Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Ey Chua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesscience reviewer
Original Title
Respiratory
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentscience reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Ey Chuascience reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
APEC SCHOOLS
1st Quarter S.Y. 2019 – 2020
SCIENCE 9
LESSON HANDOUT #3: COORDINATED FUNCTION – THE HUMAN
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Learning Objectives 4. Bronchi it is the two tubes that carries the
Describe the mechanism of respiratory air into the lungs. Each bronchus branches
system repeatedly, giving rise to the bronchioles.
Determine the parts and functions of the 5. Bronchioles are very fine tubes. Each
respiratory system bronchiole ends in a cluster of air sacs or
Enumerate common respiratory diseases alveoli.
that are caused by tobacco and cigarette 6. Air sacs or Alveoli – It is where gas
smoking exchange happened. It is made-up of tiny
blood vessels that allows air to be diffused
into the blood.
Respiration – important life process that allows
the gas exchange in organisms MECHANISM OF BREATHING
Breathing – it is a part of the gas exchange
Respire – means to breathe in and out to allow process. It refers to the contraction of the
gas exchange. muscles and the movement of the ribs which
helps in the moving in and out of air in the lungs.
Gas exchange – the exchange of gases
between an organism and the environment. Two phases:
Organisms have different ways to perform gas Inhalation – Taking in of air (oxygen)
exchange with the environment. Exhalation – Giving out of air (carbon dioxide)
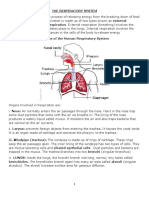
PARTS OF THE HUMAN RESPIRATORY Parts Involved in the Breathing Mechanism:
SYSTEM
1. Air Passages – it is composed of the following: Chest Cavity - This is composed of 12 pairs of
a.1 External Nostrils ribs, wherein 10 of which is attached to the
a.2 Nasal Passages backbone (at the back) to the sternum (in front).
a.3 Pharynx Between each rib are muscles we call as
a.4 Larynx intercostal muscles (external and internal) that
a.5 Trachea contract and relaxes when we breathe. The ribs
a.6 Bronchi and the muscles caged the lungs and the heart
a.7 Bronchioles and provides protection to both the lungs and the
a.8 Alveoli heart.
2. Lungs
3. Thoracic cavity (Chest Cavity), Ribs and Diaphragm – It is an elastic tissue that
Diaphragm separates the chest cavity to the abdomen. It
controls the volume of air inside the lungs.
PATH OF AIR INTO THE LUNGS
1. External Nostrils is where the air usually Components Inhalation Exhalation
enters your body. It leads to the nasal
Diaphragm Contracts Relaxes and
passages lined with mucus that makes the
and Flattens Arches
inhaled air warm and moist.
2. Pharynx or also known as the throat. upwards
3. Trachea or also known as windpipe. It is a Intercostal External – External –
made up of rings of C-shaped cartilages that Muscles contracts relaxes
is lined with mucus-secreting cells and cilia Internal - Intercostal -
(small hairs) that dust-trapped. relaxes contracts
Ribs Moves Moves RESPIRATORY DISEASES
upwards and downwards Prolonged exposure to chemicals present in
outwards and inwards tobacco smoke may cause the following
Lungs Expands Compressed common diseases:
Volume of Air Increases Decreases 1. Chronic Bronchitis
Atmospheric Higher Lower (Allows It is characterized by having inflamed
Pressure (Allows air to air to move bronchi, excessive mucus, cilia are
paralyzed and cannot remove dust particles,
compared to enter the out of the
air passages are blocked and has difficulty in
the Lungs lungs) lungs)
breathing with too persistent coughing.
2. Emphysema
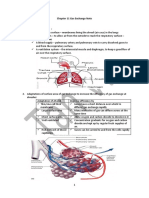
MECHANISM OF GAS EXCHANGE It is characterized by lungs losing its
1. Blood that enters the lungs has a low elasticity, decreased in the surface area for
concentration of oxygen and high gas exchange which results to violent
concentration of carbon dioxide coughing difficulty in breathing with
(deoxygenated blood). wheezing sound.
2. While in the alveoli, there is a high 3. Lung cancer
concentration of oxygen and low It is characterized by the uncontrollable
concentration of carbon dioxide. division of the cells producing lumps of
3. Through the process of diffusion, oxygen tissues. Cancer cells can spread in different
from the alveoli diffuses into the blood organs such as mouth, throat, pancreas,
capillaries. Carbon dioxide will be diffused in kidneys and urinary bladder.
the opposite direction.
4. This continuous oxygen-carbon dioxide
concentration gradient between the blood ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
and the alveoli are maintained by:
http://wikieducator.org/Respiratory_Syst
a continuous flow of blood through the blood em
capillaries; and
https://www.edhelper.com/teachers/heal
movement of the air in and out of the alveoli, th_Respiratory_System.htm
caused of breathing.
