Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MLC Reaction Detection of Alloreactive T Cells
Uploaded by
Muthi KhairunnisaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MLC Reaction Detection of Alloreactive T Cells
Uploaded by
Muthi KhairunnisaCopyright:
Available Formats
Mixed Lymphocyte Culture / Reaction (MLC / MLR)
Principle
T cells from one individual are mixed and co-cultured with lymphocytes from a second
individual. If the cells of one individual recognized other’s MHC molecules as foreign,
they proliferate and divide. The proliferative response is usually measured with 3H-
labeled thymidine uptake assay.
There are two variants of the test: “two-way” – cells of both individuals are free to
proliferate, and “one-way” – cells of one of the individuals are irradiated or treated with
mitomycin so they can’t proliferate. Thus, cells of only one of the individuals can
proliferate.
Objective
- To detect alloreactive T cells and histoincompatibility
- Used for selection of donors for bone marrow transplants - lowest possible
alloreactive response is essential (limitation: no accurate quantitation of
alloreactive T cells)
- Selection of donors for living-related renal allotransplantation
- Typing of HLA-D antigens
- Used in diagnosis of immunodeficiency diseases.
Procedure (“one-way” test)
Isolation of lymphocytes from peripheral blood from two individuals
Irradiation/treatment with
mytomicin C of lymphocytes from
one of the individuals (yellow)
Irradiated cells act as stimulator
cells but cannot proliferate
Cells from the two individuals
are mixed
3 to 7 days later: T-cell
proliferation assay (e.g. 3H-
thymidine uptake) (if the
unirradiated lymphocytes contain
alloreactive T cells, they will
proliferate and differentiate to
effector cells as a result of
recognition of foreign MHC
molecules).
Molecular Biology of the Cell 4th ed. Alberts, Bruce Et al.
Example
Taken from: Goutarou Katsuno et al. The immunosuppressive effects of ciprofloxacin
during human mixed lymphocyte reaction. Clinical Immunology (2006) 119, 110—119
The goal of this experiment was to check the effects of ciprofloxacin on intracellular
expression of IFN-γ in monocytes and T-cells during MLR. Cells from two unrelated
individuals were mixed and incubated under different conditions for 24 hours. All the
reagents were added at the beginning of MLR. Next, expression of IFN-γ was determined
with flow cytometry
Results:
CIP at 100 µg/ml had no effect on the expression of intracellular IFN-γ in both
monocytes and T-cells
IL-18 at 100 µg/ml upregulated the expression of intracellular IFN-γ both in
monocytes and T-cells
CIP suppressed the IL-18-enhanced expression of intracellular IFN-γ both in
monocytes and T cells
CIP also suppressed the LPS enhanced intracellular IFN-γ expression in T-cells during
MLR
References:
http://www.mercksource.com/pp/us/cns/cns_hl_dorlands.jspzQzpgzEzzSzppdocs
zSzuszSzcommonzSzdorlandszSzdorlandzSzdmd_c_66zPzhtm#12270597
Goutarou Katsuno et al. The immunosuppressive effects of ciprofloxacin during
human mixed lymphocyte reaction. Clinical Immunology (2006) 119, 110—119
Molecular Biology of the Cell 4th ed. Alberts, Bruce et al.
