Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integrales Inmediatas
Uploaded by
Aero MathOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integrales Inmediatas
Uploaded by
Aero MathCopyright:
Available Formats
Integrales Inmediatas
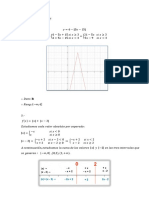
x n +1 1
∫x
n
dx =
n +1
+c n = −1 ∫ x dx = ln x + c
n=0 ∫ dx = x + c
ax
∫ a dx =
x
+c a=e ∫e
x
dx = e x + c
ln a
∫ Senxdx = −Cosx + c ∫ Senhxdx = Coshx + c
∫ Cosxdx = Senx + c ∫ Coshxdx = Senhx + c
∫ Tgxdx = − ln Cosx + c = ln Secx + c ∫ Tghxdx = ln Coshx + c
∫ Ctgxdx = ln Senx + c ∫ Ctghxdx = ln Senhx + c
∫ Secxdx = ln( Secx + Tgx ) + c ∫ Sechxdx = ArcTgSenhx + c
∫ Cscxdx = ln( Cscx − Ctgx ) + c ∫ Cschxdx = − ArgThCoshx + c
∫ Sec xdx = Tgx + c ∫ Sech xdx = Tghx + c
2 2
∫ Csc xdx = −Ctgx + c ∫ Csch xdx = −Ctghx + c
2 2
∫ SecxTgxdx = Secx + c ∫ SechxTghxdx = − Sechx + c
∫ CscxCtgxdx = −Cscx + c ∫ CschxCtghxdx = −Cschx + c
∫
1
x +1
2
(
dx = ArgSenhx + c = ln x + x 2 + 1 + c )
1
∫ dx = ArcSenx + c 1
dx = ArgCoshx + c = ln ( x + − 1) + c
1− x2 ∫ x2
−1
x2
1
∫ 1 + x 2 dx = ArcTgx + c 1 1 1+ x
1
∫ 1 − x 2 dx = ArgTghx + c = 2 ln 1 − x + c
∫ x x 2 − 1 dx = ArcSecx + c 1+ 1− x2
1 +c
∫ x 1− x2 dx = − ArgSechx + c = − ln
x
You might also like
- Algebra Lineal Entregable 1Document7 pagesAlgebra Lineal Entregable 1LEONARDO VICTORIANo ratings yet
- Curso Básico de Econometría ClásicaDocument173 pagesCurso Básico de Econometría Clásicabasura1985100% (2)
- Taller 2Document7 pagesTaller 2CRISTHIAN DAVID TABORDA TABORDANo ratings yet
- Integrales Por Tabla PDFDocument5 pagesIntegrales Por Tabla PDFRichard Rangel100% (1)
- MÉTODOS DE FACTORIZACIÓNDocument5 pagesMÉTODOS DE FACTORIZACIÓNDavid LLontop100% (1)
- Integrales Inmediatas ResueltasDocument3 pagesIntegrales Inmediatas ResueltasJazmin Reyes OteroNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de IntegralesDocument6 pagesEjercicios de Integralesfranz charlieNo ratings yet
- 00reglas IntegracionDocument3 pages00reglas IntegracionmarcoiqNo ratings yet
- Taller 07 - Coeficientes Indeterminados, Variacion de Parametros PDFDocument3 pagesTaller 07 - Coeficientes Indeterminados, Variacion de Parametros PDFMaryelys Donado100% (1)
- Guia # 4 de Solucion de Sistemas de Ecuacion - Gauss JordanDocument10 pagesGuia # 4 de Solucion de Sistemas de Ecuacion - Gauss JordanMelissa100% (1)
- Derivación ImplícitaDocument10 pagesDerivación ImplícitaAMYNNXXXX100% (1)
- 8 Derivada Funciones Trigonometricas InversasDocument6 pages8 Derivada Funciones Trigonometricas Inversasedison condoyNo ratings yet
- Integración Por Método TabularDocument8 pagesIntegración Por Método TabularmendobeceNo ratings yet
- Funciones Exponenciales y LogarítmicasDocument9 pagesFunciones Exponenciales y Logarítmicasvilivan2No ratings yet
- EcuacionesDocument13 pagesEcuacionesHades InfernoNo ratings yet
- Modelo de Ejercicios de Derivadas 1º de BachilleratoDocument1 pageModelo de Ejercicios de Derivadas 1º de Bachilleratojose domingo100% (1)
- 5. Convergencia de Integrales Impropias. Las Funciones Γ y Β de Euler.Document8 pages5. Convergencia de Integrales Impropias. Las Funciones Γ y Β de Euler.Jose FabrichNo ratings yet
- LimitesDocument4 pagesLimitesmetal_zenNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de Ecuaciones LinealesDocument7 pagesSistemas de Ecuaciones LinealesJosé Barros Troncoso0% (1)
- Trabajo Práctico Integrales DefinidasDocument3 pagesTrabajo Práctico Integrales DefinidasLuis Dario CavigliaNo ratings yet
- AntiderivadaDocument20 pagesAntiderivadaJose E. La Torre JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Teorema Del BinomioDocument11 pagesTeorema Del BinomioMartin Carrasco Rios100% (1)
- 2da GUÍA FUNCIÓN EXPONENCIAL Y LOGARÍTMICADocument26 pages2da GUÍA FUNCIÓN EXPONENCIAL Y LOGARÍTMICAsmallviviNo ratings yet
- Funciones y archivos .mDocument17 pagesFunciones y archivos .mJuan Ruiz TelloNo ratings yet
