Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Https WWW - Sigmaaldrich.com Technical-Documents Articles Biology Ir-Spectrum-Table - Printerview.html
Uploaded by
nissaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Https WWW - Sigmaaldrich.com Technical-Documents Articles Biology Ir-Spectrum-Table - Printerview.html
Uploaded by
nissaCopyright:
Available Formats
Return to Web Version
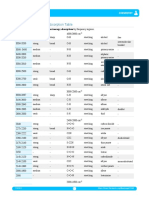
IR Spectrum Table & Chart
The IR Spectrum Table is a chart for use during infrared spectroscopy. The table lists IR spectroscopy frequency ranges,
appearance of the vibration and absorptions for functional groups. There are two tables grouped by frequency
range and compound class.
IR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range
Use this table when you already know the frequency of your material. Find the frequency range in the first column on the left side
of the chart and corresponding values in adjacent columns.
If you need to find the frequency of a material go to the IR table by compound.
Frequency Absorption
Appearance Group Compound Class Comments
Range (cm-1)
4000-3000 3700-3584 medium, O-H stretching alcohol free
cm-1 sharp
3550-3200 strong, O-H stretching alcohol intermolecular bonded
broad
3500 medium N-H stretching primary amine
3400
3400-3300 medium N-H stretching aliphatic primary
amine
3330-3250
3350-3310 medium N-H stretching secondary amine
3300-2500
strong,
O-H stretching carboxylic acid usually centered on 3000 cm-
1
broad
weak,
3200-2700 O-H stretching alcohol intramolecular bonded
broad
3000-2800 strong, N-H stretching amine salt
broad
3000-2500
cm-1
3000-2500 strong,
3333-3267 C-H stretching alkyne
cm-1 sharp
3100-3000 medium C-H stretching alkene
3000-2840 medium C-H stretching alkane
2830-2695 medium C-H stretching aldehyde doublet
2600-2550 weak S-H stretching thiol
2400-2000
cm-1
2400-2000 O=C=O
2349 strong carbon dioxide
cm-1 stretching
2275-2250 strong, N=C=O isocyanate
broad stretching
2260-2222 weak CΞN stretching nitrile
2260-2190 weak CΞC stretching alkyne disubstituted
2175-2140 strong S-CΞN thiocyanate
stretching
2160-2120 strong N=N=N azide
stretching
2150 C=C=O ketene
stretching
N=C=N
2145-2120 strong carbodiimide
stretching
2140-2100 weak CΞC stretching alkyne monosubstituted
N=C=S
2140-1990 strong isothiocyanate
stretching
2000-1900 medium C=C=C allene
stretching
2000 C=C=N ketenimine
stretching
2000-1650
cm-1
2000-1650 2000-1650 weak C-H bending aromatic overtone
cm-1 compound
1870-1540
1818 strong C=O stretching anhydride
1750
1815-1785 strong C=O stretching acid halide
1800-1770 strong C=O stretching conjugated acid
halide
conjugated
1775 strong C=O stretching
anhydride
1720
vinyl / phenyl
1770-1780 strong C=O stretching
ester
1760 strong C=O stretching carboxylic acid monomer
1750-1735 strong C=O stretching esters 6-membered lactone
1750-1735 strong C=O stretching δ-lactone γ: 1770
1745 strong C=O stretching cyclopentanone
1740-1720 strong C=O stretching aldehyde
1730-1715 strong C=O stretching α,β-unsaturated or formates
ester
1725-1705 strong C=O stretching aliphatic ketone or cyclohexanone or
cyclopentenone
1720-1706 strong C=O stretching carboxylic acid dimer
1710-1680 strong C=O stretching conjugated acid dimer
1710-1685 strong C=O stretching conjugated
