Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1) Bacterial Skin Inf
Uploaded by
smrutuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1) Bacterial Skin Inf
Uploaded by
smrutuCopyright:
Available Formats
Bact skin inf
Bacterial skin inf
Bacterial skin inf is the single most common diagnosis among those with skin problems. The most common bacterial skin inf is impetigo (superficial pyoderma)
Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus commonest cause of skin inf Colonization of unbroken skin by GABS precedes pyoderma by 10 days Intradermal inoculation by insect bite, scabies or minor trauma leads to impetigo, ecthyma &cellulitis
Cutan bact inf
Colonization or pyoderma may predispose the child to later pharyngeal colonization with the same strain Staph aureus spread from the nose to normal skin and then infect the skin Clinically the 2 lesions cannot be distinguished
S.Pyogenes
Noninvasive strains
Invasive trainss
impetigo
pharyngitis
Pyrogenic exotoxins
proteinase
Spreading factors
nephritogenic
Rheumatogenic strain
Scarlet fever
Necrotizing cellulitis/fascitis
Cellulitis erysipelas
psgn
Rheumatic fever
Toxic shock syndrome
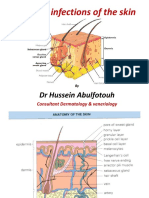
Bact skin inf
Those with recurrent inf should be evaluated for immunodef (neutrophil dysfunction)
Impetigo: bullous non bullous Non bullous accts for >70% of the cases Tiny vesicle or pustule forms and rapidly develops into a honey colored crusted plaque Inf spreads by towels, fingers, clothings
Contact sports
Little or no pain, no erythema, no constitutional symptoms
Bullous impetigo: infants and young children Caused by coagulase-positive staph aureus Flaccid transparent bullae develop on the skin of face, buttocks, trunk, perineum, & extremities. Neonatal bullous impetigo can begin in the diaper area
Culture of fluid from an intact blister should yield the causative lesion. Complications are potential but rare: OM septic arthritis,pneumonia &septicemia
Deeper soft tissue inf may occur. Erysipelas is an acute well demarcated inf of the skin with lymphagitis involving the face (ass with pharyngitis) &extremities (wounds). The skin is erythematous &indurated The advancing borders are raised& firm Ass with fever, vomiting& irritability
Bact skin inf
CELLULITIS Strept cellulitis is a painful, erythematous, indurated inf of the skin and subcut tissue usually follows some injury to the skin Proteinase producing strain causes a more severe type of necrotizing fascitis or myositis Also more common in diabetics & immunocompr
Bact skin inf
Organisms : St.Pyogenes &S.aureus. many other org can cause Presents as local edema, warmth erythema &tenderness.the margins are indistinct Regional adenopathy,constitutional S/S fever, chills &malaise
Bact skin inf
Complications : OM, sep arthritis, bacteremia, necrotizing fasciitis Treatment :specific antibiotics,after proper evaluation , cultures from the site In a newborn a full septicemic work up Cover for strep and staph
Necrotising Fasciitis (Meleneys streptococcal gang, Fourniers
Is a destructive invasive infection of skin, subcutaneous tissue &deep fascia with relative sparing of muscle. Bacteriology could be polymicrobial or monomicrobial due to group A Beta Haemolytic Strep. Common sites are genetalia, groin & lower abdomen. Pts are unwell, febrilewith areas of subcutaneous induration & erythema.Necrotic patches of skin develop.
Bact skin inf
Treatment is by wide excision of all effected soft tissue, anibiotics and supportive treatment. Wide skin deffects will need surgical procedures to repair them. Mortality is high and increases if surgical excision is delayed. Risk factors are D.M., malnutrition,obesity, steroids & immune defecieny.
Vaginitis :beta hemolytic strep. Are a common cause of vaginitis in prepubertal girls.pts usually have a serous discharge& marked erythema & irritation of the vulvar area,discomfort in walking &urination
Perianal dis: perianal strep cellulitis produces local itching,pain,blood streaked stools, erythema & proctitis.
