Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition 9th Science Amir Shehzad
Uploaded by
joshwaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition 9th Science Amir Shehzad
Uploaded by
joshwaCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Chapter No.1
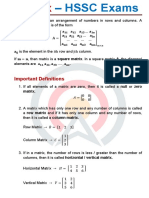
Matrix
A rectangular array of number arranged into rows and columns is called matrix
OR
The combination of rows and columns in square or rectangular form is called matrix
Order of Matrix
The number of rows and columns in a matrix specifies its order. If a matrix M has a rows and a columns
them M is said to be of order, m-b-n
e.g
é1 2 3ù
M =ê
2úû
is order of 2-by-3
ë1 0
Equal matrix
Two numbers are said to be equal if and only
They have same order
They corresponding entries are equal
e.g
é7 0ù é4 + 3 0ù
A= ê B=ê
2 úû 2 úû
are equal
ë3 ë3
Row Matrix
A matrix is called a row matrix, if it has only one row
e.g M=[5 3]
Column Matrix
A matrix is called column matrix, if it has only one column
é1 ù
e.g M = ê ú
ë2û
Rectangular matrix
A matrix is called rectangular. If the number of rows not equal to number of columns
é1 2 3ù
e.g M = ê
ë3 2 1 úû
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 1
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Square matrix
A matrix is called square matrix, if the number of rows are equal to number of columns
é4 0ù
e.g H = ê
ë6 2 úû
Null or Zero matrix
A matrix is called a Null or Zero matrix, if each of its entries is Zero (0)
é0 0ù
e.g N = ê
ë0 0úû
Symmetric matrix
A matrix is called symmetric matrix if At=A
é1 2 ù
e.g ê
ë2 -1úû
Skew Symmetric matrix
A square matrix is called skew symmetric At=-A
é0 -4 ù
e.g A = ê
ë4 0 úû
Scalar matrix
A matrix is called scalar matrix if all the diagonal entries are same
é3 0ù
e.g ê
ë0 3úû
Diagonal matrix
A square matrix is called diagonal matrix if at least any one of the entries of its diagonal is not zero and non
diagonal entries must all be zero
é1 0 0ù
e.g A = ê0 2 0ú
ê ú
êë0 0 2úû
Identity matrix
A diagonal matrix is called identity (unit) matrix if all diagonal entries are 1
é1 0ù
e.g B = ê
ë0 1 úû
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 2
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Singular matrix
A square matrix is called singular matrix if the determinant of M is equal to zero I,e [M]=0
é4 4ù
M =ê
ë3 3 úû
i.g
é4 4ù
| M |= ê = 12 - 12 = 0
ë3 3 úû
Non singular matrix
A square matrix is called non singular matrix, if the determinant M is not equal to zero
i.e |M|¹O
é6 2ù
e.g M = ê
ë3 4úû
Transpose of matrix
A matrix obtained by changing the rows into columns or to columns in to rows of a matrix is called
Transpose of matrix
é1 2 ù
é1 2ù
At = ê0 -1ú
0
A= ê
ë2 -1 3 úû ê ú
êë 2 3 úû
Negative of matrix
Let A be a matrix then its negative –A is obtained by changing the signs of all the entries.
é1 -2 ù é -1 2 ù
A= ê Then - A = ê
ë3 4 úû ë -3 -4 úû
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 3
Subject: Mathematics 9th
CHAPTER # 2
REAL AND COMPLEX NUMBERS
Set of real number:
Union of two disjoint sets, the set of rational number Q and the set of irrational number Q`.
R= QUQ`
Complex Number:
A number of the form Z=a+bί where a and b are the real numbers and ί= is called complex number.
e.g. Z=6+2ί
Complex conjugate:
The number a+bί and a-bί are conjugate of each other.
Rational Number:
The number of the form where p,q integers and q≠0 are called ra onal numbers.
e.g. ,
Irrational Number:
The number which cannot be express in the form of where p,q integers and q≠0 are called irra onal numbers.
e.g. √2, 3.14
Natural Numbers:
The numbers 1,2,3,….. which we use for counting object are called natural numbers.
e.g. N= {1,2,3,…..}
Whole Numbers:
If we include 0 in the set of natural numbers then it is called whole number and it is denoted by W.
e.g. W= {0,1,2,3,…..}
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 4
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Integers:
Set of integers consist of positive integers,0 and negative and is denoted by Z.
e.g. Z= {……,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…..}
Radicals and Radicands:
If a real number then any real number x such that X=nÔ is called the nth root of a, in the radical nÔ , n is radical
and a is called radicand.
