Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brainstem and Cerebellum
Uploaded by
wifol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
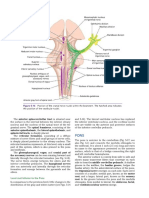
17 views3 pagesThe midbrain, pons, and medulla are parts of the brainstem. [1] The midbrain contains structures involved in vision, hearing, motor control, arousal, and pleasure/reward pathways. [2] The pons contains fiber tracts connecting the brain and cerebellum and nuclei that control eye movements, hearing, facial muscles, and posture. [3] The medulla contains fiber tracts to and from the cerebellum and spinal cord and nuclei that control breathing, vomiting, and other vital functions.
Original Description:
neuroanatomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe midbrain, pons, and medulla are parts of the brainstem. [1] The midbrain contains structures involved in vision, hearing, motor control, arousal, and pleasure/reward pathways. [2] The pons contains fiber tracts connecting the brain and cerebellum and nuclei that control eye movements, hearing, facial muscles, and posture. [3] The medulla contains fiber tracts to and from the cerebellum and spinal cord and nuclei that control breathing, vomiting, and other vital functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesBrainstem and Cerebellum
Uploaded by
wifolThe midbrain, pons, and medulla are parts of the brainstem. [1] The midbrain contains structures involved in vision, hearing, motor control, arousal, and pleasure/reward pathways. [2] The pons contains fiber tracts connecting the brain and cerebellum and nuclei that control eye movements, hearing, facial muscles, and posture. [3] The medulla contains fiber tracts to and from the cerebellum and spinal cord and nuclei that control breathing, vomiting, and other vital functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
BRAINSTEM
MIDBRAIN PONS MEDULLA
TECTUM: TECTUM NO TECTUM
- quadrigeminal plate (coprora quadrigemina) - not very prominent since 4 ventricle occupy a large area
th
- roof entirely formed by 4th ventricle and cerebellum (on top of 4th ventricle)
o superior colliculi (visual pathway) - superior medullary velum seen
o inferior colliculi (auditory pathway)
à (lateral lemniscus fibers à inferior colliculi à medial geniculate
nucleus/body of thalamus)
- Pretectal nuclei
o gets afferent fibers retina and gives efferent fibers to Edinger-Westphal Nuclei
o pupillary constriction
§ (lightà retinaà afferent fibers à pretectal nuclei à efferent fibers
à Edinger-Westphal Nuclei)
§ do not pass through occipital cortex
- Quadrigeminal Plate: reflex arcs
o auditory stimulus à inferior colliculi à superior colliculi
o makes you look towards (a sound) or make you close your eyes (from visual
stimulus) and look away
o efferent arms
§ tectospinal tract (cervical muscles) (aversion of head)
§ tectonuclear tract (orbicularis oculi) (eye closure/blink reflex)
- Periaqueductal gray
o surrounds the aqueduct
o descending autonomic tracts
à lesion: defensive behavior, reproductive behavior, aggression
o Endorphin-producing cells (sensitive to opioids for pain control)
o Micturition, penile erection
TEGMENTUM TEGMENTUM - Ascending Tracts
- Red nucleus (RN) - Medial lemniscus o Nucleus Cuneatus, nucleus gracilis, medial lemniscus
o ---à inferior olives - spinothalamic tract o Spinothalamic tract
o afferent input: emboliform and dentate nuclei - CN V, VI, VII, VIII nuclei o Spinocerebellar tract (A & P)
o efferent input: rubrospinal and ruboreticular tracts - PPRF, MLF - Descending Tracts : CST, Pyramids and decussation
o dentate-rubro-thalamic reflex: body posture - Lateral lemniscus – auditory pathway - Nuclei
(dentate nuclei à red nucleus à thalamus) - Superior olivary nucleus (pontomedullary junction) o CN IX, X, XI, XII nuclei
o rubrospinal tract - Central tegmental tract (RN---inferior olivary nucleus) o CN V spinal nucleus
