Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MX of Stroke
Uploaded by
Syafiq RahimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MX of Stroke
Uploaded by
Syafiq RahimCopyright:
Available Formats
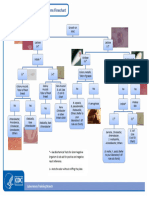
Mx of stroke (ischemic) General management maintain airway and o2 observe vitals + pulse oxi BP can increase but do not
require treatment if < 220/120 , maintain at 160-180/90-100mmhg. If more than this, reduce it by using Labetalol or captopril (15% reduction -dr uduman) Hyperglycemia common; treat if random >11mmol/L using insulin; If hypo <3mmol/L treat with glu infusion Nutrition- make sure pt don't aspirate. perform water swallow test (Rx NGT/PEG) Infection - Pneumonia / UTI ( give antibiotics, avoid bladder catheter) initial bed rest ( make sure pt don't fall, ripple mattress, bed sores) , encourage to mobilize once stable look for increase ICP signs ( cerebral edema);Rx: hyperventilation or give mannitol immediate investigations : ABG, FBC, BUSE, Coagulation profile, random bld sugar, ECG, CXR, Brain CT Acute Management of ischemic stroke A. IV rt-PA (0.9mg/kg) with 10% given as a bolus followed by an infusion over one hour within 3 hours of the onset Diagnosis is certain with measurable neuro deficit - don't give if pt had taken aspirin within 24 hr give only if imaging is available within 24 hr ( brain Ct should be normal) capable of tx complication of thrombolysis Bp should be <185/110 No CI to thrombolysis 1. Current use of oral anticoagulant or a promthrombin time (PT) > 15 seconds (INR > 1.7) 2. Use of heparin in the previous 48 hours and a prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT) 3. A platelet count < 100,000/mm3 4. Another stroke or any serious head injury in the previous 3 months 5. Major surgery within the preceding 14 days 6. Arterial puncture at noncompressible site within the last 21 days 7. Pre-treatment systolic blood pressure > 185mmHg or diastolic blood pressure > 110mmHg 8. Neurological signs that are improving rapidly 9. Isolated mild neurological deficits, such as ataxia alone, sensory loss alone, dysarthria alone or minimal weakness 10. Prior intracranial haemorrhage 11. A blood glucose < 2.7mmol/l or > 22.2mmol/l 12. Seizure at the onset of stroke 13. Gastrointestinal or urinary bleeding within the preceding 24 days 14. Recent myocardial infarction ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2. Admit the patient to an ICU / stroke unit. 3. Perform neurological assessments every 15 minutes during the infusion of rt-PA and every 30 minutes for the next 6 hours and then every hour until 24 hours from treatment. 4. If the patient develops severe headache, acute hypertension, n/v discontinue the infusion if agent is still being administered and obtain a CT scan of brain. 5. Measure blood pressure every 15 minutes for the first 2 hours, every 30 minutes for the next 6 hours and then every hour until 24 hours from treatment. 6. Increase blood pressure measurements if a systolic blood pressure > 180mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure >105mm Hg is recorded. Administer anti-hypertensive medications to maintain blood pressure at or below these levels. 7. Delay placement of nasogastric tubes, indwelling bladder catheters or intra-arterial pressure catheters. If there is neuro deterioration, think hge complication. stop transfusion of Rt-PA, obtain bld for coag test, FFP, cryo
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Essay #01 (First Draft)Document2 pagesEssay #01 (First Draft)thanhtam3819No ratings yet
- Hussam Al-Furqan Ala Mann Haajj Al-Qur'anDocument34 pagesHussam Al-Furqan Ala Mann Haajj Al-Qur'anNoori al-Qadiri0% (1)
- AMX-3 Prom AdaptorDocument18 pagesAMX-3 Prom AdaptorEmmanuel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Rods NonStool Pathogens FlowchartDocument1 pageGram Negative Rods NonStool Pathogens FlowchartKeithNo ratings yet
- MELCs Briefer On SPJDocument27 pagesMELCs Briefer On SPJKleyr QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Cable Drag ChainDocument44 pagesCable Drag ChainsunhuynhNo ratings yet
- CM105 18to19Document30 pagesCM105 18to19api-3849444100% (2)
- Protecting The Pianist's Hand: The Carrezando Touch and MoreDocument6 pagesProtecting The Pianist's Hand: The Carrezando Touch and MoreAdrianNo ratings yet
- HavellsDocument4 pagesHavellsanurag_iiitmNo ratings yet
- Literature Review BUS 507 PDFDocument18 pagesLiterature Review BUS 507 PDFtanmoy8554No ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila - Freshmen AdmissionDocument6 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila - Freshmen AdmissionPoppy HowellNo ratings yet
- Three Laws of RoboticsDocument2 pagesThree Laws of RoboticsBav VAansoqnuaetzNo ratings yet
- TLC Treatment and Marketing ProposalDocument19 pagesTLC Treatment and Marketing Proposalbearteddy17193No ratings yet
- Eight Directions Feng ShuiDocument6 pagesEight Directions Feng Shuifree_scribdNo ratings yet
- The Remains of The Day-Excerpts-1Document2 pagesThe Remains of The Day-Excerpts-1DajanaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: Thermal Activity and Fluid MotionDocument14 pagesHeat Exchangers: Thermal Activity and Fluid Motionishu vohraNo ratings yet
- Baroque MusicDocument15 pagesBaroque Musicthot777100% (2)
- 4.6.6 Lab View Wired and Wireless Nic InformationDocument4 pages4.6.6 Lab View Wired and Wireless Nic InformationThắng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training, at DCCPPDocument26 pagesIndustrial Training, at DCCPPGaganil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Image/Data Encryption-Decryption Using Neural Network: Shweta R. Bhamare, Dr. S.D.SawarkarDocument7 pagesImage/Data Encryption-Decryption Using Neural Network: Shweta R. Bhamare, Dr. S.D.SawarkarPavan MasaniNo ratings yet
- Nestle CompanyDocument5 pagesNestle CompanymehakNo ratings yet
- VFTO DocumentationDocument119 pagesVFTO DocumentationSheri Abhishek ReddyNo ratings yet
- Blasting 001 Abb WarehouseDocument2 pagesBlasting 001 Abb WarehouseferielvpkNo ratings yet
- OE & HS Subjects 2018-19Document94 pagesOE & HS Subjects 2018-19bharath hsNo ratings yet
- LUTS Spot TestDocument2 pagesLUTS Spot TestHardiTariqHamma100% (1)
- Galen and The Antonine Plague - Littman (1973)Document14 pagesGalen and The Antonine Plague - Littman (1973)Jörgen Zackborg100% (1)
- Financial Modeling Interview Questions AnsweredDocument6 pagesFinancial Modeling Interview Questions AnsweredBHAVEN ASHOK SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter #11: Volume #1Document35 pagesChapter #11: Volume #1Mohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ozone Layer EssayDocument7 pagesOzone Layer Essayb71bpjha100% (2)
- On The Optimum Inter-Stage Parameters For Co Transcritical Systems Dr. Dan ManoleDocument8 pagesOn The Optimum Inter-Stage Parameters For Co Transcritical Systems Dr. Dan Manolemohammed gwailNo ratings yet