Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arabic Final) Kritika
Uploaded by
Parul SharmaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arabic Final) Kritika
Uploaded by
Parul SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Arabic Revolution: Introduction: Arabs have faced a lot of revolution and the country has survived many tragedies
related to the leaders. The outer world is looking to the Arab, as they have the oil-fields. The introduction to the revolution mainly consists of two revolutions. The Arab revolution was initiated by the Sherif Hussain Bin Ali from the year 1916 to1918. The revolt started with the aim of securing independence from the Ottoman Turks and creating a unified state spanning from Aleppo in Syria to Aden in Yemen. There was another revolution. The Arabic revolution was in Palestine. The 1936-1939 Arab Revolt was caused by the Palestinian Arabs against the British Colonial Rule and mass Jewish Immigration (The Countries and People of Arabia, 2010). The Arab revolution (1919-1918): The Arabic countries have faced a lot of revolution due to the Islamic outlook that is different from the rest of the world. The revolution of 1919 was due to the rise of nationalism under the Ottoman Empire. The background goes back to 1821 and has its roots in the Mashiq, which is in the east of Egypt and the countries of Sham. The political tilt of the people of Arab prior to the Great War was moderate. The Young Turk Revolution began on 3 July 1908. The period is known as the Second Constitutional Era, as it resulted in the Sultans announcement of the restoration of constitution of the year 1876. The people of Arab wanted reformation in the policies of the country, they wanted there demands to be fulfilled that ranges from general to autonomy, the use of their mother tongue in the education. In 1908, there were elections, the Young Turks from Committee
of Union and Progress (CUP) won the election, as they held an upper hand against their rival group led by Prens Sabahaddin. The party CUP won as they had liberal point of view, influenced by British and were closer to sultan. The CUP in the Ottoman parliament gave importance to centralization and modernization of the country. They were not supported as the nationalism was not on its peak. Arabs gave primary loyalty to their religion and sect, tribe or the government. The Arabs had strong ideologies. They were orthodox and possessive about their religion in particular. The ideology of Ottomans and Pan-Islamism were competing for the Arab Nationalism. The countercoup was supported by the members of the parliament. The aim was to take to pieces the constitution and restore the monarchy of Abdul Hamid ll. There was trial to put an end to the secular policies of the young Turks, by dethroned Sultan. In this attempt, the Sultan faced failure; he was driven to exile in the Selanik and was replaced by his brother Mehmed V Resad. In 1913, many politicians, economist and intellectuals met in Paris and demanded that Ottoman army should be required to serve the country at the time of war. The Arab Revolution of 1936-1939: The Arab revolution had two phases. The first phase of the revolution was directed by elitist Higher Arab Committee and consists of strikes and other political protest. The first phase was defeated by the British Civil Administration by means of international policy, concessions, international diplomacy and threat of martial law. The second phase began late in 1937, which targeted British army and the Palestine police force. This phase was violent and had peasant showed resistance. This revolution converted into peasant resistance movement. These rebellions
were suppressed by use of force and brutal killing performed by British Army and the Palestine Police force (Freedman, 1991). Causes of the revolt: The Sheikh Izz ad-Din al-Qassam established the Black Hand, an anti-Zionist and antiBritish militant organization. The team was equipped with bombes and firearms, which they employed to murder Jewish settlers as well as vandalized trees, planted and rail lines constructed by the British. The British were annoyed by the group and they launched a manhunt to find alQassam. He was killed in a cave near Yabad. This all led to outrage in the Arab community. The revolution was further supported by the discovery of large arms shipment in October 1935 at the port of Jaffa. They feared that Jews military will take over Palestine. The population of the Jewish people doubled bringing significant decline in relations between Palestinian Arabs and Jews. The uprising began on 15 April 1936 and then on 17 April at the funeral of Khazan in Tel Aviv it turned into nationalist movements when Jewish rioters beat Arab Children and destroyed property. There were various economic factors that played a key role in the outbreak of the Arab Revolt. The first reason was that the peasants were pushed off the land in increasing numbers into the urban cities where they had to face poverty and social marginalization. The revolt produced leaders and they helped in national revolt. World War 1 left people of Palestine poor and lack of basic amenities. The authorities in Ottoman levied high taxes on farming and agricultural produce. The fellah had to pay high rents due to increasing population density, and transfer of lands from Arabs to the Jewish settlement agencies. The disruption of agrarian life in Palestine led to landless peasants farmers.
