flap in Distal Leg and Foot ReconstructionyennysabriniNo ratings yet
- Foot Artery Aneurysms: A Case SeriesDocument4 pagesFoot Artery Aneurysms: A Case SeriesYahya AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Varicose VeinsDocument11 pagesVaricose Veinsshahalashirin987No ratings yet
- Hemodynamics and Diagnosis Venous Disease-Jvs 1207Document21 pagesHemodynamics and Diagnosis Venous Disease-Jvs 1207Fahrudin ŠabanovićNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Venous ThromboembolismDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of Venous ThromboembolismKate RodasNo ratings yet
- The Wiltse para Spinal Approach To The LumbarDocument6 pagesThe Wiltse para Spinal Approach To The LumbarJoao Domingos Carneiro LeaoNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pediatric Surgery CASE REPORTSDocument3 pagesJournal of Pediatric Surgery CASE REPORTSCristhian Saavedra DomenackNo ratings yet
- Conduits For Coronary Bypass: Vein Grafts: Hendrick B Barner, M.D., Emily A Farkas, M.DDocument12 pagesConduits For Coronary Bypass: Vein Grafts: Hendrick B Barner, M.D., Emily A Farkas, M.DGaetano Di GiovanniNo ratings yet
- New OpenDocument Text - OdtDocument13 pagesNew OpenDocument Text - OdtalaaNo ratings yet
- Waitayawinyu 2007Document13 pagesWaitayawinyu 2007Milton Ricardo de Medeiros FernandesNo ratings yet
- Vascular Supply To The Acetabular LabrumDocument6 pagesVascular Supply To The Acetabular Labrumharo.r9524No ratings yet
- Chimmeny For Aberrant SubclavianDocument4 pagesChimmeny For Aberrant SubclavianNonaNo ratings yet
- Operative Classification of Sylvian Veins for Distal Transsylvian ApproachDocument8 pagesOperative Classification of Sylvian Veins for Distal Transsylvian ApproachBUBULACULNo ratings yet
- Corona Mortis: An Anatomical Study With Clinical Implications in Approaches To The Pelvis and AcetabulumDocument7 pagesCorona Mortis: An Anatomical Study With Clinical Implications in Approaches To The Pelvis and Acetabulummartina marinoNo ratings yet
- Doppler Venoso MMSSDocument12 pagesDoppler Venoso MMSSPaola TuerosNo ratings yet
- Abordajequirrgico. Histerectomia Radical.Document45 pagesAbordajequirrgico. Histerectomia Radical.Nancy UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Revisiting The Vertebral Venous Plexus BatsonDocument15 pagesRevisiting The Vertebral Venous Plexus BatsonMorteza Mazloom Farsi BafNo ratings yet
- Visweswar Bhattacharya, Rajesh Kumar WattsDocument6 pagesVisweswar Bhattacharya, Rajesh Kumar WattsViswanath_Poli_2693No ratings yet
- Khan 2012Document7 pagesKhan 2012Daniel PredaNo ratings yet
- Anatomia Del Pie en Insuficiencia VenosaDocument13 pagesAnatomia Del Pie en Insuficiencia VenosaDinOritha AtiLanoNo ratings yet
- BTSCME 3452 XWZYTISM 698 BoyleEClinicalCaseASVDocument15 pagesBTSCME 3452 XWZYTISM 698 BoyleEClinicalCaseASVShiv RajNo ratings yet
- Endovascular Repair in Aorto-Iliac, PAD, and Vascular Access HDDocument23 pagesEndovascular Repair in Aorto-Iliac, PAD, and Vascular Access HDEzar HadiyanNo ratings yet
- Study Protocol 2.3Document16 pagesStudy Protocol 2.3Orim AzizNo ratings yet
- Overview of Hemodialysis Access and Assessment - PMCDocument17 pagesOverview of Hemodialysis Access and Assessment - PMCvwyldrNo ratings yet
- Embriologia CerebroDocument11 pagesEmbriologia CerebroAriel DiazNo ratings yet
- Groin DissectionDocument19 pagesGroin Dissectiondewiswahyu100% (1)
- 2017 - Egemen - Anatomy of Cerebral Veins and Dural SinusesDocument5 pages2017 - Egemen - Anatomy of Cerebral Veins and Dural SinusesmuelmiharNo ratings yet
- Anatomy VeinDocument12 pagesAnatomy VeinReinaldo AbenteNo ratings yet
- Clinical Notes of The Lower LimbDocument12 pagesClinical Notes of The Lower LimbsahrNo ratings yet
- ANA L8 - Blood Vessels and Lymphatics of Upper LimbDocument55 pagesANA L8 - Blood Vessels and Lymphatics of Upper LimbjexshimadaNo ratings yet
- Patologia Venosa+Document13 pagesPatologia Venosa+Mario Alejandro Resendiz GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Incision SkinDocument6 pagesIncision Skinarga scorpianusNo ratings yet
