Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
kamirure02Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
kamirure02Copyright:
Available Formats
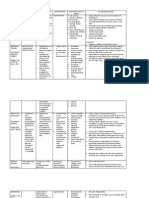
DRUG NAME Salbutamol neb, 1 neb q 4 CLASSIFICATI ON: Bronchodilator (therapeutic); adrenergics (pharmacologi c)
ACTION It relieves nasal congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bronchioles. The relief from nasal congestion and bronchospasm is made possible by the following mechanism that takes place when Salbutamol is administered. First, it binds to the beta2adrenergic receptors in the airway of the smooth muscle which then leads to the activation of the adenyl cyclase and increased levels of cyclic- 35adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
INDICATION To control and prevent reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) Quick relief for bronchospasm For the prevention of exerciseinduced bronchospasm Long-term control agent for patients with chronic or persistent bronchospasm
CONTRAINDICA TION Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons
SIDE EFFECT Nervousness Restlessness Tremor Headache Insomnia Chest pain Palpitations Angina Arrhythmias Hypertension Nausea and vomiting Hyperglycemia Hypokalemia
EVALUATION Assess lung sounds, PR and BP before drug administration and during peak of medication. Observe for paradoxical spasm and withhold medication and notify physician if condition occurs. Administer PO medications with meals to minimize gastric irritation. Extended-release tablet should be swallowed-whole. It should not be crushed or chewed. If administering medication through inhalation, allow at least 1 minute between inhalation of aerosol medication. Advise the patient to rinse mouth with water after each inhalation to minimize dry mouth. Inform the patient that Albuterol may cause an unusual or bad taste.
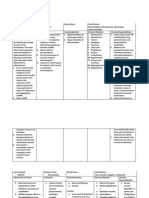
When cAMP increases, kinases are activated. Kinases inhibit the phosphorylation of myosin and decrease intracellular calcium. Decreased in intracellular calcium will result to the relaxation of the smooth muscle airways. Budesonide controls the rate of protein synthesis, depresses the migration of polymorphonuclea r leukocytes, fibroblasts, reverses capillary permeability and lysosomal stabilisation at the cellular level to prevent or control inflammation
Budesonide neb, 1 neb q 12 CLASSIFICATI ON:Corticoster oid
Management of symptoms of seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children; nonallergic perennial rhinitis in adults
Hypersensitivity. Acute infections uncontrolled by antimicrobial chemotherapy
Loss of skin collagen and SC atrophy; local hypopigmentatio n of deeply pigmented skin; dryness, irritation, epistaxis, rarely ulceration or perforation of the nasal septum; smell and taste disturbances; hoarseness and
Assessment History: Untreated local nasal infections, nasal trauma, septal ulcers, recent nasal surgery, lactation Physical: BP, PR, auscultation; RR, adventitious sounds; examination of nares Interventions Nasal inhalation Prime pump eight times before first use. If not used for 2 consecutive days, reprime with 1 spray or until
candidiasis of the mouth or throat Unknown. May inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, to produce antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects. It works by blocking the action of a substance in the body called cyclooxygenase. Cyclooxygenase is involved in the production of various chemicals in the body, some of which are known as prostaglandin s. Prostaglandin s are produced in response to injury or certain diseases and would otherwise go on to cause pain, swelling and CNS Contraindicated in patients Headache, hypersensitive to dizziness, drug and in those nervousness, with angioedema, aseptic syndrome of meningitis. nasal polyps, or CV bronchospastic Peripheral reaction to edema, fluid aspirin or other retention, NSAIDs. edema. EENT Contraindicated Tinnitus in pregnant GI women. Epigastric distress, Use cautiously in nausea, patients with GI occult blood disorders, history loss, peptic of peptic ulcer ulceration, disease, cardiac diarrhea, decompensation, constipation, hypertension, abdominal asthma, or pain, intrinsic bloating, GI coagulation fullness, defects. dyspepsia, flatulence, heartburn, decreased appetite.
