Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ippt2004 3
Uploaded by
dhirajkapilaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ippt2004 3
Uploaded by
dhirajkapilaCopyright:
Available Formats
1
William Blake (1757 1827)
The enormous
and the minute are
interchangable
manifestations
of the eternal
The enormous
and the minute are
interchangable
manifestations
of the eternal
The Parable of the Wise and Foolish Virgins
To see a World in a Grain of Sand And a Heaven in a Wild Flower, Hold Infinity in the palm of your hand And Eternity in an hour
in Forschungsverbund Berlin e.V., Mohrenstrasse 39, D - 10117 Berlin, Germany
Weierstrass lnstitute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics
2
KRZYSZTOF WILMANSKI
mail: wilmansk@wias-berlin.de
web:http://www.wias http://www.wias http://www.wias http://www.wias- -- -berlin.de/people/wilmansk berlin.de/people/wilmansk berlin.de/people/wilmansk berlin.de/people/wilmansk
in Forschungsverbund Berlin e.V., Mohrenstrasse 39, D - 10117 Berlin, Germany
Weierstrass lnstitute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics
Przejcia mikro-makro
w modelowaniu orodkw granulowanych
Wykad w Zakadzie Teorii Orodkw Cigych
lnstytut Podstawowych Problemw Techniki PAN
Warszawa, 12 marca, 2004
3
Contents:
Contents:
1. Linear poroelastic model
- macroscopic unknown fields of the linear model
- linear constitutive relations
2. Micro-macrotransitions
- geometrical compatibility
- changes of porosity
- changes of porosity solution of the porosity equation
- Gedankenexperiments for homogeneous microstructure
- solutions of field equations and geometrical compatibility
- numerical example
3. Dependence of
S
,K
d
and K
b
on porosity?
4. Conclusions
4
1. Linear poroelastic model
1. Linear poroelastic model
5
. ) (
) (
, ) (
, ) (
, 0 , 0
0
0
0 0
E
S F
E
F F S F F
F
F
S S S F S
S
S
F F
F
S S
S
n n
div
t
n n
div
t
div
t
div
t
div
t
= +
+ =
+ + =
= +
= +
v v
b v v T
v
b v v T
v
v v
.
S
S
grad sym
t
v
e
=
Balance equations
linear model
Macroscopic unknown fields of the linear model
{ } n
S F S F
, , , , e v v
- partial mass density of the fluid
- velocity of the skeleton
- velocity of the fluid
- Almansi-Hamel deformation tensor of
the skeleton
- porosity
6
Linear constitutive relations
Partial stresses
. : , :
), ( , ) N(
, ) N( 2
0
0
0 0 int 0 int
0 0
F
F F
S
F F F F F
S S S S S
tr e
Qe p p n n p
n n Q e
= =
+ = + =
+ + + =
e
1 1 T
1 1 e 1 T T
Porosity
. ), 1 (
0
const e n n
E
= + =
Linear field equations
( ) [ ] . , ,
, N ) (
, N ) ( 2
0 0
0
0 0
0
e n n n
e e n n
t
div
t
grad sym
t
n grad grad e Qgrad
t
n grad Qgrad div e grad
t
F S
S
S F F
F
F
S F S S S
S
S
= +
+ + =
+ + + =
v v
e
v v
v
v v e
v
material constants
7
1) How to find material constants in simple
laboratory and field experiments?
2) How to find microstructural properties
such as porosity, permeability
or saturation?
Micro-macrotransitions?
Statistical averaging (REV)?
Time averaging?
Kinetic theory and macroscopic
moments?
8
2. Micro-macrotransitions
2. Micro-macrotransitions
(homogeneous microstructure) (homogeneous microstructure)
9
Geometrical compatibility
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( )
.