- Gelberman 1980Document6 pagesGelberman 1980antoanetaNo ratings yet
- Lnvaginated Axial Stripping and Stab Avulsion (Hook) Phlebectomy: A Definitive Outpatient Procedure For Primary Varicose VeinsDocument9 pagesLnvaginated Axial Stripping and Stab Avulsion (Hook) Phlebectomy: A Definitive Outpatient Procedure For Primary Varicose VeinsAbrar SabawiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pelvic FloorDocument78 pagesAnatomy of Pelvic Floorfahim ahamedNo ratings yet
- Radial Forearm Flap: DR G Avinash Rao Fellow Hand and Microsurgery Skims, SrinagarDocument71 pagesRadial Forearm Flap: DR G Avinash Rao Fellow Hand and Microsurgery Skims, Srinagaravinashrao39No ratings yet
- Minami 1999Document5 pagesMinami 1999yeapdshengNo ratings yet
- A Study On Division of Brachial Artery and Its Clinical CorrelationsDocument5 pagesA Study On Division of Brachial Artery and Its Clinical CorrelationsRivaldo RuffNo ratings yet
- Knee Bursitis - UpToDateDocument37 pagesKnee Bursitis - UpToDateanweridrisejazNo ratings yet
- walter JVB 2016 below kneeDocument7 pageswalter JVB 2016 below kneeCesar GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- Wound Management of Venous Leg Ulcer, Hartmann, 2006Document47 pagesWound Management of Venous Leg Ulcer, Hartmann, 2006Karen PinemNo ratings yet
- Activating Geospatial Information For Sudans Sustainable Investment MapDocument13 pagesActivating Geospatial Information For Sudans Sustainable Investment MapEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development A PrimerDocument9 pagesSustainable Development A PrimerEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Design Simulation and Hardware Construction of An Arduino Microcontroller Based DC DC High Side Buck Converter For Standalone PV SystemDocument6 pagesDesign Simulation and Hardware Construction of An Arduino Microcontroller Based DC DC High Side Buck Converter For Standalone PV SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Sustainable EnergyDocument8 pagesSustainable EnergyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- To Assess The Knowledge and Attitude of Non Professionals Regarding COVID 19 Vaccination A Descriptive StudyDocument4 pagesTo Assess The Knowledge and Attitude of Non Professionals Regarding COVID 19 Vaccination A Descriptive StudyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On The Use of Image Design With Generative AI TechnologiesDocument4 pagesAn Analysis On The Use of Image Design With Generative AI TechnologiesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining and Employee Prosocial Behaviour in The Hospitality Sector in Port HarcourtDocument10 pagesCollective Bargaining and Employee Prosocial Behaviour in The Hospitality Sector in Port HarcourtEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Educational Unity Embracing Diversity For A Stronger SocietyDocument6 pagesEducational Unity Embracing Diversity For A Stronger SocietyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Deconstructing The Hijra Narrative Reimagining Trans Identities Through Literary PerspectivesDocument6 pagesDeconstructing The Hijra Narrative Reimagining Trans Identities Through Literary PerspectivesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Women Before and After Islam With Special Reference To ArabDocument3 pagesWomen Before and After Islam With Special Reference To ArabEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by The Media in An Attempt To Play Their Roles in Public Awareness On Waste Management in Buea and DoualaDocument18 pagesChallenges Faced by The Media in An Attempt To Play Their Roles in Public Awareness On Waste Management in Buea and DoualaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Temperature Effect On Solar Panel Efficiency Based On IoT TechnologyDocument7 pagesAn Investigation of The Temperature Effect On Solar Panel Efficiency Based On IoT TechnologyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)Document13 