Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 7
Uploaded by
Ali AlabidOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 7
Uploaded by
Ali AlabidCopyright:
Available Formats
MONASH UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING ECE2041 Telecommunications /TRC4801 Digital Communications Practice Class
7: Line Coding, Modulation and Media Properties Sunway Version
1. Most digital transmission systems are self-clocking in that they derive the bit synchronization from the signal itself. To do this the systems use the transitions between positive and negative voltage levels. These transitions help define the boundaries of the bit intervals. a. The nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ) signaling method transmits a 0 with a +1 voltage of duration T, and a 1 with a 1 voltage of duration T. Plot the signal for the sequence n consecutive 1s followed by n consecutive 0s. Explain why this code has a synchronization problem. b. In differential coding the sequence of 0s and 1s induces changes in the polarity of the signal; a binary 0 results in no change in polarity, and a binary 1 results in a change in polarity. Repeat part (a). Does this scheme have a synchronization problem? c. The Manchester signaling method transmits a 0 as a +1 voltage for T/2 seconds followed by a 1 for T/2 seconds; a 1 is transmitted as a 1 voltage for T/2 seconds followed by a +1 for T/2 seconds. Repeat part (a) and explain how the synchronization problem has been addressed. What is the cost in bandwidth in going from NRZ to Manchester coding?
2. A phase modulation system transmits the modulated signal Acos(2fc t + )
where the phase is determined by the 2 information bits that are accepted every T-second interval: for 00, = 0 ; for 01, = /2 ; for 10, = ; for 11, = 3/2
a. Plot the signal constellation for this modulation scheme.
b. Explain how an eight-point phase modulation scheme would operate.
3. Suppose that the receiver in a QAM system is not perfectly synchronized to
the carrier of the received signal; that is, it multiplies the received signal by 2cos(2fc t + ) and by 2sin(2fc t + ) where is a small phase error. What is the output of the demodulator? 4. A twisted-wire pair has an attenuation of 0.7 dB/kilometer at 1 kHz. a. How long can a link be if an attenuation of 20 dB can be tolerated? b. A twisted pair with loading coils has an attenuation of 0.2 dB/kilometer at 1 kHz. How long can the link be if an attenuation of 20 dB can be tolerated?
5. Calculate the bandwidth of the range of light covering the range from 1200
nm to 1400 nm. How many Hz per person are available if the population of the world is six billion people? Repeat for 1400 nm to 1600 nm. Keep in mind that the speed of light in fiber is approximately 2 x 108 m/sec. 6. Suppose that we wish to delay an optical signal by 1 nanosecond. How long a length of optical fiber is needed to do this? How much is the signal attenuated? Repeat for 1 millisecond. 7. Compare the attenuation in a 100 km link for optical fibers operating at 850 nm, 1300 nm, and 1550 nm.
8. The power of an optical signal in dBm is defined as 10 log10P where P is in
milliwatts. a. What is the power in milliwatts of a 30 dBm signal ? 6dBm signal? b. What is the power in dBm of 1 microwatt signal? c. What is the power of an optical signal if initially it is 2 mW and then undergoes attenuation by 10 dB? output signal power if the loss per device is 1 dB?
9. A 10 dBm optical signal propagates across N identical devices. What is the
10. A satellite is stationed approximately 36,000 km above the equator. What is the attenuation due to distance for the microwave radio signal? Sample Exam Questions
11. A phase modulation system transmits the modulated signal x ( t ) = sin ( 2 fc t + )
where the phase is determined by the two information bits that are accepted every T-second interval: for 00, = 0; for 01, = /2; for 10, = ; for 11, = 3/2. Calculate x ( t ) for the information bits 00, 01, 10 and 11. b. Plot the signal constellation for this modulation scheme. c. If 00 is represented by the following modulated signal, then plot the modulated waveform for the binary sequence 01100011.
a.
d. Explain how an eight point phase modulation scheme would operate. (5 marks)
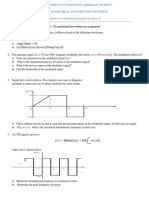
12. (Part of a question worth 10 marks) The figure below was discussed in
lectures. It shows the attenuation of different gauges of twisted wire pairs.
