Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Guide - Protist and Fungi Test
Uploaded by
Camila Ziti GaiarimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide - Protist and Fungi Test
Uploaded by
Camila Ziti GaiarimCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide Plants Chapter 22 and 23
**Study From Class Notes use the text as a backup. Ch 22-1 / Plants 1) What is a plant? Plants are multicellular eukariotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b. 2) What is the cell wall made of? A cell wall is made of cellulose. They develop from multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b. 3) Know the functions of roots, stems, leaves and flowers. Roots:are underground organs that absorb water and minerals. Leaves: Are photosynthetic organs that contain one or more bundles of vascular tissue. Veins: Made of xylem and phloem. Stems: are supporting structures that connect roots and leaves, carrying water and nutrients between them. Flowers: in angiosperns is to attract pollinators (vectors) to facilitate pollination. in gymnosperms into separate male and female cones as the primary method of pollination is by wind. 4) Know how the plant is adapted for life on land. What adaptations allowed them to move from water to land? The lives of a plants center on the need of sunlight, water and minerals, gas exchange, and the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant body.Most plants have specialized tissues that carry water and nutrients upward from the soil and distribute the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant body. 5) Know the general plant life cycle. What are gametophytes, sporophytes, fertilization, meiosis, haploid, diploid, zygotes, alternation of generations. The Plant Life Cycle: Reproductive Cell: Gametes & Spores Alternation of Generation: Diploid(2n)-Knwon as Sporophyte Haploid(n)-Gametophyte Plant spores are haploid(n), reproductive cells formes in the sporophyte plant by meiosis that can grow into new indivuduals.The new individual is the gameophyte. A gamate is a reproductive cell that is produce a new individual, the diploid sporophyte. Many plants also have forms of vegetative, or assexual, reproduction.
Vocabulary Plant Stem Root Cuticle Leaf vascular tissue Sporophyte Gametophyte Haploid Diploid Xylem Tracheids Phloem Spore Bryohyta Pterophyta Sori Sporangia Gymnosperm Angiosperm Alternations of generations Stigma Style Ovary Pistil Stamen Anther Filament Seed Cones seed coat Fruit Flower (pg 612) leaf veins Annual Biennial Perennial Fertilization Meiosis Mitosis sperm and egg Pollen Frond Rhizome Sori
6) What did plants evolve from? They evolved from Green Algae 7) Know the difference between meiosis and mitosis Meiosis: is a process of reductional division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is halved. Mitosis: is the cell division process in which a eukaryotic cell divides the chromosomes into two identical sets of two daughter nuclei in its cell nucleus
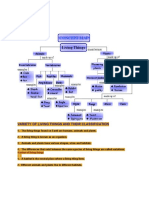
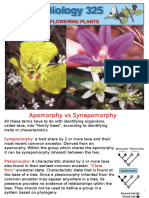
Ch 22-2 Bryophyta 1) What are bryophytes. 2) Know that they are non-vascular, seedless 3) Be able to identify the sporophyte and gametophyte from pictures (remember the gametophyte is the dominant generation and photosynthetic) 4) Knowand be able to draw the life cycle from your notes and your folder. Remember, the gametophytes are either male or female Ch 22-3 Pterophyta 1) What are pterophyta. 2) Know that they are vascular, seedless 3) Be able to identify the sporophyte and gametophyte from pictures (remember the sporophyte is now the dominant generation and photosynthetic) 4) Know and be able to draw the life cycle from your notes and your folder. Remember, the gametophytes are both male and female (hermaphrodites). Where are the sporangia? What do the sporangia make up? Ch 22-4 Gymnosperms 1) What are conifer? What is a cone? 2) Know that they are vascular and make seeds 1) How are seeds an advantage over spores? Why can they colonize drier habitats? 2) The sporophyte is the dominant generation and photosynthetic. The gametes are pollen and eggs. Where are pollen and egg produced? How does the pollen get to the egg in most conifers? 3) Be able to identify a conifer from a picture. Ch 22-5 Flowering plants - Angiosperms 1) What are the characteristics of flowering plants. 2) Know that they are vascular and make seeds 3) What do seeds consist of? Vocab: seed coat, embryo, food supply 4) Explain the role of the flowers and fruits. How are they advantages over cones. 5) The sporophyte is the dominant generation and photosynthetic. The gametes are pollen and eggs. Where are pollen and egg produced? How does the pollen get to the egg in most angiosperms? 6) Know the parts of the flower and their functions (pg 612) 7) How can you tell monocots from dicots See Back
Ch 23-1 / Specialized Tissues in Plants 1) 2) 3) 4) What are roots leaves stems and their purposes? What are the four types of tissue? What types of cells can be found in ground tissue? Know the root tip diagram (page 585). Know where you can find the root cap, apical meristem and vascular tissue 5) Know the leaf diagram (Page 596). Be able to identify the following structures, guard cells, stomata, vascular tissue, ground tissue (the palisade and spongy mesophyl is the ground tissue), epidermis and cuticle