Bact skin inf
Staph scalded skin syndrome (Ritter dis) Agent :staph aureus phage grp 2 str.71,55 Predominantly in infants& children<5 yrs Range of dis from local bullous impetigo to generalized cutaneous lesions with systemic involvement Malaise, fever, irritability
Bact skin inf
The scarlatiniform erythema develops diffusely & is accentuated in flexural & periorificial areas Conjuntivas : inflammed, discharge may be purulent Skin is brightly erythematous& rapidly wrinkled Severe cases- sterile flaccid blisters & erosions develop diffusely
Bact skin inf
Nikolsky sign may be positive(areas of epidermis separate in response to gentle shear force As large sheets of epidermis peel away,moist glistening denuded areas may get sec infected ,fluid &electrolyte imbalances Healing without scarring in 10 14 days
Bact skin inf
Antibiotics :orally or parenterally with semisynthetic penicillinase- res penicillin Gently moisten the skin and cleanse with Burow or Dakin soln or N saline Emolient application for lubrication to decrease discomfort Recovery is rapid Complications-Pneum,sept,cellulitis,fluid& electrolyte imbalincreased morbidity
Bact skin inf
Ecthyma :resembles non bullous impetigo in onset and appearance Gradually deeper,into the dermis, more chronic inf and forms an ulcer with elevated margins Ulcer becomes obscure by a dry heaped up crust that contributes to the persistence of inf and scar formation Spread :autoinoculation
Lesions may be as large as 4 cm Frequently on legs Predisposing factors :as impetigo Causative agent: GABHS (staph is cultured sec pathogen) Crust softened by warm compressions & removed by antibact soap Syst antibiotic tt as in impetigo
Bact skin inf
Blastomycosis like pyoderma Exuberant cutaneous reaction to bact inf in children who r malnourished and immunosupp Organism: GABHS,staph aureus
Various clinical presentations of Staph. Skin infections.
Boil (fruncle)- is an infection of hair root including sebaceous gland which usually proceeds to suppuration and central necrosis. Boils are common on face, neck and head. Boils are infrequently associated with overwork, worry, debelity or may be presenting feature of D.M. Stye is due to infection of an eyelash follicle, if suppuration occurs removal of eyelash will allow drainage.
Various clinical presentations of Staph. Skin infections.(ct)
Carbuncle- is an infective gangrene of subcutaneous tissue which usually occurs in the nape of neck. The subcutaneous tissue becomes painful and indurated, overlying skin is red. Unless the condition is aborted by prompt treatment extension occurs and after few days areas of softening appear, skin sloughs out and discharges pus. Usually there is one large central slough and surrounded by a rosette of smaller area of necrosis. Treatment is as for boil.
Lupus vulgaris (T.B. of skin)
Occurs between the age of 10-25 face being the site of election. One or more cutaneous nodules appear with cogestion of surrounding skin. Extension occurs very slowly but ulceration is likely to follow sooner or later.The resulting ulcer heals in one area as it expands to another. The mucous membrane of mouth and nose could be attacked primarily or as extension from face. Treatment is by ATT, lesion can be excised if healing is slow. Squamous cell carcinoma tend to occur in scars.
Lupus vulgaris
Advance Lupus vilgaris
You might also like
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infectons 1Document51 pagesSkin and Soft Tissue Infectons 1AISHWARYA T DNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument31 pagesBacterial InfectionsWendielynne MillomedaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Skin InfectionsDocument53 pagesOverview of Skin Infectionsadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections: Impetigo, Ecthyma, Furuncles, Carbuncles & AbscessesDocument139 pagesBacterial Skin Infections: Impetigo, Ecthyma, Furuncles, Carbuncles & AbscessesArianne Joy C. TamarayNo ratings yet
- PiodermaDocument43 pagesPiodermashlprtNo ratings yet