You might also like
- Specific Host Defenses: The Immune ResponseDocument54 pagesSpecific Host Defenses: The Immune Responseadyaly44No ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue Culture TechniquesDocument44 pagesCell and Tissue Culture Techniquesdrashti shah100% (1)
- Assessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using.12Document9 pagesAssessment of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using.12Muhammad Rifki100% (1)
- Protein Microarray Naveed Up MushtaqDocument16 pagesProtein Microarray Naveed Up MushtaqAngumaniNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 Lab Safety and DNA Isolation PDFDocument14 pagesPractical 1 Lab Safety and DNA Isolation PDFAbery AuNo ratings yet
- Basics of Cell Culture in 40 CharactersDocument33 pagesBasics of Cell Culture in 40 CharactersSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Cell Junction Types and Functions in 40 CharactersDocument30 pagesCell Junction Types and Functions in 40 CharactersNavodit GoelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Structural GenomicsDocument4 pagesUnit 1: Structural GenomicsLavanya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1B - Benzer's Work and Complementation TestDocument5 pagesLecture 1B - Benzer's Work and Complementation TestLAKSHAY VIRMANI100% (1)
- Animal Cell Culture - Cytotoxicity AssaysDocument30 pagesAnimal Cell Culture - Cytotoxicity AssaysVinod Sivadasan0% (2)
- Flow Cytometry Capabilities GuideDocument16 pagesFlow Cytometry Capabilities GuideirmaNo ratings yet
- Blotting Techniques: The Muscular SystemDocument33 pagesBlotting Techniques: The Muscular SystemPrasanna BabuNo ratings yet
- Immunohistochemistry Principles Uses and MethodsDocument10 pagesImmunohistochemistry Principles Uses and MethodsKailash PrajapatNo ratings yet
- PlasmidsDocument53 pagesPlasmidsPrerana SikarwarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Oncology: Retroviruses, Oncogenes, and Cancer DevelopmentDocument22 pagesIntroduction to Oncology: Retroviruses, Oncogenes, and Cancer DevelopmentkurniawanNo ratings yet
- Marker Assisted Selection Speeds Crop BreedingDocument34 pagesMarker Assisted Selection Speeds Crop Breedingvijjumandula0% (1)
- Animal Cells BioreactorsDocument13 pagesAnimal Cells BioreactorsRuben MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lab 18: Immunology 18.1 The ELISA: Activity 1: Using An ELISA To Diagnose Lupus To BeginDocument6 pagesLab 18: Immunology 18.1 The ELISA: Activity 1: Using An ELISA To Diagnose Lupus To BeginValerie OkakpuNo ratings yet
- Jaipur National University: Presented By: Richa Kumari Branch: B.Tech Biotech 6 SEMDocument27 pagesJaipur National University: Presented By: Richa Kumari Branch: B.Tech Biotech 6 SEMRamkrishna100% (1)
- PCR, RT-PCR, Nested-Pcr, Multiplex PCR, Quantitative PCRDocument116 pagesPCR, RT-PCR, Nested-Pcr, Multiplex PCR, Quantitative PCRYunizardiNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell CultureDocument33 pagesAnimal Cell CultureMd. Babul AktarNo ratings yet
- ELISA-Principle, Types and ApplicationsDocument4 pagesELISA-Principle, Types and ApplicationsSeema NegiNo ratings yet
- Plant Biotechnology (Tissue Culture)Document11 pagesPlant Biotechnology (Tissue Culture)Hewa HusenNo ratings yet
- Article in Press: Seminars in Cell & Developmental BiologyDocument13 pagesArticle in Press: Seminars in Cell & Developmental BiologyJosé Hernández ArriagaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells and Organ CultureDocument18 pagesStem Cells and Organ CultureGEETA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Culture EquipmentDocument59 pagesAnimal Cell Culture EquipmentLeonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 10 Viable Plate Counts Results and DiscussionDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 10 Viable Plate Counts Results and Discussionvanessa olga100% (1)
- Microbiology Methods of Monitoring PopulationsDocument17 pagesMicrobiology Methods of Monitoring PopulationsStephen MooreNo ratings yet