CHAPTER#3
LOGARITHM
Scientific Notation:
Number written in the form a x 10n where 1≤a <10 and n is an integer called scientific notation.
Common Logarithm:
If the base of logarithm is taken as 10 then logarithm is called common logarithm.
Natural Logarithm:
Logarithm having base e is called Napier logarithm or Natural logarithm.
Characteristic:
The integral part of the logarithm of any number is called the characteristic.
Mantissa:
The decimal part of the logarithm of a number is called the mantissa and is always positive.
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 5
Subject: Mathematics 9th
CHAPTER#4
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND ALEBRAIC FORMULAS
Algebraic expression:
An algebraic expression is that in which constants and variables or both are combined by addition and subtraction.
e.g. 5x2-4x
Rational expression:
The quotient p(x)/q(x) of two polynomial p(x) and q(x) where q(x) ≠0 is called a ra onal expression.
e.g.
Surd:
An irrational radical with radicand is called a surd.
e.g. √3 ,3√7
Monomial Surd:
A surd which contain a single term is called monomial surd.
e.g. √2, √3
Binomial Surd:
A surd which contain sum of two monomial surds is called binomial surd.
e.g. √3+√7
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 6
Subject: Mathematics 9th
CHAPTER#5
FACTORIZATION
Factorization:
The process of expressing an algebraic expression in term of its factor is called factorization.
Remainder theorem:
If a polynomial f(x) is a divided by a linear divisor (x-a), then the remainder is f(a)
Factor theorem:
The polynomial (x-a) is a factor of the polynomial f(x) if and only if f(a)=0
Zero of polynomial:
If a specific number x=a is substituted for the variable x in a polynomial p(x) so that the value.
P(a) is zero then x=a is called zero of polynomial p(x)
CHAPTER#6
ALGEBRAIC MANIPULATION
HCF (Highest common factor):
If two or more algebraic expression are given then their common factor of highest power is called HCF of the
expression.
LCM (Least common multiple):
The product of common factor together with non common factors of the given expression is called LCM.
Relation between HCF and LCM:
LCM . HCF =p(x)+q(x) Where p(x) and q(x) are given expression.
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 7
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Chapter No.7
LINEAR EQUATION & INEQUAALITTIES
EQUATION
An equation is a statement that says the two given algebraic expressions are
e.g x+2=3
LINEAR EQUATION
A linear equation in one unknown variable x is an equation of the form ax+b=0
A,b Î R and a¹0
Types of equations
DENTITY EQUATION
An identity is an equation that is satisfied by every number for which both sides are defined
e.g x+3=3+x
CONDITIONAL EQUATION
A conditional equation is an equation that is satisfied by at least one number but is not an identity
Eg 2x+1=9
INCONSISTENT EQUATIN
An inconsestent equation is an equation whose solution set is the empty set
Eg. x=x+5 because no value of x satisfied it
RATIONAL EQUATION
When the variable in an equation occurs under a radical sign the equation is called rational equation
e.g 2x - 3 - 7 = 0
EXTRANEOUS SOLUTION
A solution that obes not satisfy the original equation is called extraneous solution
LINEAR INEQUALITY IN ONR BSTISBLR
A linear inequality is one variable x is an inequality in which the variable x occurs only to the first power
and is of the form
ax+b<0 a¹0
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 8
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Chapter No.8
LINEAR GRAPHS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
1. CARTESIAN PLANE
The plane formed by two straight lines perpendicular to each other is called Cartesian plane.
2. CO ORDINATE AXES
The line intersecting each other perpendicularly are called Co-Ordinate Axes.
3. ORDER PAIR OF ELEMENTS
An order pair is a pair of elements in which elements are written in specific order
4. ORIGIN
The point of intersection of two co-ordinate axes is called origin.
