Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5-Ad and As: Basic Macroeconomics Econ 70 XA, Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan
Uploaded by
Mitch Bonita AbarcaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5-Ad and As: Basic Macroeconomics Econ 70 XA, Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan
Uploaded by
Mitch Bonita AbarcaCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Macroeconomics
Econ 70 XA, Xavier University- Ateneo de Cagayan
CHAPTER 5- AD AND AS
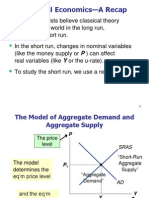
AS -- # of Y firms are willing to apply AD -- combination of price level and Y evel at which the goods market and money market are simultaneously equilibrium AD shifts if: Increase in money supply other expansionary policies: tax; spending; i , Thus, theres an increase money to spend, consumption increases AS shifts to the rights Any expansionary policy can be inflationary. Think of a vertical AS. If the AD shifts to the right, there is a new (and higher price).
1. AS
C1. Long-run Classical AS curve
Figure 2
Accumulating more inputs and technology; AS
full employment: If: D; Production
Page 1
Basic Macroeconomics
Econ 70 XA, Xavier University- Ateneo de Cagayan
Then: focus on D sector, not on D sector If economy-wide: But if: all factors are used up, you cannot production. So, just price 100 w; D; no more w so just wages; Price of output At FE Potential GDP (target)
C2 Short-run Keynesian AS curve
supply any Y at existing P Due to u; they exploit u at current wage; So AS production do not change Price sticky => firms dont want P; when demand . But it only decrease or increase output. Notes: At CAS (LR) => GDP Potential depend on price level KAS (SR) => Price level dont depend on GDP level Definitions: - Frictional unemployment => usual searching for jobs. (labor mobility) - NRU => arising from natural labor market frictions
Page 2
Basic Macroeconomics
Econ 70 XA, Xavier University- Ateneo de Cagayan
2. AD
Expansionary policies: shift AD (right) ( G; t; m)v.v.
AD depends on real money supply (M/P) Expansion Money market: If M/P ; Spending ; I; I ; AD v.v. If P; M/P ; AD ; v.v. Expansion goods market If consumer confidence ; => AD v.v. Tax cuts
By: Quantity Theory of Money explains this: GDP nominal = Pxy Velocity = V => (M) (V) = (P) (Y) Money supply = M If V is constant; then (M) (V) = P Y changes For M= PY; V= constant
Page 3
Basic Macroeconomics
Econ 70 XA, Xavier University- Ateneo de Cagayan
3. Aggregate Demand Policies in Extreme Cases
a.) Keynesian Case C1. If AD , expected price is constant, then: Y* Y** v.v. (ex. G; tax cuts; m.) C2. If AS ; P, Y* Y C3. If AS ; P ; Y C4. If AD , Price is constant; Y
Page 4
Basic Macroeconomics
Econ 70 XA, Xavier University- Ateneo de Cagayan
b.) Classical Case
C1. C2. C3. C4.
If AD ; P , Y is constant If AD ; P , Y is constant If AS ; P ; Y If AS ; P , Y
Page 5
Basic Macroeconomics
Econ 70 XA, Xavier University- Ateneo de Cagayan
c.) If LR; AD ; AS : P; Y
Page 6
You might also like
- Aggregate Demand and Supply Models ExplainedDocument37 pagesAggregate Demand and Supply Models ExplainedLakshmi NairNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - InflationDocument25 pagesUnit 4 - InflationAmanda RuthNo ratings yet
- Keynesian Economics I: The Keynesian System (I) : The Role of Aggregate DemandDocument29 pagesKeynesian Economics I: The Keynesian System (I) : The Role of Aggregate DemandhongphakdeyNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Le Phuong Thao Quynh Faculty of International Economics Mobile: 0987027398Document43 pagesMacroeconomics: Le Phuong Thao Quynh Faculty of International Economics Mobile: 0987027398MinhThuyNguyenNo ratings yet
- AD - As Model Chapter 20Document30 pagesAD - As Model Chapter 20Steven SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8Hiba JafarNo ratings yet
- CH 25 - Aggregate Demand SupplyDocument11 pagesCH 25 - Aggregate Demand SupplyTrent BranchNo ratings yet
- Macro history key concepts and schools of thoughtDocument7 pagesMacro history key concepts and schools of thoughtFrancesca ChiappettaNo ratings yet
- 1 LECTURES: PART I: The Classical Model: AggregateDocument11 pages1 LECTURES: PART I: The Classical Model: AggregateLiu JACKMANNo ratings yet
- ECON 301 Review Sheet Test 3Document13 pagesECON 301 Review Sheet Test 3HoavantranNo ratings yet
- MacroDocument6 pagesMacrocorvids75% (4)
- Monetary LEC1Document11 pagesMonetary LEC1Nitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Supply: Aggregate Supply Is The Aggregate of All TheDocument3 pagesAggregate Supply: Aggregate Supply Is The Aggregate of All TheAnonymous AKdppszR5MNo ratings yet
- AP Macroeconomics Page 1 of 5 Assignment: Apply The Keynesian Model To AD/ASDocument6 pagesAP Macroeconomics Page 1 of 5 Assignment: Apply The Keynesian Model To AD/ASMadiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 (Original)Document5 pagesWorksheet 3 (Original)dixitBhavak DixitNo ratings yet
- Keynesian Model of IncomeDocument17 pagesKeynesian Model of IncomeMD. MAMUN SARDERNo ratings yet
- 312 PS4 AnsDocument7 pages312 PS4 AnsAnne LamedicaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Chapter 5 (2023)Document25 pagesWorksheet For Chapter 5 (2023)Ncebakazi DawedeNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 FP NotesDocument15 pagesLECTURE 6 FP NotesFarah Abdel AzizNo ratings yet
- Ec103 Week 05 and 06 s14Document42 pagesEc103 Week 05 and 06 s14юрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Demand Supply EquilibriumDocument7 pagesDemand Supply EquilibriumdijojnayNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - FinalDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet - FinalAhmedAlhosaniNo ratings yet
