Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Science Form 1
Uploaded by
Nur Atiah DaudOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Science Form 1
Uploaded by
Nur Atiah DaudCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
1 INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE
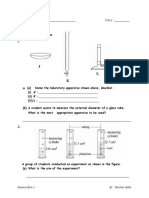
1. i) Name the following apparatus with the word given.
Retort stand Measuring cylinder Bunsen burner Conical flask
a.. b. c. d.
ii)
Burette Round bottomed flask Test tube Gas jar
e. f. g. h.
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
iii)
External calipers Pipette Burette Internal calipers
i. j. k. l.
iv)
Filter funnel Stop watch Spring balance Level balance
m. n.. o. p.
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
v)
Stethoscope Opisometer Thermometer Hand lens
q. r. s.. t.
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
b) Draw lines to show the correct match between the apparatus and their
functions
Name the apparatus Function
1.Beaker A. To measure the weight of an
object
2.Measuring cylinder B. To measure the volume of a
liquid
3.Gas jar C. To contain liquid and chemicals
4.Spring balance D. To measure temperature
5.Thermometer
E. To collect gases
6.Pipette F. To measure fixed volume of
liquid
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
2. Give the function of apparatus below.
i) Pipette:
…………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………...
ii) Thermometer:
…………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………..
iii) Measuring cylinder :
…………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………...
iv) Gas jar
…………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………..
v) Spring balance
…………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………...
vi) Thermometer:
…………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………..
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
3. Name the apparatus below.
i) ii)
iii) iv)
v) vi)
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
4. Diagram 4 shows a thermometer.
a) What is the reading of the thermometer?
……………………………………………
b) Name liquid P
P: …………………………..
40
30 P
c) Put a ( / ) in the correct box on the figure to show the correct eye when taking a
reading?
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
1.2 CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
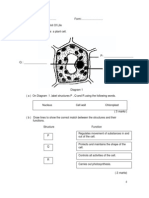
1.Name the parts of microscope.
P
T
R
S
U
a) Draw lines to show the correct match between the part of the microscope and
its function.
PART FUNCTION
P 1.Hold the objective lenses
Q 2.Regulates the amount of light reaching the
objective lens
R 3.Holds the eye piece
S 4.The lens that magnifies the specimen
T 5.Reflects light into the microscope
uestion
U 6.Platform where the slide is placed
V 7.Control the height of the microscope tube
with more accurately
W 8.Control the height of the microscope tube
for focusing
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
Questions
2. (i) What is the function of eyepiece?
…………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) What is the function of stage?
…………………………………………………………………………………… .
(iii) What is the function of mirror?
…………………………………………………………………………………… .
(iv) What is the function of objective lens?
…………………………………………………………………………………… .
(v). What is the function of coarse focus knob?
……………………………………………………………………………………
(vi). What is the function of fine focus knob?
……………………………………………………………………………………
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
Cell as a unit of life
3. Diagram 3 shows an animal cell.
Diagram 3
Label each part of the cell with a suitable word from the following list.
Nucleus Cell membrane Cytoplasm
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
4. Diagram 4 shows a plant cell
Diagram 4
Label each part of the cell with a suitable word from the following list.
Cell membrane Cytoplasm Chloroplast Nucleus Vacuole cell wall
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
5 Diagram 5 shows the structure of a cell.
Q U
Diagram 5
Match the labeled cell structures to their names and functions.
Cell structure Name Function
P Nucleus Maintains the shape of cell
Q Cell membrane Controls all cell activities
R Cytoplasm Absorb sunlight for
photosynthesis
S Chloroplast Stores water and
dissolved minerals
T Cell wall Site of chemical
processes
U Vacuole Control the movement of
Substances in and out of
The cell
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
UNICELLULAR AND MULITICELLULAR
6. a) Name the organisms shown in Diagram 6.
P : ___________________ Q : ____________________
R : __________________ S : _____________________
Diagram 6
b) Group the organisms in Diagram 6 into unicellular or multicellular
organisms
Unicellular Multicellular
i ______________________ i __________________________
ii ______________________ ii _________________________
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
Cell organisation
7. Match the name to the correct part of the cell organisation in human.
Name Part of cell organisation
Cell
P
System
Tissue R
Organ S
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
8. Show the organisation of cells in the human body by filling in the boxes below with the
words given.