5. ABSCISSA AND ORDINATE
The x co ordinate of point is called Abscissa and y co ordinate is called ordinate
e.g (3,6) have 3 is Abscissa and 5 is ordinate
6. COLLINEAR POINT
The set of points which lie on the same line are called Collinear point
Chapter No.9
INTRODUCTION TO CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY
1. PLANE GEOMETRY AND CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY
The study of geometrical shapes in a plane is called plane geometry. Co- ordinate geometry is the study of
geometrical shapes in the Cartesian plane
2. DISTANCE FORMULA
The distance between two points A(x1,y1) and B (x2,y2) is define as
d = ( x2 - x1 )2 + ( y2 - y1 ) 2
3. COLLINEAR POINT
Two or more than two points which lie on the same straight line are called collinear point
4. NON COLLINEAR POINT
Points are non collinear is they do not lie on the same straight line are called non collinear point
5. RECTANGLE
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 9
Subject: Mathematics 9th
A figure formed in the plane by four non collinear points is called a rectangle if
i. Its opposite sides are of equal measure
ii. Its opposite sides are parallel to each other
6. PARALLELOGRAM
A figure formed by four none collinear point in the plane is called parallelogram if
i. Its opposite sides are of equal measure
ii. Its opposite sides are parallel
iii. Measure of none of the angle is 90o
7. EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE
If the length of all the three sides of a triangle are same then the triangle is called an equilateral triangle
8. ISOSCELES TRIANGLE
If length of two sides of the triangle is equal and length of the 3rd side is different then that triangle is called
isosceles triangle
9. RIGHT TRIANGLE
A right triangle is that in which one of the angles has measure equal to 90o
10. SQUARE
A square is a closed figure in the plane formed by four non collinear points such that length of all sides
equal and measure of each angle is 90o
11. Scalene triangle
Its measure of three sides of the triangle are different then the triangle is called scalene triangle
Chapter No.10
CONGURENT TRIANGLES
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 10
Subject: Mathematics 9th
CONGURENT TRIANGLES
Two triangles as said to the congruent if there exists a Correspondence between them such that all the
corresponding sides and angles are congruent
ASA postulate
In any correspondence of two triangles if one side and any angles of the triangle are congruent to the
corresponding sides and angles of the other then the triangle are congruent. This statement is called ASA
postalate
SSS postulate
In any correspondence of two triangles of these sides of a triangle are congruent to the corresponding. Three
sides of the other then the triangles are congruent. This statement is called SSS postulates
H.S postulate
In any correspondence of two right angles triangles if hypotenuse and one side of a triangle are congruent to
the corresponding hypotenuse and side of the other then the triangle are congruent
Chapter No.11
PARALLELOGRAM AND TRIANGLES
TRAPEZIUM
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 11
Subject: Mathematics 9th
A trapezium is a quadrilateral with two parallel sides and two non parallel sides
PARALLELOGRAM
If two opposite sides of a quadrilateral and congruent and parallel. It is a parallelogram
RECTANGLE
A rectangle is a parallelogram with all the angles at the vertices equal to 90o
Areas of rectangle = length ×width
Q. How many congruent triangles are formed by each diagonal parallelogram. Draw a diagram
Ans. Each diagonal of a parallelogram bisect at into two congruent triangles
ABD and BCD are two triangles
Q. If the line segment joining the mid points of the sides of a triangle is parallel to third side what is the
relation with 3rd size?
Ans. If the line segment joing the mid point of the sides of a triangle is parallel to the 3rd sides and is
equal one half of its length here
Chapter No.12
LINE BISECTOR AND ANGLE BISECTOR
Right bisector of a line segment
A line l is called a right bisector of a line segment if l is perpendicular to the line segment and passes
through its mid point
Angle bisector
Angle bisector is the ray which divide and angle into two equal parts
Chapter No.13
SIDES AND ANGLES OF A TRIANGLE
Scalene triangle
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 12
Subject: Mathematics 9th
A triangle is called scalene triangle if measure of all the sides is different
Q. It two sides of a triangle are unequal in length then which angle will be of greater measure ?
Ans. If two sides of a triangle are un equal in length the longer sides has an angle of greater measure
opposite to it.
