Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz 1-Genchem2-Set-A
Uploaded by
Benson Aplaon RoxasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz 1-Genchem2-Set-A
Uploaded by
Benson Aplaon RoxasCopyright:
Available Formats
SET B
SET B
General Chemistry 2
Quiz No. 1 General Chemistry 2
Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Quiz No. 1
Properties of Solutions Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
Properties of Solutions
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
WRITE YOUR ANSWERS IN ALL CAPITAL READ THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY.
LETTERS. WRITE YOUR ANSWERS IN ALL CAPITAL
USE BLACK OR BLUE PERMANENT BALLPEN LETTERS.
USE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR WITHOUT COVER USE BLACK OR BLUE PERMANENT BALLPEN
FOR COMPUTATIONS USE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR WITHOUT COVER
USE THE BACK OF ANSWER SHEET AS YOUR FOR COMPUTATIONS
SCRATCH. USE THE BACK OF ANSWER SHEET AS YOUR
SCRATCH.
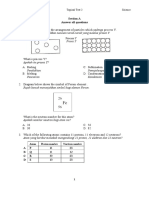
1. Which of the following can exhibit a dipole-dipole
interaction? 1. Which of the following can exhibit a dipole-dipole
A. Carbon dioxide C. Methane interaction?
B. Ethane D. Na in H2O A. Carbon dioxide C. Methane
B. Ethane D. Na in H2O
2. Which of the following forces of attraction can be considered
as intermolecular forces of attraction? 2. Which of the following forces of attraction can be considered
A. covalent bond C. ionic bond as intermolecular forces of attraction?
B. hydrogen bond D. metallic bond A. covalent bond C. ionic bond
B. hydrogen bond D. metallic bond
3. What do you think is the reason why some liquid molecules
are slower to flow? 3. What do you think is the reason why some liquid molecules
A. cohesion of water molecules C. viscosity are slower to flow?
B. hydrogen bonding D. surface tension A. cohesion of water molecules C. viscosity
B. hydrogen bonding D. surface tension
4. How many atoms are there in simple cubic cell?
A. 1 atom C. 2 atoms 4. How many atoms are there in simple cubic cell?
B. 1 ½ atoms D. 3 atoms A. 1 atom C. 2 atoms
B. 1 ½ atoms D. 3 atoms
5. Which of the following solid is a crystalline solid?
A. diamond C. graphite 5. Which of the following solid is a crystalline solid?
B. glass D. rubber A. diamond C. graphite
B. glass D. rubber
6. Which of the following mixture is NOT a solution?
A. alloy of Zn and Fe C. distilled water 6. Which of the following mixture is NOT a solution?
B. air D. mineral water A. alloy of Zn and Fe C. distilled water
B. air D. mineral water
7. What is the molarity of the solution if 20.0g of HNO3 was
dissolved in water, forming 500.mL of solution? 7. What is the molarity of the solution if 20.0g of HNO3 was
(MM HNO3 = 63.01 g/mol) dissolved in water, forming 500.mL of solution?
A. 0.0634M C. 0.63M (MM HNO3 = 63.01 g/mol)
B. 0.0.158M D. 0.634M A. 0.0634M C. 0.63M
B. 0.0.158M D. 0.634M
8. How many moles of sodium chloride is needed to react with
50mL of 4M silver nitrate? 8. How many moles of sodium chloride is needed to react with
A. 0.5 mole C. 2 moles 50mL of 4M silver nitrate?
B. 1 mole D. 4 moles A. 0.5 mole C. 2 moles
B. 1 mole D. 4 moles
9. How much magnesium hydroxide, in grams, are needed to
neutralize 1 L of 10.0M nitric acid? (MM Mg(OH)2=58.33g/mol) 9. How much magnesium hydroxide, in grams, are needed to
A. 2.91g C. 1110g neutralize 1 L of 10.0M nitric acid? (MM Mg(OH)2=58.33g/mol)
B. 291g D. 1116g A. 2.91g C. 1110g
B. 291g D. 1116g
10. What would be the change in boiling point of water when
20.0g of sucrose is dissolved in 100.g of water? 10. What would be the change in boiling point of water when
(MM sucrose=342.3 g/mol) (kb = 0.52oC/m) 20.0g of sucrose is dissolved in 100.g of water?