System tissue organ cell organism
Made up of different
systems that work
d together
Made up of
c different organs
made up of
different tissues
b
made up of
a the same type
of cells
the basic
unit
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
1.3 MATTER
1. Classify the following matter into solids, liquids or gases
a) e)
Air in the
balloon
hot water
_____________
_______________
f)
`
b)
Hot air
balloon
______________
g)
___________________ Wind from
windmill
c) Carbon monoxide
__________________ h)
d)
aeroplane
kerosene
___________________ _________________
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
2) Match objects/substances below to their arrangement of particles
a) glue
b) coffee
i
c) smoke
i
d) breeze
e) mercury
f) blood
ii.
g) book
h) steam
i) oxygen
j) rainwater
iii.
k) thumbtack
l) cloth
m) droplets
n) salt solution
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
1.4 THE VARIETY OF RESOURCES ON EARTH
THE CONCEPT OF DENSITY
The density of substance is the mass of the substance in a unit
volume.
The unit for density is kg/m³ or g/cm³
DENSITY (D) = MASS (M)
VOLUME (V)
1. What is …………
M
a. D = _______
D V
V = _________
Example 1
The mass of 5cm³ of iron is 10.0g. What is its density?
The density of iron = Mass
Volume
= 10.0g
5cm³
= 2 g/cm³
2.The mass of an object is 30 g. What is its density if it has a volume
of 12 cm³ ?
3.The volume of R was determined to be 40cm³ in an experiment. If the
density of solid R is 0.5 g/cm³. What is its mass?
4.The mass of piece of stone is 360g and its volume is 200cm³. What is the
density of the stone?
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
A less dense substance FLOATS in a denser liquid
Whereas a denser substance SINKS in a less denser liquid
STONE WATER OIL CORK
5. The substances are put together according to a, b, c, and d.Draw the
position.
a. Stone and Water b. Water and oil
c. Cork , water and oil d. Stone, water ,oil and Cork
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
6. Diagram 6 shows the densities of liquids Z, Y and X and solids P, Q and
R which are put into a measuring cylinder.
a. Arrange the density of liquid X, Y and Z in an ascending order?
b. Arrange the density of liquid X, Y and Z in a descending order?
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
c. Arrange the solids P, Q and R in an ascending order?
d. Arrange the solids P, Q and R in a descending order?
e. Arrange P,Q, R , X, Y and Z in an ascending order?
f . Arrange P, Q ,R , X, Y and Z, in a descending order?
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
7. Diagram 7 shows the arrangement of particles in three substances, J, K and L.
Label J, K and L using the following words:
Element Compound Mixture
J K L
E_ _ _ _ _ t C _m_ _ und M_ xt__e
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
8. Draw lines to show the correct match between the names of the substances
and the diagrams.
Compound
Mixture
Element
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
1.5 THE AIR AROUND US
1. Diagram 1 shows the composition and percentage of the constituents of air.
C 0.03% D
1%
B
21%
A
78%
Diagram 1
a) Identify the following gases based on Diagram 1
Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon dioxide
i. Gas A : ___________________________
ii Gas B : ____________________________
iii Gas C : _____________________________
b) State the confirmation test for the gases below :
i) Gas B :
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
ii) Gas C :
________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
1.6 SOURCES OF ENERGY
1. State the forms of energy involved in the picture shown using the following word
Chemical energy Sound energy Kinetic energy Nuclear energy Light energy
Heat energy
a) b) c)
d) e) f)
g) h) i)
DIAGRAM 1.1
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
2. Diagram 2 shows various sources of energy on earth
D
D G
E F
C
Diagram 2
Name the energy sources that represented by
A : ..................................................................................
B : ..................................................................................
C: ...................................................................................
D : ..................................................................................
E : ……………………………………………………………
F :……………………………………………………………
G :……………………………………………………………
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
1.7 HEAT
1. On diagram 1, draw and label the heat flow of sea breeze and land
breeze using the given information.
Hot air rises cool air from the sea hot air from land
a. ……………….....
______
Land breeze
c………………..
Hot air
b. …………..