§ flexion of upper extremities - Locus Coeruleus o nucleus of tractus solitarius
§ differentiate decorticate and decerebrate position o rostral pons to caudal midbrain o nucleus ambiguous
o Mollaret’s triangle: o Norepinephrine o olivary nuclear complex
§ red nucleus (midbrain) o -à entire CNS § inferior olive
§ inferior olive (medulla) o activated during stress • Sheet of gray matter
§ dentate nucleus (cerebellum) • afferent (via central tegmental tract): red
§ lesions: palatal myoclonus (involuntary jerky movements of soft nucleus, striatum, PAG, RF, cortex
palate) à popping in the ear • efferent: olivocerebellar tract
- Medial lemniscus [inferior cerebral peduncle à cerebellum
- Spinothalamic tract à neocerebellar cortex]
- CN V mesencephalic nucleus (sensory nucleus) (coordination of voluntary movement)
- CN III and IV nuclei § accessory olive – maintenance of balance
- Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF): gaze pathway - Area Postrema
(PPRF à MLF à contralateral CN III/ same side CN VIà medial rectus) o floor of the caudal 4th ventricle
- Substantia Nigra (SN): large motor nucleus o lacks blood brain barrier
o dopamine production o stimulation induced vomiting – emesis center
o Pars compacta- dorsal à melanin
o Pars reticulata – ventral à iron
o contains pirmented and non pigmented neurons
o movement disorders: Parkinson’s ALS, Huntington’s
- Reticular formation
o connections: SC, CN, Cerebellum, Cerebral Cortex
o part of ascending reticular activating system (ARAS)
à arousal/ wakefulness
- Ventral tegmental area
o rostral midbrain
o dopaminergic innervation
o activated by pleasure (reward, fear pathway)
BASE/ BASIS PONTIS BASE/ BASIS PONTIS
- Cerebral peduncles/ Crus cerebri - Corticospinal Tract (scattered): voluntary movement
o Corticospinal tract - Pontine nuclei: Corticopontocerebellar pathway
o Corticobulbar tract – facial muscle innervation o regulates smooth and precise coordination of voluntary
o Corticopontine fibers movement (corticospinal tract makes the movement itself)
- Raphe nuclei
o serotonin
o arousal, sleep-wake cycle, pain control
MIDBRAIN PONS MEDULLA
BLOOD SUPPLY: BLOOD SUPPLY: BLOOD SUPPLY:
• Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) • Basilar Artery • Vertebral artery (VA)
- Posterior choridal artery - Paramedian branches (medial area) - Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA)
- Interpeduncular branches - Short circumferential branches o posterolateral portion
• Others: Superior cerebellar artery (SCA), Pcomm - long circumferential branches (posterior portion) o infarct will NOT cause weakness on muscles supplied
• Landmark: CN III nuclei in the middle by corticospinal tract (bc corticospinal tract is located
medially and supplied by anterior spinal artery)
- Others: anterior spinal artery, vertebral spinal artery, vertebral
paramedian artery
o medial portions of caudal medulla
SYNDROMES:
CAUSE (area of AFFECTED AREA CLINICAL FEATURES
infarct/occlusion/embolism)
Wallenburg (Dorsolateral Medullary PICA or Vertebral artery lateral medullary areas
Syndrome/ Lateral Medullary Syndrome) • horner syndrome, nystagmus, dysarthia, dysphagia
• analgesia and thermanesthesia
• ataxia and aysngergia
Medial Medullary Syndrome (Dejerine Vertebral artery or paramedian paramedian areas • hypoglossal palsy
Syndrome) branches of Basilar artery CN XII (hypoglossal) • nonspastic paralysis
• impairment of touch, position, and vibration sense (medial lemniscus,
contralateral)
Locked – In Syndrome Ventral Pons Bilateral Corticosponal absent motor function
Corticobulbar tracts intact sensation and cognition
Cerebellopontine Angle Syndrome no definitive cause CN VII, VIII, cerebellum Unilateral hearing loss
high frequency HL
decreased corneal reflex
facial weakness
Parinaud’s Syndrome Pineal region tumors Dorsal midbrain Impairment of vertical gaze
