Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Corpus Alienum Auricular
Uploaded by
Auliya AndiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Corpus Alienum Auricular
Uploaded by
Auliya AndiCopyright:
Available Formats
CASE REPORT
Corpus Alienum Auricular
Presented by:
Afifah Al Azizah 17/421280/KU/20211
Ma Wan Hui 17/421304/KU/20235
Muhammad Ifan Alfian 17/421308/KU/20239
Gavrilo Giardi 17/421297/KU/20228
Azaria N. Paramastri 17/421286/KU/20217
Dinda Ajeng A. 17/421289/KU/20220
Moderator: Dr. dr. Sagung Rai Indrasari, M.Kes., Sp. THT-KL (K), FICS
Departement of Otorhinolaringology, Head and Neck Surgery
Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada
RSUP Dr. Sardjito
2018
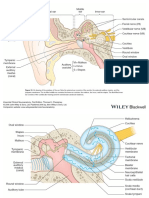
INTRODUCTION The objects themselves are variable,
The ear is an organ for hearing and ranging from beads to insects. Cases are
balance, which consists of the external ear, seen mostly but not exclusively in children
middle ear and inner ear. The external ear and are a relatively common case in
captures sound waves that are converted emergency medicine. Patients may
into mechanical energy by the middle ear. sometimes realize that a foreign object is
The middle ear converts mechanical lodged inside their external ear canal,
energy into nerve waves, which are then coming in with the chief complaint the
delivered to the brain. The inner ear also insertion of a foreign object in their ear.
helps maintain body balance. But some may not even realize the
The external ear consists of earlobes presence of an object in their ear canal,
(pinna or aurikel) and ear canal (meatus leading up to patients presenting with
auditory externa). The outermost part of hearing loss, or a sense of fullness.
the ear which is the auricle is composed Significant discomfort, or complain of
mainly by elastin cartilage and skin. It nausea and vomiting may be present if a
consists of: root/crus of the helix, helix, live insect enters the ear canal.1
antihelix, scaphoid fossa, triangular fossa, In children, the child does not
crura of antihelix, antitragus, lobule, and complaint before the pain due to infection
tragus. The external acoustic meatus is an in the ear, the ears can be smelled bad if
“S” shaped canal that leads to tympanic the foreign body stay for a long time in the
membrane from the auricle. 1/3 of the ear canal. If the child’s ear smelled bad,
outer part of the canal is composed of parents should suspect it as a result of
cartilage while 2/3 of the canal’s inner part foreign body in the ear canal. Do not
is made out of bone (temporal), with its handle it yourself because the objects may
length measured to be around 2.5-3 cm. actually go inside because of the anatomy
The cartilaginous part of the canal of the ear canal that is notched. In the ears
produces cerumen from sebaceous and there are many nerves and injuries can
ceruminous glands, while 2/3 of the bony occur. Foreign body in the ear canal
part of the canal has only a few of these usually can only be evacuated by ENT
glands compared to the other. doctors using equipment and specific
Foreign body (corpus alienum) in the skills.
ear are objects lodged in the ear which Foreign bodies in the ears, nose or
originates from outside the body or even throat are a common occurrence in
from within which is normally not present. otorhinolaryngology (ENT) emergency
services. Foreign bodies have been laceration of the skin and the wound of the
estimated to account for approximately tympanic membrane, it will cause hearing
11% of the cases seen in ENT services.2 loss, ear pain / otalgia and possible risk of
There are several factors that can infection.
cause foreign objects in the ear that is 3: Severe complications can occur in
Intentional factor, usually occurs in 22% of the cases found, and the morbidity
children under five. associated with foreign bodies, therefore,
Carelessness factors often occur in foreign matter must be handled correctly.2
adults when using earwashers such as Improper handling can lead to bleeding,
cotton, a matchstick or sticker left trauma to the ear canal, trauma to the
inside the ear, the latter being accidental membrane tympanic and hearing bones.
factors in which a foreign object enters This will increase the patient's morbidity,
the ear for example insects, so it will require exploratory action with
cockroaches, flies and mosquito. general anesthesia to remove the foreign
Here are some foreign objects that object. Lack of experience in foreign body
often enter the ear canal: water, cotton management in the ear is one of the factors
bud, small things and insect. The effects of causing iatrogenic complications.4
the entry of foreign matter into the ear can
range in no symptoms until the symptoms CASE REPORT
of severe pain and the presence of hearing A 19 years old female visited RSUD
loss. Other symptoms that may arise are: Tjitrowardojo Purworejo on January 18th,
feeling uncomfortable, clogged, impaired 2018 because she claims an insect-like
hearing and earache / otalgia. thing burrowed itself in her right ear since
The entry of foreign objects into the this morning. She also complained a
ear that is to the external auditorius canal feeling of discomfort in her right ear.
