Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PPP - Cholelithiasis
Uploaded by
알파Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PPP - Cholelithiasis
Uploaded by
알파Copyright:
Available Formats
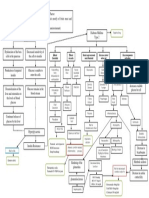
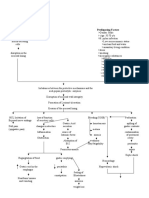
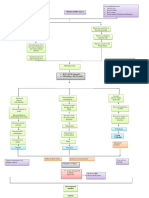
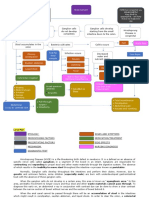
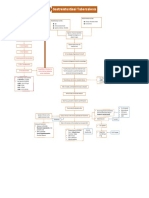
CHOLELITHIASIS
Cholesterol Gallstones Black Pigmented Gallstones Brown Pigmented Gallstones
Non-modifiable Factors: Modifiable Factors: Non-modifiable Factors: Modifiable Factors: Non-modifiable Factors:
volume of unconjugated Lifestyle E. Coli Age: >40 years old
Age: >40 years old Lifestyle Age: >40 years old
bilirubin in bile Systemic Disorders that Ascaris Lumbrcoides Gender: Female
Gender: Female Systemic Diseases Gender: Female
result in excessive (roundworm) Genetic
Genetic Obesity & Insulin Resistance Genetic
bilirubin production Clonorchis sinesis (liver fluke) Predisposition
Predisposition DM Predisposition
Geography/Ethnicity: Diseases of the Ileum Geography/Ethnicity: Bilirubin precipitates Hemolytic anemia Geography/Ethnicity:
Western countries Spinal cord injuries Western countries Cirrhosis Asian Countries
Biliary tract E. Coli invasion in the
Drugs
infections gallbladder
Estrogen, Clofibrate, Ca2+ readily binds with bilirubin
Ostreotide, Ceftriaxone
Total Parenteral Nutrition
Brings about hydrolytic enzymes
Gallbladder hypersecretes Diet
Formation of solid Ca2+ that hydrolyzes both conjugated
mucins, as a result of Rapid weight loss
Supersaturated bile formation bilirubinate bilirubin and phospholipids
stimulation by some Pregnancy and Parity
components of saturated bile
Cholesterol content can't be Agglomeration Hydrolyzed components
solubilized at equilibrium by bile precipitate along with Ca2+
Carbohydrate groups of the
salts and phospholipids
polymers of mucins avidly bind
Growth of the crystals into
to H2O to form gels
mature and macroscopic stones Agglomeration
With the presence of
heterogeneous pronucleating
The hydrophobic polypeptides in Black-pigmented Ca2+
agents, cholesterol precipitates Growth of the crystals into
the core of mucin glycoproteins bilirubinate gallstones mature and macroscopic stones
bind with bilirubin and Ca in bile
Cholesterol nucleation and
crystallization Brown-pigmented stones
Results to H2O-insoluble
complex of mucin glycoproteins = UCB + hydrolyzed phospholipids
and Ca Bilirubinate + Ca2+
Formation of solid plate-like
cholesterol monohydrate
crystals in bile
Provides a surface for nucleation
of cholesterol monohydrate
crystals and a matrix for growth Gallbladder stasis facilitates
of stones Agglomeration retention
Growth of the crystals into
mature and macroscopic stones
Cholesterol gallstones
You might also like
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPa Tho Physiologypumpkin21No ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis GRAND CASE PRESDocument52 pagesCholelithiasis GRAND CASE PRESKyle Cholo CholoNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument2 pagesPATHOad3_aaaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Patho1 OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE 2' CHOLEDOLITHIASIS, CHOLELITHIASISDocument1 pagePatho1 OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE 2' CHOLEDOLITHIASIS, CHOLELITHIASISKyle Cholo CholoNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis CholecystitisDocument1 pageCholelithiasis Cholecystitissamliebareng77No ratings yet
- Assaz Predisposing Factors: Advanced Age Gender Ileal Resection/Disease RaceDocument3 pagesAssaz Predisposing Factors: Advanced Age Gender Ileal Resection/Disease RaceryanNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 pagesPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalNo ratings yet
- Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mixed Hyperbilirubinemia Conjugated HyperbilirubinemiaDocument4 pagesUnconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mixed Hyperbilirubinemia Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemiakilladim992No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYstrawberryNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab M2 Routine FecalysisDocument4 pagesParasitology Lab M2 Routine Fecalysiseumhir7No ratings yet