hydrocephalus Pretectal area large, irregular pupils
eyelid abnormalities (bilateral lid contraction to bilateral ptosis)
impaired convergence
Weber Syndrome Interpeduncular branches of PCA or Corticopontine tract Supranuclear facial and hypoglossal nerve palsies
Posterior choroidal artery Substantia nigra oculomotor nerve palsy
CN VII, IX-XII spastic paralysis
rigidity, parkinsonism, rest tremor
You might also like
- Neuroanatomy Brainstem SummaryDocument11 pagesNeuroanatomy Brainstem SummaryStd Dlshsi100% (2)
- Abducent Nerve: DR. Nirmal Jayadev Final Year PG Student (MS Ophthalmology) MKCG Medical College Berhampur OdishaDocument58 pagesAbducent Nerve: DR. Nirmal Jayadev Final Year PG Student (MS Ophthalmology) MKCG Medical College Berhampur OdishaZeptalanNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience II: CerebellumDocument13 pagesNeuroscience II: CerebellumTrina CardonaNo ratings yet
- The MeningesDocument23 pagesThe Meningesanjhulz0% (1)
- Neuroana 11 Brainstem Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesNeuroana 11 Brainstem Cranial Nervest4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- The Rhombencephalon or Hind BrainDocument108 pagesThe Rhombencephalon or Hind BrainReagan MwesigwaNo ratings yet
- Nervioso First AidDocument62 pagesNervioso First Aidadrenalina1238No ratings yet
- 2-Long Ascending TractsDocument27 pages2-Long Ascending Tractsyaram3512No ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Structure and FunctionsDocument23 pagesMedulla Oblongata Structure and FunctionsHassan Ilyas100% (1)
- netterDocument2 pagesnetternclov.00No ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument50 pagesSpinal CordReem 10No ratings yet
- 4bi 1le Active RecallDocument4 pages4bi 1le Active RecallAlexandryaHaleNo ratings yet
- Active Recall Neuroanatomy 4B1LEDocument8 pagesActive Recall Neuroanatomy 4B1LEAlexandryaHaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology MnemonicsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology MnemonicsLalajimNo ratings yet
- PonsDocument18 pagesPonsDr.Saber - Ar - RaffiNo ratings yet
- Pons and MidbrainDocument11 pagesPons and MidbrainhusshamNo ratings yet
- (REV) Neuroanatomy and NeurophysiologyDocument8 pages(REV) Neuroanatomy and NeurophysiologyReichelleNo ratings yet
- 11-CNS & BrainDocument6 pages11-CNS & Brainapi-3757921No ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument40 pagesMedulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd Gradetuhin100% (1)
- ANAPHY SpinalCord PeripheralNervousSystemDocument7 pagesANAPHY SpinalCord PeripheralNervousSystemAysha AishaNo ratings yet
- PonsDocument61 pagesPonsAyberk ZorluNo ratings yet
- Table of Tracts NCSDocument3 pagesTable of Tracts NCSLuis Manuel Vegas IsasiNo ratings yet
- 09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFDocument24 pages09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFVidya BalaNo ratings yet
- Development of the pig embryo anterior regionsDocument11 pagesDevelopment of the pig embryo anterior regionsvada_soNo ratings yet
- The 2 Lecture Today: Structure and Connections of The Basal Ganglia. Motor Pathways Arising From The Brain StemDocument34 pagesThe 2 Lecture Today: Structure and Connections of The Basal Ganglia. Motor Pathways Arising From The Brain StemJimach Bol WieNo ratings yet
- Imaging the Brachial Plexus: Anatomy, Pathology, and TechniquesDocument67 pagesImaging the Brachial Plexus: Anatomy, Pathology, and TechniquesChrista Levina DaniswaraNo ratings yet
- Snell's Clinical Neuroanatomy Chapter PonsDocument6 pagesSnell's Clinical Neuroanatomy Chapter PonstsidazizyNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument62 pagesCerebellumadelina.jianu9991No ratings yet
- Pons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy LectureDocument47 pagesPons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy LecturePlutokidNo ratings yet