pagesInternational Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Third Order Inhomogeneous Linear With Boundary ConditionsDocument6 pagesDifferential Equations Third Order Inhomogeneous Linear With Boundary ConditionsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence A Boon in Expanding Online Education Through Social Media and Digital Marketing Post Covid 19Document9 pagesArtificial Intelligence A Boon in Expanding Online Education Through Social Media and Digital Marketing Post Covid 19Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- A Pharmaceutical Review On Kaanji and Its Wide Range of ApplicabilityDocument6 pagesA Pharmaceutical Review On Kaanji and Its Wide Range of ApplicabilityEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Art Therapy To Reduce Depression Among Old Age Clients Admitted in Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Thandalam, ChennaiDocument5 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Art Therapy To Reduce Depression Among Old Age Clients Admitted in Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Thandalam, ChennaiEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Consumers' Impulsive Buying Behavior in Social Commerce PlatformsDocument5 pagesConsumers' Impulsive Buying Behavior in Social Commerce PlatformsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Related To Diabetes Mellitus and Self Care Practice Related To Diabetic Foot Care Among Diabetic PatientsDocument4 pagesKnowledge Related To Diabetes Mellitus and Self Care Practice Related To Diabetic Foot Care Among Diabetic PatientsEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- H1 L1 Boundedness of Rough Toroidal Pseudo Differential OperatorDocument8 pagesH1 L1 Boundedness of Rough Toroidal Pseudo Differential OperatorEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Role of Dashamooladi Niruha Basti Followed by Katibasti in The Management of "Katigraha" W.R.S To Lumbar Spondylosis A Case StudyDocument3 pagesRole of Dashamooladi Niruha Basti Followed by Katibasti in The Management of "Katigraha" W.R.S To Lumbar Spondylosis A Case StudyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Video Teaching Program On Knowledge Regarding 5Fs of Disease Transmission Food, Finger, Fluid, Fomite, Faces Among Children at Selected Setting, ChennaiDocument3 pagesEffectiveness of Video Teaching Program On Knowledge Regarding 5Fs of Disease Transmission Food, Finger, Fluid, Fomite, Faces Among Children at Selected Setting, ChennaiEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Evan Syndrome A Case ReportDocument3 pagesEvan Syndrome A Case ReportEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Pineapple Cultivation A Case Study of Pineapple Orchards in TripuraDocument4 pagesChallenges in Pineapple Cultivation A Case Study of Pineapple Orchards in TripuraEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Concept of Shotha W.S.R To Arishta LakshanaDocument3 pagesConcept of Shotha W.S.R To Arishta LakshanaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Financial Risk, Capital Adequacy and Liquidity Performance of Deposit Money Banks in NigeriaDocument12 pagesFinancial Risk, Capital Adequacy and Liquidity Performance of Deposit Money Banks in NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Importance of Controlled CreditDocument3 pagesImportance of Controlled CreditEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- A Study On Human Resource AccountingDocument3 pagesA Study On Human Resource AccountingEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- An Approach To The Diagnostic Study On Annavaha Srotodusti in Urdwaga Amlapitta WSR To Oesophagogastroduodenoscopic ChangesDocument4 pagesAn Approach To The Diagnostic Study On Annavaha Srotodusti in Urdwaga Amlapitta WSR To Oesophagogastroduodenoscopic ChangesEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Reproductive Age Women in Selected Community ThrissurDocument4 pagesA Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Reproductive Age Women in Selected Community ThrissurEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