- Logaritmos PDFDocument7 pagesLogaritmos PDFricardo_guitierrez_1No ratings yet
- Derivada Del Pastel-Calculo IDocument8 pagesDerivada Del Pastel-Calculo IErik Arias CoronelNo ratings yet
- Matemática IVDocument94 pagesMatemática IVAlejandro ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Derivada de Una FunciónDocument7 pagesDerivada de Una FunciónJorge Lanz NightrayNo ratings yet
- Funciones logarítmicas y sus característicasDocument10 pagesFunciones logarítmicas y sus característicasEvelyn Duarte100% (1)
- Función Valor AbsolutoDocument3 pagesFunción Valor AbsolutoLeonardo Rodriguez ChavezNo ratings yet
- SEMANA 4 - U2-5 - La Derivada - Funciones Logarítmicas - TERMINADODocument20 pagesSEMANA 4 - U2-5 - La Derivada - Funciones Logarítmicas - TERMINADOLoren Jesús Paredes GarayNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document20 pagesAlgebra 1DEALPEASNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales Lineales de Primer OrdenDocument4 pagesEcuaciones Diferenciales Lineales de Primer Ordenleonardo2994No ratings yet
- Actividad2 - Calculo DiferencialeintegralDocument9 pagesActividad2 - Calculo DiferencialeintegralLuis GarciaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Investigación - Superficie de RevoluciónDocument8 pagesTrabajo de Investigación - Superficie de RevoluciónFernando JuelaNo ratings yet
- Tercero Funcion CuadraticaDocument6 pagesTercero Funcion CuadraticaROMINA JAVIERA GONZALEZ BARRIENTOSNo ratings yet
- LímitesDocument6 pagesLímitesfrancozamora0100No ratings yet
- Matematica para Ingenieria Tramo I (Parte D)Document19 pagesMatematica para Ingenieria Tramo I (Parte D)MegaFBI2009No ratings yet
- Funciones Trigonométricas Inversas e HiperbólicasDocument4 pagesFunciones Trigonométricas Inversas e HiperbólicasDaniel BenítezNo ratings yet
- Formulario de Calculo IntegralDocument2 pagesFormulario de Calculo IntegralAlexis Leon Mendoza100% (1)
- EcuacionesDiferencialesPrimerOrdenDocument15 pagesEcuacionesDiferencialesPrimerOrdenDuglas Rivera EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Factorización de PolinomiosDocument8 pagesFactorización de PolinomiosJesus RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Función Cuadrática - Rios, Maria FernandaDocument4 pagesFunción Cuadrática - Rios, Maria FernandaMaite CarrizoNo ratings yet
- Calculo Integral Trabajo Modificado Mil Ocho Mil 1Document194 pagesCalculo Integral Trabajo Modificado Mil Ocho Mil 1JoseAlexeiAcostaAlvaradoNo ratings yet
- GUIA I (Limites Indeterminados)Document4 pagesGUIA I (Limites Indeterminados)Francisco GilNo ratings yet
- Función LinealDocument5 pagesFunción LinealColegioAulaXXINo ratings yet
- Gráficas Funciones PolinómicasDocument3 pagesGráficas Funciones Polinómicassacha100% (1)
- Integración Por Partes: Método TabularDocument3 pagesIntegración Por Partes: Método TabularOscar Mtz FtsNo ratings yet
- Cómo Calcular Los Puntos de Inflexión de Una FunciónDocument17 pagesCómo Calcular Los Puntos de Inflexión de Una FunciónGermán DiezNo ratings yet
- UNIDAD 4 Operaciones Con PolinomiosDocument132 pagesUNIDAD 4 Operaciones Con PolinomiosNestor Huamani BarriosNo ratings yet
- El Método de Integración Por PartesDocument16 pagesEl Método de Integración Por PartesWilfrido ToMartNo ratings yet
- Tema 3. Ejercicios PropuestosDocument12 pagesTema 3. Ejercicios PropuestosmeimolNo ratings yet
- Integrales IndefinidasDocument19 pagesIntegrales IndefinidasplotoiNo ratings yet
- Serie de Fourier para funciones periódicas: conceptos básicos y problemas resueltosDocument6 pagesSerie de Fourier para funciones periódicas: conceptos básicos y problemas resueltosNorberto Zavaleta PozoNo ratings yet
- Reglas de Derivación de Funciones TrascendentesDocument2 pagesReglas de Derivación de Funciones TrascendentesBrands AillonNo ratings yet