- Cba 1104 - Theory of Price DeterminationDocument46 pagesCba 1104 - Theory of Price DeterminationPhainos Simon GwariNo ratings yet
- In This Chapter, There Are Four Objectives We Want To LearnDocument11 pagesIn This Chapter, There Are Four Objectives We Want To LearnelvienNo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document6 pagesChap 6Umer IqbalNo ratings yet
- Macro Chapter 11Document26 pagesMacro Chapter 11Tri WidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics CH 9Document22 pagesMacroeconomics CH 9karim kobeissiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyThuy Dung NguyenNo ratings yet
- IS-LM PPT 2Document17 pagesIS-LM PPT 2Ruchin DwivediNo ratings yet
- Income and Employment TheoryDocument4 pagesIncome and Employment TheorysukhmanchawlaNo ratings yet
- EconDocument4 pagesEconKianna SabalaNo ratings yet
- Keynes vs Classical Economists: Early Debate on Policy ActivismDocument29 pagesKeynes vs Classical Economists: Early Debate on Policy ActivismMsKhan0078No ratings yet
- Understanding Economics in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Economics in 40 CharactersCharmaine CapaNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document26 pagesCH 5Voka Xx19No ratings yet
- IS-LM Model ExplainedDocument36 pagesIS-LM Model ExplainedSyed Ali Zain100% (1)
- UGmacro19b - Midterm (With Answers)Document4 pagesUGmacro19b - Midterm (With Answers)Ho Chi SinNo ratings yet
- Dornbusch (10th Ed.) Ch. 05 Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocument23 pagesDornbusch (10th Ed.) Ch. 05 Aggregate Demand and SupplyShishir Agarwal100% (1)
- Keynesian ApproachDocument15 pagesKeynesian ApproachJasmine NandaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (PART 1) : Case & Fair (Ch. 26)Document48 pagesTopic 6: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (PART 1) : Case & Fair (Ch. 26)chan xianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Chapter 23)Document22 pagesLecture 7 (Chapter 23)raymondNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes IS LM CurveDocument13 pagesLecture Notes IS LM CurvemNo ratings yet
- Answer Set 2: OxfordDocument15 pagesAnswer Set 2: OxfordlowchangsongNo ratings yet
- Econ 304 HW 10Document4 pagesEcon 304 HW 10Pulki Mittal100% (1)
- IBDP Macroeconomics 3.2docxDocument21 pagesIBDP Macroeconomics 3.2docxanish.goel.4720No ratings yet
- The Keynesian Cross DiagramDocument3 pagesThe Keynesian Cross DiagramSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument34 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyGazal ReyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Open Economic SystemDocument65 pagesChapter 4 Open Economic Systemtigabuyeshiber034No ratings yet
- 2172 - 3580 - 1 - Micro Economic AssignmentDocument10 pages2172 - 3580 - 1 - Micro Economic AssignmentMoazzam AleeNo ratings yet
- 20201221203332YWLEE003Perfect Compyp SolutionDocument19 pages20201221203332YWLEE003Perfect Compyp SolutionDương DươngNo ratings yet
- Capital-Based Macroeconomics: Adapted From Time and Money: by Roger W. Garrison London: Routledge, 2001Document35 pagesCapital-Based Macroeconomics: Adapted From Time and Money: by Roger W. Garrison London: Routledge, 2001Ayush RampuriaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Aggregate DemandDocument1 pageIntroducing Aggregate DemandMr Aycock100% (1)
- ECON 2123 Problem Set 3 Solution MacroeconomicsDocument11 pagesECON 2123 Problem Set 3 Solution MacroeconomicsBrenda WijayaNo ratings yet
- Q α α P α P α M α α α: X d X X Y Y MDocument14 pagesQ α α P α P α M α α α: X d X X Y Y MJolly CharmzNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document6 pagesTutorial 5Zhenjie YueNo ratings yet
- PracticeQuestion CH11Document9 pagesPracticeQuestion CH11metilla2010No ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 (Tentative)Document34 pagesLecture - 6 (Tentative)Naretzis FloresNo ratings yet
- Topic 7Document8 pagesTopic 7Gwen Stefani DaugdaugNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument29 pagesMicroeconomicsNhi Nguyễn Trần LiênNo ratings yet
- Econ 70 - Final Grages2Document1 pageEcon 70 - Final Grages2Mitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- We Do Not Remember Days We Remember Moments..Document1 pageWe Do Not Remember Days We Remember Moments..Mitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Econ20.1 Acb Finals IdDocument1 pageEcon20.1 Acb Finals IdMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Econ20.1 BB Finals IdDocument2 pagesEcon20.1 BB Finals IdMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Econ 20 Chapter 8-10Document31 pagesEcon 20 Chapter 8-10Mitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Macro Ab - Az ch01Document13 pagesMacro Ab - Az ch01himjobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Part 1 and Part 2) - More ComprehensiveDocument27 pagesChapter 6 (Part 1 and Part 2) - More ComprehensiveMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2Mitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Econ 20 XU Lecture SlidesDocument28 pagesEcon 20 XU Lecture SlidesMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 4Mitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Part2 7 (Whole) NWDocument19 pagesChapter 6 Part2 7 (Whole) NWMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- June 30 AssignmentDocument1 pageJune 30 AssignmentMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet
- C3 Solow ModelDocument4 pagesC3 Solow ModelMitch Bonita AbarcaNo ratings yet