Land
Sea breeze
Sea breeze
Diagram 1
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
2. The change of state of matter involves absorption or release of heat energy.
a) Draw the particles arrangement of ice when heated
Before heating After heating
b) Draw the particles arrangement of ice when melted
Before melting After melting
c) Draw the particles arrangement of water when frozen
Before freezing After freezing
d) Draw the particles arrangement of water when boiled
Before boiling After boiling
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
e) Draw the particles arrangement of water when cooled
Before cooling After cooling
f) Draw the particles arrangement of iodine crystals when heated
Before sublimation After sublimation
g) Draw the particles arrangement of steam when cooled
Before condensation After condensation
h) Draw the particles arrangement of water when evaporated
Before evaporation After evaporation
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
5. Draw the particles of X, Y and Z in the box given.
X Y Z
MODUL 1 FORM 1 STF 2007
You might also like
- Modul Science Form 2Document36 pagesModul Science Form 2Nur Atiah Daud94% (18)
- Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesForm 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeJames WongNo ratings yet
- Name : Chapter 1 - Scientific InvestigationDocument10 pagesName : Chapter 1 - Scientific InvestigationRozaini Othman84% (32)
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 1Document7 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 1Syahrul89% (66)
- Form 1 Chapter 2Document7 pagesForm 1 Chapter 2ajakazNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Objective TestDocument7 pagesScience Form 1 Objective TestSITI ZAIDAH AHMAD50% (6)
- Revision exercise answers science form 1 cells processes gasesDocument4 pagesRevision exercise answers science form 1 cells processes gasesNor Adila100% (4)
- Science Form 1Document11 pagesScience Form 1uminoriah67% (6)
- Science Form 1Document13 pagesScience Form 1Aziah Husain67% (3)
- Example Form 1 Science Paper (With Answers)Document10 pagesExample Form 1 Science Paper (With Answers)Kenny Cheah Soon Lee100% (8)
- Science Form 1 Exam QuestionDocument7 pagesScience Form 1 Exam QuestionNorliyana Ali57% (7)
- Name : .. Chapter 2 - Cell As A Unit ofDocument17 pagesName : .. Chapter 2 - Cell As A Unit ofRozaini Othman81% (27)
- Soalan Science Tingkatan 1Document8 pagesSoalan Science Tingkatan 1Sabri AwangNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 - Model QuestionDocument7 pagesScience Form 1 - Model Questionuminoriah68% (25)
- Exercise BiodiversityDocument17 pagesExercise BiodiversityAl Amin Azman100% (9)
- Answer All Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options, A, B, C and D. For Each Question, Choose One Answer OnlyDocument7 pagesAnswer All Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options, A, B, C and D. For Each Question, Choose One Answer OnlyNurAnnyss AzizNo ratings yet
- MOdul Science Form 3Document27 pagesMOdul Science Form 3Nur Atiah Daud95% (19)
- Exercise Science Form 1 (Chapters 1-7Document9 pagesExercise Science Form 1 (Chapters 1-7Wan Shuhaimi50% (4)
- Form 2 Chapter 5Document10 pagesForm 2 Chapter 5naza977587% (15)
- Form 1 Science Chapter 4Document33 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 4qq23595% (21)
- Form 2 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3naza977588% (8)
- Science Form 1Document14 pagesScience Form 1suhaila bakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2naza9775100% (17)
- Form 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Form 1 Science NotesDocument20 pagesForm 1 Science NotesMyName Tiff68% (25)
- Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Air Composition and RespirationDocument9 pagesAir Composition and RespirationAimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- Monthly Test Science Form 2Document3 pagesMonthly Test Science Form 2Qit_C100% (3)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2Document29 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2qq23588% (68)
- Form 2 Chapter 2Document7 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2naza977578% (18)
- Science Form 3 RevisionDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 RevisionstanleyleeNo ratings yet
- Intro to Science Chapter 1Document19 pagesIntro to Science Chapter 1Mzari Mzain100% (5)
- Chapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofRozaini Othman100% (15)
- Introduction to Science Chapter 1Document56 pagesIntroduction to Science Chapter 1Halizah Ramthan88% (16)
- Form 3 Chapter 9Document3 pagesForm 3 Chapter 9naza9775100% (5)
- Exercise Science Form 1Document1 pageExercise Science Form 1Komalata Manokaran50% (2)
- Matter Module Form 1Document8 pagesMatter Module Form 1AnnaalPhilip100% (1)