aldehyde
1690 strong C=O stretching primary amide free (associated: 1650)
1690-1640 medium C=N stretching imine / oxime
1685-1666 strong C=O stretching conjugated
ketone
1680 strong C=O stretching secondary amide free (associated: 1640)
1680 strong C=O stretching tertiary amide free (associated: 1630)
1650 strong C=O stretching δ-lactam γ: 1750-1700 β: 1760-1730
1670-1600
cm-1
1670-1600 1678-1668 weak C=C stretching alkene disubstituted (trans)
cm-1
1675-1665 weak C=C stretching alkene trisubstituted
1675-1665 weak C=C stretching alkene tetrasubstituted
1662-1626 medium C=C stretching alkene disubstituted (cis)
1658-1648 medium C=C stretching alkene vinylidene
1650-1600 medium C=C stretching conjugated
alkene
1650-1580 medium N-H bending amine
1650-1566 medium C=C stretching cyclic alkene
1648-1638 strong C=C stretching alkene monosubstituted
α,β-unsaturated
1620-1610 strong C=C stretching
ketone
1600-1300
cm-1
1600-1300 1550-1500 strong N-O stretching nitro compound
cm-1
1372-1290
1465 medium C-H bending alkane methylene group
1450 medium C-H bending alkane methyl group
1375
1390-1380 medium C-H bending aldehyde
1385-1380 medium C-H bending alkane gem dimethyl
1370-1365
1400-1000
cm-1
1400-1000
1440-1395 medium O-H bending carboxylic acid
cm-1
1420-1330 medium O-H bending alcohol
1415-1380 strong S=O stretching sulfate
1200-1185
1410-1380 strong S=O stretching sulfonyl chloride
1204-1177
1400-1000 strong C-F stretching fluoro compound
1390-1310 medium O-H bending phenol
1372-1335 strong S=O stretching sulfonate
1195-1168
1370-1335 strong S=O stretching sulfonamide
1170-1155
1350-1342 strong S=O stretching sulfonic acid anhydrous
1165-1150 hydrate: 1230-1120
1350-1300 strong S=O stretching sulfone
1160-1120
1342-1266 strong C-N stretching aromatic amine
1310-1250 strong C-O stretching aromatic ester
1275-1200 strong C-O stretching alkyl aryl ether
1075-1020
1250-1020 medium C-N stretching amine
1225-1200 strong C-O stretching vinyl ether
1075-1020
1210-1163 strong C-O stretching ester
1205-1124 strong C-O stretching tertiary alcohol
1150-1085 strong C-O stretching aliphatic ether
secondary
1124-1087 strong C-O stretching
alcohol
1085-1050 strong C-O stretching primary alcohol
1070-1030 strong S=O stretching sulfoxide
1050-1040 strong, CO-O-CO anhydride
broad stretching
1000-650
cm-1
1000-650
995-985 strong C=C bending alkene monosubstituted
cm-1
915-905
980-960 strong C=C bending alkene disubstituted (trans)
895-885 strong C=C bending alkene vinylidene
850-550 strong C-Cl stretching halo compound
840-790 medium C=C bending alkene trisubstituted
730-665 strong C=C bending alkene disubstituted (cis)
690-515 strong C-Br stretching halo compound
600-500 strong C-I stretching halo compound
900-700
cm-1
900-700 880 ± 20 strong C-H bending 1,2,4-
cm-1 trisubstituted
810 ± 20
880 ± 20 strong C-H bending 1,3-disubstituted
780 ± 20
(700 ± 20)
810 ± 20 strong C-H bending 1,4-disubstituted
or
1,2,3,4-
tetrasubstituted
1,2,3-
780 ± 20 strong C-H bending
trisubstituted
(700 ± 20)
755 ± 20 strong C-H bending 1,2-disubstituted
750 ± 20 strong C-H bending monosubstituted
700 ± 20 benzene
derivative
IR Table by Compound Class
If you already know the frequency range use this IR spectrum chart. If you already know the frequency use the IR frequency
table above.
