Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Wong Kiong Nguong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views1 pageHeat transfer is the transfer of heat from One point to another. Heat flux is the rate at which heat is transferred between two points. Heat transfer is governed by the physical laws that govern each mode of heat transfer. How much heat is transferred through a copper plate maintained at 4000C?
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHeat transfer is the transfer of heat from One point to another. Heat flux is the rate at which heat is transferred between two points. Heat transfer is governed by the physical laws that govern each mode of heat transfer. How much heat is transferred through a copper plate maintained at 4000C?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views1 pageTutorial 1
Uploaded by
Wong Kiong NguongHeat transfer is the transfer of heat from One point to another. Heat flux is the rate at which heat is transferred between two points. Heat transfer is governed by the physical laws that govern each mode of heat transfer. How much heat is transferred through a copper plate maintained at 4000C?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
SWINBURNE UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY (SARAWAK CAMPUS) SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, COMPUTING AND SCIENCE HES4330 THERMODYNAMICS 2 / SEMESTER 2 2011 TUTORIAL
1 INTRODUCTION TO HEAT TRANSFER
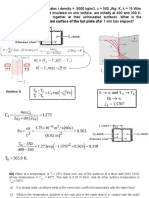
1. How does the science of heat transfer differ from the science of thermodynamics? 2. Review any standard text on thermodynamics and define: a) Heat, b) Internal energy, c) Work, d) Enthalpy. 3. What is the driving force for (a) heat transfer, (b) electric current flow, and (c) fluid flow? 4. What is heat flux? How is it related to the heat transfer rate? 5. How are heat, internal energy, and thermal energy related to each other? 6. An ideal gas is heated from 50C to 80C (a) at constant volume and (b) at constant pressure. For Which case do you think the energy required will be greater? Why? 7. Define thermal conductivity and explain its significance in heat transfer. 8. What are the mechanisms of heat transfer? How are they distinguished from each other? 9. Write down the expressions for the physical laws that govern each mode of heat transfer, and identify the variables involved in each relation. 10. Define emissivity and absorptivity. What is Kirchhoffs law of radiation? 11. One face of a copper plate 3 cm thick is maintained at 4000C, and the other face is maintained at 1000C. how much heat is transferred through the plate. 12. Air at 200C blows over a hot plate 50 by 75 cm maintained at 2500C. The convection heat transfer coefficient is 25 W/m20C. Calculate the heat transfer. 13. Determine the heat transfer through the plane of length 6m, height 4m and thickness 0.30m. The temperatures of inner and outer surfaces are 1000C and 400C respectively. Thermal conductivity of wall is 0.55 W/m.K. 14. The wall of a furnace is constructed from 15 cm thick fire brick having constant thermal conductivity of 1.7 W/m.K. The two sides of the wall are maintained at 1400 K and 1150 K, respectively. What is the rate of heat loss through the wall which is 50 cm X 3 m on a side. 15. An electric current is passed through a wire 1 mm in diameter and 10 cm long. The wire is submerged in liquid water at atmospheric pressure, and the current is increased until the water boils. For this situation h=5000W/m20C, and the water temperature will be 1000C. How much electric power must be supplied to the wire to maintain the wire surface at 1140C? 16. Two infinite black plates at 800 and 3000C exchange heat by radiation. Calculate the heat transfer per unit area. 17. A refrigerator stands in a room, where air temperature is 210C. The surface temperature on the outside of the refrigerator is 160C. The sides are 30 mm thick and has an equivalent thermal conductivity of 0.10 W/m.K. The heat transfer coefficient on the outside is 10 W/m2.K. Assume one dimensional conduction through the sides, calculate the net heat flow rate and the inside surface temperature of the refrigerator. 18. A black surface is positioned in a vacuum container so that it absorbs incident solar radiant energy at the rate of 950 W/m2. If the surface conducts no heat to its surroundings, determine its equilibrium temperature. 19. Name some good conductor of heat; some poor conductor. 20. What is the order of magnitude for the convection heat transfer coefficients in free convection? Forced convection? Boiling? 21. Can all three modes of heat transfer occur simultaneously (in parallel ) in a medium?