- Guide To Protein Purification, Volume 463Document6 pagesGuide To Protein Purification, Volume 463Dawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- cDNA Libraries and Gene CloningDocument8 pagescDNA Libraries and Gene CloningRoberto RomeroNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Cell Fractionation Procedures and Cytochemical TestsDocument6 pagesEvaluating Cell Fractionation Procedures and Cytochemical TestsJosh Zollman100% (1)
- Culture of HeLa CellsDocument5 pagesCulture of HeLa CellsanymousNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Animals: Production and ApplicationDocument15 pagesTransgenic Animals: Production and ApplicationAll rounders studyNo ratings yet
- AdenovirusDocument18 pagesAdenovirusNovika Ayuni RambeNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Chapter 1: An Overview of The Immune SystemDocument52 pagesImmunology: Chapter 1: An Overview of The Immune SystemMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- Primary Lymphoid Organs Generate Immune CellsDocument10 pagesPrimary Lymphoid Organs Generate Immune CellsKarthigaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Isolation of Bacteria From SoilDocument9 pagesSampling and Isolation of Bacteria From SoilKishmala BatoolNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Protein ProductionDocument23 pagesRecombinant Protein ProductionAnamitra SenNo ratings yet
- Restriction Digestion of Plasmid DNADocument22 pagesRestriction Digestion of Plasmid DNAMichelle100% (4)
- Bacterial Genetic Recombination MechanismsDocument31 pagesBacterial Genetic Recombination Mechanismssharkkzz17No ratings yet
- Molecular Carcinogenesis Endometrium PDFDocument7 pagesMolecular Carcinogenesis Endometrium PDFMelati HasnailNo ratings yet
- Gene Cloning TechnologyDocument16 pagesGene Cloning TechnologyNguyen Thanh Anh NiiroNo ratings yet
- Antigen Antibody Precipitation ReactionsDocument21 pagesAntigen Antibody Precipitation Reactionsvinupv88No ratings yet
- Methods To Study Soil Microbial DiversityDocument25 pagesMethods To Study Soil Microbial Diversityrd2165scribdNo ratings yet
- Cloning VectorsDocument5 pagesCloning VectorsMilo Kai HeeNo ratings yet
- NanomedicineDocument64 pagesNanomedicinePrabisha PrabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Bacteriophage-Lysis & LysogenyDocument16 pagesBacteriophage-Lysis & LysogenyIlyas MathakiyaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Vectors Lecture Molecular Biology CourseDocument20 pagesGenetic Vectors Lecture Molecular Biology CourseDr. Adnan Al-KanaanNo ratings yet
- Immunology - SyllabusDocument3 pagesImmunology - SyllabusAlaa' Al-AbdulrazzaqNo ratings yet
- Quorum Sensing in Bacteria and A Glance On Pseudomonas Aeruginosa 2327 5073.1000156Document10 pagesQuorum Sensing in Bacteria and A Glance On Pseudomonas Aeruginosa 2327 5073.1000156Tanjila IslamNo ratings yet
- SirajDocument15 pagesSirajSiraj AnsariNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Hela CellsDocument4 pagesMaintaining Hela CellsSathya DevNo ratings yet
- Unit-V 5.1.0 Production of Recombinant ProteinsDocument17 pagesUnit-V 5.1.0 Production of Recombinant ProteinsBharathiNo ratings yet
- Isolation of DNA From Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesIsolation of DNA From Animal TissuesAnura BandaraNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometry of DnaDocument7 pagesSpectrophotometry of DnaMel June FishNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometry. Principle and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesSpectrophotometry. Principle and Applicationsmdusman2010No ratings yet
- B Pharma 3rd Year Biotechnology 21-04-2020Document5 pagesB Pharma 3rd Year Biotechnology 21-04-2020Shailesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Ethanol Extracts of Leaves Keladi Tikus (Typhonium Flagelliforme Lodd.) On Human Tongue Cancer Cell Invasion (SP-C1) in VitroDocument7 pagesEffects of Ethanol Extracts of Leaves Keladi Tikus (Typhonium Flagelliforme Lodd.) On Human Tongue Cancer Cell Invasion (SP-C1) in VitroRahmayunitha MurianaNo ratings yet
- UTAR Centre for Foundation Studies Course Plan for Fundamentals of Cell BiologyDocument5 pagesUTAR Centre for Foundation Studies Course Plan for Fundamentals of Cell BiologyEngNo ratings yet
- Hak Paten DR Karry MullisDocument51 pagesHak Paten DR Karry Mullispln up2ksulselNo ratings yet