Absorption (cm-
Compound Class Group 1 Appearance Comments
)
acid halide C=O stretching 1815-1785 strong
alcohols O-H stretching 3700-3584 medium, free
sharp
O-H stretching 3550-3200 strong, broad intermolecular bonded
O-H stretching 3200-2700 weak, broad intramolecular bonded
O-H bending 1420-1330 medium
aldehyde C-H stretching 2830-2695 medium doublet
C=O stretching 1740-1720 strong
C-H bending 1390-1380 medium
aliphatic ether C-O stretching 1150-1085 strong
aliphatic ketone C=O stretching 1725-1705 strong or cyclohexanone or
cyclopentenone
aliphatic primary N-H stretching 3400-3300 medium
amine
alkane C-H stretching 3000-2840 medium
C-H bending 1465 medium methylene group
C-H bending 1450 medium methyl group
C-H bending 1385-1380 medium gem dimethyl
C-H stretching 3100-3000 medium
C=C stretching 1678-1668 weak disubstituted (trans)
C=C stretching 1675-1665 weak trisubstituted
C=C stretching 1675-1665 weak tetrasubstituted
C=C stretching 1662-1626 medium disubstituted (cis)
C=C stretching 1658-1648 medium vinylidene
C=C stretching 1648-1638 strong monosubstituted
C=C bending 995-985 strong monosubstituted
C=C bending 980-960 strong disubstituted (trans)
C=C bending 895-885 strong vinylidene
C=C bending 840-790 medium trisubstituted
C=C bending 730-665 strong disubstituted (cis)
alkyl aryl ether C-O stretching 1275-1200 strong
alkyne C-H stretching 3333-3267 strong, sharp
CΞC stretching 2260-2190 weak disubstituted
CΞC stretching 2140-2100 weak monosubstituted
allene C=C=C stretching 2000-1900 medium
amine N-H bending 1650-1580 medium
C-N stretching 1250-1020 medium
amine salt N-H stretching 3000-2800 strong, broad
anhydride C=O stretching 1818 strong
CO-O-CO
1050-1040 strong, broad
stretching
aromatic amine C-N stretching 1342-1266 strong
aromatic compound C-H bending 2000-1650 weak overtone
aromatic ester C-O stretching 1310-1250 strong
azide N=N=N stretching 2160-2120 strong
benzene derivative 700 ± 20
carbodiimide N=C=N stretching 2145-2120 strong
carbon dioxide O=C=O stretching 2349 strong
carboxylic acid O-H stretching 3300-2500 strong, broad usually centered on 3000 cm-1
C=O stretching 1760 strong monomer
C=O stretching 1720-1706 strong dimer
O-H bending 1440-1395 medium
conjugated acid C=O stretching 1710-1680 strong dimer
conjugated acid
C=O stretching 1800-1770 strong
halide
conjugated aldehyde C=O stretching 1710-1685 strong
conjugated alkene C=C stretching 1650-1600 medium
conjugated anhydride C=O stretching 1775 strong
conjugated ketone C=O stretching 1685-1666 strong
cyclic alkene C=C stretching 1650-1566 medium
cyclopentanone C=O stretching 1745 strong
ester C-O stretching 1210-1163 strong
esters C=O stretching 1750-1735 strong 6-membered lactone
fluoro compound C-F stretching 1400-1000 strong
halo compound C-Cl stretching 850-550 strong
C-Br stretching 690-515 strong
C-I stretching 600-500 strong
imine / oxime C=N stretching 1690-1640 medium
isocyanate N=C=O stretching 2275-2250 strong, broad
isothiocyanate N=C=S stretching 2140-1990 strong
ketene C=C=O stretching 2150
ketenimine C=C=N stretching 2000
monosubstituted C-H bending 750 ± 20 strong
nitrile CΞN stretching 2260-2222 weak
nitro compound N-O stretching 1550-1500 strong
none 3330-3250
none 1870-1540
none 1750
none 1720
none 1372-1290
none 1375
none 1370-1365
none 1200-1185
none 1204-1177
none 1195-1168
none 1170-1155
none 1165-1150 hydrate: 1230-1120
none 1160-1120
none 1075-1020
none 1075-1020
none 915-905
none 810 ± 20
none 780 ± 20
none (700 ± 20)
none (700 ± 20)
phenol O-H bending 1390-1310 medium
primary alcohol C-O stretching 1085-1050 strong
primary amide C=O stretching 1690 strong free (associated: 1650)
N-H stretching 3500 medium
secondary alcohol C-O stretching 1124-1087 strong
secondary amide C=O stretching 1680 strong free (associated: 1640)
secondary amine N-H stretching 3350-3310 medium
sulfate S=O stretching 1415-1380 strong
sulfonamide S=O stretching 1370-1335 strong
sulfonate S=O stretching 1372-1335 strong
sulfone S=O stretching 1350-1300 strong
sulfonic acid S=O stretching 1350-1342 strong anhydrous
sulfonyl chloride S=O stretching 1410-1380 strong
sulfoxide S=O stretching 1070-1030 strong
tertiary alcohol C-O stretching 1205-1124 strong
tertiary amide C=O stretching 1680 strong free (associated: 1630)
thiocyanate S-CΞN stretching 2175-2140 strong
thiol S-H stretching 2600-2550 weak
vinyl / phenyl ester C=O stretching 1770-1780 strong
vinyl ether C-O stretching 1225-1200 strong
α,β-unsaturated ester C=O stretching 1730-1715 strong or formates
α,β-unsaturated C=C stretching 1620-1610 strong
ketone
δ-lactam C=O stretching 1650 strong γ: 1750-1700 β: 1760-1730
δ-lactone C=O stretching 1750-1735 strong γ: 1770
1,2,3,4-
tetrasubstituted
1,2,3-trisubstituted C-H bending 780 ± 20 strong
C-H bending 880 ± 20 strong
1,2-disubstituted C-H bending 755 ± 20 strong
C-H bending 880 ± 20 strong
1,4-disubstituted or C-H bending 810 ± 20 strong
How to Read an IR Spectrum Table
To use an IR spectrum table, first find the frequency or compound in the first column, depending on which type of chart you are
using. Then find the corresponding values for absorption, appearance and other attributes. The value for absorption is usually in
cm-1.