A. 2.53x10-4 oC C. 100 oC (MM sucrose=342.3 g/mol) (kb = 0.52oC/m)
B. 3.04x10-4 oC D. 101 oC A. 2.53x10-4 oC C. 100 oC
-4 o
B. 3.04x10 C D. 101 oC
11-15. Problem solving
How many liters of 5M nitric acid is needed to neutralize 7M of 11-15. Problem solving
sodium hydroxide? How many liters of 5M nitric acid is needed to neutralize 7M of
sodium hydroxide?
1 point – given
1 point – balanced equation 1 point – given
1.5 points – solution 1 point – balanced equation
1.5 points – correct answer 1.5 points – solution
1.5 points – correct answer
You might also like
- ChE Day 1 Mock Board 5.0Document6 pagesChE Day 1 Mock Board 5.0zzrot1No ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science Major 1 PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science Major 1 PDFOvelia KayuzakiNo ratings yet
- AKU EB - Chemistry - XI - Paper I - 2010 - MayDocument8 pagesAKU EB - Chemistry - XI - Paper I - 2010 - MayZulkaif IrshadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Exam Drill IDocument6 pagesChemistry - Exam Drill IJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Choose the Best Answer for Chemistry ProblemsDocument1 pageChoose the Best Answer for Chemistry ProblemsMarc Liam LuNo ratings yet
- S6 Chem Eng1Document35 pagesS6 Chem Eng1LearningNo ratings yet
- SCH 3U Final Exam: Practice: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesSCH 3U Final Exam: Practice: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Question소피아No ratings yet
- Chemistry Review For Ee, Me, & EceDocument9 pagesChemistry Review For Ee, Me, & Ecejasiel pascuaNo ratings yet
- Gradeup Practice Questions on Science and PhysicsDocument7 pagesGradeup Practice Questions on Science and PhysicsSONU DYADENo ratings yet
- May 2020 Chem Engg Refresher 3Document2 pagesMay 2020 Chem Engg Refresher 3Master JaguarNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Chem Tech ReviewerDocument10 pagesPart 1 Chem Tech ReviewerSandra EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Mock Exam PCPDocument10 pagesProblem Set Mock Exam PCPJeremy Allan Bartolo0% (1)
- Mastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11Document3 pagesMastery Test in Physical Science - Gr.11kert mendozaNo ratings yet
- Section A Answer All Questions: 1511 Topical Test 2 ScienceDocument13 pagesSection A Answer All Questions: 1511 Topical Test 2 ScienceYong Chee KiengNo ratings yet
- CH 12 and 13 Study GuideDocument9 pagesCH 12 and 13 Study GuideLamees El BehearyNo ratings yet
- Section 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizer: CE: Section 7 MC P.1Document3 pagesSection 7 Nitrogenous Fertilizer: CE: Section 7 MC P.1Kai Keung ChiuNo ratings yet
- Day1 CompiledDocument39 pagesDay1 CompiledWinsletJoyDauagNo ratings yet
- Practice-Problems-7_ChemistryDocument1 pagePractice-Problems-7_ChemistryJayve BasconNo ratings yet
- ECE198L Questionaire SALEDocument120 pagesECE198L Questionaire SALEMiloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (1) RevisionDocument10 pagesChemistry (1) RevisionJesse ChimnecheremNo ratings yet
- 10th Biology - Life ProcessesDocument8 pages10th Biology - Life ProcessesShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument24 pagesChemistry Reviewerchristy janioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science MajorDocument6 pagesChemistry Practice Test With Answer For Physical Science MajorJesmar Quirino TutingNo ratings yet
- 0 044422 Revisionsheetwithak10satDocument11 pages0 044422 Revisionsheetwithak10sathajalisalem4No ratings yet
- Chem PDocument162 pagesChem PAduchelab AdamsonuniversityNo ratings yet
- MSU Chemistry Review for Class of 2012Document3 pagesMSU Chemistry Review for Class of 2012Mahater SalicNo ratings yet
- Preboard Exam Day1 SET ADocument12 pagesPreboard Exam Day1 SET AJeanne Cortez0% (1)
- Matematika-Fisika dan Kimia Ujian AkhirDocument4 pagesMatematika-Fisika dan Kimia Ujian AkhirArda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- SPT11 PDFDocument2 pagesSPT11 PDFLeeann LeeNo ratings yet