will cause a clogging sensation in the ear, Tinnitus, discharge and itchiness were
so the patient will try to remove the denied. There was no history of
foreign object. However, the actions that swimming, cleaning the ear canal with
the patient undertakes to expel the foreign cotton bud, and scratching her ear with
body often leads to further exacerbation of nails. She has seen the doctor in primary
the foreign body to the external canal health care before going to RSUD
bone, causing skin laceration and injury to Tjitrowardojo Purworejo. The doctor said
the tympanic membrane. As a result of that the insect-like thing were burrowed
deep in the right ear and there were no
adequate equipments to evacuate the thing physical examination, the patient was
so she had to go to the ENT specialist. She diagnosed with Corpus Alienum Auricular
has no history of food allergy as a kid. She Dextra. The evacuation of the foreign
also denied nasal congestion, cough, body was done, and no drug was
hoarseness and upper respiratory infection prescribed to the patient.
before her complaints appeared.
On otoscopic examination, the left ear DISCUSSION
was within normal. The external auditory The patient present with a feeling of
canal of the left ear was not hyperemic, no discomfort in the right ear. Physical
discharge and no swelling. The tympanic examination revealed a foreign body deep
membrane were intact with good light in the CAE with no discharge, tenderness,
reflection. The patient felt no pain when redness, and swelling on the right ear.
we palpated her left ear and the Based on the signs and symptoms we
paraauricular area. diagnosed the patient with corpus alienum
Compared to the left ear, the right ear auricular dextra. The physical
was within normal. The external auditory examination is the main diagnostic tool for
canal was not hyperemic, no discharge, corpus alineum in the ear canal.
and no swelling but we can see the foreign Physical examination is done with the
body deep in the ear, right in front of the use of an otoscope while retracting the
tympanic membrane. The tympanic pinna in a posterosuperior direction. A
membrane itself were intact. There were head mirror with a strong light source,
no pain when we palpated her right ear and operating otoscope, or operating
paraauricular area. Inspection of the microscope also may be used. The result
external nose was normal. From anterior that may be gathered from the examination
rhinoscopy examination, both of her are:
nostril was normal, no edema or • Redness, foul odor and swelling indicate
hyperemic concha and no discharge was infection
seen. • The bluish color and cone shaped
Physical examination on the throat indicate a pile of blood behind the
was within the normal limit. tympanic membrane.
Tonsilopalatina, pharynx, larynx was in • The possibility of a tympanic membrane
normal limit, no swelling nor hyperemic perforation.
were seen. No granule was seen in There is no specific prehospital
oropharynx. Based on history taking and management for the presence of a foreign
body, immediate visit to the hospital is since the catheter must be placed
needed. Occasionally if the patient suffers directly on the object with a good seal
from discomfort, pain, or nausea, obtained. The catheter does not work as
symptomatic treatment can be well for foreign bodies in the medial
administered to the patient. two thirds of the ear canal where it is
There are some tools that required for narrower, and it is sometimes difficult
removal foreign body: to keep enough suction pressure on
Otoscope for ensure the located foreign theforeign body for removal.
body. Magnet. It is used for metallic foreign
Headlamp used for lighting/ bodies.
visualization. Mineral oil or lidocaine 2%. It is used
Curved hook. This tool is ideal for hard, to kill the insect in the ear canal.
spherical shaped objects in the lateral Sedation (if needed)
one third of the ear canal. There are 3 techniques commonly
Alligator forceps. The most common used by practitioner to evacuate the foreign
tool used for removal of an ear foreign bodies: mechanical extraction, irrigation,
body. The alligator forceps is ideal for and suction. In this patient, the technique
graspable objects such as paper, erasers, used was irrigation because the foreign
cotton or tissue. They are not ideal for body was a small accessory located in the
hard, spherical shapes such as beads inner two third of CAE, right in front of
(unless there is a hole) or seeds. the tympanic membrane. Mechanical
Alligator forceps are also useful when extraction and suction techniques are best
the foreign body can be directly used when the foreign bodies had a mushy
visualized from the external ear canal. consistency. The side effect was minimal
Irrigation equipment. Syringe and after the foreign body evacuation, so no
angiocatheter 20 gauge usually is used drug was prescribed to the patient.
for irrigation in the ear canal. • Mechanical extraction
Suction equipment. One of the tools for Briefly repeat the ear examination
suction is catheter. The catheter is ideal while observing the location and depth of
for hard, round, spherical shaped the foreign body. Move the headlamp for
objects specifically in the lateral one better visualization and carefully introduce
third of the ear canal. Direct alligator forceps through ear canal.