Note that not all frequencies have a related compound.
You might also like
- Bảng phổ IRDocument5 pagesBảng phổ IRĐan KhanhNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum TableDocument18 pagesIR Spectrum Table노래하는?서효민100% (1)
- IR SpectrumDocument8 pagesIR SpectrumRizki100% (1)
- IR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range: Frequency Range Absorption (CM) Appearance Group Compound Class CommentsDocument7 pagesIR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range: Frequency Range Absorption (CM) Appearance Group Compound Class CommentsRyo CaesarNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum Table by Frequency RangeDocument5 pagesIR Spectrum Table by Frequency RangeDiego RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum Table and ChartDocument9 pagesIR Spectrum Table and ChartBožidarka TripkovićNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum Table & Chart - Sigma-AldrichDocument6 pagesIR Spectrum Table & Chart - Sigma-Aldrichnouman ashraf0% (1)
- IR spectroscopy guide for organic functional group analysisDocument24 pagesIR spectroscopy guide for organic functional group analysisakshantratwanNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum TableDocument17 pagesIR Spectrum TableAndres Felipe MNo ratings yet
- TechNote Hydrogen Peroxide Shelf LifeDocument4 pagesTechNote Hydrogen Peroxide Shelf LifeKumarNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Characteristic IR Absorption Peaks of Functional Groups Vibration Position (CM) Intensity Notes Alkanes AlkenesDocument6 pagesTable 1. Characteristic IR Absorption Peaks of Functional Groups Vibration Position (CM) Intensity Notes Alkanes AlkenesBag VatiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Redox TitrationsDocument50 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Redox TitrationsAshton Poovarasu Jhonson0% (1)
- Tutorial 4 Achem PDFDocument12 pagesTutorial 4 Achem PDFyassinroslanNo ratings yet
- Complexometry TitartaionDocument50 pagesComplexometry TitartaionHaritNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic AcidsDocument25 pagesCarboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic AcidsOhmark VeloriaNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument62 pagesDistillationKenil JaganiNo ratings yet
- InorganicDocument19 pagesInorganicah_16036566100% (1)
- Radox TitrationDocument24 pagesRadox TitrationPooja Shinde100% (1)
- AMINESDocument58 pagesAMINESHarsh Shah100% (1)
- Rhodoline 3000 Series PDFDocument2 pagesRhodoline 3000 Series PDFKurumi YamamotoNo ratings yet
- CHM580-Tutorial IR Dan RamanDocument6 pagesCHM580-Tutorial IR Dan RamanSuhailyShukri100% (1)
- Nomenclature Sheet 2021,13thDocument89 pagesNomenclature Sheet 2021,13thsane jha vlogsNo ratings yet
- Complexation and Precipitation Reactions and TitrationsDocument53 pagesComplexation and Precipitation Reactions and TitrationsDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Ninety Years of Using Azo Compounds of The Pyridine SeriesDocument5 pagesNinety Years of Using Azo Compounds of The Pyridine SeriesrajdewaanNo ratings yet
- Enol Dan EnolatDocument40 pagesEnol Dan EnolatRiyan KateeNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic TRB Syllabus of ChemistryDocument4 pagesPolytechnic TRB Syllabus of ChemistrysanjeevNo ratings yet
- SCH 206-Carboxylic Acids PDFDocument48 pagesSCH 206-Carboxylic Acids PDFShivani DamorNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument19 pagesLab Manualanon_467104036No ratings yet
- Alkaloids and TerpenoidsDocument24 pagesAlkaloids and TerpenoidskiNo ratings yet
- 78 Armohib Ci-28 e Ci-31 - Ficha TecnicaDocument13 pages78 Armohib Ci-28 e Ci-31 - Ficha TecnicaEnio Miguel Cano LimaNo ratings yet
- 7 Coordination CompoundsDocument329 pages7 Coordination CompoundsArka100% (1)