- 10-PART I - MULTIPLE CHOICE (30 Multiple Choice Questions. Each Multiple Choice Question Is Worth 2 Points)Document7 pages10-PART I - MULTIPLE CHOICE (30 Multiple Choice Questions. Each Multiple Choice Question Is Worth 2 Points)Nesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- 2CA - S5 - final - term - exam - 2018 - eng - 複本Document31 pages2CA - S5 - final - term - exam - 2018 - eng - 複本connieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2pointsDocument4 pagesChemistry 2pointsjovanniNo ratings yet
- Jamb-Chemistry-Past-Questions-11-15 UnibenpgDocument55 pagesJamb-Chemistry-Past-Questions-11-15 UnibenpgEhigie promiseNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - MockboardsDocument12 pagesDay 1 - MockboardsKhiara Claudine Espinosa100% (1)
- Chemistry 0715 MCG (6) - 1 PDFDocument7 pagesChemistry 0715 MCG (6) - 1 PDFTalatouremi FruNo ratings yet
- BEED - SCIENCE Biology, Chemistry, Earth Sci EtcDocument11 pagesBEED - SCIENCE Biology, Chemistry, Earth Sci EtcAnastasia Enriquez0% (1)
- QC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1ADocument12 pagesQC - 2019-20 - Mock - S6 - Chem 1AOof GucciNo ratings yet
- Chem DiagnosticDocument3 pagesChem DiagnosticHeather Nicole BelinoNo ratings yet
- Feb 2023 Master Plumber Refresher Chemistry 3Document2 pagesFeb 2023 Master Plumber Refresher Chemistry 3Master JaguarNo ratings yet
- Jamb Chemistry Past QuestionsDocument84 pagesJamb Chemistry Past QuestionsOlawunmi bosola80% (5)
- Final HSSC-I Chemistry Model Paper MergedDocument10 pagesFinal HSSC-I Chemistry Model Paper MergeddasddaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations CASE BASED MCQsDocument43 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations CASE BASED MCQsVikesh KansalNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA AFS BEGUMPET PERIODIC TEST - 1 CHEMISTRY CLASS 12Document2 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA AFS BEGUMPET PERIODIC TEST - 1 CHEMISTRY CLASS 12KhushiNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Chemistry Learning Cycle 1 AssessmentDocument11 pagesYear 12 Chemistry Learning Cycle 1 AssessmentjimNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Boards Practice ExamDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry Boards Practice ExamKriel MuñezNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Part 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhysical Science Part 2 Reviewerjerick de veraNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE ReviewerDocument65 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE ReviewerjaywarvenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers Set ADocument5 pagesChemistry For Engineers Set AMark Jecel RapirNo ratings yet
- SASE Chemistry W - Key Ans.Document4 pagesSASE Chemistry W - Key Ans.Hiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Chemistry Remedial ExamDocument4 pagesSenior High School Chemistry Remedial ExamOliric FabiolasNo ratings yet
- Mini Practice Exam A: PAPER 1: Do Not Use A Calculator or The Data Booklet. Allow 23 Minutes. 1Document10 pagesMini Practice Exam A: PAPER 1: Do Not Use A Calculator or The Data Booklet. Allow 23 Minutes. 1nadia sykesNo ratings yet
- Ap Ipe 2023 3Document11 pagesAp Ipe 2023 3asaabhi9059No ratings yet
- DiagnosticsDocument8 pagesDiagnosticsNORBERTUS KRISNU PRABOWONo ratings yet
- 1Q Gen Chem IDocument3 pages1Q Gen Chem Ijessica ignacioNo ratings yet
- 2024 Mock 2 Science 1Document3 pages2024 Mock 2 Science 1Ebenezer ArhinNo ratings yet