Q. An a scalene triangle what will be the measure of angle opposite to the largest side ?
Ans. An a scalene triangle the angle opposite to the largest side is of measure greater than 60o
Q. Which side of a right angle triangle is longer then each of other two sides ?
Ans. The hypotenuses of right angle triangle is longer than each of other two sides
Chapter No.14
RATIO AND PROPORTION
RATIO
a
Ratio a : b = is the compassion of two alike quantities having same unit
b
PORPORTION
The equality of two ratios is called proportional four number a,b,c,d are in proportion if A:B=C:D
Similar triangles
Triangles are called similar if they are equiangular and measure of their corresponding sides are proportional
Practical application of similar triangle
Photographer can develop prints of different sizes from the same negative. In spite of the difference in sizes.
There picfures look like each other. One photograph is simply on enlargement of another
Congruent triangles
Two triangles are said to be congruent if there exists a correspondence between them. Such that all the
corresponding sides are angles are congruent
Chapter No.15
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM
Pythagoras Theorem
In a right angle triangle the square of the length of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the length
of the other two sides
(Hyp)2=(base)2+(perp)2
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 13
Subject: Mathematics 9th
Right triangle
A right triangle is that in which one of the angles as measure equal to 90o.
Acute angle triangle
If sum of square of two sides is greater than the square of 3rd side then the angle is called acute angle triangle
a2+b2>c2
Obtuse angle triangle
The triangle in which of sum of squares are two sides is less then the square of 3rd side is called obtuse angle
triangle
Chapter No.16
THEOREMS RELEATED WITH AREA
Area of the figure.
The region enclosed by bounding lines of a closed figure is called the area of the figure
Triangular region
A triangular region is the union of a triangle and its interior i.e The three line segments forming the triangle
and its interior
Rectangular region
A Rectangular region is the union of a rectangle and its interior
Parallel lines
Two lines which on extending in both the directions infinitely never intersect at a point are called parallel
lines
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which opposite sides are parallel opposite sides are of equal length and
the measure of opposite angles are equal
Altitude or height of a parallelogram
If one side of parallelogram is taken as its base the perpendicular distance between that sides parallel to it is
called altitude or height parallelogram
Chapter No.17
PRACTICAL GEOMETORY TRIANGLE
Centriod of a triangle
The point where the three medians of a triangle meet is called centriod of the triangle
Circumcentre of a triangle
The point of concurrency of three right bisectors of sides of triangle is called its circumcentre.
Written By: Amir Shehzad Page 14
You might also like
- Definitions: Mathematics (Science Group) : 9Document13 pagesDefinitions: Mathematics (Science Group) : 9Muhammad Attiq Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Matrix AlgebraDocument39 pagesMatrix Algebraamosoundo59No ratings yet
- Subject: General Mathematics: Sarfraz TalibDocument10 pagesSubject: General Mathematics: Sarfraz TalibAthar Iqbal KhitranNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SSC-IDocument9 pagesMathematics SSC-IZaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Matrices Unit IDocument13 pagesMatrices Unit IMadhu spoorthiNo ratings yet
- Determinant and MatricesDocument5 pagesDeterminant and MatricesFarid HossainNo ratings yet
- Design of Experiments Notes - IIT DelhiDocument352 pagesDesign of Experiments Notes - IIT DelhivicksgeorgeNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5-StudentDocument47 pagesWEEK 5-Studenthafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Objectives: in Yo11 5/ro11/d 1H Able 10.-Identify MatricesDocument7 pagesObjectives: in Yo11 5/ro11/d 1H Able 10.-Identify MatricesVimla OliNo ratings yet
- 1 Matrix Algebra Fall 22-23Document20 pages1 Matrix Algebra Fall 22-23md soyeb shahriyer sivanNo ratings yet