There were culture and political reasons also that led to this uprising. Zionism has made Palestinian Arab conservative in cultural, political, behavior, social and religious affair. The Palestinians were motivated to conserve their heritage and respect against the British rule and Jewish innovation. There were transition in the political organization, as earlier it was lacking real leadership. Now, new political organizations and activists appeared leading to major population involvement in the process. Youth participated in the whole process, women organization became active in social matters and few militant secret societies were formed that advocated armed struggle against the British and Jewish. Response: All these things lead to pressure mounting on the Arabs. The first argument is that women came up in the revolt, which showed their active participation for the first time in the political scenario of the country. Military law led to administrative detention of the Arabs without trial and without proper sanitation. British followed the principle of collective punishment because of which heavy burden was there for poor Palestinian villagers. The full implementation of collective punishment led to destruction of property. The royal Air Force developed close air support, so that they did air patrolling to keep convoys and trains free from attack. Haifa had strategic importance as British had laid pipeline from the Iraqi oilfields to Haifa in 1935. The British policy makers were willing to make concessions on the Palestine issue to secure their position in Arab. Impact of British Empire, Palestinian Arab and Jewish Settlement:
The impact of these bodies brings an argument in front of the public of Arab. The role played by each one them was to see their interest and the comers suffered because of all these factors. Is it good that commoners suffer due to the political and social disturbances in the society? The bodies have an impact on the public. The Jewish settlement was destroyed and damaged in the war but other immigrants arrived. The Palestine destroyed the Jewish commoners but was not ready to settle the matter. Although there were development in the economy and infrastructure accelerated but the people suffer a lot in the whole scenario. The Jewish employment condition improved due to immigration, but the Arabs got unemployed as laborers was replaced when they were on strikes. The Palestinian Arabs houses were destroyed and massive financial costs was incurred due to strikes and devastation of the crops. The Arab economy lost the sales and increased unemployment. The positive effect of the revolt was that it led to the birth of the Arab Palestinian identity. The British Empire decided to rely on the support of the Jewish Population in Palestine. Synthesis& Arguments: The second argument is that the Arab revolution led to decline of west. This argument is related to the present situation prevailing in Arab. The Wests position is not right, as they do not show the real commitment to human rights. They are adopting the Jimmys Carter worldview, which will lead to severe consequences. West is ignoring Hosni Mubarak, President will lead to severe results. It has showed that Arab lack the leaders but the betrayal by the west showed that loyal people also not valued. The conflict between the West in the Middle East and Arab will bring deterioration in the relations. The stable and moderation ill reduce and west will stop
leading and stabilizing force around the world. The Arab Liberation revolution will change the total chemistry between the Arabs and west. The overall result will be destruction of North Atlantic political hegemony (Shavit, 2011). The third argument is that Arab revolution was affected by the social media. The countries in which, Arabians are residing like Egypt, Middle East and North Africa. Egypt has only 20% of people using internet so one cannot say that the revolution will be impacted by the internet or media. The Western media use platforms like facebook and Twitter to spread awareness about the Arab Revolution to protest against authoritarian government and restricted freedom. The 68% Egyptian have television but internet access is limited to 5% in Libya and 34% in Tunisia. Thus, social media alone cannot aid the Arab Revolution, but it will act, as a successful catalyst when it is combined with digital and traditional media. Digital media is a source to freely express ones view. Al-Jazeera news channel has reach to 40 million viewers in the Arab World but the lack of digital support has lead to loophole in the communication stream (Hunter, 2011). The fourth argument is that whether revolutions in home country affect the outsiders like Arabs families residing in Switzerland and whether the change is positive. After the revolution and fall of absolute and corrupt regime the number of Arab refugees in Switzerland would be reduced. This can be seen as a positive change in the economy of Arab. The people would be returning to their homeland. The revolution of February 17, 2011 is seen as a source of radical change in the people mentality and had impact on the psychological and social levels. The Libyan Revolution has led to return of values and morals that were missing for four decades. But there are concerns regarding the drastic change. How people will react to the change because they have been under such rule for a long time. One can say that economic security, strict laws
protecting people and the culture of dialogue has a great impact on the people of the nation (Abdeleli, 2011).
