Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Light and Thin Converging Lens
Uploaded by
Tyas Ajeng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesVocabulary and basic principle of refraction on thin converging lens
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVocabulary and basic principle of refraction on thin converging lens
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesPhysics Light and Thin Converging Lens
Uploaded by
Tyas AjengVocabulary and basic principle of refraction on thin converging lens
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name : ____________________________________ Date: _________________
LENSES
Section A: Vocabulary
A piece of glass (or other transparent material) that can bend
parallel rays of light so that they cross or appear to cross, at a
single point.
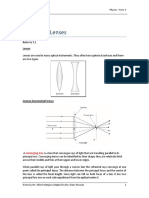
A lens that is thickest in the middle, causing parallel rays of
light to converge to a focus. Also known as convex lens.
A lens that is thickest in the middle, causing parallel rays of
light to converge to a focus. Also known as converging lens.
A lens that is thinnest in the middle, causing parallel rays of
light to diverge. Also known as concave lens.
A lens that is thinnest in the middle, causing parallel rays of
light to diverge. Also known as diverging lens.
The line joining the centres of curvature of the surfaces of a
lens.
For a converging lens, the point at which a beam of light
parallel to the principal axis converges. For a diverging lens,
the point from which such a beam appears to come.
The distance between the center of a lens and either focal
point.
An image that is formed by converging light rays and that can
be displayed on a screen.
A diagram showing rays that can be drawn to determine the
size and location of an image formed by a mirror or lens.
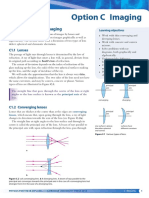
Section B: Parts of Lens
Name type of the lens on diagram below and label parts of it.
Section C: Standard Rays Must use pencil and
In ray diagrams of convex lens, any two of the following rays ruler for drawing a ray
are needed to fix the image position and size. diagram!
Any ray through the centre passes
1
straight through the lens.
A ray parallel to the principal axis
2 passes through F after leaving the
lens.
A ray through F’ leaves the lens
3
parallel to the principal axis.
You might also like
- Image Formation in Lenses AaliyaDocument15 pagesImage Formation in Lenses AaliyaAaliya PatelNo ratings yet
- Physics - Convex LensDocument15 pagesPhysics - Convex LensdivyapriyaNo ratings yet
- My FileDocument7 pagesMy Fileمؤمل فاضلNo ratings yet
- IBPhysics ImagingOption PDFDocument47 pagesIBPhysics ImagingOption PDFVish DhingraNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument12 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesGiovan George MendezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Week 6Document5 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Week 6Jess Anthony Efondo100% (1)
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (3)
- Lens PresentationDocument40 pagesLens PresentationNayeem HakimNo ratings yet
- Curve Lens Class NotesDocument9 pagesCurve Lens Class Noteswoman in stemNo ratings yet
- Refraction Through A Lens PDFDocument3 pagesRefraction Through A Lens PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Refraction Lesson 5Document29 pagesRefraction Lesson 5Yohanes Fevian100% (2)
- Lens & MirrorsDocument219 pagesLens & MirrorsChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Physics-Option-CDocument39 pagesPhysics-Option-Cuser2No ratings yet
- 11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsDocument6 pages11.9 Images in Curved MirrorsAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesJohn MaligNo ratings yet
- Image Formation by Curved Mirrors & Thin Converging LensesDocument38 pagesImage Formation by Curved Mirrors & Thin Converging LensesAndrewD2404No ratings yet
- AP Physics - Geometric Optics: Spherical MirrorsDocument10 pagesAP Physics - Geometric Optics: Spherical MirrorsJames HansenNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Ch13.1 TBDocument3 pagesGr10 Ch13.1 TBnr46jpdxbpNo ratings yet
- LensDocument13 pagesLensDebkanta ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesMirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - Image Formation in LensesRhian PanaganeNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument31 pagesLensesDejaunae LawsonNo ratings yet
- Light MirrorsDocument57 pagesLight MirrorsPhylicia RamosNo ratings yet
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 pagesRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashNo ratings yet
