Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CKD NCP
Uploaded by
Arlene Macatangay100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesckd
Original Title
ckd ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentckd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesCKD NCP
Uploaded by
Arlene Macatangayckd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
XI.
LIST OF IDENTIFIED PROBLEMS (LIST OF PRIORITY)
Assessment Nursing Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
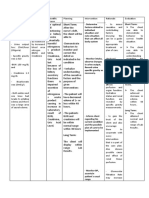
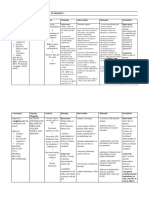
Subjective: INEFFECTIVE Acute Short term: -Establish rapport - to asses precipitating and Short term:
“lagi akong TISSUE glumerulonephritis Within 7-8hrs of causative factors After 8hrs of
nahihilo” as PERFUSION nursing intervention -assessed and monitored vital -general indicators of nursing
verbalized by the RELATED TO the client will able signs, skin color, sensation, circulatory status and intervention goal
Inflammation of to: movement, and capillary adequancy of perfusion
patient ANEMIA was partially met,
refill on extremities
glomerular as evidenced by:
-demonstrate -assess presence, location -useful in identifying or
Objective: capillaries increase perfusion and degree of swelling or quantifying edema in -partially
pale palpebral as individually edema formation involved extremity demonstrate
conjunctiva appropriate -inspect lower extremities for -that often accompany increased in
pale lips Kidney cannot skin texture and skin breaks diminished peripheral perfusion as
present of produce Long term: or ulcerations circulation individually
edema on both erythropoietin Within 1-2weeks of -palpate arterial pulses -to determine level of appropriate
lower nursing intervention circulatory blockage
extremities the patient will: -check for calf tenderness or -indicators of deep vein Long term:
nausea Decrease hgb and -demonstrate pain on dorsiflexion of foot, thrombosis (DVT), although After 2weeks of
hct count behaviours and swelling and redness. DVT is often present without
-hgb: 80 g/;L nursing
lifestyle changes to a positive Homan’s sign.
-Hct: 24 vol% intervention goal
improve circulation -measure I&O, nothing -to obtain baseline data
-RBC: 2.65x10 9/L -have normal hgb positive balance –intake in was not met, as
-BUN: 58.5mmol/L Anemia evidence by :
from 80g/L to L to excess output
-creatinine: 1810.0 -review laboratory studies -to determine probability, -laboratory still
135g/L
umol/L such as, hgb/hct, RBC,BUN, location and degree of remain and need
Hct from 24% to
creatinine, and diagnostic important. to be improved
40% , RBC from studies - demonstrate
2.65x10 9/L to 4.5- behaviours and
5.9x10 9L Collaborative: lifestyle changes
Creatinine from Administer ferrous sulphate to improved
1810.0 to 110, BUN + folic acid as prescribed circulation
from 58.5 to 7.2
Assessment Nursing Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
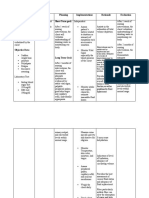
Subjective: ACTIVITY Decrease oxygen Short term: -monitor vital signs -to reassess vital function Short term:
“nanghihina ako” As INTOLERANCE carrying capacity of Within 6-8hrs of changes After 7hrs of
Hgb
verbalized by the RELATED TO nursing nursing
patient IMBLANCE intervention the -assess patients ability to -influence choice of intervention goal
OXYGEN Decreased patient will: perform ADLs noting interventions or needed was met, as
nutrition in cells assistance
Objective: SUPPLY AND reports of weakness, evidence by:
weakness DEMAND -verbalize fatigue and difficulty of -the patient,
fatigue Decreased ATP understanding of accomplishing task verbalized
pale skin and production since potential loss of understanding of
conjunctiva oxygen is needed ability in relation -promote independence in -mild/moderate activities potential loss of
chest pain for oxidation of to existing self-care activities as and improve self-esteem ability in relation
Hgb:80g/L condition tolerated are promoted to existing
CHO/glucose
Hct:24 vol% condition
T:37.1 -encourage alternating -minimized exhaustion and
Decreased energy
PR:89bpm Long term: activity with rest helps balance oxygen Long term:
or muscle
RR:17cpm Within 1-2weeks supply and demand after 1week of
weakness
BP:120/80mmHg of nursing nursing
intervention the -enhance lung expansion to interventions,
Activity maximize oxygen for
patient will: -elevate head of the bed as Goal was
intolerance cellular uptake
tolerated partially met, as
-completely -bed rest is maintained to evidence by:
independent on all -explain importance of bed decrease metabolic -the patient
ADLs and without rest demands thus conserving verbalized partial
assistance with the energy dependence on
S/O ADLs with his S/O
such as able to
-have good skin -promote quiet -to promote rest feed himself,
turgor environment assistance in
-have normal toileting and
-to identify the extent of bathing
haemoglobin level -monitor laboratory results
deficiency and for better -demonstrated
from 80 g/L to like hgb and hct treatment plan
135g/L good skin turgor
and well being
Hct from 24% to -encourage to increase -to increase iron
-able to
40% intake of iron-rich foods supplement of the body
participate in
-reports increase self-activities
sense of well (grooming
being dressing)