fine mist appears. If not used for more than 14 days, rinse applicator and reprime with 2 sprays or until fine mist appears
Tell patient to take with meals or milk to reduce adverse GI reactions. Note: Drug is available at OTC. Instruct patient not to exceed 1.2 g daily, not to give to chidren younger than age 12, and not to take for extended periods ( longer than 3 days for fever or longer than 10 days for pain) without consulting presciber. Tell patient that full therapeutic effect for arthritis may be delayed for 2 to 4 weeks. Although pain relief occurs at low dosage levels, inflammation doesnt improve at dosages less than 400 mg q.i.d. Teach patient to watch for and report to prescriber immediately signs and symptoms of GI bleeding, including blood in vomit, urine, or stool or coffee ground vomit, and black, tarry stool. Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require mental alertness until effects on CNS are known. Advise patient to wear sunscreen to avoid hypersensitivity to sunlight.
Ibruprofen 200 mg/5ml, 9 ml q 6 for T >= 37.5 C CLASSIFICATI ON: Antipyretic and antiinflammatory analgesics
inflammation. Ibuprofen is therefore used to relieve pain and inflammation. All the medicines in this group (NSAIDs) reduce inflammation caused by the body's own immune system, and are effective pain killers. Ibuprofen can be used to relieve pain such as muscular aches and pains, period pains, headache, backache, rheumatic pain, dental pain and neuralgia. It can also reduce feverishness
GU Acute renal failure, azotemia, cystitis, hematuria. HEMATOLOGIC Plonged bleeding time, anemia, neutropenia, pancytopenia , thrombocyto penia, aplastic anemia, leucopenia, agranulocyst ocis. METABOLIC Hypoglycemi a, hyperkalemia . RESPIRATORY: Bronchospas m SKIN Pruritus, rash, urticaria, stevens Johnson syndrome
Loratadine CLASSIFICATI ON: Antihistamine (nonsedating type)
It works by selectively binding to peripheral histamine H1 -receptors on effector cells.
and the symptoms of colds and flu. Symptomatic Pregnancy, relief of lactation, perennial and children <2 yr. seasonal allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, and mild, uncomplicate d urticaria and angioedema Treatment of rhinitis and chronic urticaria in children > 2 yr
Fatigue, giddiness, dizziness, dry mouth, headache, nausea, somnolence.
Assessment History: Allergy to any antihistamines; narrow-angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, asthma, bladder neck obstruction, pyloroduodenal obstruction; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Skin color, lesions, texture; orientation, reflexes, affect; vision examinations; R, adventitious sounds; prostate palpation; serum transaminase levels Interventions Administer without regard to meals. Teaching points If using rapid or orally dissolving tablets, place on tongue, tablet will dissolve within seconds, swallow with or without water. Avoid the use of alcohol; serious sedation could occur. You may experience these side effects: Dizziness, sedation, drowsiness (use caution if driving or
performing tasks that require alertness); headache; thickening of bronchial secretions, dryness of nasal mucosa (use a humidifier). Report difficulty breathing, hallucinations, tremors, loss of coordination, irregular heartbeat. NaCl nasal spray CLASSIFICATI ON: Decongestants A mist of saline solution is delivered to help moisturize dry or irritated nostrils. They can also relieve nasal congestion and remove airborne irritants such as pollen, dust etc. thereby providing sinus allergy relief. The solution can be either isotonic or hypertonic. Isotonic solutions have the same salt concentration as the human body whereas hypertonic solutions have a higher salt content. Moisturizes dry, crusted, and stuffy nostrils due to allergy, colds, overuse of antihistaminic decongestant s None reported Temporary burning, stinging, dryness in the nose, runny nose, and sneezing may occur. Ask client to clean nostril first before giving medication Ask parent to place infant or child to supine position Spray to each nostril as indicated Inform to remain in position for a while for the medication to absorb in the nasal passage Inform patient to keep medication bottle away from sunlight Discard bottle after symptoms are not present anymore Dont share medication to another
Ceftriaxone 750 mg q 12 (-) ANST CLASSIFICATI ON: 2nd Generation Cephalosphori ns
Hypertonic solutions may be more useful at drawing moisture from the mucus membrane and relieving nasal congestion. Inhibits cellw a l l synthesis, promoting osmotic instability;usuall y bactericidal
Used for treatment of serious infections of the lower respiratory tracts.
