Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Motherboard I. Computer Motherboard: Property of STI
Uploaded by
Rachelle GandaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Motherboard I. Computer Motherboard: Property of STI
Uploaded by
Rachelle GandaCopyright:
Available Formats
SH1608
Computer Motherboard
I. Computer Motherboard
A printed circuit board that is the foundation of a computer, located inside the computer case.
It allocates power to the CPU, RAM, and all other computer hardware components.
Allows hardware components to communicate with one another.
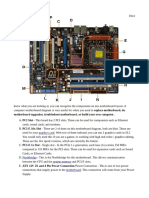
II. Parts of the Motherboard
Photo source from mpsaz.org
A. PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) Slot
This board has two (2) PCI slots. These can be used for components such as Ethernet
cards, sound cards and modems.
B. PCI- E (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) 16x Slot
There are two on this motherboard diagram. These are used for graphics card. With two
(2) of them onboard, you can run two (2) graphic cards, which is good if you are a
gamer.
C. PCI- E 1x Slot
Single slot- In the PCIe 1.x generation, each lane (1x) carries 250 MB/s compared to
133 MB/s for the PCI slots. These can be used for expansion cards such as sound card
or Ethernet card.
D. North Bridge
This allows communication between the CPU and the system memory and PCI-E slots.
04 Handout 1 *Property of STI
Page 1 of 4
SH1608
E. 4-Pin power Connector
It is a 12V power supply cable like that shown in the picture used with motherboards
that have an Intel Pentium 4 processor. The P4 cable has two (2) black wires that serve
as a ground and two (2) yellow wires that are +12VDC.
F. CPU Fan Connection
This is where your CPU fan will connect. Using this connection over one (1) from your
power supply will allow the motherboard to control the sped of your fan, based on the
CPU temperature.
G. CPU Socket
CPU socket or processor socket is a connection that allows a computer processors to
be connected to a motherboard.
H. Memory Slots
A memory slot, memory socket, or RAM slot is what allows computer memory (RAM)
to be inserted into the computer. Depending on the motherboard, there may be two (2)
to four (4) memory slots (sometimes more on high-end motherboards) and are what
determine the type of RAM used with the computer.
I. ATX Power Connector
It is one (1) of the largest connectors inside a computer. It connects a power supply to
an ATX style motherboard. This is the main power connection of motherboard and
comes from the power supply.
J. IDE Connection
Short for Integrated Drive Electronics or IBM Disc Electronics, IDE is more
commonly known as ATA or Parallel ATA (PATA). It is a standard interface for IBM
compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives.
K. Southbridge
It is an IC on the motherboard responsible for the hard drive controller, I/O controller
and integrated hardware. Integrated hardware can include the sound card and video card
if on the motherboard, USB, PCI, ISA, IDE, BIOS, and Ethernet.
L. SATA Connections
SerialATA is capable of delivering 1.5 Gbps (1500 MBps) of performance to each drive
within a disk array. It has the benefit of being backwards-compatible with ATA and
ATAPI devices, and offers a thin, small cable solution, as seen in the photo on the right.
This cable helps make a much easier cable routing and offers better airflow in the
computer when compared to the earlier ribbon cables used with ATA drives.
M. Front Panel Connections
This is where you will hook in the connections from your case. These are mostly the
different controls on your case such as power on, reset button and LEDs.
N. FDD Connection
It is where the floppy drive connects to the computer motherboard.
O. External USB Connections
This is where you will plug in external USB connections for your case or USB
bracket.
P. CMOS Battery
CMOS is an on-board, battery powered semiconductor chip inside computers that
stores information. This information ranges from the system time and date to system
hardware settings for your computer.
04 Handout 1 *Property of STI
Page 2 of 4
SH1608
III. Types of Motherboards
Photo source from Cengage learning
04 Handout 1 *Property of STI
Page 3 of 4
SH1608
References:
Adrian, B. a. (2003-2016). Retrieved from study.com: http://study.com/
Kopplin, J. (2002). An illustrated history of computers. Retrieved from Computer Science Lab:
http://www.computersciencelab.com/ComputerHistory/History.htm
M., M., & Verma, G. K. (2016). Retrieved from Tutorial Point: http://www.tutorialspoint.com/
Marcelo, A. (2008). Understanding PC hardware. Jemma Inc.
Parsons, J., & Oja, D. (2014). Computer concepts. Cengage Learning Asia Pte Ltd.