- Primer Design Using IDT Quest: Identifying NCBI Transcript & Associated PrimersDocument3 pagesPrimer Design Using IDT Quest: Identifying NCBI Transcript & Associated PrimersAqsa MuzammilNo ratings yet
- Cell As Basic Unit of Life: MesokaryoteDocument79 pagesCell As Basic Unit of Life: MesokaryotetabilinNo ratings yet
- Personal Philosophy of NursingDocument5 pagesPersonal Philosophy of NursingsarahreyNo ratings yet
- BIOINFORMATICS LAB ReportDocument14 pagesBIOINFORMATICS LAB ReportKaleemUllah SulimankhailNo ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsNayan Netaji KumbharNo ratings yet
- Target Identification and ValidationDocument21 pagesTarget Identification and ValidationManuel Christopher MontesclarosNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy ReviewDocument6 pagesTaxonomy ReviewRia DeviNo ratings yet
- Name Department::: Aiman AmjadDocument9 pagesName Department::: Aiman AmjadMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument39 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Investor's Presentation (Company Update)Document19 pagesInvestor's Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- DNA EkstrakromosomalDocument33 pagesDNA EkstrakromosomalSoraya Aya100% (1)
- # Category Image Product Name Producer Package Hs Code Remark Key FeaturesDocument9 pages# Category Image Product Name Producer Package Hs Code Remark Key Featuresiq_dianaNo ratings yet
- PR Truenat WHO Endorsement 02072020Document4 pagesPR Truenat WHO Endorsement 02072020KantiNareshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument211 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologyGaurav JoshiNo ratings yet
- Resume Anurag Mani Tripathi: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesResume Anurag Mani Tripathi: Career Objectivekrishna16No ratings yet
- Genetic RecombinationDocument24 pagesGenetic Recombinationkai dollNo ratings yet
- MBB 10 2nd Long Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesMBB 10 2nd Long Exam ReviewerAnonymous YRORccnMNo ratings yet
- Pierce Chapter 2Document30 pagesPierce Chapter 2Sarah HanNo ratings yet
- DesignerbabiesseniorresearchpaperDocument8 pagesDesignerbabiesseniorresearchpaperapi-311634646No ratings yet
- Listanco Abegail Lab Exercise#6Document3 pagesListanco Abegail Lab Exercise#6Abegail ListancoNo ratings yet
- Mitokondria 1Document40 pagesMitokondria 1Nilam CahyaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells - WorksheetDocument4 pagesPlant and Animal Cells - WorksheetsabaNo ratings yet
- Implications of Immunogenicity in Drug DevelopmentDocument7 pagesImplications of Immunogenicity in Drug DevelopmentnstefankoNo ratings yet
- CHEM F343: Inorganic Chemistry III: PilaniDocument29 pagesCHEM F343: Inorganic Chemistry III: PilaniANANYA PUPNEJANo ratings yet
- pGLO Transformation Lab: Tak MagaDocument8 pagespGLO Transformation Lab: Tak Magaapi-332475419100% (1)
- Plants & Animals Reproduce Through Sexual & Asexual MethodsDocument14 pagesPlants & Animals Reproduce Through Sexual & Asexual MethodsAleli Joy Profugo DalisayNo ratings yet
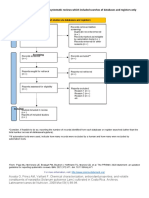
- PRISMA 2020 Flow Diagram For New Systematic Reviews Which Included Searches of Databases and Registers OnlyDocument2 pagesPRISMA 2020 Flow Diagram For New Systematic Reviews Which Included Searches of Databases and Registers OnlyJavier Gio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (396)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesFrom EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Mitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfFrom EverandMitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesFrom EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (55)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (389)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Unthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsFrom EverandUnthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsNo ratings yet
- The Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceFrom EverandThe Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (45)
- Awkward: The Science of Why We're Socially Awkward and Why That's AwesomeFrom EverandAwkward: The Science of Why We're Socially Awkward and Why That's AwesomeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)