- Progress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6From EverandProgress in Reaction Kinetics: Volume 6K. R. JenningsNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms 1982: An annual survey covering the literature dated December 1981 through November 1982From EverandOrganic Reaction Mechanisms 1982: An annual survey covering the literature dated December 1981 through November 1982A. C. KnipeNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryFrom EverandThe Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Brchembase LRDocument4 pagesBrchembase LRRavindra PawarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering HoustonDocument603 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering HoustonRino ApicellaNo ratings yet
- Industrial FRP Tank Water Media FilterDocument4 pagesIndustrial FRP Tank Water Media FilterT Nagaraju AF VetaranNo ratings yet
- GED Physics Note4 (Electricity and Magnetism)Document6 pagesGED Physics Note4 (Electricity and Magnetism)Shahadat Hussain ParvezNo ratings yet
- Module3 MCQDocument2 pagesModule3 MCQLukkuman ANo ratings yet
- Solution To Problem 4.5, Mandl-ShawDocument4 pagesSolution To Problem 4.5, Mandl-ShawMikael Souto MaiorNo ratings yet
- Total Internal Reflection at a Single Curved SurfaceDocument30 pagesTotal Internal Reflection at a Single Curved SurfaceIlakkiyaa KPNo ratings yet
- University of San CarlosDocument3 pagesUniversity of San CarlosJade Lynn MagsambolNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide: Pressure - Enthalpy Diagram: R 90 0 Sity 7 00 KG/MDocument1 pageCarbon Dioxide: Pressure - Enthalpy Diagram: R 90 0 Sity 7 00 KG/MJackNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Price For Water Treatment Chemicals by The Following 3 VendorDocument1 pageComparison of Price For Water Treatment Chemicals by The Following 3 VendorAK TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Slug Catcher Conceptual DesignDocument8 pagesSlug Catcher Conceptual Designfanziskus100% (1)
- Anisotropy Measurement For Architectural Glass - GPD 2019Document3 pagesAnisotropy Measurement For Architectural Glass - GPD 2019Louis MoreauNo ratings yet
- Rheology Study of LiquidsDocument9 pagesRheology Study of LiquidsQi YingNo ratings yet
- MalachiteDocument2 pagesMalachiteAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Moisture Sorption IsothermsDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Moisture Sorption IsothermsKumar NareshNo ratings yet
- Blood Brain BarrierDocument25 pagesBlood Brain BarrierAdlai PappyNo ratings yet
- TH-L32C10R2: Model NoDocument121 pagesTH-L32C10R2: Model Nozerson13No ratings yet
- Blast furnace burden calculation methods and parametersDocument2 pagesBlast furnace burden calculation methods and parametersJaymart Hernandez Mojica75% (4)
- Lidocaine Base and Hydrochloride: Groningsson, Lindgren, Lundberg, SandbergDocument37 pagesLidocaine Base and Hydrochloride: Groningsson, Lindgren, Lundberg, SandbergtikaNo ratings yet
- IScience 6-Teachers ManualDocument98 pagesIScience 6-Teachers ManualAngelica TalaveraNo ratings yet
- On Scalable Analytical Models For Heap Leaching PDFDocument6 pagesOn Scalable Analytical Models For Heap Leaching PDFInfernuzNo ratings yet
- Azo DyesDocument55 pagesAzo Dyessmit18950% (2)
- Elastomers: Dr. Dmitri KopeliovichDocument10 pagesElastomers: Dr. Dmitri KopeliovichBara Giat PrakarsaNo ratings yet
- Vapor Phase Soldering TechniqueDocument5 pagesVapor Phase Soldering TechniquealisakeerpkNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument31 pagesPeriodic TrendsAndrew Bondad100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument396 pagesPhysicsIndroneil KanungoNo ratings yet
- 3.7.12. Metal Matrix Composites: Matrices and Processing: T.W.ClyneDocument14 pages3.7.12. Metal Matrix Composites: Matrices and Processing: T.W.ClyneVizay KumarNo ratings yet
- AC Transformer LectureDocument4 pagesAC Transformer LectureDE VERA, KENNETH GABRIEL D.No ratings yet
- Crude Oil Assay Database - Crude Oil Data Properties and Definitions - KnovelDocument6 pagesCrude Oil Assay Database - Crude Oil Data Properties and Definitions - KnovelValeanu ErmilNo ratings yet
- Wae Oarp WebDocument8 pagesWae Oarp WebRoberto Leon MendezNo ratings yet