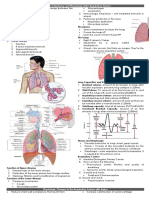
- Lecture 1 and 2 Cardiac PhysiologyDocument40 pagesLecture 1 and 2 Cardiac PhysiologyRobert BakerNo ratings yet
- Arteries of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesArteries of Lower LimbAlli NdahuraNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardiovascular Physiology-Pasquale Pagliaro, Raffaella RastaldoDocument438 pagesBasic Cardiovascular Physiology-Pasquale Pagliaro, Raffaella RastaldoJihuhn YuNo ratings yet
- ECMO in Adults Provides Respiratory and Circulatory SupportDocument5 pagesECMO in Adults Provides Respiratory and Circulatory SupportRAGHAVENDRA VAGYANNAVARNo ratings yet
- Winslow PathwayDocument3 pagesWinslow PathwayMia MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Thorax-Anatomy DiagramDocument145 pagesThorax-Anatomy DiagramHarishNo ratings yet
- 112 NotesDocument9 pages112 NotesDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Central Venous Monitoring 2022Document17 pagesCentral Venous Monitoring 2022AngieNo ratings yet
- 1criza Hipertensiva 2018Document47 pages1criza Hipertensiva 2018NicoletaStanNo ratings yet
- Skills - Masuring Apical - Radial PulseDocument1 pageSkills - Masuring Apical - Radial PulseJoanna Mae Movido CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Case Study NSTEMIDocument25 pagesCase Study NSTEMImichpadua100% (2)
- Internal Medicine: INTERNAL MEDICINE - 3rd YEAR SCHEDULE (5-Years Dentistry Program) Schedule - Gr. CDocument2 pagesInternal Medicine: INTERNAL MEDICINE - 3rd YEAR SCHEDULE (5-Years Dentistry Program) Schedule - Gr. CAliceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument68 pagesChapter 19 - Lymphatic System and ImmunityAurea Nazaire100% (1)
- Crvo CraoDocument80 pagesCrvo CraoRakshit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Arterial Thrombosis and Stenosis in Blood Vessel Using Bioimpedance AnalysisDocument7 pagesDiagnosis of Arterial Thrombosis and Stenosis in Blood Vessel Using Bioimpedance AnalysisAli OucharNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesActivity 7 The Cardiovascular SystemEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Trans CardioDocument128 pagesTrans CardioWaiwit KritayakiranaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Etiology of Edema in AdultsDocument15 pagesPathophysiology and Etiology of Edema in AdultsJovie Anne CabangalNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Campbell Biology: Concepts & ConnectionsDocument88 pagesCirculation: Campbell Biology: Concepts & ConnectionsBehshxbxNo ratings yet
- Flashcards for Admin ConsiderationsDocument1 pageFlashcards for Admin ConsiderationsAntonette Joy SolinapNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Product PeripheralDocument72 pagesProduct PeripheralAsep SetiawanNo ratings yet
- FundaDocument5 pagesFundaGreggy Francisco LaraNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension SurgeryDocument6 pagesPortal Hypertension SurgeryjackSNMMCNo ratings yet
- Puerperal Venous ThrombosisDocument25 pagesPuerperal Venous ThrombosisAnitha ThankappanNo ratings yet
- % Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodDocument33 pages% Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodK CNo ratings yet
- Flotrac BrochureDocument6 pagesFlotrac BrochureAnestesia 2017 UDECNo ratings yet
- Interpreting The Coronary-Artery Calcium ScoreDocument3 pagesInterpreting The Coronary-Artery Calcium ScoreGaby Alejandra Ordonez AndradeNo ratings yet
- UKMLA QbankDocument1 pageUKMLA Qbankdrjames730No ratings yet
- (Tips and Tricks) Shuvanan Ray - Tips and Tricks in Interventional Cardiology-Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (2015)Document204 pages(Tips and Tricks) Shuvanan Ray - Tips and Tricks in Interventional Cardiology-Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (2015)TRẦN VIẾT AN100% (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeFrom EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (17)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)