visualization of the objectis important Advance the forceps incrementally through
the external auditory canal until the foreign • Suction
body is grasped. Gently withdraw the Connect the soft-tipped suction
forceps, with attached foreign body, from catheter to low wall suction and position
the auditory canal. Always check for the patient comfortably. Visualize the
complete removal of the foreign body, foreign body with the headlamp/otoscope.
perforation of the tympanic membrane, Introduce the catheter through ear canal
and abrasions of the auditory canal. and gently advance it incrementally until
• Irrigation the foreign body is contacted. Gently
To irrigate, first attach a 20-ga withdraw the suction catheter tip and
angiocatheter to a 60-mL syringe. attached foreign body from the external
Warming the irrigation fluid (water or auditory canal. Repeat a postprocedural ear
normal saline) greatly enhances patient examination to confirm complete removal
comfort. Position the patient comfortably of the foreign body and to check for
and drape the area to keep the patient dry. complications.
Position an emesis basin under the affected Insects, organic matter and objects
ear to collect irrigation runoff. Place the with the potential to become friable and
flexible angiocatheter tip gently in the break into smaller evasive pieces are often
external auditory canal. Advancing the tip better extracted with suction than with
too far risks damage to the tympanic forceps. Live insects in the ear canal
membrane. With the angiocatheter tip held should be immobilized before removal is
gently in position, slowly inject irrigation attempted.5 The insect should be killed
fluid until the foreign body washes out. prior to removal, using mineral oil or
Always conduct a postprocedural ear lidocaine 2%.6-7
examination to confirm complete removal Always examine the opposite ear for
of the foreign body and to check for additional foreign bodies and the external
complications. auditory canal after the removal of a
Irrigation is contraindicated for foreign body to identify preexisting or
organic matter that may swell through iatrogenic tympanic membrane
osmosis and enlarge within the auditory perforations or abrasions.
canal. Disk batteries and vegetable matter There are some prevention for the
are also absolute contraindications to entry of object in the ear, that:
irrigation. The habit of using cottonbud to clean
the ears should be stopped because it
can cause some side effects: our ears
which have fine hairs that are useful for Am Fam Physician. 2007, Oct 15;
76(8): 1185-89.
making sweeping movements of dirt in
4. Edwad Y, Fitria H. Trauma pada
our ears will be damaged, so this Tingkap Lonjong Akibat Ekstraksi
Benda Asing di Liang Telinga. 2013.
natural cleansing mechanism will be
5. Figueiredo RR, Azevedo AA, Kos AO,
lost. If our skin is blistered there can be Tomita S. Complications of ent foreign
bodies: a retrospective study. Braz J
a very uncomfortable outer ear infection
Otorhinolaryngol. 2008 Jan-Feb.
and other possibilities if we are too 74(1):7-15.
6. Antonelli PJ, Ahmadi A, Prevatt A.
deep in pushing cottonbud, it can injure
Insecticidal activity of common
or penetrate the eardrum. reagents for insect foreign bodies of
the ear. Laryngoscope. 2001 Jan.
Avoid giving toys in the form of seeds 111(1):15-20.
to the children since the children can 7. Leffler S, Cheney P, Tandberg D.
Chemical immobilization and killing
put the small toys into the ear or can of intra-aural roaches: an in-vitro
also be swallowed. It can be fatal if it comparative study. Ann Emerg Med.
1993 Dec. 22(12):1795-8.
clogged the airway.
CONCLUSION
A 19 years old woman was presented
with Corpus Alienum Auricular Dextra.
The evacuation of the foreign body was
done with irrigation and no prescribed
drug was given. The diagnosis was defined
by the clinical presentation of the patient.
REFERENCES
1. Wright A. Anatomy and Ultrastructure
of the Human Ear, Basic Science,
Dalam : Scott- Brown's
Otolaryngology, 6"' ed, Vol I, Oxford ;
Butterworth- Heinemann Ltd.
2. Fornazieri MA, Cutolo D, Moreira JH,
et al. Foreign-body in External
Auditory Meatus: Evaluation of 462
Cases. Intl. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol.,
São Paulo – Brazil. 2010;14(1):45-49.
3. Heim SW, Maughan KL. Foreign
Body in the Ear, Nose, and Throat.