References: Shavit, A. (2011). The Arab revolution and Western decline. Retrieved October 24, 2011, from http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/opinion/the-arab-revolution-and-westerndecline-1.340967. Hunter, E. (2011). The Arab Revolution and Social Media. Retrieved October 24, 2011, from http://flipthemedia.com/index.php/2011/02/the-arab-revolution-and-social-media/. Abdeleli, A. (2011). Arab Refugees return home following Revolutions. Retrieved October 24, 2011, from http://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/specials/the_arab_spring/Arab_refugees_return_home_ following_revolutions.html?cid=31134110 The Countries and People of Arabia. (2010). Retrieved October 24, 2011, from http://www.hejleh.com/countries/
Freedman, R.O. (1991). The Intifada: its impact on Israel, the Arab World, and the superpowers. USA: University Press of Flourida.
You might also like
- The Origins of The Arab-Israeli ConflictDocument12 pagesThe Origins of The Arab-Israeli ConflictNicole Balbi100% (1)
- Massacre of Muslims in PalestineDocument6 pagesMassacre of Muslims in PalestineTabassum UsmanNo ratings yet
- Reading Workshop-Teacher's HandoutDocument18 pagesReading Workshop-Teacher's HandoutileanamoramarinNo ratings yet
- Radical Palestinian Revolutionary Jabra Nicola and the Early Anti-Zionist LeftDocument17 pagesRadical Palestinian Revolutionary Jabra Nicola and the Early Anti-Zionist LeftHamad Al-RayesNo ratings yet
- Crisis in The Middle EastDocument28 pagesCrisis in The Middle EastWajid AliNo ratings yet
- The History of IsraelDocument3 pagesThe History of Israelhafsa mahboobNo ratings yet
- The Arab Revolt 1936-1937 - Ghassan KanafaniDocument43 pagesThe Arab Revolt 1936-1937 - Ghassan Kanafanirewandn100% (1)
- Tool Kit: Useful StuffDocument13 pagesTool Kit: Useful StuffAIGA, the professional association for design100% (2)
- The History of The United States Part 5Document44 pagesThe History of The United States Part 5TimothyNo ratings yet
- Zionism: Zionism, Jewish Nationalist Movement That Has Had As Its Goal TheDocument3 pagesZionism: Zionism, Jewish Nationalist Movement That Has Had As Its Goal TheAsad Mehmood100% (2)
- Classical Film ViolenceDocument343 pagesClassical Film ViolenceŠtefan Sitáni100% (4)
- 4999EDN: The Griffith Education Internship Professional Learning PlanDocument7 pages4999EDN: The Griffith Education Internship Professional Learning Planapi-469331794No ratings yet
- Social Sciences Compilation of Activities and IdeasTITLE Compilation of Social Sciences Disciplines and Concepts TITLE Activities Report on Social Sciences Ideas and KnowledgeDocument10 pagesSocial Sciences Compilation of Activities and IdeasTITLE Compilation of Social Sciences Disciplines and Concepts TITLE Activities Report on Social Sciences Ideas and KnowledgeKath Tan Alcantara74% (34)
- The Green Book of Language Revitalization in PracticeDocument468 pagesThe Green Book of Language Revitalization in PracticeAmairaniPeñaGodinez50% (2)
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 Cultural, Social and Political InstitutionsDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 Cultural, Social and Political InstitutionsAnna Liza LingatNo ratings yet
- Israeli Rejectionism: A Hidden Agenda in the Middle East Peace ProcessFrom EverandIsraeli Rejectionism: A Hidden Agenda in the Middle East Peace ProcessNo ratings yet
- Community Participation in Quality EducationDocument9 pagesCommunity Participation in Quality EducationBishnu Prasad Mishra100% (5)
- STS, Learning EnhancementDocument3 pagesSTS, Learning EnhancementDeb BringNo ratings yet
- American RevolutionDocument3 pagesAmerican RevolutionDeb BringNo ratings yet
- Pal at StakeDocument10 pagesPal at StakeHarry ClarkNo ratings yet
- Factors Behind Rise of Arab NationalismDocument9 pagesFactors Behind Rise of Arab Nationalismramanand pandeyNo ratings yet
