Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer (Ii) . . .: © Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed To ST George's School 1
Uploaded by
Alan PottsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer (Ii) . . .: © Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed To ST George's School 1
Uploaded by
Alan PottsCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
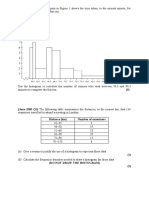
Findlay draws a bar chart to show how many pairs of shoes he has sold in his shop in one week. 1 5
1 F r e q u
0 e n c y
4 S
5 h o e s i z e
(i)
Use the information in the bar chart to complete the frequency table below. Shoe size Frequency
[2]
3 and 4
5 and 6
7 and 8
9 and 10
(ii)
Which is the modal class in the frequency table? Answer (ii) ...
[1]
Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to St George's School
2.
(a) 100 students are given a question to answer. The time taken (t seconds) by each student is recorded and the results are shown in the table.
t 0 < t 20 10 20 < t 30 10 30 < t 35 15 35 < t 40 28 40 < t 50 22 50 < t 60 7 60 < t 80 8
Frequency
(i) (ii)
Calculate an estimate of the mean time taken.
[4]
Two students are picked at random. What is the probability that they both took more than 50 seconds? Give your answer as a fraction in its lowest terms.
[3]
Answer part (b) on a sheet of graph paper. (b) The data in part (a) is re-grouped to give the following table. t Frequency (i) (ii) 0 < t 30 p 30 < t 60 q 60 < t 80 8
Write down the values of p and q.
[2]
Draw an accurate histogram to show these results. Use a scale of 1 cm to represent 5 seconds on the horizontal time axis. 2 Use a scale of 1 cm to 0.2 units of frequency density (so that 1 cm on your histogram represents 1 student).
[4]
Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to St George's School
3.
Kristina asked 200 people how much water they drink in one day. The table shows her results. Amount of water (x litres) 0 < x 0.5 0.5 < x 1 1 < x 1.5 1.5 < x 2 2 < x 2.5 2.5 < x 3 3 < x 3.5 3.5 < x 4 (a) (b) (c) Write down the modal interval.
[1]
Number of people 8 27 45 50 39 21 7 3
Calculate an estimate of the mean.
[4]
Make a cumulative frequency table for this data.
[2]
(d)
Using a scale of 4 cm to 1 litre of water on the horizontal axis and 1 cm to 10 people on the vertical axis, draw the cumulative frequency graph.
[5]
(e)
Use your cumulative frequency graph to find (i) (ii) (iii) the median,
[1]
the 40 percentile,
[1]
th
the number of people who drink at least 2.6 litres of water.
[2]
Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to St George's School
(f)
A doctor recommends that a person drinks at least 1.8 litres of water each day. What percentage of these 200 people do not drink enough water?
[2]
4.
Answer the whole of this question on one sheet of graph paper. The heights (h cm) of 270 students in a school are measured and the results are shown in the table. h 120 < h 130 130 < h 140 140 < h 150 150 < h 160 160 < h 170 170 < h 180 180 < h 190 190 < h 200 (a) Write down the modal group.
[1]
Frequency 15 24 36 45 50 43 37 20
(b) (ii)
(i)
Calculate an estimate of the mean height.
[4]
Explain why the answer to part (b)(i) is an estimate.
[1]
Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to St George's School
(c)
The following table shows the cumulative frequencies for the heights of the students. h h 120 h 130 h 140 h 150 h 160 h 170 h 180 h 190 h 200 Write down the values of p, q and r.
[2]
Cumulative frequency 0 p q r 120 170 213 250 270
(d)
Using a scale of 1cm to 5 units, draw a horizontal h-axis, starting at h = 120. Using a scale of 1cm to 20 units on the vertical axis, draw a cumulative frequency diagram.
[5]
(e)
Use your diagram to find (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) the median height,
[1]
the upper quartile,
[1]
the inter-quartile range,
[1]
the 60th percentile.
[1]
(f)
All the players in the schools basketball team are chosen from the 30 tallest students. Use your diagram to find the least possible height of any player in the basketball team.
