Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dermatophyta Non Kandidiasis
Uploaded by
heavyrainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dermatophyta Non Kandidiasis
Uploaded by
heavyrainCopyright:
Available Formats
KEPANITERAAN KLINIK KULIT & KELAMIN RSUP FATMAWATI DERMATOPHYTA-NON-CANDIDIASIS
Miftahul Jannah 108103000060
FAKULTAS KEDOKTERAN DAN ILMU KESEHATAN UIN SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH JAKARTA
Tinea nigra Uniformly tan macule on the plantar foot, present for several years. KOH preparation showed hyphae
Tinea pedis: interdigital dry type The interdigital space between the toes shows erythema and scaling; the toenail is thickened, indicative of associated distal subungual onychomycosis
Tinea pedis: interdigital macerated type The webspace between the fourth and fifth toes is hyperkeratotic and macerated in a black individual with plantar keratoderma and hyperhidrosis. The greenish hue is caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa superinfection of this moist intertriginous site. Erythrasma also occurs in the setting of moist intertriginous sites and may occur concomitantly with interdigital tinea pedis and/or Pseudomonas intertrigo
Tinea pedis: moccasin type Fairly sharply marginated erythema of the plantar foot with a mild keratoderma associated with distal/lateral subungual onychomycosis, typical of T. rubrum infection.
Tinea pedis: moccasin type Hyperkeratosis and scaling of the dorsa of the feet occurring on the portion of the foot covered by a moccasin; note the associated distal/lateral subungual onychomycosis, typical of T. rubrum infection
Tinea pedis: bullous type Ruptured vesicles, bullae, erythema, and erosion on the plantar aspect of the great toe. Hyphae were detected on KOH preparation obtained from the roof of the inner aspect of the bulla. In some cases, superficial white onychomycosis may also be seen with this T. mentagrophytes infection.
Bentuk Subungual distalis: Dimulai dari tepi distal menjalar ke proksimal. Leukonikia trikofita (keputihan di permukaan kuku). Kukunya hancur(untuk membedakannya dg candidiasis )
Tinea manuum Erythema and scaling of the right hand, which was associated with bilateral tinea pedum; the "one-hand, two-feet" distribution is typical of epidermal dermatophytosis of the hands and feet. In time, distal/lateral subungual onychomycosis occurs on the fingernails
Tinea cruris Confluent, erythematous, scaling plaques on the medial thighs, inguinal folds, and pubic area. The margins are slightly raised and sharply marginated. Erythrasma should be ruled out by Wood's lamp examination
Tinea corporis Inflammatory annular plaques, becoming confluent on the medial thigh. This type of inflammatory lesion is seen with zoophilic dermatophytic infection and with topical glucocorticoid use.
Tinea corporis: acute and subacute Multiple, bright red, sharply marginated lesions with only minimal scaling of several weeks' duration on the trunk of a child. Three lesions are more inflammatory and thicker. Microsporum canis was isolated on fungal culture, which had been contracted from a pet guinea pig
Tinea corporis: chronic Sharply marginated, hyperpigmented plaques of many months' duration on the back, buttocks, and thighs. The lesions have a psoriasiform appearance. Associated tinea cruris and tinea pedis are usually present
Tinea facialis Sharply marginated, ertythematous, scaling, and crusted plaques on the face of a child. Note asymmetry
Tinea facialis Erythematous plaque with a geographic shape; scaling is minimal but adequate for KOH preparation
Tinea incognito Arcuate red plaques on the medial ankle in a patient who had applied a fluorinated glucocorticoid cream. Moccasin-type tinea pedis is apparent on the plantar foot
Tinea capitis: "black dot" variant A subtle, asymptomatic patch of alopecia due to breaking off of hairs on the frontal scalp in a 4-year-old black child. The lesion was detected because her infant sister presented with tinea corporis. Trichophyton tonsurans was isolated on culture
Tinea capitis: "gray patch" type A large, round, hyperkeratotic plaque of alopecia due to breaking off of hair shafts close to the surface, giving the appearance of a mowed wheat field on the scalp of a child. Remaining hair shafts and scales exhibit a green fluorescence when examined with a Wood's lamp. Microsporum canis was isolated on culture
Kerion An extremely painful, boggy, purulent inflammatory nodule on the scalp of this 4-year-old child. The lesion drains pus from multiple openings and there is retroauricular, tender lymphadenopathy. Infection was due to T. verrucosum contracted from an infected rabbit.