-hgb and hct still
-is free from needs to be
weakness and risk evaluated
for complications
has been
prevented and will
deliver safely
Assessment Diagnosis Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
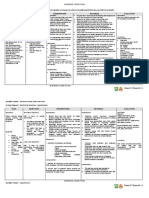
Subjective: Ineffective Bacterial/ Viral After 8 hours of Independent: After 8 hours of
“Nahihirapan akong airway clearance invasion nursing -Encourage deep breathing -Deep breathing promotes nursing
huminga” as related to intervention, exercise oxygenation before interventions goal
verbalized by the increased secretions will be controlled coughing partially met, the
patient production of Multiplication of mobilized; airway patient was able
respiratory bacteria/ Virus patency will be to:
Objective: secretions enters the lungs free of secretions, -Assist in patient coughing -To improve productivity -Demonstrate
Rapid breathing as evidence exercise of the cough coughing and
Positive patients’ ability to deep breathing
productive Cells in the effectively cough -Monitor rate, rhythm, -Provides a basis for exercise every 1-2
Crackles immune system and secretions, depth and effort of evaluating adequacy of hours during the
Dyspnea gathers in lungs to clear lung sounds respirations ventilation day
Vital Signs taken as stop infection and -Respiratory
follows uncompromised -Assist patient into -To promote drainage of crackles can still
T:37.1 Inflammation and respiratory rate. moderate high backrest secretions and better lung be heard at the
PR:89bpm production of position expansion right lower lobe
RR:30cpm secretions increaseLong Term: -Cough continues
Pulmonary Free of infection -Auscultate lung fields, -Decreased airflow occurs to be productive
BP:140/90mmHg infection that may cause of nothing areas of decreased in areas consolidated with
sputum. of absent airflow and fluid. Bronchial breath
Expectorate adventitious breath sound sounds can also occur in
Sputum sputum, relax the consolidated areas
production excess, patient within the
accumulated shift, free of Dependent:
secretions in the shortness of Administer ordered -To help loosen and clear
airways breathing. Patient medications such as the mucus from the
may do the activity mucolytic agents, airways(mucolytic);
Airway Blockage daily living. bronchodilators and decrease resistance in the
expectorant. respiratory airway and
increase airflow to the
lungs
You might also like
- Esrd NCPDocument7 pagesEsrd NCPSharmaine Camille de LeonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For ESRDDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For ESRDChester Manalo94% (17)
- Dka NCPDocument3 pagesDka NCPMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument2 pagesFluid Volume ExcessRodel Yacas100% (5)
- Risk For Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageRisk For Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Nursing Care PlanTrixia Dacles100% (1)
- NCP CKDDocument6 pagesNCP CKDBenjie Dimayacyac100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis DKA Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis DKA Care Planعبدالله خليل العسلNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureKian Herrera100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing DiagnosisJoehoney BarreraNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's Nursing Care PlanKristine Young100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121No ratings yet
- Student Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDocument25 pagesNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancerobbiematro100% (1)
- NCP RiskDocument3 pagesNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure NCPDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure NCPShaira Ann Calamba100% (1)
- NCP For StrokeDocument4 pagesNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChristine LebicoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Betty Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesBetty Impaired Skin IntegrityBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Managing Malnutrition in Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesManaging Malnutrition in Chronic Renal Failurejustin_sane40% (5)
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDocument5 pagesNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDocument4 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesAssessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's Diseaseria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureRalph Dumawaa60% (5)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearancePatrick Arvin Ballesteros BarcarseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresKwini Jeyn50% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- NCP AfDocument3 pagesNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Document3 pagesNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- CRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesCRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPchubbielitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Improving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeDocument1 pageImproving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEsther RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Generalized Edema and Fluid Volume Excess (38Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Generalized Edema and Fluid Volume Excess (38Angel Moorer92% (12)