- School of Advanced Sciences: MAT2002 Applications of Differential and Difference EquationsDocument3 pagesSchool of Advanced Sciences: MAT2002 Applications of Differential and Difference Equationsanshul jainNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument14 pagesMatricesthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Chapter HighlightsDocument29 pagesMatrices: Chapter HighlightsANURAG SHUKLANo ratings yet
- 5 Matrices PDFDocument14 pages5 Matrices PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- 3 MatricesDocument15 pages3 MatricesHarsh Ravi100% (1)
- MathsDocument137 pagesMathsDGanesh100% (2)
- For More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsDocument16 pagesFor More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsRishabhNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differential and Difference EquationsDocument177 pagesApplications of Differential and Difference EquationsEswar RcfNo ratings yet
- M 1Document38 pagesM 1Divya TejaNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument44 pagesMatrixJomil John ReyesNo ratings yet
- LAODE Introduction & RankDocument11 pagesLAODE Introduction & Rankasfvkjsv asgbaegbNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument22 pagesMatrixlorago3042No ratings yet
- MatrixDocument2 pagesMatrixSiti Nurul ArasyNo ratings yet
- LA&AC Unit 1 NOTESDocument41 pagesLA&AC Unit 1 NOTESlakshmi pulugu100% (1)
- MATRIX TITLEDocument8 pagesMATRIX TITLEAma RahmahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MatricsDocument37 pagesUnit 2 MatricsAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument8 pagesMatricesAngel PariNo ratings yet
- M-Iii, 2 Marks (2017-18) - 1Document28 pagesM-Iii, 2 Marks (2017-18) - 1umarfarookshaik786No ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Notes on Matrices, Determinants, EigenvaluesDocument4 pagesLinear Algebra Notes on Matrices, Determinants, EigenvaluesCathy DengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matrices MATV101 UpdatedDocument35 pagesChapter 2 Matrices MATV101 Updated1jabujohnshibambo12No ratings yet
- 2matrices Its OperationsDocument27 pages2matrices Its OperationsJoelar OndaNo ratings yet
- 1 Linear AlgebraDocument5 pages1 Linear AlgebraSonali VasisthaNo ratings yet
- Mathprimer NupDocument2 pagesMathprimer NupMayam AyoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IVDocument29 pagesMathematics IVAnkon Gopal BanikNo ratings yet
- MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXPLAINEDDocument7 pagesMATRICES AND DETERMINANTS EXPLAINEDherooNo ratings yet
- Matrices, Determinant and InverseDocument12 pagesMatrices, Determinant and InverseRIZKIKI100% (1)
- Gi Part1 PDFDocument57 pagesGi Part1 PDFasdfghjNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Session - 1-PPT - Venugopal - SSNDocument63 pagesDay 2 - Session - 1-PPT - Venugopal - SSNVDRATNAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Matrix and Determinants NotesDocument7 pagesMatrix and Determinants NotesYash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Matrices: 0 For I JDocument7 pagesMatrices: 0 For I JVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- 4.matrices and DeterminantsDocument28 pages4.matrices and DeterminantsAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- 02549e5d7a665-Chapter 2. Matrices - Advance Maths HSSC PDFDocument8 pages02549e5d7a665-Chapter 2. Matrices - Advance Maths HSSC PDFAmit SolankiNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algebra Fundamentals for Solving Systems of EquationsDocument17 pagesMatrix Algebra Fundamentals for Solving Systems of EquationsAiram MorellNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 1 Rational ExponentsDocument21 pagesLesson 9 1 Rational Exponentsapi-233527181No ratings yet
- Algebra of MatrixDocument14 pagesAlgebra of MatrixRajeenaNayimNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Anova Matrix PDFDocument16 pagesChapter1 Anova Matrix PDFsricharitha6702No ratings yet
- 16 Matrices and DeterminantsDocument110 pages16 Matrices and Determinantstusharfiitjee80No ratings yet
- Linear Systems Matrix PropertiesDocument18 pagesLinear Systems Matrix PropertiesAbhi bus 1No ratings yet
- WorkBook - Matricespattern-2 (2) - CompressedDocument13 pagesWorkBook - Matricespattern-2 (2) - CompressedDhruv KuchhalNo ratings yet
- MR 2015matricesDocument9 pagesMR 2015matricesManisha AldaNo ratings yet