30 Attenuation (dB/mi) 24 18
26 gauge 24 gauge 22 gauge 19 gauge
12 6 f (kHz) 10 100 1000
a. What is the attenuation of 1 mile of 24 gauge at 10 kHz?
b. c.
What is the attenuation of 1 mile of 24 gauge at 200 kHz? What is the attenuation of 2miles of 24 gauge at 200kHz? subscriber loops for high speed internet connection.
d. Explain the effect of the results above on the use of digital
You might also like
- Question BankDocument6 pagesQuestion Banksweetkhushboo786_592No ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015Document3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015shreyas_stinsonNo ratings yet
- B1 - CAT 1 - KeyDocument6 pagesB1 - CAT 1 - KeyVamshidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4-SolutionDocument11 pagesTutorial 4-SolutionZaidi Mat ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- DCDocument8 pagesDCharshit420No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentpaper.2014No ratings yet
- CUIB – SCHOOL OF IT TELECOMMUNICATIONS II TUTORIALDocument6 pagesCUIB – SCHOOL OF IT TELECOMMUNICATIONS II TUTORIALAnnNo ratings yet
- Extra Tut 5 SolsDocument4 pagesExtra Tut 5 SolsNOMPUMELELO MTHETHWANo ratings yet
- Digital Communications Exercise Solution for Zero ISI ConditionDocument2 pagesDigital Communications Exercise Solution for Zero ISI ConditiondebealNo ratings yet
- Data Communication NotesDocument5 pagesData Communication NotesitsmelittyNo ratings yet
- Comm AssntIIDocument6 pagesComm AssntIIkalNo ratings yet
- VI Sem ECE AssignmentsDocument11 pagesVI Sem ECE AssignmentsManoj VarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Sample Questions, Problems and Solutions Bölüm 2: Örnek Sorular, Problemler Ve ÇözümleriDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Sample Questions, Problems and Solutions Bölüm 2: Örnek Sorular, Problemler Ve ÇözümleriDhana WinksNo ratings yet
- Baseband Questions StudentsDocument3 pagesBaseband Questions StudentsRishi JhaNo ratings yet
- KFUPM EE370 Final Exam Signals and SystemsDocument6 pagesKFUPM EE370 Final Exam Signals and Systemsthinkberry22No ratings yet
- VL2022230500824 DaDocument5 pagesVL2022230500824 DaAditya Bonnerjee 21BEC0384No ratings yet
- Assignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationDocument3 pagesAssignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationRhelf Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- 3C5 Tutorial Sheet 6: Dr. David Corrigan 18 March 2011Document5 pages3C5 Tutorial Sheet 6: Dr. David Corrigan 18 March 2011Naresh KadyanNo ratings yet
- A Modulating Signal MDocument6 pagesA Modulating Signal MxepilNo ratings yet
- Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Dayalbagh, Agra Faculty of EngineertingDocument8 pagesDayalbagh Educational Institute, Dayalbagh, Agra Faculty of EngineertingTanmayKabraNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- QB 2Document10 pagesQB 2Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- QB 2Document10 pagesQB 2Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- Rr220401 Communication TheoryDocument8 pagesRr220401 Communication TheorySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Communication: (Important Formulae and Concepts)Document4 pagesCommunication: (Important Formulae and Concepts)tutulkarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (2019) PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 (2019) PDFRishabh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsDocument3 pagesBEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsSiam hasanNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument6 pagesAnalog CommunicationsSri KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Transmit Diversity Technique For Wireless Communications: By, Undety Srinu, EC094220 (ACS)Document21 pagesTransmit Diversity Technique For Wireless Communications: By, Undety Srinu, EC094220 (ACS)Patel JigarNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Systems Worksheet: N at T, 0 T TDocument5 pagesDigital Communication Systems Worksheet: N at T, 0 T TAbrham GojjamNo ratings yet
- School of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Document2 pagesSchool of Electronics Engineering: Specific Instruction To Students (If Any)Dinesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATION3Document3 pagesCOMMUNICATION3october87No ratings yet
- HW2Document2 pagesHW2mohammad hoseyniNo ratings yet