- 6 NCPDocument8 pages6 NCPKlint IntervencionNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen Supplykarthi karthiNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJezza RequilmeNo ratings yet
- NCP Lack of KnowledgeDocument3 pagesNCP Lack of KnowledgeFaye BartianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NCPDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia and AnemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia and AnemiaSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Gastrointestinal BleedingMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Date Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Renal Perfusion Through Nursing InterventionsDocument2 pagesOptimizing Renal Perfusion Through Nursing InterventionsJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- DM NCP - Trixia U. Almendral GRP 6Document3 pagesDM NCP - Trixia U. Almendral GRP 6Trixia AlmendralNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationbambem aevanNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- V. Diagnostic ExaminationDocument3 pagesV. Diagnostic ExaminationArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric AssignmentDocument2 pagesPsychiatric AssignmentArlene Macatangay100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- CKD NCPDocument4 pagesCKD NCPArlene Macatangay100% (1)
- CKD NCPDocument4 pagesCKD NCPArlene Macatangay100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Intracranial PressureDocument27 pagesIntracranial PressureArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument3 pagesAnatomyArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Course in the Ward CareDocument2 pagesCourse in the Ward CareArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing ConsiderationsArlene MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Thopaz InstructivoDocument54 pagesThopaz InstructivomichelRamirezNo ratings yet
- Appstat PDFDocument197 pagesAppstat PDFrfactor0976No ratings yet
- Ibogaine Treatment NotesDocument4 pagesIbogaine Treatment NotesjesterstableNo ratings yet
- Cervical Incompetence Moh AbdallaDocument46 pagesCervical Incompetence Moh AbdallaDr. mohammed50% (2)
- Strategic ManagementDocument24 pagesStrategic ManagementSonetAsrafulNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of A Patient With An Ectopic PregnancyDocument8 pagesNursing Management of A Patient With An Ectopic PregnancySummer SuarezNo ratings yet
- MisoprostolDocument3 pagesMisoprostolMichael Aditya LesmanaNo ratings yet
- QaDocument16 pagesQaAnn Caroline FerrerNo ratings yet
- PONTIC DESIGN FACTORS FOR SUCCESSDocument53 pagesPONTIC DESIGN FACTORS FOR SUCCESSmanjulikaNo ratings yet
- British Homeopathic AssociationDocument195 pagesBritish Homeopathic AssociationNasarMahmoodNo ratings yet
- First Aid Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesFirst Aid Multiple Choice QuestionsArunkumar Rangaswamy100% (2)
- New England Journal Medicine: The ofDocument11 pagesNew England Journal Medicine: The ofahmadto80No ratings yet
- Signatory Guide To CREST Completion 2024Document5 pagesSignatory Guide To CREST Completion 2024junior docNo ratings yet
- III. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesIII. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationSTEPHANIE JOSUENo ratings yet
- Learning Related Vision ProblemsDocument38 pagesLearning Related Vision Problemseva.benson100% (1)
- A Study On Stroop Effect Among Government and Private High School Students.Document17 pagesA Study On Stroop Effect Among Government and Private High School Students.Sindhuja Iyer100% (1)
- Drug Study and NCPDocument9 pagesDrug Study and NCPDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Hawaii Medical PediatricsDocument10 pagesHawaii Medical PediatricstinkictijoNo ratings yet
- VenesectionDocument2 pagesVenesectionMorounshayo OshodiNo ratings yet
- OSPEDocument28 pagesOSPEsubashikNo ratings yet
- 500 Item CoachingDocument76 pages500 Item CoachingRoan Roan Roan100% (3)
- DR InstrumentsDocument16 pagesDR InstrumentsKrisia Castuciano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired AdjustmentDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Adjustmentderic100% (2)
- Chapter 4 of 10 - Kelsey HillDocument3 pagesChapter 4 of 10 - Kelsey HillspiritualbeingNo ratings yet
- C BollasDocument8 pagesC BollasVarun ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pico KMBDocument7 pagesJurnal Pico KMBOktaviani Putri PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal DrugsDocument37 pagesAntiprotozoal DrugsMoneto CasaganNo ratings yet
- Chatterjee, A., & Coslett, H.B. (Eds.) (2014) - The Roots of Cognitive Neuroscience. Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychology. Oxford University Press PDFDocument431 pagesChatterjee, A., & Coslett, H.B. (Eds.) (2014) - The Roots of Cognitive Neuroscience. Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychology. Oxford University Press PDFReg A. Derah100% (1)
- SOP Instalasi Bedah SentralDocument71 pagesSOP Instalasi Bedah SentralyeniNo ratings yet
- Morales-Roman ResumeDocument2 pagesMorales-Roman Resumeapi-301624882No ratings yet