[2]
Doublestruck & CIE - Licensed to St George's School
You might also like
- Statistics ClassifiedDocument56 pagesStatistics ClassifiedShaaminiNo ratings yet
- 0580 w10 QP 41Document16 pages0580 w10 QP 41MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- 0580 w11 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w11 QP 42Aryan RajputNo ratings yet
- 0580 w14 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w14 QP 42Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Topic - 19Document13 pagesTopic - 19Zakaria SajolNo ratings yet
- 0580 w05 QP 4Document8 pages0580 w05 QP 4Freddie Leo Dollaga RiveraNo ratings yet
- Questions 161261Document3 pagesQuestions 1612613t4e5yuezryhNo ratings yet
- 0580 w12 QP 43Document20 pages0580 w12 QP 43Freddie Leo Dollaga RiveraNo ratings yet
- 4024 w06 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w06 QP 2Beatrice RossNo ratings yet
- Representation of DataDocument27 pagesRepresentation of DataEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency WorksheetDocument20 pagesCumulative Frequency WorksheetBurhan AzharNo ratings yet
- 0580 w10 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w10 QP 42Aryan RajputNo ratings yet
- 2015 Paper 4 Specimen Paper PDFDocument16 pages2015 Paper 4 Specimen Paper PDFRekha PrasadNo ratings yet
- 0580 s11 QP 41Document16 pages0580 s11 QP 41Amina Koi DowuiNo ratings yet
- 0580 Y15 SP 4Document16 pages0580 Y15 SP 4Haider AliNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Educationnisa1673100% (1)
- 0607 w12 QP 4Document20 pages0607 w12 QP 4AnshulNo ratings yet
- 0580 s11 QP 42Document16 pages0580 s11 QP 42MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Frequency Past Paper Questions M/J2019 to 2005 P1 & P2Document28 pagesCumulative Frequency Past Paper Questions M/J2019 to 2005 P1 & P2Burhan AzharNo ratings yet
- 2016 HSC Maths General 2Document40 pages2016 HSC Maths General 2HIMMZERLANDNo ratings yet
- 0580 w14 QP 42Document20 pages0580 w14 QP 42Bobby SNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 2Document9 pagesIGCSE Mathematics Model Paper - 2Kothakonda Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Histogram Speed Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesHistogram Speed Data AnalysisaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Math Nov 2014 QP - 41Document20 pagesIGCSE Math Nov 2014 QP - 41CorinSaputraNo ratings yet
- 4024 w08 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w08 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 1.2 PracticeDocument7 pages1.2 PracticeLauren DarbyNo ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Sample Test PaperDocument16 pagesMaths IGCSE Sample Test PaperMarvin LuoNo ratings yet
- Stats1 Chp3 SupplementaryHistogramExerciseDocument4 pagesStats1 Chp3 SupplementaryHistogramExerciseConorNo ratings yet
- 0580 w06 QP 4Document8 pages0580 w06 QP 4MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Statistics Paper 2 Practice: Price ($) Number of BooksDocument5 pagesStatistics Paper 2 Practice: Price ($) Number of BooksclermaehoNo ratings yet
- Maths General 2 Specimen Paper 14Document41 pagesMaths General 2 Specimen Paper 14tedwong314No ratings yet
- 2015 Paper 3 Specimen PaperDocument16 pages2015 Paper 3 Specimen Paperseyka4No ratings yet
- Al Noor International School Maths ExamDocument21 pagesAl Noor International School Maths ExamKhadija mNo ratings yet
- Statistical Data Cs2Document5 pagesStatistical Data Cs2MCHNo ratings yet
- 0580 s10 QP 41Document20 pages0580 s10 QP 41Haider AliNo ratings yet
- 0580 s11 QP 41Document16 pages0580 s11 QP 41Haider AliNo ratings yet
- 0580 w14 QP 41Document20 pages0580 w14 QP 41Haider Ali100% (1)
- Class IX Chapter 14 - Statistics Maths: Exercise 14.1 Question 1Document41 pagesClass IX Chapter 14 - Statistics Maths: Exercise 14.1 Question 1Brij Vishal RajputNo ratings yet
- November 2011 Question Paper 31coreDocument16 pagesNovember 2011 Question Paper 31coreVikas AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- Maths Specimen Paper 2 2012Document14 pagesMaths Specimen Paper 2 2012ujjawalkediaNo ratings yet
- 0580 s12 QP 41Document16 pages0580 s12 QP 41Darwin ManoNo ratings yet
- Diagrams: Question Paper 5Document5 pagesDiagrams: Question Paper 5rogchen666No ratings yet
- Icjemapu 05Document8 pagesIcjemapu 05namish gambhirNo ratings yet
- GenEd Math Reviewer: 50 Problems with Detailed SolutionsDocument9 pagesGenEd Math Reviewer: 50 Problems with Detailed SolutionsArnel Jr Ambrocio100% (1)