- CS Ass1Document1 pageCS Ass1hargobindbNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 2: School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument1 pageWork Sheet 2: School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringfikaduNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation & DemodulationDocument11 pagesFrequency Modulation & DemodulationALINo ratings yet
- Numericals On AMDocument2 pagesNumericals On AMV Sree Suswara SuswaraNo ratings yet
- FrostDocument8 pagesFrostMnshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 AssignmentDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 AssignmentbaaaaNDSNo ratings yet
- Knotes Chapter-2 Amplitude ModulationDocument66 pagesKnotes Chapter-2 Amplitude ModulationGp Bhupinder100% (1)
- Digital CommunicationsDocument12 pagesDigital CommunicationsAnime MetrixNo ratings yet
- Definition of Signal States: (1 / Duration Baud Rate)Document33 pagesDefinition of Signal States: (1 / Duration Baud Rate)SSNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission ExercisesDocument23 pagesData Transmission ExercisesSubash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - III Unit - BEC - 43Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet - III Unit - BEC - 43Prisha SinghNo ratings yet
- UManitoba ECE 4260 Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesUManitoba ECE 4260 Midterm Examspoof183No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4+ SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 4+ SolutionsMujaahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Duo Binary Modulation For Optical SystemsDocument10 pagesDuo Binary Modulation For Optical SystemsErasmo VizzaccaroNo ratings yet
- Mod C A C M 4 C MDocument17 pagesMod C A C M 4 C MJKNo ratings yet
- Modullation PPT NewDocument58 pagesModullation PPT NewMayank TripathiNo ratings yet
- 6184419Document122 pages6184419Sky BlueNo ratings yet
- K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering (Autonomous), Samayapuram, Trichy-621112 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC8491 Communication TheoryDocument2 pagesK.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering (Autonomous), Samayapuram, Trichy-621112 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC8491 Communication Theorykrithikgokul selvamNo ratings yet
- Amplitude ModulationDocument31 pagesAmplitude ModulationNaga Raju MaadhuNo ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractice Questionspratik shuklaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications & WLAN BasicsDocument123 pagesDigital Communications & WLAN BasicsDeepthiNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- FIT1029 Tutorial 8 Solutions: MergeSort, QuickSort and Backtracking AlgorithmsDocument9 pagesFIT1029 Tutorial 8 Solutions: MergeSort, QuickSort and Backtracking AlgorithmsAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- FIT1029: Tutorial 6 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Task 1Document5 pagesFIT1029: Tutorial 6 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Task 1Ali AlabidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8: FIT 1029 - Algorithmic Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesTutorial 8: FIT 1029 - Algorithmic Problem SolvingAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- FIT1029: Tutorial 5 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Activity 1Document6 pagesFIT1029: Tutorial 5 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Activity 1Ali AlabidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4: FIT 1029 - Algorithmic Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesTutorial 4: FIT 1029 - Algorithmic Problem SolvingAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6: Euclidgdc (A, B)Document2 pagesTutorial 6: Euclidgdc (A, B)Ali AlabidNo ratings yet
- FIT 1029 Algorithmic Problem Solving TutorialDocument2 pagesFIT 1029 Algorithmic Problem Solving TutorialAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- FIT1029: Tutorial 3 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Task 1Document4 pagesFIT1029: Tutorial 3 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Task 1Ali AlabidNo ratings yet