- 083 - Neurology Physiology) Pons Anatomy & FunctionDocument6 pages083 - Neurology Physiology) Pons Anatomy & Functionice.bear.wolfoNo ratings yet
- 03 Meninges, Neuron, NMJ, CSF (Students Copy)Document2 pages03 Meninges, Neuron, NMJ, CSF (Students Copy)Hillary DangananNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument40 pagesBasal GangliaEnkefalos KardiaNo ratings yet
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieNo ratings yet
- NEUROSCIENCEDocument4 pagesNEUROSCIENCEArijeet77No ratings yet
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- 2.6. Cranium Contents and Paranasal Sinuses-1Document16 pages2.6. Cranium Contents and Paranasal Sinuses-1spoelstratjibbeNo ratings yet
- UERM GROSS Spinal Cord and BrainstemDocument44 pagesUERM GROSS Spinal Cord and Brainstemroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- Spinal Nerves and DermatomesDocument8 pagesSpinal Nerves and DermatomesNoreen Hannah GabrielNo ratings yet
- Brain & Its Surrounding Structures: Anatomi Blok 1.5Document6 pagesBrain & Its Surrounding Structures: Anatomi Blok 1.5RizkiWikantyasningNo ratings yet
- Basal Ganglia and ThalamusDocument5 pagesBasal Ganglia and Thalamust4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- TITLE Introduction to the Brainstem AnatomyDocument4 pagesTITLE Introduction to the Brainstem AnatomyANGELI SIAOTONGNo ratings yet
- High-Yield Neurology and Senses ReviewDocument72 pagesHigh-Yield Neurology and Senses ReviewMahmoud Abu MayalehNo ratings yet
- Cranil ForaminaeDocument9 pagesCranil Foraminaemero1983No ratings yet
- Histology of The Spinal Cord, Nerve, Sensory and Vegetative GangliaDocument23 pagesHistology of The Spinal Cord, Nerve, Sensory and Vegetative Gangliashmirtb100% (2)
- Perception and Coordination Module ADocument3 pagesPerception and Coordination Module ARosmary100% (1)
- 2 01 Peripheral Nerves and Spinal Cord EDITED Dra DoqueniaDocument31 pages2 01 Peripheral Nerves and Spinal Cord EDITED Dra DoqueniaCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Simplified NotesDocument5 pagesBrainstem Simplified Noteslailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- The Brainstem: Ot1024: NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesThe Brainstem: Ot1024: NeuroscienceReyna MedinaNo ratings yet
- Di Encephalo NDocument6 pagesDi Encephalo NbolivarsefNo ratings yet
- My Encephalo NDocument2 pagesMy Encephalo NC1 - RAZALAN NICKA JOYNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-1Document46 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-1a-tldNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesJade ElevazoNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument5 pagesCEREBELLUMAIRA BIANCA B. MANALANGNo ratings yet
- Anatomy No.2Document71 pagesAnatomy No.2hendalzeer02No ratings yet
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Frog EmbryoCHRISTIAN LOYD ARUPENo ratings yet
- Introduction To Neuroanatomy: - Structure-Function Relationships - Non-Invasive Brain ImagingDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Neuroanatomy: - Structure-Function Relationships - Non-Invasive Brain ImagingriskadesmaraniNo ratings yet
- Brainstem CN1-6Document31 pagesBrainstem CN1-6Dhanen Dran100% (1)
- Echidnas: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyFrom EverandEchidnas: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNo ratings yet
- Feels Like It Only Go BackwardsDocument1 pageFeels Like It Only Go BackwardswifolNo ratings yet
- July grammar updates capitalization punctuationDocument1 pageJuly grammar updates capitalization punctuationwifolNo ratings yet
- Detect Cancer Gene Mutations in Family with 40-Character TitleDocument5 pagesDetect Cancer Gene Mutations in Family with 40-Character TitlewifolNo ratings yet
- Higher Cortical Functions Multimodal Association AreasDocument1 pageHigher Cortical Functions Multimodal Association AreaswifolNo ratings yet