- Funciones Exponenciales y LogarítmicasDocument6 pagesFunciones Exponenciales y Logarítmicasjoseangelmadrid100% (3)
- Formulas de Integracion InmediataDocument1 pageFormulas de Integracion InmediataCarlos BlankNo ratings yet
- Tabla de IntegralesDocument5 pagesTabla de Integralesapi-26274418No ratings yet
- Tabla de IntegralesDocument5 pagesTabla de Integralesjosefer100% (16)
- Tabla de Integrales PDFDocument5 pagesTabla de Integrales PDFDenisse Cedeño IturraldeNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Integrales PDFDocument5 pagesTabla de Integrales PDFMiguelNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Convalidacion - Ing - Ind - Pensum 2016Document1 pageTabla de Convalidacion - Ing - Ind - Pensum 2016Sobeida JimenezNo ratings yet
- Ejemplos de Dev C ++Document6 pagesEjemplos de Dev C ++Jonathan Arley Torres CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Conceptos Basicos de BioestadisticaDocument3 pagesConceptos Basicos de BioestadisticaVialy Santana100% (1)
- Catalogo LenticularDocument20 pagesCatalogo LenticularEduwin FuentesNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 7Document35 pagesCapitulo 7lissetNo ratings yet
- Curso AF-MianaDocument148 pagesCurso AF-MianaAlejandro Pujol100% (1)
- Protocolo Individual Fundametos de MateDocument3 pagesProtocolo Individual Fundametos de Matejuandamxpro ytNo ratings yet
- Conclusiones Descriptivas de La Comptetencia-Iii CicloDocument6 pagesConclusiones Descriptivas de La Comptetencia-Iii CicloAna Ramos Rojas100% (2)
- Angulos MultiplesDocument66 pagesAngulos MultiplesTeresa Isabel Tandaypan Pereda33% (3)
- Auditoría contableDocument29 pagesAuditoría contableLuz Georgina Ramos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 14 Taller Matematicas PDFDocument8 pages14 Taller Matematicas PDFelcanoeroNo ratings yet
- Dinamica IndustrialDocument10 pagesDinamica IndustrialViviana CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Esfuerzo TriaxialDocument1 pageEsfuerzo TriaxialLKiller HolosNo ratings yet
- Dibujo TécnicoDocument18 pagesDibujo TécnicoJose AguilarNo ratings yet
- Taller Nivelacion Matematicas NovenoDocument2 pagesTaller Nivelacion Matematicas NovenodanichavesNo ratings yet
- Métodos numéricos actividad evaluableDocument4 pagesMétodos numéricos actividad evaluableYesid David Martinez0% (1)
- 04 Limites - Material - EstudiantesDocument11 pages04 Limites - Material - Estudiantesbreyder99No ratings yet
- Unidad1 Tarea1 Maykol - MorenoDocument6 pagesUnidad1 Tarea1 Maykol - MorenoAdolfo BustosNo ratings yet
- ScriptsDocument5 pagesScriptsIvan Jahuira CervantesNo ratings yet
- Tema N Teoria Cinetica de Los GasesDocument42 pagesTema N Teoria Cinetica de Los GasesRocio Guadalupe Ortega SanchezNo ratings yet
- UD5 Resolución de Circuitos Con Varias MallasDocument7 pagesUD5 Resolución de Circuitos Con Varias MallasSergio ValeroNo ratings yet
- Representación gráfica y conceptual de límitesDocument2 pagesRepresentación gráfica y conceptual de límitesvirginiaNo ratings yet
- Tipos de levantamientos topográficos para proyectos de construcciónDocument4 pagesTipos de levantamientos topográficos para proyectos de construcciónDaniel MonjarasNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Deflexiones y Pendientes en VigasDocument8 pagesTabla de Deflexiones y Pendientes en VigasCarlos LuNo ratings yet
- Modulación FDM y técnicas de multiplexaciónDocument51 pagesModulación FDM y técnicas de multiplexaciónPepe GlezNo ratings yet
- Transformadores Crovisa - Normal PDFDocument8 pagesTransformadores Crovisa - Normal PDFJustin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Diseño de captación convencional para caudal de 0.8 m3/sDocument16 pagesDiseño de captación convencional para caudal de 0.8 m3/sStephani Espinosa Pepa100% (2)
- Aritmética 13Document4 pagesAritmética 13Oswaldo Aguirre MendozaNo ratings yet