Hypersensitivity to cefuroxime, any component, or other cephalospo rin
Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, rash, pain, temperature elevation
Assess for previous history of reactions to other cephalosporin or penicillin Modify dosage in patients with severe renal impairment. Prolonged use may result in super infection. A low incidence of crosshypersensitivity to penicillins exist.
You might also like
- Non-Surgical Spinal DecompressionDocument23 pagesNon-Surgical Spinal Decompressionshivnair0% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Al Ries Jack Trout-The 22 Immutable Laws of Marketing-EnDocument141 pagesAl Ries Jack Trout-The 22 Immutable Laws of Marketing-EnLily WangNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain and SciaticaDocument24 pagesLow Back Pain and SciaticaOVVCMOULINo ratings yet
- Otc Drug Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesOtc Drug Drug InteractionsDavid HosamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs GuideDocument56 pagesRespiratory Drugs GuideIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Head and Neck Pain PDFDocument129 pagesHead and Neck Pain PDFPrashanth89% (9)
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesDrugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemKerk JanerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Diclofenac KDocument3 pagesDrug Study Diclofenac KCarl Julienne Masangcay100% (1)
- Micro-Needling Post Treatment InstructionsDocument1 pageMicro-Needling Post Treatment InstructionsMarian YuqueNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen - Pharmacology, Therapeutics and Side Effects. 2012Document260 pagesIbuprofen - Pharmacology, Therapeutics and Side Effects. 2012VuqarNo ratings yet
- The Common Cold GuideDocument27 pagesThe Common Cold Guidehappyscottlee3438No ratings yet
- Drug Study QiDocument7 pagesDrug Study QiJeremiah Mauricio100% (1)
- Drugs NclexDocument30 pagesDrugs Nclexawuahboh100% (1)
- 24 Emergency DrugsDocument7 pages24 Emergency DrugsApple BelicanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Therapeutic Diet To Control Different Types of DiseasesDocument79 pagesTherapeutic Diet To Control Different Types of DiseasesSouvik TewariNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAbdullah Mascardo BarabagNo ratings yet
- Refer Mrs Karen Smith for Neurological AssessmentDocument1 pageRefer Mrs Karen Smith for Neurological AssessmentOETNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 pagesGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Budesonide Drug CardDocument3 pagesBudesonide Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsdeepika kushwah100% (1)
- SulodexideDocument7 pagesSulodexideZera Cortez100% (1)
- NG163Document24 pagesNG163Tim BrownNo ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- Bronchodilators Guide for Asthma and COPDDocument5 pagesBronchodilators Guide for Asthma and COPDdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 pagesVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesEpinephrine Drug StudyJhoy Iris SarangayaNo ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Patient's Name: C.R. Age: 24y/o Drug: Mupirocin Ointment Diagnosis: Pott's DiseaseDocument4 pagesPatient's Name: C.R. Age: 24y/o Drug: Mupirocin Ointment Diagnosis: Pott's DiseaseCzelmar del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument186 pagesDrug StudyTheresa Sombilla FacunlaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Chapter 36Document11 pagesPharmacology Chapter 36languha NgatiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Sas1 ClinpharDocument7 pagesSas1 ClinpharAlyssa Marie Petonio BialaNo ratings yet
- Indications:Treatment & Therapeutic Effect: Reduces: Drug StudyDocument1 pageIndications:Treatment & Therapeutic Effect: Reduces: Drug StudyBien EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric Namewilfred_prontoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- AtroventDocument1 pageAtroventSheri490100% (1)
- Generic and Trade Names, Mechanisms, InterventionsDocument4 pagesGeneric and Trade Names, Mechanisms, InterventionsSonia FernandesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs GuideDocument56 pagesRespiratory Drugs GuideShang MacarayonNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- NCP and Drug StudyDocument11 pagesNCP and Drug StudyTonio PagaoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 - NCMA216 - PHARMA - Respiratory System AgentsDocument50 pagesWEEK 9 - NCMA216 - PHARMA - Respiratory System AgentsOther AccountNo ratings yet