- Conrad-Limpach Quinoline Synthesis: A. General Description of The ReactionDocument5 pagesConrad-Limpach Quinoline Synthesis: A. General Description of The ReactionLe Tu0% (1)
- Unit 3 Introduction To Organic Molecules and Functional GroupsDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Introduction To Organic Molecules and Functional Groupsroxane mae villacoraNo ratings yet
- Ketones Can Be Converted Into Esters Via The Insertion of An Oxygen Atom Baeyer-Villiger OxidationDocument3 pagesKetones Can Be Converted Into Esters Via The Insertion of An Oxygen Atom Baeyer-Villiger OxidationDawit BirhanuNo ratings yet
- 09Document12 pages09ZenPhiNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument3 pagesAspirinMAYUR CHATURNo ratings yet
- Chemometrics for dummies explainedDocument29 pagesChemometrics for dummies explainedKalpesh MalooNo ratings yet
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument11 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformVardhan BunnuNo ratings yet
- Zinc and Lead..Document3 pagesZinc and Lead..Swapon RoyNo ratings yet
- IR&NMR ProblemsDocument43 pagesIR&NMR ProblemsAndrew Ronaldi Tandio100% (2)
- Diazonium Salts, Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts, Azo DyesDotsha Raheem100% (4)
- Isopoly and Heteropoly Acids and SaltsDocument39 pagesIsopoly and Heteropoly Acids and SaltsAhilya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Name Reaction 3569Document38 pagesName Reaction 3569Ashish AmbekarNo ratings yet
- Review in Azo Compounds and Its Biological Activity 2161 1009 1000169Document4 pagesReview in Azo Compounds and Its Biological Activity 2161 1009 1000169Christa-Gay CampbellNo ratings yet
- Types and Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument68 pagesTypes and Reactions of Alkyl HalidesAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- 5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFDocument16 pages5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFArinjayNo ratings yet
- CN102807528-PREPARATION METHOD OF 10-Methoxy IminostilbeneDocument4 pagesCN102807528-PREPARATION METHOD OF 10-Methoxy IminostilbeneDipti DodiyaNo ratings yet
- Qoiii I Class1Document25 pagesQoiii I Class1valentina viveros riosNo ratings yet
- Aepd VOX 1000: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesAepd VOX 1000: Technical Data SheetCoco HüniNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Synthetic ImportanceDocument28 pagesReactions of Synthetic ImportanceRx Nadeem ChhipaNo ratings yet
- Organic Structure Elucidation WorkbookDocument100 pagesOrganic Structure Elucidation WorkbookThái HàNo ratings yet
- Diazonium Salts Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts Azo DyesAnthony Basanta100% (1)
- Studies On Schiff Base Transition Metal ComplexesDocument10 pagesStudies On Schiff Base Transition Metal ComplexesDebraj Dhar PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- 40 Conductivity Meter LMCM 20 PDFDocument1 page40 Conductivity Meter LMCM 20 PDFrajap02No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument133 pagesClass 11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles and Techniqueschandrika1417fgNo ratings yet
- HydrolysisH PDFDocument12 pagesHydrolysisH PDFEuwan Tyrone PriasNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum Table: Quick Reference for Functional Group IdentificationDocument5 pagesIR Spectrum Table: Quick Reference for Functional Group IdentificationMike Dinh100% (3)
- IR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range: Frequency Range Absorption (CM) Appearance Group Compound Class CommentsDocument10 pagesIR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range: Frequency Range Absorption (CM) Appearance Group Compound Class CommentsNegru Laura MariaNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum TableDocument22 pagesIR Spectrum TableJanno MallariNo ratings yet