- Dermatosis-WPS Office-1Document111 pagesDermatosis-WPS Office-1PriyaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Primary Skin Lesions and Basics of DermatologyDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Primary Skin Lesions and Basics of DermatologyUsmanNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Class NotesDocument48 pagesDermatology Class Notesapi-26938624100% (6)
- Skin Conditions Part II-1Document54 pagesSkin Conditions Part II-1mohamedkallon1996No ratings yet
- General Surgery Copy 2Document37 pagesGeneral Surgery Copy 2sowmyaraja09No ratings yet
- ErysipelasDocument57 pagesErysipelasLusyDianaJacob100% (1)
- Bacterial: Viral FungalDocument53 pagesBacterial: Viral FungalNATTAPAT SANGKAKULNo ratings yet
- Tropical DiseasesDocument59 pagesTropical DiseasesSHANo ratings yet
- Bullous Disorders, Bacterial and Fungal Skin InfectionsDocument95 pagesBullous Disorders, Bacterial and Fungal Skin InfectionsDeborah ChemutaiNo ratings yet
- l9 - Neoplastic - Non-Neoplastic Skin DisordersDocument69 pagesl9 - Neoplastic - Non-Neoplastic Skin DisordersVenniilaaSaravananNo ratings yet
- Integument System PATH-321Document29 pagesIntegument System PATH-321abdullahNo ratings yet
- Pyodermas 2014Document41 pagesPyodermas 2014Dudy Humaedi100% (6)
- Mon Surgical Infections Boils, Abscess, Ulcer, Cellulitis, Curbuncle, Gangrene, Sinus, Fistula CDocument48 pagesMon Surgical Infections Boils, Abscess, Ulcer, Cellulitis, Curbuncle, Gangrene, Sinus, Fistula CPanna SahaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Disorders of The Integumentary SystemDocument70 pagesPediatric Disorders of The Integumentary SystemJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Eye Adnexa Diseases: Catedra OftalmologieDocument39 pagesEye Adnexa Diseases: Catedra OftalmologieDanielaNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous InfectionsDocument148 pagesCutaneous InfectionsPratzNo ratings yet
- DERMATOLOGY QuinterDocument177 pagesDERMATOLOGY QuinterstaceyatienoomaNo ratings yet
- NTU Skin Pathology 2024Document75 pagesNTU Skin Pathology 2024Chen HouyuNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of the Skin and EyesDocument29 pagesMicrobial Diseases of the Skin and Eyesbriterry2008No ratings yet
- Acne VulgarisDocument60 pagesAcne Vulgarischarmaine_olivia_1100% (2)
- Pathology of SkinDocument105 pagesPathology of SkinGonshiro Ar RayyanNo ratings yet
- LCD Kuliah Dermatitis Wa2008Document32 pagesLCD Kuliah Dermatitis Wa2008Made Wardhana100% (2)
- Derm Quick ReviewDocument124 pagesDerm Quick ReviewRohit NalamasuNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Dermatology (Notes)Document24 pagesPaediatric Dermatology (Notes)Ahmad Syarafi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Prev Next: © 2014 Webmd, Llc. All Rights ReservedDocument5 pagesPrev Next: © 2014 Webmd, Llc. All Rights ReservedOlfaktorius GoenawanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial - Viral InfectionsDocument61 pagesBacterial - Viral InfectionsMoayad NawaflehNo ratings yet
- Interventions for Common Skin ProblemsDocument202 pagesInterventions for Common Skin ProblemsMj Briones100% (1)
- Gram Positive Cocci: StaphylococciDocument57 pagesGram Positive Cocci: StaphylococciJill PardoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 LabDocument75 pagesModule 1 Labkrystal ongNo ratings yet
- Benign Gynecologic LesionsDocument53 pagesBenign Gynecologic LesionsChristopher Goodman-SmithNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument5 pagesImpetigoInges PSNo ratings yet
- Micr Biology: Microbial Diseases of The Skin and EyesDocument62 pagesMicr Biology: Microbial Diseases of The Skin and EyesIvy L VonierNo ratings yet
- Skin-PathologyDocument32 pagesSkin-PathologyArfa BaigNo ratings yet
- PYODERMA: Classification and Management of Common Pyodermas Including Impetigo, Folliculitis, Furuncle, Carbuncle, Echtyma, Paronikia, Erysipelas and Staphylococcal Scalded Skin SyndromeDocument43 pagesPYODERMA: Classification and Management of Common Pyodermas Including Impetigo, Folliculitis, Furuncle, Carbuncle, Echtyma, Paronikia, Erysipelas and Staphylococcal Scalded Skin SyndromeAnisaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology - PedsDocument16 pagesDermatology - PedsbencleeseNo ratings yet
- finalPEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGYDocument58 pagesfinalPEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGYShiva RamNo ratings yet
- 1 - Facial Dermatoses and Hair Disorders - 2023Document87 pages1 - Facial Dermatoses and Hair Disorders - 2023mesexel246No ratings yet
- Book Review - CellulitisDocument3 pagesBook Review - CellulitisMary RiveroNo ratings yet
- Reactive Disorders of The SkinDocument46 pagesReactive Disorders of The SkinhaniNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Pts Lucy KellyDocument31 pagesDermatology Pts Lucy KellyOlivia Genevieve El JassarNo ratings yet
- Diseases of SkinDocument18 pagesDiseases of SkinrishikeshkallaNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory-Skin-Diseases 231101 174335 (2462)Document37 pagesInflammatory-Skin-Diseases 231101 174335 (2462)Moayad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections GuideDocument41 pagesBacterial Skin Infections GuideUmmi Rinandari100% (1)
- Vesiculo-bullous lesions of the oral cavityDocument26 pagesVesiculo-bullous lesions of the oral cavityHem pushp lata MewaraNo ratings yet
- Lumps N BumpsDocument54 pagesLumps N BumpsAnis100% (1)
- Bacterial Infections: Infections Caused by Gram Positive OrganismsDocument81 pagesBacterial Infections: Infections Caused by Gram Positive OrganismsJamalul AdilNo ratings yet
- Guide to Understanding BlepharitisDocument39 pagesGuide to Understanding BlepharitisNailul RosyidaNo ratings yet
- Dr. R. Sekhon - Dermatology Telehealth Jan 27 MRDocument45 pagesDr. R. Sekhon - Dermatology Telehealth Jan 27 MRAnissa ADNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections of SkinDocument72 pagesBacterial Infections of SkinSiddharth DashNo ratings yet
- 2 EczemaDocument5 pages2 Eczemaحسين طاهر حاتم طاهرNo ratings yet
- Dermatology 3Document24 pagesDermatology 3حسين طاهر حاتم طاهرNo ratings yet
- Module 3 HomeworkDocument6 pagesModule 3 HomeworkCj LinceNo ratings yet
- IZZ - PiodermaDocument51 pagesIZZ - PiodermavivilmNo ratings yet
- Complete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisFrom EverandComplete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisNo ratings yet
- Sebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Surgical Anatomy of the Thyroid GlandDocument86 pagesSurgical Anatomy of the Thyroid GlandsmrutuNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DiseaseDocument25 pagesThyroid DiseasesmrutuNo ratings yet
- DysphagiaDocument8 pagesDysphagiasmrutuNo ratings yet
- Pertussis Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesPertussis Diagnosis and TreatmentsmrutuNo ratings yet
- 3) Typhoid FeverDocument36 pages3) Typhoid FeversmrutuNo ratings yet
- 1) Measles & RubellaDocument10 pages1) Measles & RubellasmrutuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Synopsis: 2/25/2012 DR Omar M.Sultan (MD, MSC, Mmed) 1Document6 pagesClinical Synopsis: 2/25/2012 DR Omar M.Sultan (MD, MSC, Mmed) 1smrutuNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer: Faina Linkov, PHD Research Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Cancer InstituteDocument22 pagesEndometrial Cancer: Faina Linkov, PHD Research Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Cancer InstitutesmrutuNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument36 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesmrutuNo ratings yet
- Mioma UteriDocument28 pagesMioma UteriAdhy HermawanNo ratings yet
- ATLS DRDocument45 pagesATLS DRNeNeei HenNieNo ratings yet
- TB3 Pneumoniae 210709 CatDocument24 pagesTB3 Pneumoniae 210709 CatsmrutuNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic HeartDocument47 pagesRheumatic HeartsmrutuNo ratings yet
- IHDDocument76 pagesIHDsmrutuNo ratings yet
- Setting TrolleyDocument19 pagesSetting TrolleyLennard SegundoNo ratings yet