- diphenhydrAMINE BenadrylDocument2 pagesdiphenhydrAMINE BenadrylMichele Gilbert BlumNo ratings yet
- Pilocarpine Action, Uses, Interactions and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesPilocarpine Action, Uses, Interactions and Nursing ConsiderationsNurrahmi Putri Anggraeni LaguligaNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesRespiratory Drugs Midterm ExamKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument2 pagesSalbutamolMarck Vincent Garcia OngNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Common Cold Allergic Rhinitispharmaceutical C P e Program Common ColdDocument27 pagesDokumen - Tips Common Cold Allergic Rhinitispharmaceutical C P e Program Common ColdVerqueza OdzongNo ratings yet
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract Infection Pharmacotherapy RevisedDocument82 pagesRespiratory Tract Infection Pharmacotherapy Revisedchuye alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin, Bactroban, Algesia, Losartan, Paracetamol, Ketorolac, Tetanus Toxoid, HTIG Drug StudyDocument34 pagesCiprofloxacin, Bactroban, Algesia, Losartan, Paracetamol, Ketorolac, Tetanus Toxoid, HTIG Drug StudygecalianNo ratings yet
- Francophone Product PPT (003) Shared by DilkanshDocument45 pagesFrancophone Product PPT (003) Shared by DilkanshDjibril WeleNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia and Concious SedationDocument43 pagesLocal Anesthesia and Concious Sedationpawi18No ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Diclofenac Sodium Drug InformationDocument9 pagesDiclofenac Sodium Drug InformationAlexander Chavez Alto100% (1)
- NR at MADocument4 pagesNR at MAAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Triggers, Signs, Treatment of Asthma EpisodesDocument3 pagesTriggers, Signs, Treatment of Asthma EpisodeswysosylwNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument7 pagesGeneric NameGia Bautista-AmbasingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EmphysemaDocument6 pagesDrug Study EmphysemaPaul MagbooNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAnaphylaxis: A Practical GuideAnne K. EllisNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Aman Dan Berbahaya Untuk Ibu Hamil Dan MenyusuiDocument17 pagesDaftar Obat Aman Dan Berbahaya Untuk Ibu Hamil Dan MenyusuiFirda LestariNo ratings yet
- Idaho ComplaintDocument62 pagesIdaho ComplaintENo ratings yet
- S 015 Med GuideDocument3 pagesS 015 Med GuideEko YuliantoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study School Nsg.Document12 pagesDrug Study School Nsg.Keila RosalesNo ratings yet
- Effervescent GranulesDocument6 pagesEffervescent GranulesVarinder KumarNo ratings yet
- Nephar 305 Nsaids - 15Document48 pagesNephar 305 Nsaids - 15NUR KINTAN APRILIANo ratings yet
- 5 Anti - Inflammatory Drugs, Anti-Gout DrugsDocument15 pages5 Anti - Inflammatory Drugs, Anti-Gout DrugsAudrey Beatrice ReyesNo ratings yet
- ALAXAN Module Part1Document30 pagesALAXAN Module Part1api-19864075No ratings yet
- Suprep Instructions Packet GDocument4 pagesSuprep Instructions Packet GssvtaaNo ratings yet
- USI Pharmaceuticals IPS, UVASDocument10 pagesUSI Pharmaceuticals IPS, UVASHamza TECHNo ratings yet
- 22 23-Jabberwock-Handbook FillableDocument36 pages22 23-Jabberwock-Handbook Fillablesunain rizwanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Pharmacology in MidwiferyDocument3 pagesDrug Study Pharmacology in MidwiferyLeander Isabelle NoolNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen (Dolan) Drug StudyDocument1 pageIbuprofen (Dolan) Drug Studyanreilegarde33% (3)
- Ibuprofen Farmakologi 3Document7 pagesIbuprofen Farmakologi 3Shafira TamaraNo ratings yet
- Drugs in OrthodonticsDocument67 pagesDrugs in OrthodonticsMaitreye PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Consumer Health in IndiaDocument8 pagesPaediatric Consumer Health in IndiaAkash GuruNo ratings yet
- AINS and EyeDocument26 pagesAINS and EyeEcaterina Borovic-PavlovschiNo ratings yet
- Temporary Crown Care InstructionsDocument1 pageTemporary Crown Care InstructionsGhostOperativeNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: College of NursingDocument3 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: College of Nursingmacleo fernandohyuhyiNo ratings yet