Monocot Dicot Cotyledon tap root fibrous root dermal tissue vascular tissue meristematic tissue ground tissue collenchymas sclerenchyma parenchyma companion cell sieve tube
You might also like
- Biology Notes PDF 1 Beq2woDocument373 pagesBiology Notes PDF 1 Beq2woarmanmalik5216No ratings yet
- Biology 12 HSC NotesDocument195 pagesBiology 12 HSC NotesShitalPatilNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of BiologyDocument15 pagesKingdom Plantae: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of BiologySalar BasherNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytes McqsDocument7 pagesPteridophytes Mcqsmzohiab12No ratings yet
- SCINCE NOTES Part IIDocument6 pagesSCINCE NOTES Part IISANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Sinh Li Thuc VatDocument83 pagesSinh Li Thuc VatNguyễn HiếuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document79 pagesLecture 4Brian Ngugi KamandeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 FactsDocument1 pageChapter 10 Factsapi-208617789No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants: A Fascinating OrganDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants: A Fascinating OrganPrathyusha MannemNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument30 pagesClassification of PlantssnpakiNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms Plantae and Animalia Classification and CharacteristicsDocument30 pagesKingdoms Plantae and Animalia Classification and CharacteristicsPriyansh Patel100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Plant KingdomDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Plant KingdomSatish Chander VermaNo ratings yet
- Major: Pre-Pharmacy: Nther: IsDocument7 pagesMajor: Pre-Pharmacy: Nther: IsFatima Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom: Class I - ChlorophyceaeDocument8 pagesPlant Kingdom: Class I - ChlorophyceaeLawrence StokesNo ratings yet
- Seed Plant Life Cycles and Reproductive StructuresDocument12 pagesSeed Plant Life Cycles and Reproductive StructuresValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Review Sheet For The Life Cycle of PlantsDocument3 pagesAP Bio Review Sheet For The Life Cycle of PlantsRana MehaiNo ratings yet
- Gr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryDocument9 pagesGr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryLutendo Assurance MadzivhaaNo ratings yet
- Archegoniate Plants: An IntroductionDocument21 pagesArchegoniate Plants: An IntroductionShubhamMalikNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesA Review of The Plant KingdomVincent OmondiNo ratings yet
- Diversity (CHAPTER 30) Development (CHAPTER 35) Biology 8 Plant Evolution and Biology (CHAPTER 5)Document5 pagesDiversity (CHAPTER 30) Development (CHAPTER 35) Biology 8 Plant Evolution and Biology (CHAPTER 5)Suzette Bantiles AseoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Living OrganismsDocument38 pagesReproduction in Living OrganismsRishi KeshNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity NotesDocument59 pagesPlant Diversity NotesEve YapNo ratings yet
- Living World DiversityDocument51 pagesLiving World DiversityDeepsha online100% (1)
- PLANTS AND FUNGI INTRODocument10 pagesPLANTS AND FUNGI INTROMeghana GorrepatiNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionExceil Matthew Carpio100% (1)
- Classification and Characteristics of Major Plant DivisionsDocument8 pagesClassification and Characteristics of Major Plant DivisionsSANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Amerita Lab 4Document7 pagesAmerita Lab 4matthiasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and MorphologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and MorphologyminichelNo ratings yet
- PBB 213 - Bryology and Pteridology at Edo University IyamhoDocument17 pagesPBB 213 - Bryology and Pteridology at Edo University IyamhoKhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity-Ii (Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Paleobotany)Document48 pagesPlant Diversity-Ii (Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Paleobotany)Anshita RajputNo ratings yet
- Adaption of Seed PlantDocument23 pagesAdaption of Seed PlantYunita Lisnaningtyas UtamiNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsGhanshyam R. ParmarNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide Answers PlantsDocument9 pagesReading Guide Answers PlantsNirmal PatelNo ratings yet
- 102 Incourse Test 2013Document17 pages102 Incourse Test 2013Sam CuthbertNo ratings yet
- Handouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFDocument6 pagesHandouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFRizwan BalochNo ratings yet
- Flower Reproduction in PlantsDocument22 pagesFlower Reproduction in Plantstechnically whoNo ratings yet
- AP Kingdom PlantaeDocument79 pagesAP Kingdom PlantaeDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - PERPETUATION OF LIFEDocument15 pagesModule 6 - PERPETUATION OF LIFEMharcjhefferson RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Phylum Bryophyta (Moss)Document10 pagesKingdom Plantae: Phylum Bryophyta (Moss)Naduku EridadNo ratings yet
- Zoo 211 Lecture NotesDocument41 pagesZoo 211 Lecture Notesmusanafisat593No ratings yet
- 5 - Plant Diversity - Third - RecordingDocument21 pages5 - Plant Diversity - Third - RecordingFarrukh ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Plant Evolution I. BackgroundDocument15 pagesLecture 8: Plant Evolution I. BackgroundRodliyah fajrinNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarDocument51 pagesClass 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarRagaviNo ratings yet