- Form 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 2Document8 pagesForm 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 2Kelvin0% (1)
- Modul 1 - Form 1 STFDocument31 pagesModul 1 - Form 1 STFmadrosli100% (3)
- Jabatan pelajaran perak Module 1 science form 1Document79 pagesJabatan pelajaran perak Module 1 science form 1Leong Wai YenNo ratings yet
- I) Namakan Alat Radas Berikut:: 1.1 Pengenalan Kepada SainsDocument29 pagesI) Namakan Alat Radas Berikut:: 1.1 Pengenalan Kepada SainssujinaliniNo ratings yet
- 1.name The Parts of Microscope. PDocument6 pages1.name The Parts of Microscope. PNur E L HudaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Late Bloomers of CLASS-X (2017-18) : Subject: Science Chapter: 1-Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank For Late Bloomers of CLASS-X (2017-18) : Subject: Science Chapter: 1-Chemical Reactions and Equationsapi-400692183No ratings yet
- CO-The Parts and Functions of A MicroscopeDocument26 pagesCO-The Parts and Functions of A MicroscopePrincy MoralesNo ratings yet
- NCSE 2013 Integrated ScienceDocument22 pagesNCSE 2013 Integrated ScienceMicahNo ratings yet
- PASCA PT3 2016 BIOLOGY: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesPASCA PT3 2016 BIOLOGY: Cell Structure and FunctionSjk TRNo ratings yet
- Obs B ScienceDocument9 pagesObs B ScienceKartelohello HemanNo ratings yet
- Biology 2023Document4 pagesBiology 2023chauhanadityarNo ratings yet
- L E Ce: KrrtistDocument14 pagesL E Ce: KrrtistSoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Cell (Bio MC)Document6 pagesChapter 2 - The Cell (Bio MC)Emily LiNo ratings yet
- Modul Science Form 1Document31 pagesModul Science Form 1Norafiza HashimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Biology Exam RevisionDocument12 pagesCambridge O Level Biology Exam RevisionLaras PutriNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 (Explanation)Document18 pagesPaper 2 (Explanation)Srp KaMie LooNo ratings yet
- Bgcse Physics Paper 3 2004Document12 pagesBgcse Physics Paper 3 2004Letso JamesNo ratings yet
- 1 Match The Meaning of Each Following Symbols. Symbols MeaningDocument8 pages1 Match The Meaning of Each Following Symbols. Symbols MeaningHasmah HalimNo ratings yet
- 2K6 en 102 - Apr. 2011Document2 pages2K6 en 102 - Apr. 2011MunavirFirozNo ratings yet
- SymmetryandvibrationalspectraDocument10 pagesSymmetryandvibrationalspectraMuhamad Tatang TaftazaniNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Cellular Components PART B (Student)Document8 pages2.2 Cellular Components PART B (Student)yong tpNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyFrom EverandThe Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNo ratings yet
- Idioms and Phrasal Verbs PracticeDocument3 pagesIdioms and Phrasal Verbs PracticeNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Poems - I Wonder (Form 1)Document1 pagePoems - I Wonder (Form 1)Nor AishahNo ratings yet
- Novel Asked in Form1 & 2 - Journey To The Centre of The EarthDocument4 pagesNovel Asked in Form1 & 2 - Journey To The Centre of The EarthNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH LANGUAGE Reading Revised BAND 1-6Document12 pagesENGLISH LANGUAGE Reading Revised BAND 1-6Nur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1-10Document16 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1-10Nur Atiah Daud57% (7)
- Making It WorksDocument25 pagesMaking It WorksNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- B Y C P: Ooting OUR Omputer and OSTDocument4 pagesB Y C P: Ooting OUR Omputer and OSTNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- A Fighter's LineDocument3 pagesA Fighter's LineNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- English Language PBS Writing Revised BAND 1-6Document10 pagesEnglish Language PBS Writing Revised BAND 1-6Nur Atiah Daud100% (2)
- ENGLISH LANGUAGE PBS Listening and Speaking Revised BAND 1-6Document15 pagesENGLISH LANGUAGE PBS Listening and Speaking Revised BAND 1-6Nur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1 - 7Document12 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 1 - 7Nur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- System Unit WorksheetDocument4 pagesSystem Unit WorksheetNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Devices/peripheralsDocument1 pageComputer Hardware Devices/peripheralsNur Atiah Daud100% (1)
- Phrasal VerbsDocument4 pagesPhrasal VerbsNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Document14 pagesScience Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Nur Atiah Daud88% (8)
- Module 2 - Operating SystemDocument2 pagesModule 2 - Operating SystemNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Computer Evolution WorksheetDocument1 pageComputer Evolution WorksheetNur Atiah Daud50% (2)