1
1
1
1
1 , 1 , 1
, ,
1
1
1 , 1 ,
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
e
e
n
n
e e n
n
n
n
n
R
R SR SR S S SR S
FR
F R
R FR FR F F FR F
+
+
=
+ = + = =
=
+
+
=
+ = + = =
Micro-macrorelations for partial mass densities in homogeneous microstructure
REV V dV t H
V
t n
t t n dV t H t
V
REV
FR
REV
FR F
volume : , ) , (
1
: ) , (
), , ( ) , ( ) , ( ) , (
1
) (
) (
= =
=
}
}
x
z
x
z
z x
x x z z
where ) , ( t H z is the characteristic function for the fluid component. Then
homogeneity
Linearity (small deformations) yields
geometrical compatibility conditions:
. ,
1
0
0
0
0
n
n n
n
n n
e e
R R
=
+ = (1)
e.g.:
10
Changes of porosity
Constitutive relations:
- macro
. ) ( ) (
) ( ) ( : m equilibriu
), ( N
), ( N ) (
0 3
2
0 0
0 0 0
0 3
2
0
Q e Q
p p p p p
n-n Qe p p
n-n Q e p p
F S S
F F S S
F F F
S S S S
+ + + =
= + =
=
+ + =
- micro
). )( 1 ( ) ( : m equilibriu
, ,
0 0 0 0
0 0
SR SR FR FR
R
s
SR SR R
f
FR FR
p p n p p n p
e K p p K p p
+ =
= =
(2)
(3)
It follows
. 2 : , ) 1 ( :
,
) (
: ,
) (
: ), (
0
3
2
0 0
0
0 0
0 0
0
Q K K n K n K
K K n
K n Q
K K n
K K
e e
n
n n
F S S
f s V
f s
f
F
f s
V
+ + + = + =
+
=
= + =
11
Changes of porosity
- the solution of the porosity equation
). 1 ( ), (
) (
0
e n n div
n n
t
n n
E
S F
E E
+ = =
v v
Mass balance equations:
. ,
0 0
t t
div
t
e
t
div
F
F
F
S
S
S
v v
Hence
}
+ =
t
s t
ds e s e
n
e
n
e
n
n n
0
0 0 0
0
. ) )( ( ) (
The micro-macrorelation follows provided
. ,
0
n
=
memory effect
12
Gedankenexperiments
for homogeneous microstructures
Preliminaries Biots notation
Bulk stress and pore pressure
Change of the fluid content:
Fluid contained in a reference volume dV
0
of the skeleton
- reference configuration:
0 0
dV
F
- current configuration:
0
) 1 ( dV e
F
+
- normalized change increment of the fluid content:
[ ] ). ( 1
1
1
: ) 1 (
1
0 0 0 0 0 0
0
+
+
= = + e n dV
e
n dV dV e
F F
FR
. N :
, :
, 2 ) 2 (
0
0
0
0
0
3
1
0
n
n n
M Ce p
n
p
p
C Ke p tr p
C e H
f
F
f
S S S F S
+ = =
+ = =
+ + = +
T
1 e 1 T T T T
. : ), ( :
,
2 2 :
2
0
0
0
1
3
4
0
0
n
M Q C
K
Q H
F
F
n
S
F S S
= + =
+ =
= + + + =
Biots constants
13
Gedankenexperiments
for homogeneous microstructures
Unjacketed test:
,
0
p p p
f f
=
Jacketed drained
, 0
0
=
f f
p p
. e i.e. , 0 = =
and undrained tests:
General equilibrium conditions:
). ( ) )( 1 (
) ( ) (
0 0 0 0
0 0
FR FR SR SR
F F S S
p p n p p n
p p p p p
+ =
= + =
Unknown: { }
0
0
, , , , , ,
f f
R R
p p p p e n e
Equations: 2 geom., 1 equilib., 4 constit., 1 test = 8.