- High School World History Practice QuizDocument3 pagesHigh School World History Practice QuizGyermie Ross CarpesoNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "World History 1914-1968" By David Thomson: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "World History 1914-1968" By David Thomson: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 - Chapter ReviewDocument15 pagesChapter 30 - Chapter ReviewAnonymous BcTQ2mNo ratings yet
- Socialist Labor Party on the Middle East ConflictDocument9 pagesSocialist Labor Party on the Middle East Conflictmetalheavy9993No ratings yet
- Israel vs. Palestine ConflictDocument15 pagesIsrael vs. Palestine ConflictJet Lemuel SalazarNo ratings yet
- PalesDocument16 pagesPalesVK CREATIONNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "1945-1995 The Decolonization Of The World" By García De Cortázar & Lorenzo Espinosa: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "1945-1995 The Decolonization Of The World" By García De Cortázar & Lorenzo Espinosa: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Churchpersecutionessay GroupDocument12 pagesChurchpersecutionessay Groupapi-643180435No ratings yet
- Ebenezer Kwadwo Kissiedu 220016747 SOT Day SchoolDocument5 pagesEbenezer Kwadwo Kissiedu 220016747 SOT Day SchoolEbenezer KissieduNo ratings yet
- Paris HistoryDocument106 pagesParis HistoryJose SanchezNo ratings yet
- Usa HistoryDocument58 pagesUsa HistoryJose SanchezNo ratings yet
- Factors For The Growth of African Nationalism HistoryDocument8 pagesFactors For The Growth of African Nationalism HistoryChrispin Msofe93% (14)
- His 386 Research PaperDocument18 pagesHis 386 Research Paperapi-356822645No ratings yet
- A New Way ForwardDocument8 pagesA New Way ForwardkbtrombonistNo ratings yet
- Arab Isarel 4Document19 pagesArab Isarel 4Shilpa Asopa JainNo ratings yet
- The Conditions of AsiaDocument7 pagesThe Conditions of AsiaNash SequitinNo ratings yet
- Israel Palestine: KeywordsDocument6 pagesIsrael Palestine: KeywordsDarshan MishraNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Revolution. HistoryDocument14 pagesEgyptian Revolution. HistoryJasnakhanNo ratings yet
- Unique Essay Supplement 02Document32 pagesUnique Essay Supplement 02kazi ahadNo ratings yet
- Fractured Militancy: Precarious Resistance in South Africa after Racial InclusionFrom EverandFractured Militancy: Precarious Resistance in South Africa after Racial InclusionNo ratings yet
- The 19th Century World of Jose RizalDocument2 pagesThe 19th Century World of Jose RizalRiza Gabaya Alia100% (2)
- History Midterm Study PacketDocument33 pagesHistory Midterm Study PacketscreamcreamvanillaNo ratings yet
- Timeline Israel and Palestines Complicated HistoryDocument13 pagesTimeline Israel and Palestines Complicated HistoryMoazzamDarNo ratings yet
- CH-2 - Early Nationalist MovementsDocument5 pagesCH-2 - Early Nationalist MovementsdebdulaldamNo ratings yet
- Community Presentation - A Brief History of BrazilDocument4 pagesCommunity Presentation - A Brief History of Braziladrianbanita28No ratings yet
- World HistoryDocument6 pagesWorld HistoryVishwam PrakashNo ratings yet
- Modern Era Essential Questions 1750-1900Document4 pagesModern Era Essential Questions 1750-1900Angela WangNo ratings yet
- History AssignmentDocument48 pagesHistory AssignmentBik WodeNo ratings yet
- IB History Paper 1 Revision Notes on the Arab-Israeli Conflict 1945-79Document9 pagesIB History Paper 1 Revision Notes on the Arab-Israeli Conflict 1945-79okolade2No ratings yet
- Causes of The Revolutions of 1848: by Dhananjay Sahai (1002)Document8 pagesCauses of The Revolutions of 1848: by Dhananjay Sahai (1002)Anonymous JEyWEyNo ratings yet
- 01.test-I (World History) SolutionsDocument35 pages01.test-I (World History) Solutionssameer bakshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2 RizalDocument11 pagesChapter 1 and 2 RizalArfela Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pro MuusDocument20 pagesPro MuuslarryfoleNo ratings yet
- Windrush Information On How Britain ReactedDocument3 pagesWindrush Information On How Britain ReactedcgallowayNo ratings yet