- KOENIG Diagnostic Imaging Oral and Maxillofacial PDFDocument1,344 pagesKOENIG Diagnostic Imaging Oral and Maxillofacial PDFMarcos Vasconcelos Costa100% (1)
- Surface Anatomy and Other LandmarksDocument7 pagesSurface Anatomy and Other LandmarksoristoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DrugsDocument6 pagesThyroid DrugsThe Real UploaderNo ratings yet
- Neuroscienze Affettive (Ripristinato Automaticamente)Document100 pagesNeuroscienze Affettive (Ripristinato Automaticamente)Rodolfo RizziNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29No ratings yet
- Meninges وهدانDocument10 pagesMeninges وهدانوسيم جمال مياسNo ratings yet
- Web of CautionDocument1 pageWeb of Cautiontiara suciNo ratings yet
- Glomus TumourDocument50 pagesGlomus TumourPratibha Goswami100% (1)
- Anterior Triangle of NeckDocument28 pagesAnterior Triangle of Neckapi-199163990% (1)
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDocument36 pagesAnchorage in OrthodonticsHARSHANo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Treatment OptionsDocument51 pagesNasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Treatment OptionsAbhishek ShahNo ratings yet
- Q2 G3 Science M1Document40 pagesQ2 G3 Science M1Maricar AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Perilymph FistulaDocument4 pagesPerilymph FistulavieeveeNo ratings yet
- Facial Trauma PDFDocument3 pagesFacial Trauma PDFHendry JohannesNo ratings yet
- Goals of the Special Senses Lab ActivitiesDocument14 pagesGoals of the Special Senses Lab ActivitiessylNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Head and NeckDocument25 pagesAnatomy Head and NeckMARISOL GALLEGO DUQUENo ratings yet
- Eye Movement AbnormalitiesDocument34 pagesEye Movement AbnormalitiesSeshagiri DoniparthiNo ratings yet
- Modul Kelas 1 - Semester 2 - Chapter II - Part of BodyDocument12 pagesModul Kelas 1 - Semester 2 - Chapter II - Part of BodyHiralius100% (2)
- The Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahDocument24 pagesThe Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahAzhar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Neurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyDocument1 pageNeurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyRavinaAhujaNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument48 pagesHuman EyeAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Hidung Dan Sinus ParanasalisDocument16 pagesHidung Dan Sinus ParanasalisChearin Dhea SNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathologic Features of Brain Herniation in AnimalsDocument7 pagesClinicopathologic Features of Brain Herniation in AnimalsDesNo ratings yet
- Beli 1 Beli 2 Harga Special ! + Free Member/ Diskon 50% ProdukDocument7 pagesBeli 1 Beli 2 Harga Special ! + Free Member/ Diskon 50% ProdukirtantikaNo ratings yet
- Asian Face Lift With The Composite Face Lift.10Document11 pagesAsian Face Lift With The Composite Face Lift.10Fabian OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Olfaction As A Marker For Depression - SpringerLinkDocument25 pagesOlfaction As A Marker For Depression - SpringerLinkAmanda HoffmannNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Schacter - The Future of Memory Remembering, Imagining, and The Brain - Schacter Et Al PDFDocument18 pages2012 - Schacter - The Future of Memory Remembering, Imagining, and The Brain - Schacter Et Al PDFAna Maria RomeroNo ratings yet
- Effects of Strokes on the BrainDocument3 pagesEffects of Strokes on the BrainDiana LuciaNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS Bing Ganjil (Human Body & Animals)Document3 pagesSoal PTS Bing Ganjil (Human Body & Animals)hamdaniyusuf20No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve ExaminationDocument3 pagesCranial Nerve ExaminationtomodachiNo ratings yet