- 1000 Plus Psychiatry MCQ Book DranilkakunjeDocument141 pages1000 Plus Psychiatry MCQ Book Dranilkakunjethelegend 20220% (1)
- Electric VehiclesDocument15 pagesElectric VehiclesJai ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Elements of PoetryDocument50 pagesElements of PoetryBeing LoisNo ratings yet
- ISO 15184 Paint Hardness TesterDocument6 pagesISO 15184 Paint Hardness TesterAvinash SilimkarNo ratings yet
- Subwoofer Box 6.5 Inch Subwoofer Ported Box Pipe9Document2 pagesSubwoofer Box 6.5 Inch Subwoofer Ported Box Pipe9Arif Kurniawan HidayatNo ratings yet
- The Development Cultural Studies in BritishDocument6 pagesThe Development Cultural Studies in BritishIeie HollyNo ratings yet
- Songs For The Deaf: Parental Advisory EdDocument5 pagesSongs For The Deaf: Parental Advisory EdTinta CafeNo ratings yet
- English Romanticism: Romantic PoetryDocument58 pagesEnglish Romanticism: Romantic PoetryKhushnood Ali100% (1)
- Case Study Dorothea Orem (Francar Jade For Sbmission) - TFNDocument2 pagesCase Study Dorothea Orem (Francar Jade For Sbmission) - TFNFrancar Jade De VeraNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Topic: Chapter 2: The Foreign Exchange Market 21 March 2021Document36 pagesWeek 1 - Topic: Chapter 2: The Foreign Exchange Market 21 March 2021Jenita singhNo ratings yet
- Volvo Penta AQ150-A-B Workshop Manual PDFDocument40 pagesVolvo Penta AQ150-A-B Workshop Manual PDFUmar ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Strategies of Literary TranslationDocument7 pagesStrategies of Literary TranslationMuhammad J H AbdullatiefNo ratings yet
- LSE100 Past Year Questions (2014/5)Document2 pagesLSE100 Past Year Questions (2014/5)Jingwen ZhangNo ratings yet
- Function: 'Gui - Name' 'Gui - Singleton' 'Gui - Openingfcn' 'Gui - Outputfcn' 'Gui - Layoutfcn' 'Gui - Callback'Document4 pagesFunction: 'Gui - Name' 'Gui - Singleton' 'Gui - Openingfcn' 'Gui - Outputfcn' 'Gui - Layoutfcn' 'Gui - Callback'Andrea IldikoNo ratings yet
- AS1684 Timber Framing GuideDocument37 pagesAS1684 Timber Framing GuidemanoliNo ratings yet
- 8086 Instruction Set and Assembly Language ProgramDocument13 pages8086 Instruction Set and Assembly Language Programwaheed azizNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics - Solution Manual (Chapter 1)Document1 pageEngineering Economics - Solution Manual (Chapter 1)Diego GuineaNo ratings yet
- Tipe Tubuh (Somatotype) Dengan Sindrom Metabolik Pada Wanita Dewasa Non-Obesitas Usia 25-40 TahunDocument9 pagesTipe Tubuh (Somatotype) Dengan Sindrom Metabolik Pada Wanita Dewasa Non-Obesitas Usia 25-40 TahunJessica Ester ExaudiaNo ratings yet
- A Complete List of Books On Mead MakingDocument3 pagesA Complete List of Books On Mead MakingVictor Sá100% (1)
- VERTICAL CYLINDRICAL VESSEL WITH FLANGED FLAT TOP AND BOTTOMDocument1 pageVERTICAL CYLINDRICAL VESSEL WITH FLANGED FLAT TOP AND BOTTOMsandesh sadvilkarNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec 5 TofdDocument6 pagesAsme Sec 5 TofdarsalanhaqNo ratings yet
- Efficient Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids With High Hydrophilicity by Pseudozyma Hubeiensis KM-59Document10 pagesEfficient Production of Mannosylerythritol Lipids With High Hydrophilicity by Pseudozyma Hubeiensis KM-59sushidombeNo ratings yet
- 5th Gen Vocational Model GuideDocument34 pages5th Gen Vocational Model GuideKieran Ryan100% (1)
- Dissertation On Havells IndutryDocument33 pagesDissertation On Havells IndutryRaj ShindeNo ratings yet
- Mufon Ufo JournalDocument25 pagesMufon Ufo JournalSAB78No ratings yet
- Disbursements Transactions PDFDocument6 pagesDisbursements Transactions PDFMarlyn Joy YaconNo ratings yet
- Pending 1667646640 ForeclosureSimulationDocument2 pagesPending 1667646640 ForeclosureSimulationpramod roy0% (1)
- Pe 4.1 - SwimmingDocument21 pagesPe 4.1 - SwimmingJacinthe Angelou D. PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- Oracle NetSuite To Oracle PBCS IntegrationDocument11 pagesOracle NetSuite To Oracle PBCS IntegrationAmit SharmaNo ratings yet