- Descriptive Statistics of Dental Fillings, Task Times, Temperatures, and Student WeightsDocument2 pagesDescriptive Statistics of Dental Fillings, Task Times, Temperatures, and Student WeightskeziajessNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionSTPMmaths100% (1)
- Year 9 Math Entrance QuestionDocument2 pagesYear 9 Math Entrance QuestionWuityi LwinNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Bergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsFrom EverandBergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Preparatory Guide -Mathematics (Part 2)From EverandSSC CGL Preparatory Guide -Mathematics (Part 2)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1From EverandA Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1No ratings yet
- Advance Optima Analyzer 50 24 01EN FinalDocument12 pagesAdvance Optima Analyzer 50 24 01EN FinalJoeyNo ratings yet
- 19Document55 pages19Daniel MosesNo ratings yet
- Mezcladora Beringer 1002 ManualDocument20 pagesMezcladora Beringer 1002 ManualJohan PosliguaNo ratings yet
- Getting Maximum Value When Evaluating ProductsDocument18 pagesGetting Maximum Value When Evaluating ProductsLilianneNo ratings yet
- Et200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USDocument50 pagesEt200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USOmar AbdussaidNo ratings yet
- Stata Item Response Theory Reference Manual: Release 14Document199 pagesStata Item Response Theory Reference Manual: Release 14Maria StfNo ratings yet
- Alkiviadis Papadakis CVDocument4 pagesAlkiviadis Papadakis CVAlkiviadis PapadakisNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 10 I. Objectives: N R andDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 10 I. Objectives: N R andJesica Blando90% (20)
- SAP WEB IDE For SAP HANA Installation Troubleshooting Guide: Public 2021-09-29Document52 pagesSAP WEB IDE For SAP HANA Installation Troubleshooting Guide: Public 2021-09-29Tariq AliNo ratings yet
- Documentation ADR 622Document2 pagesDocumentation ADR 622CROIX ROUGENo ratings yet
- NO Nama Barang Jumlah Merek/Tipe Spesifikasi Harga SatuanDocument6 pagesNO Nama Barang Jumlah Merek/Tipe Spesifikasi Harga SatuanJuju Stiker DindingNo ratings yet
- Security Automation in Information Technology: Sikender Mohsienuddin Mohammad, Surya LakshmisriDocument5 pagesSecurity Automation in Information Technology: Sikender Mohsienuddin Mohammad, Surya LakshmisriramramNo ratings yet
- Huawei Bts3900 Hardware Structure Issue1.0Document96 pagesHuawei Bts3900 Hardware Structure Issue1.0Soman AunNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Emerging Technology 1Document5 pagesEthical Issues in Emerging Technology 1evans kiplimoNo ratings yet
- Servlet Filter - JavatpointDocument4 pagesServlet Filter - JavatpointHarsha Vardhan VNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument20 pagesStabilityravalNo ratings yet
- DI Cloud-GamingDocument20 pagesDI Cloud-GamingJosé Rafael Giraldo TenorioNo ratings yet
- Samsung Digital Camera Specification and Setup GuideDocument59 pagesSamsung Digital Camera Specification and Setup Guidejota_60254No ratings yet
- BHASYS SoftwareDocument81 pagesBHASYS SoftwareJayro LeninNo ratings yet
- Pgdis and AciseDocument67 pagesPgdis and AcisebhutrotterNo ratings yet
- CELSIUS W420 Technicka SpecifikaceDocument8 pagesCELSIUS W420 Technicka SpecifikaceAndre GasoNo ratings yet
- Delta Ltl2000sDocument45 pagesDelta Ltl2000sDritta Anies CahayaNo ratings yet
- Software Development With Visual QP BankDocument11 pagesSoftware Development With Visual QP BankveluswamiNo ratings yet
- Huawei UMTS RAN KPI & Counter Introduce (RAN10.0) Nicole V1Document41 pagesHuawei UMTS RAN KPI & Counter Introduce (RAN10.0) Nicole V1bayuNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management: Q.1 A) 'Statistics Is The Backbone of Decision Making'. CommentDocument10 pagesStatistics For Management: Q.1 A) 'Statistics Is The Backbone of Decision Making'. Commentkhanal_sandeep5696No ratings yet
- CustomSim VCS WPDocument11 pagesCustomSim VCS WPManda SwamyNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission Via Ethernet - Ip - Sd01293cen - 05.20Document94 pagesData Transmission Via Ethernet - Ip - Sd01293cen - 05.20Alex AlvesNo ratings yet
- MP Lab ManualDocument36 pagesMP Lab Manualapi-19951707No ratings yet
- Network Programming Notes - SignalsDocument6 pagesNetwork Programming Notes - Signalstaleysha vuyanziNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Aspect of Cyber CrimeDocument29 pagesBehavioral Aspect of Cyber CrimeShanky DhamijaNo ratings yet