5. Blood that leaves the lungs has a high
concentration of oxygen and low
concentration of carbon dioxide (oxygenated
blood).
TOBACCO AND SMOKING
Tobacco smoke or cigarette contains more than
4000 chemicals, most of which are harmful to the
body. Below are the list of common chemicals
and their effects on the body.
Chemicals in Effects on the body.
tobacco or
cigarette
Nicotine Increase heartbeat rate and
blood pressure.
Increase blood clotting
Tar and Increase the risk of lung
Irritants (e.g. cancer.
formaldehyde,
hydrogen Trapped dust particles in the
cyanide) lungs that cannot be
removed.
Carbon Reduces the ability of the
monoxide blood to carry oxygen.
Increase heartbeat rate and
blood pressure.
You might also like
- Ophthalmology 7th Edition (Oftalmología 7a Edición)Document1,671 pagesOphthalmology 7th Edition (Oftalmología 7a Edición)Víctor SaRi100% (1)
- 3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pages3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDjej100% (1)
- Module 18 Respiratory FinalDocument15 pagesModule 18 Respiratory FinalJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Psycho Dynamic Psychotherapy For Personality DisordersDocument40 pagesPsycho Dynamic Psychotherapy For Personality DisorderslhasniaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian Medicine Systems OverviewDocument11 pagesAncient Indian Medicine Systems OverviewAmrutha AyinavoluNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection 2018Document213 pagesRadiation Protection 2018Ricardo EdanoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Larynx EpiglottisDocument12 pagesRespiratory System: Larynx Epiglottisangel sychingNo ratings yet
- SYS-3010 Syringe Pump Operation Manual - V1.1Document62 pagesSYS-3010 Syringe Pump Operation Manual - V1.1bprz50% (2)
- OXYGENATIONDocument8 pagesOXYGENATIONJo Marchianne Pigar0% (1)
- Project WorkPlan Budget Matrix ENROLMENT RATE SAMPLEDocument3 pagesProject WorkPlan Budget Matrix ENROLMENT RATE SAMPLEJon Graniada60% (5)
- Sspc-Ab 2Document3 pagesSspc-Ab 2HafidzManafNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Project Name: Proposed Icomc & BMC Building Complex Phe Design ReportDocument19 pagesProject Name: Proposed Icomc & BMC Building Complex Phe Design ReportAmit Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument80 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Precision Performance of Quantitative Measurement Methods Approved Guideline-Second EditionDocument56 pagesEvaluation of Precision Performance of Quantitative Measurement Methods Approved Guideline-Second EditionHassab Saeed100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Respiratory Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516Document8 pagesModule 2: Respiratory System SEM 2 SESI 2019/2020 Group: A: Name: Mohamad Aiman Iqbal Bin Nordin MATRIC NO: D20192091516muhd ariffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Holy HaeinNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzDocument12 pagesANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- X Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesX Respiratory SystemHannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Holy HaeinNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory Systemefe shanNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemJohn marcus ViadoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System I.: Subject: Subject TeacherDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory System I.: Subject: Subject TeacherHyacinth FarinasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemElle MateoNo ratings yet
- M7 RespiratoryDocument6 pagesM7 RespiratoryNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance)Document17 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance)Michelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesBiology Notes - Respiratory SystemnoorbdeirNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in the Lungs - How Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are TransferredDocument15 pagesGas Exchange in the Lungs - How Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are TransferredThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument44 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKlaudette Collin PaynorNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Notes ExplainedDocument6 pagesGas Exchange Notes ExplainedKai TongNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (1)Document21 pagesRespiratory System (1)Cordelia AntoinetteNo ratings yet
- Breathing System: Function of Respiratory System Parts of Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesBreathing System: Function of Respiratory System Parts of Respiratory SystemEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- 172 Anatomy Resp SystemDocument29 pages172 Anatomy Resp SystemJerry ZahidNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-512058127No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesRespiratory SystemCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesRespiratory SystemRotan CirebonNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemDocument36 pages2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology GuideDocument21 pagesRespiratory Physiology GuideKingsley UdeajaNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument6 pagesGas Exchangerasha nadaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemCookies AndcreamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Respiratory SystemDocument36 pagesWeek 1 Respiratory SystemManuel Andreus Damian B.No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System: Gas Exchange ProcessDocument15 pagesHuman Respiratory System: Gas Exchange Processpraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesRespiratory SystemCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- Notes On Respiratory System, Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesNotes On Respiratory System, Gaseous Exchangeshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- Respi SystemDocument33 pagesRespi SystemJohn Harzel NagaNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument15 pagesHuman Resource ManagementKIPNGENO EMMANUELNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesRespiratory SystemLulaNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Document13 pagesGas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Archel GalorportNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory Systemjimboy baddiriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemCraigNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemMiss Glozirie An BacangNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Respiratory System Functions in 5 StepsDocument16 pagesRespiratory System Functions in 5 Stepshellofrom theothersideNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument13 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMANAMAZING CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumanDocument17 pagesGas Exchange in HumanGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Biology IgcseDocument6 pagesChapter 11 Biology Igcsemeri zanniniNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing SystemDocument10 pagesGas Exchange in Humans: 7.1 Human Breathing Systemka klklklNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- DS-7600NI-K1/4P Series NVR: Features and FunctionsDocument3 pagesDS-7600NI-K1/4P Series NVR: Features and Functionsxmaster2007No ratings yet
- Inverter DimensionDocument2 pagesInverter DimensionEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Hikvision 4 MP ColorVu Fixed Bullet CameraDocument7 pagesHikvision 4 MP ColorVu Fixed Bullet CameraEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Ds-2Cd1047G0-L (Uf) 4 MP Colorvu Fixed Bullet Network CameraDocument5 pagesDs-2Cd1047G0-L (Uf) 4 MP Colorvu Fixed Bullet Network CameraEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- IPTV DiagramDocument1 pageIPTV DiagramEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- 5Ghz 3Ft Mimo Dish Antenna: Model: Ant4965D34Pa-DpDocument1 page5Ghz 3Ft Mimo Dish Antenna: Model: Ant4965D34Pa-DpPSW TelecomNo ratings yet
- Ds-2Cd1147G0 4 MP Colorvu Fixed Turret Network CameraDocument5 pagesDs-2Cd1147G0 4 MP Colorvu Fixed Turret Network CameraEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- LG32 33 FaDocument3 pagesLG32 33 FaEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Reviewer GuideDocument5 pagesMath 8 Reviewer GuideEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Airmux-400 Series: Presented byDocument39 pagesAirmux-400 Series: Presented byEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Multicontrol Level 2: Cat. No. Pack Name Packaging (Content)Document2 pagesMulticontrol Level 2: Cat. No. Pack Name Packaging (Content)NonameNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Dr. Ebtisam El - HamalawyDocument20 pagesStatistics: Dr. Ebtisam El - Hamalawydruzair007No ratings yet
- Schedule - Topnotch Moonlighting and Pre-Residency Seminar Nov 2022Document2 pagesSchedule - Topnotch Moonlighting and Pre-Residency Seminar Nov 2022Ala'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Drug in PregnancyDocument5 pagesDrug in PregnancyjokosudibyoNo ratings yet
- Sir 2014 SouthamericaDocument33 pagesSir 2014 SouthamericahusseinNo ratings yet
- Senior Counsel or Associate General Counsel or Assistant GeneralDocument3 pagesSenior Counsel or Associate General Counsel or Assistant Generalapi-76922317No ratings yet
- DRRM Plan2020 2021Document5 pagesDRRM Plan2020 2021SheChanNo ratings yet
- Stok Benang Kamar OperasiDocument5 pagesStok Benang Kamar OperasirendyNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Medical Officer 7.10.13Document3 pagesAyurveda Medical Officer 7.10.13Kirankumar MutnaliNo ratings yet
- 09022016att ComplaintDocument25 pages09022016att Complaintsarah_larimerNo ratings yet
- Civil Tender Volume-1Document85 pagesCivil Tender Volume-1Aditya RaghavNo ratings yet
- Ethical Counselling and Defense MechanismsDocument9 pagesEthical Counselling and Defense MechanismscklynnNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument7 pagesChronic Renal FailureMary Jane Tiangson100% (1)
- Overcoming The Pilot Shortage PDFDocument16 pagesOvercoming The Pilot Shortage PDFTim ChongNo ratings yet
- Abc Sealant SDSDocument5 pagesAbc Sealant SDSKissa DolautaNo ratings yet
- Eye Ear Dental Examinations Form 3300Document2 pagesEye Ear Dental Examinations Form 3300Khyaree EspañaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Feeding and Swallowing Difficulties in PDFDocument118 pagesThe Nature of Feeding and Swallowing Difficulties in PDFLisa NurhasanahNo ratings yet
- Semi Solids PDFDocument3 pagesSemi Solids PDFAsif Hasan NiloyNo ratings yet
- Sop Cleaning Rev 06 - 2018 Rev Baru (Repaired)Document20 pagesSop Cleaning Rev 06 - 2018 Rev Baru (Repaired)FajarRachmadiNo ratings yet
- SPS321 Sports Safety and Emergency Care Mohd Fadzil B. Hj. Kamarudin Sr113 Uitm/InstedtDocument9 pagesSPS321 Sports Safety and Emergency Care Mohd Fadzil B. Hj. Kamarudin Sr113 Uitm/InstedtMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- 80-Article Text-264-1-10-20200729Document6 pages80-Article Text-264-1-10-20200729ulfaNo ratings yet