You might also like
- Calorimetry Lab SEDocument13 pagesCalorimetry Lab SEOindrilla Chakrabarty73% (11)
- Heat Transfer Question BankDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Question BankkarthikNo ratings yet
- AHMT Assignment 01Document2 pagesAHMT Assignment 01shubhamNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialJayden ChanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 HMTDocument5 pagesWorksheet 1 HMTmubarekjemal3279No ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1 eDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1 eRotten AppleNo ratings yet
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDocument4 pages9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through Multi-Layered WallDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Through Multi-Layered WallRutvikLathiaNo ratings yet
- HMT Unit 1Document9 pagesHMT Unit 1rp0212No ratings yet
- Sheet Ch.1Document4 pagesSheet Ch.1Ahmed KingNo ratings yet
- ME1251-Heat and Mass TransferDocument11 pagesME1251-Heat and Mass Transfermanoj kumar GNo ratings yet
- Updated ProblemsDocument3 pagesUpdated Problemsmahmoud koriemNo ratings yet
- HT QB A2Document27 pagesHT QB A2Shakil MaddilaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lectures Chemical Engineering Department University of Technology, IraqDocument1 pageHeat Transfer Lectures Chemical Engineering Department University of Technology, IraqChemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - HMTDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - HMTSUNDARAMAHALINGAM ANo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank Subject Name: HEAT & MASS TRANSFER Year/Sem: III / V Unit - I Conduction Part - ADocument20 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank Subject Name: HEAT & MASS TRANSFER Year/Sem: III / V Unit - I Conduction Part - AjoeannieNo ratings yet
- HTDocument101 pagesHTNandam HarshithNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Practice QuestionsLucky 230503No ratings yet
- QB For HMTDocument11 pagesQB For HMTsmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- PANIMALAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER MODEL EXAMDocument2 pagesPANIMALAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER MODEL EXAMPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1-13 PDFDocument27 pagesTutorial 1-13 PDFPavanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer AssignmentDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer AssignmentrajNo ratings yet
- Special Question BankDocument8 pagesSpecial Question BankAKHIL HARINo ratings yet
- HT Problems-1Document25 pagesHT Problems-1abhiram pasupuletiNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFER: CONDUCTION, CONVECTION & RADIATIONDocument33 pagesHEAT TRANSFER: CONDUCTION, CONVECTION & RADIATIONAlex Philip0% (1)
- Heat & MassQuestion BankDocument9 pagesHeat & MassQuestion Banksiva_marimuthu_2No ratings yet
- SRM University Heat and Mass Transfer Model Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesSRM University Heat and Mass Transfer Model Exam QuestionsRuby SmithNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TutorialsDocument30 pagesHeat Transfer Tutorialssagar100% (1)
- ME6502Document10 pagesME6502Thulasi RamNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Prob Sheet S S C With Heat GenerationDocument2 pages4.1 Prob Sheet S S C With Heat GenerationAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Sri Ramanujar Engineering CollegeDocument3 pagesSri Ramanujar Engineering CollegeVenkatesh ArumugamNo ratings yet
- HT QuestionsDocument3 pagesHT QuestionsSanthoshirathnam GunjaNo ratings yet
- HT QuestionsDocument3 pagesHT QuestionsSanthoshirathnam GunjaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank HTDocument12 pagesQuestion Bank HTgreatrijuvanNo ratings yet
- HMT QBDocument14 pagesHMT QBsandeepsai369No ratings yet
- QP-2 HMTDocument3 pagesQP-2 HMTtagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Anna University Question BankDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer: Anna University Question BankaeroacademicNo ratings yet
- HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER SOLUTIONSDocument11 pagesHEAT AND MASS TRANSFER SOLUTIONSanithayesurajNo ratings yet
- 8S 2105 Mepc22 1Document2 pages8S 2105 Mepc22 1Challa YachendraNo ratings yet
- Question Bank HMTDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank HMTBhavesh KapilNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer AssignmentDocument7 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer AssignmentAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- HMT Question Bank-1Document10 pagesHMT Question Bank-1parasuramanNo ratings yet
- HMT5Document9 pagesHMT5SriniNo ratings yet
- Heat & Mass Transfer Question BankDocument4 pagesHeat & Mass Transfer Question BankBhavesh Kapil50% (2)
- (An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaDocument2 pages(An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaMohammed Maaz100% (1)
- Ejercicios TransferDocument12 pagesEjercicios TransferBryanNo ratings yet
- SUB: Heat & Mass Transfer (EME 504) : Assignment-IDocument2 pagesSUB: Heat & Mass Transfer (EME 504) : Assignment-IdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios I EnvioDocument14 pagesEjercicios I Envioomar pillajoNo ratings yet
- 34 Tutorial 1 HT1Document2 pages34 Tutorial 1 HT1jameeloNo ratings yet
- HT Notes For ESEDocument25 pagesHT Notes For ESEM BhurleNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Long AnswerDocument32 pagesHeat Transfer Long Answerdipzbarma5No ratings yet
- Stainless steel heat transfer problemDocument9 pagesStainless steel heat transfer problemshreya guptaNo ratings yet