= 7;
}
14
Solutions of field equations and geometrical compatibility
( )
( ) , 0 ) (
, :
, :
,
, 1
,
) ( N
0 0
) 1 ( 1
) 1 (
N
N
0
0
b
N
0
2
0
0
b
=
=
=
=
+ =
=
+
M K
C K
K
K
M
C
K
K
n
n n
s n
M
C
b
n n
n n
CK
K
M K
C
K
p
M K
C
K
p
b n
s
b
s
b
K
s
K
M K
C
n b
n b
n n
K K
K K
p K
p
e
jacketed drained
. :
, N
,
, ,
0 0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
n
n - 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
f s W
K
C
W
K
C
s
K
C
W
K
b
MK
K
C
W
K
C
s
K
C
W
K
K
K
C
W
K
C
K
n
K
n
K
K
K
M C
K
p
K
K
n
n n
K
p
K
p
K
e
+ =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
unjacketed
. ) 1 ( :
, ) (
, N
, , 0 ,
0 0
N
0
) N (
0
) N (
0
0
f s V
K
K C
f s V
K K
K C
K
C
f f
K K
K C
n
n n
K
p
K n K n K
K K n K K
p p p
p e
f
f
f
f
f
f
+ =
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
= = =
jacketed undrained
1
2
3
. N
f f
K K C < >
4
&
( )
ally. experiment given -
1
1
N
=
M K
C
b d
n
K K
15
( )
{ } . : , 1
, : , N
, : , 0 ) (
, ) 1 ( : , ) (
) 1 ( 1
) 1 (
1
N
1
1
1
1
1
1
) ( N
0 0
0 0 N 0
0
0
b
N
0
0 0
0
0
2
b
K
s
K
M K
C
n
f s W
K
C
W
K
C
s
K
C
W
K
b
MK
b n
s
b
s
f
f
n
n n
s n M K
C
b d
K
n
K
n
K K
K
n
-n
M C
M
C
b M K
C K
K
K
M
C
K
K
f s V K
K C
f s V
K K K K
K
K K n n
K n K n K K K n K K
+
+
= + =
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
+ = =
Full set of equations for K, C, M, N:
,
) 1 (
,
) 1 (
) (
,
) 1 (
) (
0
2
0 0
2
b s
s
b s
b s s
b
b s
b s
K n K
K
M
K n K
K K K
C K
K n K
K K
K
+
=
+
= +
+
. 1 : =
f
s
K
K
For N=0: A):
B): N belongs to the set of macroscopic
material parameters but it is small in com-
parison with other compressibilities - iteration
C) Full solution for K, C, M, N
16
Material parameters K, C, M in the zeroth
approximation (Gassmann)
.
20 1
or : ) (empirical Geertsma
10 25 . 2 , 10 48
0
9 9
n
K
K K
Pa K Pa K
s
d b
f s
+
=
= =
Numerical example
Coupling parameter Q
in Biots model
). (
0 0
M n C n Q =
17
Material parameters K, C, M in the zeroth
approximation (Gassmann)
Material parameters K, C, M in the first
approximation (Gassmann)
18
Material parameters K, C, M, N
in the full model
Coupling parameters C, N
in the full model
n
K
K
s
d
20 1
: Geertsma
+
= Full model:
Coupling parameter Q
in the full model
Fraction of coupling
parameter: Q/K
in the full model
19
Material parameters K, C, M in the zeroth
approximation (Gassmann)
Material parameters K, C, M in the first
approximation (Gassmann)
Comparison with the full solution (green)
20
speed of propagation of P1-wave
in the low frequency approximation
Carlo Lai (July 2002)
Some results for P1-waves:
. 2 . 0 : number Poisson
, 1000
, 4000 ) 1 (
3
3
0 0
0 0
=
=
=
m
kg
F
m
kg
S
n
n
21
3. Dependence of
S
,K
d
and K
b
on porosity
3. Dependence of
S
,K
d
and K
b
on porosity
22
In the drained simple test the material behaves as
there were no fluid in pores. Hence the stress strain
relation should be the same as in the classical elasti-
city with the compressibility modulus K
d
and shear
modulus
S
, i.e.
,
) 1 ( 2
2 1
3
) 1 ( 2
2 1
3
0 N=
+
=
+
b d
S
K K
where is the Poissons number.
Simultaneously speeds of propagation react weakly on changes
of Poissons number see: results of Carlo Lai. Hence we can
choose, for instance, =0.2 and either calculate K
d
(K
b
) from the
above formula provided
S
was measured by the speed of shear
wave or calculate
S
provided K
d
(K
b
) is given empirically.
Important practical case: given two speeds of propagation
(P1- and shear wave) and the Poissons number. Then
by means of MICRO-MACRO one can calculate porosity
(inverse problem).