- RX 25 Protein MetDocument18 pagesRX 25 Protein Metgiyan77No ratings yet
- CAAG HepatologyDocument52 pagesCAAG HepatologyBenjamin PophamNo ratings yet
- Lack of Insulin Decreases Available Glucose For CellDocument1 pageLack of Insulin Decreases Available Glucose For CellvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CholeClyde AleczandreNo ratings yet
- OB PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesOB PathophysiologyCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- NEMATODESxDocument5 pagesNEMATODESxJulia BascoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Biliary AtresiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology Biliary AtresiaPATHOSHOPPENo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GallstonesDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of GallstonesNicol John CeballosNo ratings yet
- FECAL ANALYSIS Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesFECAL ANALYSIS Lecture NotesanonacadsNo ratings yet
- Hepatocellular Jaundice - JaundiceDocument1 pageHepatocellular Jaundice - JaundiceKierzteen Brianna TaromaNo ratings yet
- The Biochemistry of Jaundice ExplainedDocument29 pagesThe Biochemistry of Jaundice ExplainedeminemizenNo ratings yet
- بروتين د 2Document15 pagesبروتين د 2hamoodNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis PathoDocument4 pagesCholelithiasis PathoahrjeyNo ratings yet
- V. Pathophysiology Predisposing FactorsDocument1 pageV. Pathophysiology Predisposing Factorsapi-3828211No ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 pagePa Tho PhysiologybrikzNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Case StudyDocument30 pagesNutrition Case StudyCher BautistaNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Group2Document53 pagesBilirubin Group2ChiNo ratings yet
- VII. Pathophysiology of PUDDocument1 pageVII. Pathophysiology of PUDJehmima Gloriani100% (1)
- Lithogenesis and Bile MetabolismDocument20 pagesLithogenesis and Bile MetabolismClaudia IlieNo ratings yet
- 05 CeDocument11 pages05 CeElizabethNo ratings yet
- Etiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsDocument2 pagesEtiology Non Modifiable Factors: Modifiable FactorsJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Metabolism: Hd. - Msc. (Biochemistry)Document18 pagesBilirubin Metabolism: Hd. - Msc. (Biochemistry)MuhamadMarufNo ratings yet
- Final-Differential Diagnosis of Increased BilirubinDocument83 pagesFinal-Differential Diagnosis of Increased BilirubinRuchita SanghaniNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Part 1Document13 pagesCholecystitis Part 1lizbughoNo ratings yet
- Task 02 Id No:181-025-031 Differentiate Between Different Types of Foodborne Illness Foodborne IllnessDocument1 pageTask 02 Id No:181-025-031 Differentiate Between Different Types of Foodborne Illness Foodborne IllnessRazia UrmiNo ratings yet
- Coledocolitiasis ResumenDocument5 pagesColedocolitiasis ResumenStefanny VillaltaNo ratings yet
- 13 - 14 StomachDocument129 pages13 - 14 StomachdrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- J Mpsur 2017 09 012Document7 pagesJ Mpsur 2017 09 012riffarsyad100% (1)
- Concept Map MarwahDocument5 pagesConcept Map MarwahAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Approach To Jaundice SummaryDocument1 pageA Clinical Approach To Jaundice SummaryKARIM MADEGENo ratings yet
- Trans Title. Lowercase Prepositions. Trans Title. Lowercase PrepositionsDocument5 pagesTrans Title. Lowercase Prepositions. Trans Title. Lowercase PrepositionsMariell ArchetaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Liver Injury Evaluation of Liver InjuryDocument59 pagesEvaluation of Liver Injury Evaluation of Liver InjuryhippohazelNo ratings yet
- Causes and Classification of JaundiceDocument23 pagesCauses and Classification of JaundicetrcfghNo ratings yet