- 4.tutorial HMTDocument5 pages4.tutorial HMTdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1A JNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer College SlidesDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer College SlidesVivaan Sharma100% (1)
- 1492Document15 pages1492_Anggyaa_No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - After The Gold RushDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 - After The Gold RushWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Topic C - 6. Malaysian Constitution - BackgroundDocument21 pagesTopic C - 6. Malaysian Constitution - BackgroundWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 11 - Toyota's Tough BossDocument1 pageTutorial 11 - Toyota's Tough BossWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Ch05 SummaryDocument5 pagesCh05 SummarydaovansangNo ratings yet
- Swinburne Lab RulesDocument5 pagesSwinburne Lab RulesWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Saf SignsDocument9 pagesSaf SignsWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- A Review On Water ElectrolysisDocument18 pagesA Review On Water ElectrolysisSilvester KolicNo ratings yet
- Saf SignsDocument9 pagesSaf SignsWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- A Review On Water ElectrolysisDocument18 pagesA Review On Water ElectrolysisSilvester KolicNo ratings yet
- HES1610 Lecture 1-Unifying Themes in BiologyDocument60 pagesHES1610 Lecture 1-Unifying Themes in BiologyWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument15 pagesElectrolysisWong Kiong Nguong100% (1)
- DasdasdasdDocument1 pageDasdasdasdWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Equipment Borrowing Application FormDocument3 pagesEquipment Borrowing Application FormWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Swinburne Lab RulesDocument5 pagesSwinburne Lab RulesWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Swinburne Lab RulesDocument5 pagesSwinburne Lab RulesWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Swinburne Lab RulesDocument5 pagesSwinburne Lab RulesWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Final Exam TT - Deg & Dip (C) - (Sem1 Feb2011) - by - DateDocument3 pagesFinal Exam TT - Deg & Dip (C) - (Sem1 Feb2011) - by - DateWong Kiong NguongNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Cooling SystemDocument8 pagesChoosing A Cooling System20633304No ratings yet
- Cheeta Software Simulation PDFDocument18 pagesCheeta Software Simulation PDFJ.Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- FenestrationDocument6 pagesFenestrationAmeni MokniNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through Vertical CylinderDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Through Vertical Cylindermilan44No ratings yet
- M1 Heat Transfer To Finned Tubes (VDI Heat Atlas)Document5 pagesM1 Heat Transfer To Finned Tubes (VDI Heat Atlas)GuillaumeNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Lecture 27: Natural ConvectionDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer: Lecture 27: Natural ConvectionDavico MartinezNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of ConvectionDocument6 pagesFundamental of Convectionfaris fauziNo ratings yet
- Mee3004 1112 L01Document5 pagesMee3004 1112 L01John BrownNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat Exchanger DesignDocument4 pagesDouble Pipe Heat Exchanger Designdip_maanNo ratings yet
- ME-330 HMT Course Outline (S-20) PDFDocument3 pagesME-330 HMT Course Outline (S-20) PDFSuaid Tariq BalghariNo ratings yet
- HT AssignmDocument9 pagesHT AssignmSai Chand Arkham KingNo ratings yet
- 314 ch1Document70 pages314 ch1Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basics of Radiation of Heat Transfer ModeDocument46 pagesBasics of Radiation of Heat Transfer ModeSamir YehyaNo ratings yet
- (An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaDocument2 pages(An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaMohammed Maaz100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentAfzaal Ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- HMT (U1)Document83 pagesHMT (U1)maniNo ratings yet
- Thermal Applicability of Two-Phase Thermosyphons in Cooking Chambers - Experimental and Theoretical AnalysisDocument17 pagesThermal Applicability of Two-Phase Thermosyphons in Cooking Chambers - Experimental and Theoretical Analysisabhishek992198No ratings yet
- MEC 536 Heat Transfer by Convection-L12Document14 pagesMEC 536 Heat Transfer by Convection-L12mohammed yaseenNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through Plane Walls and CylindersDocument34 pagesHeat Transfer Through Plane Walls and CylindersabasNo ratings yet
- Safety Relief Valve SizingDocument9 pagesSafety Relief Valve SizingLiam MoylanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan No 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan No 1hafeez ahmed0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Heat Transfer ModesDocument51 pagesFundamentals of Heat Transfer ModesSandeep MishraNo ratings yet
- HMTDocument4 pagesHMTSuthan RNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Burner Technology For Industrial Furnaces: January 2009Document22 pagesHandbook of Burner Technology For Industrial Furnaces: January 2009Leyston CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Module THERMO Thermodynamics BEXET 2 BSIT RACT X BMET MT 2 OKDocument124 pagesModule THERMO Thermodynamics BEXET 2 BSIT RACT X BMET MT 2 OKHiraishin JutsuNo ratings yet
- Table 2.1.1.2.ADocument1 pageTable 2.1.1.2.AiwguNo ratings yet
- Heat Diffusion EquationDocument8 pagesHeat Diffusion EquationSrikar GhooliNo ratings yet
- f2. Heisler-Grober ChartsDocument3 pagesf2. Heisler-Grober Chartssyazwani ridzuan100% (1)
- Transport PhenomenaDocument6 pagesTransport PhenomenaMITZINo ratings yet
- MEC554Document43 pagesMEC554loqmannazli100% (1)