- Bảng tra cứu các dao động của nhóm chức trong Phổ IRDocument17 pagesBảng tra cứu các dao động của nhóm chức trong Phổ IRntrangthu1409No ratings yet
- D BlockDocument20 pagesD BlockRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance of Styrene Copolymers: BASF Plastics Key To Your SuccessDocument12 pagesChemical Resistance of Styrene Copolymers: BASF Plastics Key To Your SuccessLuisNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluids CROSS REFERENCES: Commercial ChemicalsDocument15 pagesDrilling Fluids CROSS REFERENCES: Commercial Chemicalsenderson cruzNo ratings yet
- Prof. Zahid Ahmad Siddiqi CarbonationDocument49 pagesProf. Zahid Ahmad Siddiqi Carbonationshahid aliNo ratings yet
- Hardness Removal: Lime-Soda Ash Softening ProcessDocument11 pagesHardness Removal: Lime-Soda Ash Softening ProcessRay RayNo ratings yet
- 77 Park Scientific LTD Polysciences Pricelist 2012 171Document68 pages77 Park Scientific LTD Polysciences Pricelist 2012 171juanescribdNo ratings yet
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- Formation of LimewaterDocument19 pagesFormation of LimewaterPraise HoNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity Data and Formulas for 49 Inorganic and Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesHeat Capacity Data and Formulas for 49 Inorganic and Organic CompoundsGabriel SugayaNo ratings yet
- IFARS generic drugsDocument5 pagesIFARS generic drugsOky Spinola IdroosNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Methods of Tests For Building LimesDocument5 pagesIndian Standard: Methods of Tests For Building LimesPramukh Test houseNo ratings yet
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Apotex Pharmachem Product ListDocument2 pagesApotex Pharmachem Product Listমোঃ এমদাদুল হকNo ratings yet
- Produk BB - Day Cream (Al-Bee Honey Beauty)Document1 pageProduk BB - Day Cream (Al-Bee Honey Beauty)ahmad baikuniNo ratings yet
- H 2 o 2Document3 pagesH 2 o 2Muzammal hoque mollahNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument31 pagesCarboxylic Acids and EstersleanneNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument18 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Etherssaksham05060% (1)
- Balea Advenski Kalendar 2023Document3 pagesBalea Advenski Kalendar 2023dzlara2007No ratings yet
- Problems With Solutions Week 3 For StudentsDocument5 pagesProblems With Solutions Week 3 For Students,No ratings yet
- HKKX Fo"K Kred Iz'U: Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument10 pagesHKKX Fo"K Kred Iz'U: Part - I: Subjective QuestionswanderedNo ratings yet
- Preparation of CrystalsDocument2 pagesPreparation of Crystalsjanu kandwalNo ratings yet
- CH 2 SCIENCE Class 10Document9 pagesCH 2 SCIENCE Class 10kulwinder Kaur brarNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN MUTASI BHP LABORATORIUM BULAN JANUARI 2019Document32 pagesLAPORAN MUTASI BHP LABORATORIUM BULAN JANUARI 2019tely rodjaNo ratings yet
- S. Testing of Raw Materials: Method-1 (Using 0.5N Hci and 0.25N Naoh Solutions)Document5 pagesS. Testing of Raw Materials: Method-1 (Using 0.5N Hci and 0.25N Naoh Solutions)Paramananda SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Upsi SKT1013 Diploma Science Experiment 4Document4 pagesLab Report Upsi SKT1013 Diploma Science Experiment 4Nur Wanyz SyazwanieNo ratings yet
- Techno-Economic Assessment About Sodium ChlorateDocument3 pagesTechno-Economic Assessment About Sodium ChlorateIntratec SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Formal Report, Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument4 pagesFormal Report, Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesVicente Romeo M Macatangay88% (8)
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Test BankDocument12 pagesAldehydes and Ketones: Test Bankhung nguyenNo ratings yet
- Resourceful Mock Ii Examinations 2017Document8 pagesResourceful Mock Ii Examinations 2017Baguma MichaelNo ratings yet