- Explore Lenses: How They Form Images and Magnify ObjectsDocument17 pagesExplore Lenses: How They Form Images and Magnify ObjectsMeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thin Lenses - University Physics Volume 3Document22 pagesThin Lenses - University Physics Volume 3Gbenga AgunbiadeNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Module 2 (Q2-Week 6-8)Document12 pagesSci10 Module 2 (Q2-Week 6-8)Chris John SantosNo ratings yet
- MIRROR VS LENSDocument5 pagesMIRROR VS LENSEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Exp ConvexconcaveDocument11 pagesExp ConvexconcaveMeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thin Converging LensesDocument19 pagesThin Converging LensesnateiddeNo ratings yet
- Mirror and LensesDocument44 pagesMirror and LensesHazzim AriffNo ratings yet
- Camera Lens Types and Their CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesCamera Lens Types and Their CharacteristicsElla Mei OralloNo ratings yet
- Thin LensesDocument37 pagesThin LensesVianca Rein MilanNo ratings yet
- Torio, John Carl T. Science 10 q2 Week 6Document12 pagesTorio, John Carl T. Science 10 q2 Week 6carl twqeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Dimaano, Jerome M. - LensesDocument6 pages3 - Dimaano, Jerome M. - LensesJerome DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument3 pagesGeometric OpticsYeizmin KimNo ratings yet
- Image FormationDocument18 pagesImage FormationArXlan XahirNo ratings yet
- Refraction in Lenses: Characteristics and Images FormedDocument17 pagesRefraction in Lenses: Characteristics and Images FormedJe NayNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document8 pagesOptics 1Stephson Micayee Da LastbornNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument35 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesdeguzmanjannellegNo ratings yet
- Reflection Mirrors 2022 2023Document92 pagesReflection Mirrors 2022 2023Jeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Astrophsics Option ADocument87 pagesAstrophsics Option AAlex KingstonNo ratings yet
- 3.2.3 Notes Thin Converging Lens P4 TeacherDocument10 pages3.2.3 Notes Thin Converging Lens P4 TeacherYokeLing ChangNo ratings yet
- L8. 13.1, 13.3 Convex & Concave LensesDocument36 pagesL8. 13.1, 13.3 Convex & Concave Lenseszhuhu2002No ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument36 pagesREVIEWEREmmanuel OdencioNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection Guide in 40 CharactersDocument72 pagesLight Reflection Guide in 40 CharactersTrendi Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Overview: - On Completion of This Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToDocument19 pagesOverview: - On Completion of This Lesson, Students Should Be Able Tothunder32xNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 3: Lenses Chapter 3: LensesDocument10 pagesPhysics Chapter 3: Lenses Chapter 3: LensesMatthewtongNo ratings yet
- Sci Quiz 4 q2Document11 pagesSci Quiz 4 q2eslNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses ReviewerDocument9 pagesMirrors and Lenses ReviewerVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument34 pagesReflection of LightTrisha Esplana SecondNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction in Mirrors and LensesDocument9 pagesReflection and Refraction in Mirrors and LensesEl CruzNo ratings yet
- Guyton and Hall Medical PhysiologyDocument34 pagesGuyton and Hall Medical PhysiologyFul VianaNo ratings yet
- LightDocument22 pagesLightPeerchand ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument30 pagesPhysicsshlokpandey0202No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument27 pagesPhysicsshlokpandey0202No ratings yet
- Optics Section Two FinalDocument49 pagesOptics Section Two FinalNahoo BekNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Expressions - Special Algebraic IdentitiesDocument2 pagesEquivalent Expressions - Special Algebraic IdentitiesTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity DetectiveDocument3 pagesStatic Electricity DetectiveTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity DetectiveDocument3 pagesStatic Electricity DetectiveTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Calculus Derivatives: Graphs of +Document1 pageCalculus Derivatives: Graphs of +Tyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - Geometrical Properties of A CircleDocument21 pagesTyas - Geometrical Properties of A CircleTyas Ajeng100% (1)