University of Virginia School of
Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- VJFDocument7 pagesVJFboss062212No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Ear Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument16 pagesEar Anatomy and PhysiologyDinda Ajeng AninditaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- A Study of Topical Phenytoin Sodium in Diabetic Foot Ulcer HealingDocument7 pagesA Study of Topical Phenytoin Sodium in Diabetic Foot Ulcer HealingDinda Ajeng AninditaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Accreditation Guide Hospitals 2011Document35 pagesAccreditation Guide Hospitals 2011Dinda Ajeng AninditaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Payment Mechanisms For Physician-Laksono Trisnantoro (Reguler-2016) PDFDocument64 pagesPayment Mechanisms For Physician-Laksono Trisnantoro (Reguler-2016) PDFDinda Ajeng AninditaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Nosocomial InfectionDocument47 pagesNosocomial InfectionDinda Ajeng Anindita100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Informed Consent Form and Interview ProtocolDocument4 pagesInformed Consent Form and Interview ProtocolAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Angle. Ribbon Arch Introduction 1916Document26 pagesAngle. Ribbon Arch Introduction 1916rrnotholtNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Inamsc Literature Review Dg1fQQFe Guideline INAMSC 2018Document20 pagesInamsc Literature Review Dg1fQQFe Guideline INAMSC 2018DevinNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Social Desirability Bias in Measuring Sensitive Topics: The Use of Forgiving Language in Item DevelopmentDocument14 pagesMinimizing Social Desirability Bias in Measuring Sensitive Topics: The Use of Forgiving Language in Item DevelopmentKillariyPortugalNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Types of Casts and Their IndicationsDocument3 pagesTypes of Casts and Their IndicationsPhylum ChordataNo ratings yet
- Cerebrolysin in Patients With Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument7 pagesCerebrolysin in Patients With Hemorrhagic StrokeZeynep Emirhan ŞenyüzNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Reasoning BookDocument38 pagesReasoning BookAshish Sharma100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- A Review On Netra Tarpana - An Ayurveda Method of Eye Care: January 2021Document10 pagesA Review On Netra Tarpana - An Ayurveda Method of Eye Care: January 2021Lepaksha GowdaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Gait Analysis: Prerequisite of Normal GaitDocument4 pagesGait Analysis: Prerequisite of Normal GaitKieran Levi100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- XxssDocument13 pagesXxssfkhunc07No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Essential hygiene and safety practices for body, home and cookingDocument3 pagesEssential hygiene and safety practices for body, home and cookingNorma Nieves QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Aj. Chulaporn-Bosutinib-Search Engine and Study EndpointsDocument5 pagesAj. Chulaporn-Bosutinib-Search Engine and Study EndpointsCalm Phurit SenachaiNo ratings yet
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocument6 pagesKlinefelter Syndromemeeeenon100% (1)
- Trace Elements Deficiencies in Belgian CattleDocument8 pagesTrace Elements Deficiencies in Belgian CattleHuber RizzoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPCharles Mallari Valdez100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemKumar Sujeet100% (1)
- Pathology of JointsDocument13 pagesPathology of JointswobblegobbleNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 13497-Texto Del Artículo-48998-1-10-20150925Document7 pages13497-Texto Del Artículo-48998-1-10-20150925Pipe Contecha BernatteNo ratings yet
- CM Lecture NotesDocument30 pagesCM Lecture NotesJefferson SorianoNo ratings yet
- Mink Dissection InstructionsDocument15 pagesMink Dissection InstructionsMark PenticuffNo ratings yet
- Aos 94 10Document11 pagesAos 94 10Andi Tiara S. AdamNo ratings yet
- Sample IQ TestDocument34 pagesSample IQ TestResIpsa LoquitorNo ratings yet
- The Hypothesis and Assumptions of The StudyDocument12 pagesThe Hypothesis and Assumptions of The StudyMaria Arlene67% (3)
- The Six-Step Formula for Hypnotic PersuasionDocument24 pagesThe Six-Step Formula for Hypnotic Persuasionmajadb100% (12)
- Surgical Services Design Guide PDFDocument465 pagesSurgical Services Design Guide PDFCharles TestaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Orthovoltage Vs MegavoltageDocument7 pagesOrthovoltage Vs MegavoltageEmmanuel Cuevas MisNo ratings yet
- Aman Foundation Internship Application FormDocument4 pagesAman Foundation Internship Application Formabdullahnisar92No ratings yet
- Sing With Distortion - 10 TipsDocument10 pagesSing With Distortion - 10 TipstjoodleNo ratings yet
- 3 Azarpour Et Al. JNBR 4 (1) 2015 PDFDocument9 pages3 Azarpour Et Al. JNBR 4 (1) 2015 PDFKamailNo ratings yet
- Iqvia Institute General Use of Medicines 2024 For WebDocument60 pagesIqvia Institute General Use of Medicines 2024 For Webaguiar.jessicapNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)