- MATRIX Theory and QuestionsDocument66 pagesMATRIX Theory and QuestionsvinayakkanchalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engg. Math MatricesDocument13 pagesAdvanced Engg. Math MatricesRomel PavillonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics One Notes PDFDocument59 pagesMathematics One Notes PDFPraise Nehumambi100% (1)
- Matrix NotesDocument52 pagesMatrix NotesSURYA KNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix 31.10.2023Document16 pagesIntroduction To Matrix 31.10.2023noelkalagoNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 MATRIX (S - Week 5)Document24 pagesChap 4 MATRIX (S - Week 5)ADELLINNE NATASYA BINTI ROSDI / UPMNo ratings yet
- MathDocument16 pagesMathArash Evan'sNo ratings yet
- Kashif Khan Assignment of Linear Algebra.Document10 pagesKashif Khan Assignment of Linear Algebra.engineerkashif97No ratings yet
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)From EverandHarmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)No ratings yet
- TS JUNIOR INTER MATHS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS 2022-23Document7 pagesTS JUNIOR INTER MATHS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS 2022-23Priya BhavanaNo ratings yet
- Positional Astronomy BR Annual ParallaxDocument4 pagesPositional Astronomy BR Annual ParallaxgarryhodgesonNo ratings yet
- RPT Add Maths F4 2023Document17 pagesRPT Add Maths F4 2023SITI HAJAR BINTI ROSLI MoeNo ratings yet
- ANSI B89.3.1-1972 1979 Measurement of Out - of - RoundnessDocument36 pagesANSI B89.3.1-1972 1979 Measurement of Out - of - Roundness1975.venkat7685100% (1)
- Fermat Contest: (Grade 11)Document6 pagesFermat Contest: (Grade 11)Keshav JindalNo ratings yet
- Sem 1-IX - MathsDocument6 pagesSem 1-IX - MathsDevika ArulNo ratings yet
- 2017 MTAP 6 Answer KeyDocument6 pages2017 MTAP 6 Answer KeyRyle SentillanosaNo ratings yet
- M.Phil, - B. Maheswari PDFDocument15 pagesM.Phil, - B. Maheswari PDFahilaNo ratings yet
- Similar Shapes Area and Volume QP Edexcel GcseDocument8 pagesSimilar Shapes Area and Volume QP Edexcel GcseYoussef TarekNo ratings yet
- C2 Trigonometry - Arc Length and Sector AreaDocument19 pagesC2 Trigonometry - Arc Length and Sector AreaIsmail WasiuNo ratings yet
- TERM END ASSESSMENT II Answer KeyDocument6 pagesTERM END ASSESSMENT II Answer KeyShipra AroraNo ratings yet
- Integral de Sinx/xDocument3 pagesIntegral de Sinx/xSebastián Carrillo SantanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Pythagoras Theorem 2Document9 pagesGrade 10 Pythagoras Theorem 2Akili ArmaniNo ratings yet
- Teacher Work SampleDocument43 pagesTeacher Work SampleMeredith100% (16)
- Instantaneous Centre Velocity CalculationDocument30 pagesInstantaneous Centre Velocity Calculationm_er100No ratings yet
- Amm 01 2017 PDFDocument100 pagesAmm 01 2017 PDFAnonymous 0Uc6FynqNo ratings yet
- Skills in Mathematics Trigonometry For JEE Main and Advanced 2022Document399 pagesSkills in Mathematics Trigonometry For JEE Main and Advanced 2022Harshil Nagwani100% (3)
- Pre-Cal - Conic Sections and Other Graphs WorksheetDocument3 pagesPre-Cal - Conic Sections and Other Graphs WorksheetFons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Manit Choudhary Aptitude FormulaDocument5 pagesManit Choudhary Aptitude Formulawimaxaaabgl100% (1)
- Famous MathematiciansDocument3 pagesFamous MathematiciansGlenn Puralan FloresNo ratings yet
- Particle motion and dynamics problemsDocument2 pagesParticle motion and dynamics problemsmhrdd222No ratings yet
- CG PracticalsDocument52 pagesCG PracticalsDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Meshing Chapter 2 IntroductionDocument171 pagesANSYS Meshing Chapter 2 IntroductionstevenNo ratings yet
- Computer Numerical Control: TransformationsDocument56 pagesComputer Numerical Control: TransformationsibraheemNo ratings yet
- Grade 4-B Contents & Samples - Math Mammoth PDFDocument46 pagesGrade 4-B Contents & Samples - Math Mammoth PDFsamrajcity67% (3)
- Solutions To The Olympiad Hamilton Paper: First SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutions To The Olympiad Hamilton Paper: First SolutionArsh TewariNo ratings yet
- Math 8 exam questionsDocument5 pagesMath 8 exam questionsRoella Mae Tudias Alod67% (3)
- Math May-June 2015Document32 pagesMath May-June 2015shaniahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Basic 2D Constraint Solving: Introduction and ScopeDocument6 pagesSummary of Basic 2D Constraint Solving: Introduction and ScopeMangesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsRaj Gupta0% (1)