- GI Problems: Guide to Hepatomegaly, Jaundice, and HepatitisDocument86 pagesGI Problems: Guide to Hepatomegaly, Jaundice, and HepatitisThitanun TungchutworakulNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasesDocument24 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Dengan Chronic Kidney DiseasestidaktahudiriNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesDocument3 pagesHirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Icterus or Jaundice: Department of Childhealth School of Medicine, University of Sumatera Utara MedanDocument39 pagesIcterus or Jaundice: Department of Childhealth School of Medicine, University of Sumatera Utara MedanSyarifah FauziahNo ratings yet
- JAUNDICE Internal Medicine PresentationDocument34 pagesJAUNDICE Internal Medicine PresentationShitanjni WatiNo ratings yet
- Icteric & Jaundice: Calvin DamanikDocument37 pagesIcteric & Jaundice: Calvin DamanikRista IreneNo ratings yet
- Physiologic & Pathologic Predisposing Factors Mother's Blood Type (O+) Newborn Prematurity Precipitating Factors Dehydration Meconium StoolDocument2 pagesPhysiologic & Pathologic Predisposing Factors Mother's Blood Type (O+) Newborn Prematurity Precipitating Factors Dehydration Meconium StoolJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- cc2 Lectures AllDocument256 pagescc2 Lectures AllJayson Dagohoy SudioNo ratings yet
- 6 JaundiceDocument36 pages6 JaundiceKamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus: Non-modifiable and modifiable risk factorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of diabetes mellitus: Non-modifiable and modifiable risk factorsMervin Ezekiel Amistoso FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- 3a 3c 4 Dopamine, A Neurotransmitter Located Primarily in TheDocument1 page3a 3c 4 Dopamine, A Neurotransmitter Located Primarily in The알파No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Fracturemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Analogy Test With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnalogy Test With Answers PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy in Suspected Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesOxygen Therapy in Suspected Acute Myocardial InfarctionPutri YunandaNo ratings yet
- Measuring MatterDocument3 pagesMeasuring Matter알파No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Analogy Test With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnalogy Test With Answers PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- Solving Radical Equations Step-by-StepDocument3 pagesSolving Radical Equations Step-by-StepJewel PottNo ratings yet
- Gordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsDocument1 pageGordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsTracy100% (37)
- BP TakingDocument4 pagesBP Taking알파No ratings yet
- Analogy Test With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnalogy Test With Answers PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- CUES CholeDocument9 pagesCUES Chole알파No ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument25 pagesHealth AssessmentGovindaraju Subramani100% (1)
- The Impact of The Tax System On Health Insurance CoverageDocument2 pagesThe Impact of The Tax System On Health Insurance Coverage알파No ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Oncology PatientsDocument35 pagesNursing Care for Oncology Patients알파No ratings yet
- Docslide - Us - Drug Study FormatDocument2 pagesDocslide - Us - Drug Study Format알파No ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing Management for Cancer Cell GrowthDocument3 pagesOncology Nursing Management for Cancer Cell Growth알파No ratings yet
- LMV 014Document5 pagesLMV 014알파No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Mass Left Upper LobeDocument8 pagesPulmonary Mass Left Upper Lobe알파No ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Oncology PatientsDocument35 pagesNursing Care for Oncology Patients알파No ratings yet
- PPP BCCDocument1 pagePPP BCC알파No ratings yet
- Triage in Emergency DepartmentDocument25 pagesTriage in Emergency Departmenthatem alsrour91% (11)