- FIT1029: Tutorial 4 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Task 1Document8 pagesFIT1029: Tutorial 4 Solutions Semester 1, 2014: Task 1Ali AlabidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Solving Problems by Identifying Invariants, Greedy Algorithms, Minimum Spanning Trees & Knapsack ProblemDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 - Solving Problems by Identifying Invariants, Greedy Algorithms, Minimum Spanning Trees & Knapsack ProblemAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- FIT1029: Tutorial 2 Solutions Semester 2, 2013: Task 1Document7 pagesFIT1029: Tutorial 2 Solutions Semester 2, 2013: Task 1Ali AlabidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2: FIT 1029 - Algorithmic Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesTutorial 2: FIT 1029 - Algorithmic Problem SolvingAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- HTML Introduction: The Basics of HTML Markup LanguageDocument26 pagesHTML Introduction: The Basics of HTML Markup LanguageAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 SolDocument4 pagesTutorial 7 SolAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- IP Final ReviewDocument48 pagesIP Final ReviewAli AlabidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (3) PNP JunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 2 (3) PNP JunctionJoel WatsonNo ratings yet
- BDX53C PDFDocument5 pagesBDX53C PDFonafetsNo ratings yet
- DVB T2 HandbookDocument25 pagesDVB T2 HandbookarsenaldoNo ratings yet
- 31 R20 IIMid Nov-December 2023Document7 pages31 R20 IIMid Nov-December 2023palivelasrinu12No ratings yet
- Menoufiya University Postgraduate ConstitutionDocument102 pagesMenoufiya University Postgraduate ConstitutionAhmedNo ratings yet
- Step-Down DC-DC Converter PDFDocument8 pagesStep-Down DC-DC Converter PDFGenetic JohnNo ratings yet
- NGP TS 1100uDocument2 pagesNGP TS 1100uxxxfarahxxxNo ratings yet
- Philips 29pfl4508-f8 29pfl4908-f7 Chassis pl13.7Document75 pagesPhilips 29pfl4508-f8 29pfl4908-f7 Chassis pl13.7fiuxy webNo ratings yet
- UF3C120040K4SDocument4 pagesUF3C120040K4SPalmNo ratings yet
- 1.4.6. Inverter Control Boards - CMC4+ - Ed2Document16 pages1.4.6. Inverter Control Boards - CMC4+ - Ed2Sami Vehmas100% (1)
- Lecture20 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture20 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Micro Pro SlidesDocument128 pagesMicro Pro SlideschandrNo ratings yet
- Czujnik Indukcyjny RN04 NP Firmy RIKO PDFDocument1 pageCzujnik Indukcyjny RN04 NP Firmy RIKO PDFLuis OrtizNo ratings yet
- URSI GASS 2021 Conference in Rome, Italy Focused on Dual-Band Crossed Dipole AntennaDocument3 pagesURSI GASS 2021 Conference in Rome, Italy Focused on Dual-Band Crossed Dipole AntennarehanNo ratings yet
- Customer of CrgoDocument18 pagesCustomer of CrgoGupta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lab Viii. Low Frequency Characteristics of Junction Field Effect TransistorsDocument6 pagesLab Viii. Low Frequency Characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistorssachinshetty001No ratings yet
- Hitachi 42PD6700U Plasma TVDocument79 pagesHitachi 42PD6700U Plasma TVTvcrepairNo ratings yet
- Training Activity MatrixDocument3 pagesTraining Activity MatrixBernadette Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Earth Station TechnologyDocument241 pagesEarth Station TechnologyJotham NyamandeNo ratings yet
- Gep 3-5Kw: Single-Phase - 2 MpptsDocument2 pagesGep 3-5Kw: Single-Phase - 2 MpptsHaidar Ali El-MalikNo ratings yet
- Mt8870, DTMF Decoder (Application Notes)Document24 pagesMt8870, DTMF Decoder (Application Notes)anmol9100% (1)
- Arduino Digital Ammeter Project With Circuit & CodeDocument11 pagesArduino Digital Ammeter Project With Circuit & CodeAlexandru Stefan0% (2)
- LcdsDocument96 pagesLcdspinterest345No ratings yet
- Wired Remote For Pioneer HUDocument22 pagesWired Remote For Pioneer HUYamilTalerNo ratings yet
- Designing a 48V Rectifier for Substation Battery ChargingDocument27 pagesDesigning a 48V Rectifier for Substation Battery ChargingMintesnot AlemuNo ratings yet
- A High Speed Feed Forward Pseudo Automallc Gain Control Circuit For An Amplifier CascadeDocument4 pagesA High Speed Feed Forward Pseudo Automallc Gain Control Circuit For An Amplifier Cascadeapi-19755952No ratings yet
- CH 02Document35 pagesCH 02greeshmaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Repair and Troubleshooting: Regulated Power Supply TroubleshootingDocument5 pagesElectronics Repair and Troubleshooting: Regulated Power Supply TroubleshootingIra CervoNo ratings yet
- 07a Backup OCEF Relay - Tech. Data Check List CompletedDocument6 pages07a Backup OCEF Relay - Tech. Data Check List CompletedAnupam0103No ratings yet