- Module 1-Intro To SoftwareDocument2 pagesModule 1-Intro To SoftwareNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Input, Output, Storage DevicesDocument4 pagesInput, Output, Storage DevicesNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Ictl Form 1 - Module 7) Computer SettingDocument21 pagesIctl Form 1 - Module 7) Computer SettingNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Ictl Form1-Module 6) Basic MaintenanceDocument20 pagesIctl Form1-Module 6) Basic MaintenanceNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- ICTL Mic. Word-Toolbar Icons ExercisesDocument2 pagesICTL Mic. Word-Toolbar Icons ExercisesNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- MOdul Science Form 3Document27 pagesMOdul Science Form 3Nur Atiah Daud95% (19)
- Puter Lab Management - Mrs AtiahDocument4 pagesPuter Lab Management - Mrs AtiahNur Atiah DaudNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Unit 6 Day 2Document18 pagesGrade 12 Unit 6 Day 2Huy GMNo ratings yet
- Animal Classification (Porifera-Echinodermata)Document164 pagesAnimal Classification (Porifera-Echinodermata)9415697349No ratings yet
- Can Can'tDocument25 pagesCan Can'tzehraNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 187.212.26.79 On Thu, 11 Aug 2022 02:01:26 UTCDocument62 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 187.212.26.79 On Thu, 11 Aug 2022 02:01:26 UTCMAURICIO ARMANDO PAEZ SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Traffic Species Reptiles1Document113 pagesTraffic Species Reptiles1AGV_FORESTALNo ratings yet
- Molecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution PDFDocument522 pagesMolecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution PDFEvandro LorensettiNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Prepared By: Maricarr Del Mundo - AlegreDocument43 pagesCell Types: Prepared By: Maricarr Del Mundo - AlegreAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- 2 Msds Potassium Hydroxide - 2Document7 pages2 Msds Potassium Hydroxide - 2Asep TheaNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Society and Social Science DocumentDocument6 pagesScience, Technology, Society and Social Science DocumentMARLO BARINGNo ratings yet
- Teori SystemDocument12 pagesTeori SystemHendrik GunawanNo ratings yet
- Ken AlibekDocument8 pagesKen AlibekHenry Escobar0% (1)
- Ormus - Spiritual and Medicinal Gold With Incredible Healing PotentialDocument5 pagesOrmus - Spiritual and Medicinal Gold With Incredible Healing PotentialDevin BoudreauNo ratings yet
- Rhode Island Coastal Buffer Zone Planting Guide - University of Rhode IslandDocument14 pagesRhode Island Coastal Buffer Zone Planting Guide - University of Rhode IslandFree Rain Garden Manuals and MoreNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay NorhanDocument23 pagesExtended Essay NorhanAbed ZaghalNo ratings yet
- Roja Ramani Vasamshetty MPT IiDocument37 pagesRoja Ramani Vasamshetty MPT Iideepuphysio100% (3)
- Predicting The Properties of Drug Molecules:: Quantum Mechanics and Molecular MechanicsDocument45 pagesPredicting The Properties of Drug Molecules:: Quantum Mechanics and Molecular MechanicsekaipNo ratings yet
- Death Watch Beetle: in CultureDocument2 pagesDeath Watch Beetle: in Culturewinofvin9No ratings yet
- Quikbib - Pea Aphids 139Document11 pagesQuikbib - Pea Aphids 139Rusdi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Probiotics, Prebiotics and The Gut Microbiota: Ilsi Europe Concise Monograph SeriesDocument40 pagesProbiotics, Prebiotics and The Gut Microbiota: Ilsi Europe Concise Monograph Seriesjimmy7forever100% (1)
- Student Exercise On PCRDocument5 pagesStudent Exercise On PCRsacannNo ratings yet
- Hello ScribeDocument6 pagesHello ScribeYogesh BagadNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes and Sister Chromatids - Biology ForumDocument4 pagesDifference Between Homologous Chromosomes and Sister Chromatids - Biology Forummpaka felliNo ratings yet
- BOOK - Advanced Pathology and Treatment of Diseases of Domestic Animals With Special Reference To Etiology, Signs, Pathology and Management 2008Document517 pagesBOOK - Advanced Pathology and Treatment of Diseases of Domestic Animals With Special Reference To Etiology, Signs, Pathology and Management 2008lumos_vnNo ratings yet
- Microorganism Identification MethodsDocument29 pagesMicroorganism Identification MethodsAlmoatazbellah AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Self StudyDocument5 pagesGas Exchange Self Study4E-27 Tsoi Cheuk Ying (Ada)No ratings yet
- Molecular Drug Targets-1Document75 pagesMolecular Drug Targets-1Phoebe Llamelo100% (1)
- Q3 M5-Formative Test in Science 10Document2 pagesQ3 M5-Formative Test in Science 10Wayne GodioNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Neck and Back Pain MASUDDocument155 pagesTreatment of Neck and Back Pain MASUDPaul Radulescu - Fizioterapeut100% (1)
- Ballistic StretchingDocument14 pagesBallistic Stretchingapi-351172625No ratings yet
- M.Sc. ZoologyDocument21 pagesM.Sc. ZoologySabyasachi DasNo ratings yet