- HI4025 ExamDocument3 pagesHI4025 ExamcecolinalessandraNo ratings yet
- 19th Century Catalyst for ChangeDocument38 pages19th Century Catalyst for ChangeLuther Ivanne M. DejesusNo ratings yet
- historyDocument3 pageshistoryseid negashNo ratings yet
- Report of The CC of Cpi To 26 Congress - March-2012Document14 pagesReport of The CC of Cpi To 26 Congress - March-2012Fahad RizwanNo ratings yet
- A Testimony To InternationalismDocument10 pagesA Testimony To InternationalismKarla Graft ThomasNo ratings yet
- Conflict in PalestineDocument20 pagesConflict in PalestineAnto Del GobboNo ratings yet
- Essay-Final Draft On Israel Arabs and PalestineDocument10 pagesEssay-Final Draft On Israel Arabs and PalestineTariq SulemanNo ratings yet
- Preface: 1.3 The Bale Peasant Rebellions . 3Document5 pagesPreface: 1.3 The Bale Peasant Rebellions . 3Liban ToleraNo ratings yet
- John Reed NegroquestionDocument3 pagesJohn Reed NegroquestionMiguel Borba de SáNo ratings yet
- Business Decision MakingDocument28 pagesBusiness Decision MakingParul SharmaNo ratings yet
- KFC Updated FinalDocument28 pagesKFC Updated FinalParul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gabriela Boroleanu BDMDocument30 pagesGabriela Boroleanu BDMParul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Sample 1Document40 pagesPart 4 Sample 1Parul SharmaNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument6 pagesLeadershipParul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Modern Languages Textbook ListDocument14 pagesModern Languages Textbook ListfrankmdNo ratings yet
- Social ProblemsDocument8 pagesSocial ProblemsRazzeev TwayanaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Essay Writing by DAWNDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Essay Writing by DAWNSyed Arsalan Tahir BukhariNo ratings yet
- Bent FlyvbjergDocument1 pageBent FlyvbjergBianca Simona BratuNo ratings yet
- Tasks and Datelines Form 3 - Reading & GrammarDocument4 pagesTasks and Datelines Form 3 - Reading & GrammarAmelia AyNo ratings yet
- Bryce, Trevor R. Anatolian Scribes in Mycenaean Greece.Document9 pagesBryce, Trevor R. Anatolian Scribes in Mycenaean Greece.Yuki AmaterasuNo ratings yet
- Critique of The Living National Treasure (LNT) System, by Aoyama WaheiDocument8 pagesCritique of The Living National Treasure (LNT) System, by Aoyama WaheigozappariNo ratings yet
- Durga Bhagwat, Indian writerDocument4 pagesDurga Bhagwat, Indian writerDhrubajyoti ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Crisis Communication enDocument131 pagesCrisis Communication enpesalpeca44No ratings yet
- Administrative Corruption PDFDocument10 pagesAdministrative Corruption PDFSandrita Tagle0% (1)
- Esports VideogamesDocument2 pagesEsports VideogamesMonica Patricia Alzamora SantanaNo ratings yet
- Arab Medicine Ibn Abi UsabeDocument357 pagesArab Medicine Ibn Abi UsabeCarmen HntNo ratings yet
- Antigone Themes - Pride, Individual vs StateDocument8 pagesAntigone Themes - Pride, Individual vs StateCynthi Joyce John100% (1)
- Rhetorical Analysis Before RevisionDocument4 pagesRhetorical Analysis Before Revisionapi-494318582No ratings yet
- Middle Range TheoryDocument8 pagesMiddle Range Theorysoukumar8305No ratings yet
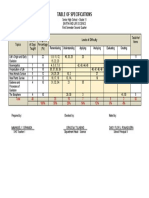
- Earth and Life 2Q TOSDocument1 pageEarth and Life 2Q TOSImmanuel Granada100% (1)
- Ncip BarangayDocument8 pagesNcip BarangayLouie LanajaNo ratings yet
- Berklee at Umbria Jazz Clinics 2018Document6 pagesBerklee at Umbria Jazz Clinics 2018djsonja07No ratings yet
- Syllabus Eeuu Bil 2017Document6 pagesSyllabus Eeuu Bil 2017api-200062650No ratings yet
- Practical Lesson8Document20 pagesPractical Lesson8VeahNo ratings yet
- Common English Errors and How to Overcome ThemDocument15 pagesCommon English Errors and How to Overcome ThemBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- REPORT: Values Education: What, How, Why and What Next?Document5 pagesREPORT: Values Education: What, How, Why and What Next?diona macasaquitNo ratings yet