- Physics Kinematics Summary Note PDFDocument1 pagePhysics Kinematics Summary Note PDFTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Kinematics AgDocument1 pageWorksheet Kinematics AgTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - Geometrical Properties of A CircleDocument29 pagesTyas - Geometrical Properties of A CircleTyas Ajeng100% (1)
- Worksheet Kinematics AgDocument1 pageWorksheet Kinematics AgTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - HeatDocument33 pagesTyas - HeatTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - HeatDocument33 pagesTyas - HeatTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - HeatDocument33 pagesTyas - HeatTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas MotionDocument25 pagesTyas MotionTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - Matter and Its State 2011Document32 pagesTyas - Matter and Its State 2011Tyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - Atoms, Molecules and Ions 2011Document23 pagesTyas - Atoms, Molecules and Ions 2011Tyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - Physics Handout MotionDocument13 pagesTyas - Physics Handout MotionTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas Ajeng Puspitasari, S.PD: Grade VIII Semester 2Document31 pagesTyas Ajeng Puspitasari, S.PD: Grade VIII Semester 2Tyas AjengNo ratings yet
- Tyas - MotionDocument25 pagesTyas - MotionTyas AjengNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Atoms and MoleculesDocument43 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Notes Atoms and MoleculesArjunNo ratings yet
- Fluid KinematicsDocument109 pagesFluid KinematicsLorence Gabayan100% (1)
- Book of Abtracts Erem 6thDocument203 pagesBook of Abtracts Erem 6thSaiful Azhar Ahmad TajudinNo ratings yet
- Outokumpu Stainless Steel Wall ChartDocument1 pageOutokumpu Stainless Steel Wall ChartSrikanth SrikantiNo ratings yet
- Aceite Roto Extreme Duty ATLAS COPCODocument7 pagesAceite Roto Extreme Duty ATLAS COPCOmadaba723504No ratings yet
- Lett 9b03210Document5 pagesLett 9b03210Yarkali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Pea Germination LabDocument3 pagesAP Biology Pea Germination Labg2gusc38No ratings yet
- Production of 100, 000 Metric Tonnes Polyvinyl Chloride Per YearDocument33 pagesProduction of 100, 000 Metric Tonnes Polyvinyl Chloride Per YearLim Ying Pei100% (1)
- LIGNIN Biomass RecalcitraneDocument63 pagesLIGNIN Biomass RecalcitraneIsroi.comNo ratings yet
- Gcse Ocr DT FlashcardsDocument8 pagesGcse Ocr DT Flashcardsapi-256027312No ratings yet
- Mass Balance Modeling For Electric Arc Furnace PDFDocument7 pagesMass Balance Modeling For Electric Arc Furnace PDFmshahNo ratings yet
- Foreign MatterDocument6 pagesForeign MatterAnonymous XuiUo2ThNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Ch07 Textbk ANSDocument4 pagesChemistry Matters Ch07 Textbk ANSZeneon73% (11)
- En-10079 Definition of Steel ProductsDocument44 pagesEn-10079 Definition of Steel ProductshugocoimbraNo ratings yet
- ChE441 Problem Set 3 PDFDocument6 pagesChE441 Problem Set 3 PDFmelihNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Density Problems SEODocument5 pagesChemistry Density Problems SEOTahir SaeedNo ratings yet
- Sigma Marine CoatingsDocument417 pagesSigma Marine CoatingsAhmed Saad80% (5)
- BS 7371-1-2009 General RequirementsDocument24 pagesBS 7371-1-2009 General RequirementsmoorthyxNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument33 pagesMichael FaradayRezie Dampog DellavaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Level in Purging Gas During Welding of Duplex Stainless Steel - Google GroupsDocument6 pagesOxygen Level in Purging Gas During Welding of Duplex Stainless Steel - Google GroupssanketNo ratings yet
- Kogi State School of Nursing Past Questions and Answers 2014-2020Document149 pagesKogi State School of Nursing Past Questions and Answers 2014-2020ADESUA PREVAIL OLUWAFEMINo ratings yet
- FAG - Lozyska Precyzyjne PDFDocument204 pagesFAG - Lozyska Precyzyjne PDFmephir666No ratings yet
- 2 Agrostudies Temperature ManagementDocument62 pages2 Agrostudies Temperature ManagementYolaina EdwarNo ratings yet
- Aspen Methanol WorkshopDocument16 pagesAspen Methanol WorkshopAllen Low0% (1)
- RAMAN Amplifier Fiber SplicingDocument5 pagesRAMAN Amplifier Fiber SplicingGheePhotobotz100% (1)
- Abdos Catlog 2013 - 14Document63 pagesAbdos Catlog 2013 - 14nirmalpharmaNo ratings yet
- Quantum PackerDocument2 pagesQuantum PackerCARLOSELSOARESNo ratings yet
- Iron CastingDocument23 pagesIron CastingDiego MoralesNo ratings yet
- Identificación de Flavonoides, Lactonas Sesquiterpenicas, Compuestos Fenolicos y Taninos de La Manzanilla.Document13 pagesIdentificación de Flavonoides, Lactonas Sesquiterpenicas, Compuestos Fenolicos y Taninos de La Manzanilla.Mabel Pinto Coronel67% (3)