- Answers To Review Questions - Chapter 36Document2 pagesAnswers To Review Questions - Chapter 361linNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Discussion QuestionsDocument16 pagesAp Bio Discussion QuestionsRoseline RobinsonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Chapter 30 Discussion AnswersDocument3 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 30 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (6)
- AP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion AnswersDocument3 pagesAP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (1)
- II PUC Biology Practical Exam Questions on Reproductive Parts of FlowersDocument10 pagesII PUC Biology Practical Exam Questions on Reproductive Parts of FlowersdharshanNo ratings yet
- Discover the Importance of Biodiversity and Ecosystem StabilityDocument36 pagesDiscover the Importance of Biodiversity and Ecosystem StabilityNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Scince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctDocument11 pagesScince Notes Part II Edited 21 OctSANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- Alido, Charlito VDocument5 pagesAlido, Charlito VCharlito AlidoNo ratings yet
- PLANT KINGDOM CLASSIFICATIONDocument20 pagesPLANT KINGDOM CLASSIFICATIONSiddhivinayak TidakeNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom (Botany) Question BankFrom EverandPlant Kingdom (Botany) Question BankRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Plants' Body Systems and Tissue TypesDocument4 pagesPlants' Body Systems and Tissue TypesPatrick KamelNo ratings yet
- BOT 101 Lecture Note On SpermatophytesDocument36 pagesBOT 101 Lecture Note On SpermatophytesAtoloye FavourNo ratings yet
- PTE Speaking Practice Test 3Document8 pagesPTE Speaking Practice Test 3siddhantspearheadNo ratings yet
- List of Systems of Plant TaxonomyDocument6 pagesList of Systems of Plant TaxonomymelatisukmaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AngiospermsDocument19 pagesReproduction in Angiospermstapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 3Document19 pagesPlant Kingdom Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 3dharun0704No ratings yet
- Exercise in Bio Lab Report 3Document4 pagesExercise in Bio Lab Report 3Ramnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction NOtes (New) (SISE9647EEEF6CF)Document35 pagesPlant Reproduction NOtes (New) (SISE9647EEEF6CF)amandeep khasaNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living Things and Their ClassificationDocument11 pagesVariety of Living Things and Their ClassificationAyuni100% (1)
- Final Assessment Essay 2022Document3 pagesFinal Assessment Essay 2022priyaNo ratings yet
- 2016 - Using Modern Plant Trait Relationships Between Observed and Theoretical Maximum Stomatal Conductance and Vein Density To Examine Patterns of Plant MacroevolutionDocument10 pages2016 - Using Modern Plant Trait Relationships Between Observed and Theoretical Maximum Stomatal Conductance and Vein Density To Examine Patterns of Plant MacroevolutionJuan Torres CastilloNo ratings yet
- (Series Entomologica 45) Kenneth A. Spencer (Auth.) - Host Specialization in The World Agromyzidae (Diptera) - Springer Netherlands (1990)Document453 pages(Series Entomologica 45) Kenneth A. Spencer (Auth.) - Host Specialization in The World Agromyzidae (Diptera) - Springer Netherlands (1990)Jose Franco Navia100% (1)
- KRM Public School: Periodic Assessment (April - 2021)Document4 pagesKRM Public School: Periodic Assessment (April - 2021)GaneshNo ratings yet
- Aaryan International School Class-XII Subject-Biology (Chapter 2)Document37 pagesAaryan International School Class-XII Subject-Biology (Chapter 2)Akshit Sharma VIII Diasy Roll no 6No ratings yet
- Class 9 Bio PracticalsDocument23 pagesClass 9 Bio PracticalsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- BIO 408-Plants and Environmental Pollution Monitoring 2Document160 pagesBIO 408-Plants and Environmental Pollution Monitoring 2Obi GoodnessNo ratings yet
- Smart Goal Life CyclesDocument4 pagesSmart Goal Life Cyclesapi-382003805No ratings yet
- MC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C03Document9 pagesMC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C03Camille HugoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Plants ExplainedDocument3 pagesClassification of Plants ExplainedKajori MondalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4Neo ChanNo ratings yet
- Vol. IIDocument663 pagesVol. IICamila Alcantara100% (1)
- Seeds of Woody Plants in The United StatesDocument916 pagesSeeds of Woody Plants in The United StatesГеоргийАкулининNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument11 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 2 2Document44 pagesGenbio2 Week 2 2kimberlyfritzzunigaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30: Seed Plants and Co-Evolution Study GuideDocument2 pagesChapter 30: Seed Plants and Co-Evolution Study GuideMadeline JensenNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument15 pagesMy TestALI ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- CH 38Document1 pageCH 38Diana Paraiso100% (1)
- Angiosperms - Origin Amd EvolutionDocument24 pagesAngiosperms - Origin Amd EvolutionYogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 NewDocument158 pagesBio 11 NewVibhor KaushikNo ratings yet