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Maintenance of Patent AirwayDocument13 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Maintenance of Patent Airway알파No ratings yet
- Approaching Disaster Management Through Social Learning 2010Document14 pagesApproaching Disaster Management Through Social Learning 2010알파No ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Management in The PhilippinesDocument32 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and Management in The PhilippinesErnan BaldomeroNo ratings yet
- Filariasis 140310130022 Phpapp02Document18 pagesFilariasis 140310130022 Phpapp02알파No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Screening: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology™Document0 pagesCervical Cancer Screening: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology™Tania Rodriguez IncerNo ratings yet
- Sodium Valproate Uses, DosageDocument2 pagesSodium Valproate Uses, DosageKhairul KhairulNo ratings yet
- BASIC DefectaDocument7 pagesBASIC Defectaafifah klinikNo ratings yet
- Septic ArthritisDocument8 pagesSeptic ArthritisLorebell100% (2)
- Clinical Trial Phases ExplainedDocument5 pagesClinical Trial Phases ExplainedDavid ThaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical AssessmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Clinical AssessmentnurmeenNo ratings yet
- Psychosis NosDocument8 pagesPsychosis Nosapi-253211220No ratings yet
- Sexual IntercourseDocument26 pagesSexual Intercoursenathan100% (2)
- Treatment of Posterior Crossbite Comparing 2 Appliances: A Community-Based TrialDocument8 pagesTreatment of Posterior Crossbite Comparing 2 Appliances: A Community-Based TrialPae Anusorn AmtanonNo ratings yet
- Foods Rich in LeucineDocument5 pagesFoods Rich in LeucineIustin CristianNo ratings yet
- Blue Book - Guidelines For The Control of Infectious DiseaseDocument271 pagesBlue Book - Guidelines For The Control of Infectious DiseaseavarathunnyNo ratings yet
- PTSD NCPDocument2 pagesPTSD NCPDanielle Quemuel Viray0% (1)
- 4 ConceptDocument1 page4 ConceptStacey GarciaNo ratings yet
- Q A Random - 16Document8 pagesQ A Random - 16ja100% (1)
- GI PathologyDocument22 pagesGI Pathologyzeroun24100% (5)
- Defining A High-Performance lCU System For The - , 21st Century: A Position PaperDocument11 pagesDefining A High-Performance lCU System For The - , 21st Century: A Position PaperRodrigoSachiFreitasNo ratings yet
- Singapore's Merchant Shipping Regulations on Medical StoresDocument36 pagesSingapore's Merchant Shipping Regulations on Medical StoresLoka Radhakrishna NarasaiahNo ratings yet
- Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesSafety Data SheettienNo ratings yet
- PsychoanalysisDocument30 pagesPsychoanalysisjaydokNo ratings yet
- s6 Pharma AnesDocument14 pagess6 Pharma AnesTara Lingating0% (1)
- Tumor of The EyeDocument30 pagesTumor of The EyenenyririNo ratings yet
- Eye Exercises For Healthy Eye: September 2015Document3 pagesEye Exercises For Healthy Eye: September 2015spiridon_andrei2011No ratings yet
- Mini-CEX Case AssessmentDocument4 pagesMini-CEX Case Assessmentsiti nur asiahNo ratings yet
- Categories of Disability Under IDEADocument6 pagesCategories of Disability Under IDEANational Dissemination Center for Children with DisabilitiesNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Department of Pediatric Dentistry Ziauddin UniversityDocument10 pagesCase Presentation: Department of Pediatric Dentistry Ziauddin UniversitySaadia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Prostho IV-Slides 2 - Assessment of The Edentulous PatientDocument60 pagesProstho IV-Slides 2 - Assessment of The Edentulous Patientبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Hepatoprotective ActivityDocument27 pagesHepatoprotective ActivityBilly Aditya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavior Theory Hbse 2Document4 pagesCognitive Behavior Theory Hbse 2Girlie Mae PondiasNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument1 pageThalassemiaghee91No ratings yet
- AquaNereda Brochure 1017 WebDocument4 pagesAquaNereda Brochure 1017 WebdmnNo ratings yet