23
Experimental measurements: c
P1
,c
S
and porosity profiles
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
D
e
p
t
h
[
m
]
Porosity
LAB (Laval)
LAB (Osterberg)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
Vp
Vs
velocity of propagation (m/s)
d
e
p
t
h
(
m
)
porosity
soil
profile
3LVD 3LVD 3LVD 3LVDVLWH VLWH VLWH VLWH After: FOT,S., LA, C., LANCELLOTTA, R.; Porosity of Fluid-saturated Porous
Media from Measured Seismic Wave Velocities, Gotechnique, Vol. 52, No. 5, 359-373
(2002).
LA, C.; Recent Advances in the Solution of Some Parameter-dentification Problems Relevant
To Soil Dynamics, Lecture, Oct. 21, 2002, ROSE School, Pavia, taly.
1 P
c
S
c
24
Testing of soils by surface waves (SASW)
Politecnico di Torino, 2003
25
4. Conclusions
4. Conclusions
2. Gassmann like relations, derived for the extended
model with a dependence on porosity gradient by means
of the Micro-MacroTransition for homogeneous microstru-
cture satisfy ALL compatibility relations for simple tests
and yield in the limit the classical Gassmann relations.
1. Biots model follows as a limit case of a gene-
ral thermodynamic model provided the relaxation
of porosity is neglected.
3. In order to fulfil geometrical compatibility relations of
micro-macrotransition the porosity balance equation must be
corrected on an equilibrium contribution to the source term.
4. Micro-MacroTransition gives rise to a possibility of a natu-
ral description of processes in unsaturated granular
materials.
26 The Ghost of a Flea (ca. 1819)
Newton (1795)
You might also like
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Shukla (SME)Document14 pagesJyoti Shukla (SME)dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- CSE 7th SEM SLLP Class InternalDocument8 pagesCSE 7th SEM SLLP Class InternaldhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Let Us C-YashwantkanetkDocument3 pagesLet Us C-YashwantkanetkdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Web DesignDocument14 pagesIntermediate Web Designwasee111No ratings yet
- 01HRMDocument61 pages01HRMdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Test 16781Document1 pageTest 16781dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- ABCDocument2 pagesABCdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- CT 2Document2 pagesCT 2g4ubhNo ratings yet
- Let Us C-YashwantkanetkarDocument3 pagesLet Us C-YashwantkanetkardhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument18 pagesSoftwaredhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- FDocument2 pagesFdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- CIME1Document59 pagesCIME1dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- BCA COBOL SYLLABUSDocument153 pagesBCA COBOL SYLLABUSHarsha GortlaNo ratings yet
- 4) Context Free GrammarsDocument41 pages4) Context Free GrammarsAditya RaiNo ratings yet
- Simple and Operator GrammarDocument19 pagesSimple and Operator GrammardhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Section B: A) B) C) D) E)Document1 pageSection B: A) B) C) D) E)dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Operator Precedence GrammerDocument36 pagesOperator Precedence GrammerdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Ns PDFDocument1 pageNs PDFDhiraj KapilaNo ratings yet
- Loaders and LinkersDocument7 pagesLoaders and LinkersSiva CharanNo ratings yet
- 06295776Document5 pages06295776dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- IP Multicasting: Concepts, Algorithms, and Protocols ExplainedDocument19 pagesIP Multicasting: Concepts, Algorithms, and Protocols ExplainedHưng Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- BALR and USING Directive in AssemblerDocument1 pageBALR and USING Directive in AssemblerdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- The MESI ProtocolDocument4 pagesThe MESI ProtocoldhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Syntax Analysis or ParsingDocument11 pagesSyntax Analysis or ParsingdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Techniques for Image Processing ExamDocument1 pageTechniques for Image Processing ExamdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Discrepancy Regarding Question Attempted After SPACE BELOW CANCELLED in MCA 501 PKTDocument1 pageDiscrepancy Regarding Question Attempted After SPACE BELOW CANCELLED in MCA 501 PKTdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Journals ListDocument2 pagesJournals ListdhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mechanical Engineer Muhammad Ibtisam's ResumeDocument1 pageMechanical Engineer Muhammad Ibtisam's ResumeshoaibNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesEngineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Ebook PDFdebra.glisson665100% (42)
- Alexco - Co.nz T Slot Catalogue 07-2019Document5 pagesAlexco - Co.nz T Slot Catalogue 07-2019Sarah WoodNo ratings yet
- P&ID Symbols (Complete List & PDFDocument13 pagesP&ID Symbols (Complete List & PDFArjhay GironellaNo ratings yet
- Ninja Part PDFDocument105 pagesNinja Part PDFErlangga AlamNo ratings yet
- SFD & BMDDocument44 pagesSFD & BMDAltaf Hossain100% (2)
- Valves CatalogueDocument33 pagesValves CatalogueDheeraj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Module 5 DC MachinesDocument94 pagesModule 5 DC MachinesABC XYZNo ratings yet
- Acom85 - 4 High Temperature Behaviour of The Austenitic SS UNS S30815 (253 MA) & Weldments PDFDocument16 pagesAcom85 - 4 High Temperature Behaviour of The Austenitic SS UNS S30815 (253 MA) & Weldments PDFpipedown456No ratings yet
- NEF Coupling Catalog English 20061201Document48 pagesNEF Coupling Catalog English 20061201Aryo WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Snowmobile Maintenance GuideDocument643 pagesSnowmobile Maintenance GuideSteven Antonio100% (5)
- Weekly Physical Science Learning PlanDocument1 pageWeekly Physical Science Learning PlanLea Mae MimayNo ratings yet
- Grundfos Catalogue Industry and Water UtilityDocument542 pagesGrundfos Catalogue Industry and Water UtilityAdina Mariana Costache100% (7)
- Catalog 6chl SeriesDocument118 pagesCatalog 6chl SeriesRizki Adrian MadridistaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Assessment: CSR HarmonisationDocument14 pagesFatigue Assessment: CSR HarmonisationThanh Duc NguyenNo ratings yet
- TIMBER BEAM DESIGNDocument144 pagesTIMBER BEAM DESIGNweng paraleNo ratings yet
- ROV and MOVDocument1 pageROV and MOVnewprocessNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Systems: Aircraft High-Pressure Pneumatic SystemsDocument14 pagesPneumatic Systems: Aircraft High-Pressure Pneumatic SystemsAndreas.G100% (1)
- The New Mercedes Arocs BrochureDocument77 pagesThe New Mercedes Arocs Brochureislamafash100% (1)
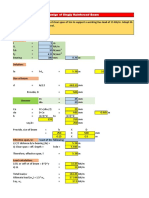
- Singly Reinforced Beam ExcelDocument3 pagesSingly Reinforced Beam ExcelVEERKUMAR100% (3)
- Fluids and Buoyancy QuizDocument2 pagesFluids and Buoyancy QuizWaleed El ShirbeenyNo ratings yet
- Shot Blasting Machines: Laser PeeningDocument2 pagesShot Blasting Machines: Laser Peeningrahul srivastavaNo ratings yet
- ITT CONTROLS Barton Chart Recorders 202e User Manual 1Document52 pagesITT CONTROLS Barton Chart Recorders 202e User Manual 1Edbaac BANo ratings yet
- Bezmasleni Kompresori Za Pet Industriata Siad PDFDocument8 pagesBezmasleni Kompresori Za Pet Industriata Siad PDFplasticos_jfm6580No ratings yet
- Mechanical System Design Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanical System Design Exam QuestionsGreyphen GreyNo ratings yet
- Keckley - Control Valves mm2Document23 pagesKeckley - Control Valves mm2DEVNo ratings yet
- Maintenence SchedulingDocument4 pagesMaintenence SchedulingCarloVanZyl0% (1)
- Lectu 14Document4 pagesLectu 14YeviraArinDiyanaNo ratings yet
- To11c5 e 00 PDFDocument526 pagesTo11c5 e 00 PDFGradimir MilanovicNo ratings yet
- Din 6914-10.9 PDFDocument2 pagesDin 6914-10.9 PDFvpjagannaathNo ratings yet