04 Handout 1 *Property of STI
Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- Basic & Major Parts of Motherboard and Its Functions - TechchoreDocument22 pagesBasic & Major Parts of Motherboard and Its Functions - Techchoreleon08jay100% (1)
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- CPH Microproject PDFDocument12 pagesCPH Microproject PDFRohanNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOMPUTER MOTHERBOARD: Main PC Circuit Board ExplainedStar Boy DavieNo ratings yet
- Motherboard SlidesDocument21 pagesMotherboard Slidesmubiru mosesNo ratings yet
- The System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterDocument10 pagesThe System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Document4 pagesDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNo ratings yet
- Cpe111-Lesson-5 Parts of ComputerDocument81 pagesCpe111-Lesson-5 Parts of ComputerLance AsioNo ratings yet
- AsssssDocument13 pagesAsssssElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Document46 pagesHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21No ratings yet
- Basic Comp 02 - Handout - 1Document6 pagesBasic Comp 02 - Handout - 1Rachelle GandaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Study NotesDocument2 pagesMotherboard Study NotesaniketiluNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard Diagram Is Very Useful For When You Need To Replace Motherboard, DoDocument2 pagesComputer Motherboard Diagram Is Very Useful For When You Need To Replace Motherboard, Dohelen adoNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 The MotherboardDocument17 pagesUnit 03 The MotherboardSneaky peteNo ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument14 pagesComponents of A MotherboardvcinfotechNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems / ServicingDocument406 pagesComputer Systems / ServicingMakaha Rutendo0% (1)
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4CABADONGA, Justin M.No ratings yet
- What Is A MotherboardDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MotherboardManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Contoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesContoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisMerry ErawatiNo ratings yet
- And The Last One IsDocument4 pagesAnd The Last One IsSơn Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Document0 pagesCompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Wasantha KumaraNo ratings yet
- ItwslabDocument77 pagesItwslabKalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- Tle-Css Grade9 q1 Las5Document11 pagesTle-Css Grade9 q1 Las5Van ImperialNo ratings yet
- Components of MotherboardDocument4 pagesComponents of MotherboardMayur GoreNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to MotherboardsDocument5 pagesThe Essential Guide to MotherboardsElleera RemorerasNo ratings yet
- Study of Motherboard Components and ConnectorsDocument5 pagesStudy of Motherboard Components and ConnectorsSarang JamwalNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lab ReportDocument37 pagesMicroprocessor Lab ReportIT79 Yash SamantNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument5 pagesMotherboardRichard Melvin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of MotherboardsDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of MotherboardsDar N. AgasangNo ratings yet
- Internal Computer Parts GuideDocument30 pagesInternal Computer Parts GuideAC BalioNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument9 pagesMotherboardAhmed AbuNasserNo ratings yet
- 2.2B Unit2 - The Motherboard. Components and ConfigurationDocument6 pages2.2B Unit2 - The Motherboard. Components and ConfigurationAngel Rodolfo Trinidad SechaNo ratings yet
- Itws ManualDocument98 pagesItws Manualapi-291463406No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris (1) KhafliDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris (1) KhafliHolisNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard: Data Exchange in The MotherboardDocument4 pagesComputer Motherboard: Data Exchange in The MotherboardryekeaanNo ratings yet
- Training ProcedureDocument24 pagesTraining Procedureladsjovero6162100% (1)
- Motherboard and Its ComponentsDocument5 pagesMotherboard and Its ComponentsVenky MudavathNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and ServicingDocument232 pagesComputer Hardware and ServicingrajeevNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts and Functions ExplainedDocument4 pagesMotherboard Parts and Functions ExplainedJaynard Paul ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument53 pagesComputer ComponentsAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 04152023Document41 pagesChapter1 04152023NICDAO, Christine JoyNo ratings yet
- Lab 02 - Intro to Computing Components (EC-102Document18 pagesLab 02 - Intro to Computing Components (EC-102Ahmad MusabNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Motherboard: Understanding the Heart of Your PCDocument37 pagesModule 5 Motherboard: Understanding the Heart of Your PCyuva_sriNo ratings yet
- Hardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFDocument8 pagesHardware Notes New Ports and Slots PDFKrish NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Report On MotherboardDocument15 pagesMicro Project Report On Motherboardabu100% (14)
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDocument10 pagesG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Bing MotherboardDocument3 pagesBing Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument55 pagesModule IHrushikesh DanduNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop PSBTEDocument21 pagesComputer Workshop PSBTEShubhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- This Is The Asus P5N32Document2 pagesThis Is The Asus P5N32Gusti Suryanata0% (1)
- Computer Motherboard PresentationDocument21 pagesComputer Motherboard PresentationKoushal JainNo ratings yet
- The MotherboardDocument8 pagesThe MotherboardVann JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok 6Document8 pagesTugas Kelompok 6Rika ElsiaNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing NC IIDocument21 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing NC IIShe Ma RieNo ratings yet
- CSS G11 Module 4 Q1Document20 pagesCSS G11 Module 4 Q1Romulo A. Cordez Jr.No ratings yet
- CSS_11_Q1_W4-5_FinalizedDocument31 pagesCSS_11_Q1_W4-5_FinalizedAC BalioNo ratings yet
- Computer Input and Output Devices ExplainedDocument3 pagesComputer Input and Output Devices ExplainedRachelle GandaNo ratings yet
- History of Computers GenerationsDocument4 pagesHistory of Computers GenerationsRachelle GandaNo ratings yet
- I. Computer Memory A. Computer Memory OverviewDocument4 pagesI. Computer Memory A. Computer Memory OverviewRachelle GandaNo ratings yet
- I. Computer Overview A. Definition of ComputerDocument3 pagesI. Computer Overview A. Definition of ComputerRachelle GandaNo ratings yet
- Basic Input Devices GuideDocument3 pagesBasic Input Devices GuideRachelle GandaNo ratings yet
- 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument33 pages8051 Microcontrollerchanoch254No ratings yet
- AMILO Pa 1510Document3 pagesAMILO Pa 1510highlander_001No ratings yet
- Comcolor FW Series Technical Manual Panel TestDocument352 pagesComcolor FW Series Technical Manual Panel Testvinh vu100% (2)
- M P I SllybusDocument2 pagesM P I SllybusVipul RamolaNo ratings yet
- Picture ItDocument10 pagesPicture ItMahboob IqbalNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guild To Building A PC: 1st EditionDocument37 pagesUltimate Guild To Building A PC: 1st EditionTony HueNo ratings yet
- Doosan Infracore 30ia TrainingDocument63 pagesDoosan Infracore 30ia TrainingSaul HercasNo ratings yet
- HD44780 CommandsDocument3 pagesHD44780 CommandsPhani ChakravarthiNo ratings yet
- CS401 - Short Notes Chapter 1Document7 pagesCS401 - Short Notes Chapter 1aafiah100% (1)
- Keil ULINK Series: Related ProductsDocument1 pageKeil ULINK Series: Related ProductsBogdanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Application Development with ThreadsDocument28 pagesCloud Application Development with ThreadsBunny HoneyNo ratings yet
- CP400 Control Panel PresentationDocument24 pagesCP400 Control Panel PresentationWilliam SilvaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledapi-233604231No ratings yet
- Cee Xerox Npcatalog Nov2005Document22 pagesCee Xerox Npcatalog Nov2005zoka4175No ratings yet
- Lq2170 Service ManualDocument172 pagesLq2170 Service ManualheruNo ratings yet
- CJ1M (Brochure) PDFDocument2 pagesCJ1M (Brochure) PDFDio Ilham Tirta AdiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - New 1Document72 pagesModule 2 - New 1Bantu AadhfNo ratings yet
- Dell Latitude d630 - Quanta Jm7b-Discrete 128mb - Rev 2b 2Document49 pagesDell Latitude d630 - Quanta Jm7b-Discrete 128mb - Rev 2b 2jj71No ratings yet
- THDB-HTG UserManual v1.0.2Document20 pagesTHDB-HTG UserManual v1.0.2Ma GaNo ratings yet
- 8255A Study Card User ManualDocument57 pages8255A Study Card User ManualbdNo ratings yet
- ReadMe S7 PLCSIM V16 enUSDocument2 pagesReadMe S7 PLCSIM V16 enUSKhalid BaddarNo ratings yet
- Computer System (Csc1033) Ver. 2003Document20 pagesComputer System (Csc1033) Ver. 2003izzul_125z1419No ratings yet
- Activity Sheets For Basic Computer OperationsDocument13 pagesActivity Sheets For Basic Computer OperationsFernan Enad100% (1)
- Maninder KaurDocument25 pagesManinder KaurRAMJI AWASTHINo ratings yet
- OPS-Chapter-3-Process ManagementDocument16 pagesOPS-Chapter-3-Process Managementom jageNo ratings yet
- Technical Test LTRDocument11 pagesTechnical Test LTRAlberto RuizNo ratings yet
- Manual Workcenter 3315Document264 pagesManual Workcenter 3315emanuel_schonNo ratings yet
- Officejet Pro X476 X576 Guia UsuarioDocument336 pagesOfficejet Pro X476 X576 Guia UsuarioVictor Martínez PomarNo ratings yet
- New COcu After Review and RefineDocument23 pagesNew COcu After Review and RefineAzzah NazNo ratings yet
- DAC - COS - Day 4Document77 pagesDAC - COS - Day 4kovol29478No ratings yet