Tinea barbae Scattered, discrete follicular pustules and papules in the moustache area, easily mistaken for S. aureus folliculitis
Tinea barbae and tinea facialis Confluent, painful papules, nodules, and pustules on the upper lip. Epidermal dermatophytosis (tinea facialis) with sharply marginated erythema and scaling is present on the cheeks, eyelids, eyebrows, and forehead. Trichophyton mentagrophytes was isolated on culture. In this case, the organism caused two distinct clinical patterns (epidermal involvement, tinea facialis versus follicular inflammation, tinea barbae, kerion), depending on whether glabrous skin or hairy skin was infected. (See also Image 23-1.)
Non dermatophyta
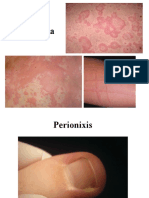
Pityriasis versicolor Sharply marginated brown macules on the trunk. Fine scale was apparent when the lesions were abraded with the edge of a microscope slide
Pityriasis versicolor Multiple, small-to-medium-sized, well-demarcated hypopigmented macules on the back of a tanned individual with white skin
Pitirosporm folikulitis penyakit kronis pada folikel pilosebasea
berupa papul, pustul folikular yang biasanya gatal
Tempat predileksi :dada, punggung dan
lengan bagian atas. Kadang di leher dan jarang dimuka.
Candida albicans: KOH preparation Budding yeast forms and sausage-like pseudohyphal forms
Cutaneous candidiasis: intertrigo Small peripheral "satellite" papules and pustules that have become confluent centrally, creating a large eroded area in the submammary region.
Cutaneous candidiasis: intertrigo Erythematous papules with a few pustules, becoming confluent on the medial thigh. The lesions occurred during a holiday trip to the Caribbean
Cutaneous candidiasis: intertrigo Vesicles, pustules, and papules becoming confluent on the perineum and perianal area. The patient had successfully undergone a bone marrow transplantation 4 weeks before the appearance of the cutaneous lesions. The initial impression by the oncologist was that the lesions were reactivated herpes simplex; KOH preparation and cultures confirmed the diagnosis of Candida intertrigo
Candidiasis: diaper dermatitis Confluent erosions, marginal scaling, and "satellite pustules" in the area covered by a diaper in an infant. Atopic dermatitis or psoriasis also occurs in this distribution and may be concomitant.
Oral candidiasis: thrush White curdlike material on the mucosal surface of the lower lip of a child; the material can be abraded off with gauze (pseudomembranous), revealing underlying erythema.
Oral candidasis: thrush Extensive cottage cheese-like plaques, colonies of Candida that can be removed by rubbing with gauze (pseudomembranous), on the palate and uvula of an individual with advanced HIV disease. Patches of erythema between the white plaques represent erythematous (atrophic) candidiasis. Involvement may extend into the esophagus and be associated with dysphagia.
Candidiasis: vulvitis Psoriasiform, erythematous lesions becoming confluent on the vulva with erosions and satellite pustules on the thighs
Candidiasis: balanoposthitis Multiple, discrete pustules on the glans penis and inner aspect of the foreskin (the preputial sac).
Lesi kemerahan, tidak bernanah, kuku tebal, mengeras, berlekuk, kadang kecoklatan, tidak rapuh seperti tinea
You might also like
- Kebijakan High AlertDocument8 pagesKebijakan High AlertheavyrainNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic CardiomyopathyDocument9 pagesAlcoholic CardiomyopathyheavyrainNo ratings yet
- ACLS 2015 Algorithm PDFDocument8 pagesACLS 2015 Algorithm PDFheavyrain100% (1)
- Benign Positional Vertigo: Taleb Mohammed Mansoor Khaleil Ebrahem Al-MatroushiDocument27 pagesBenign Positional Vertigo: Taleb Mohammed Mansoor Khaleil Ebrahem Al-MatroushiSheila CantikNo ratings yet
- Eye EmergenciesDocument18 pagesEye EmergenciesdrDre91No ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Liver InvolvementDocument7 pagesPathogenesis Liver InvolvementheavyrainNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument19 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeheavyrainNo ratings yet
- BPPVDocument27 pagesBPPVheavyrainNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HuddersfieldDocument1 pageHuddersfieldNdumiso MoyoNo ratings yet
- International Undergraduate Prospectus 2015 2016Document130 pagesInternational Undergraduate Prospectus 2015 2016Juank GarcésNo ratings yet
- Outbreaks Epidemics and Pandemics ReadingDocument2 pagesOutbreaks Epidemics and Pandemics Readingapi-290100812No ratings yet
- Genital Herpes: Aarthi (2012)Document36 pagesGenital Herpes: Aarthi (2012)Aiman TymerNo ratings yet
- MyiasisDocument3 pagesMyiasisMohiedden M Abdul-FattahNo ratings yet
- Application Form Defacto SpecialistsDocument6 pagesApplication Form Defacto SpecialistsNancy De BriyneNo ratings yet
- NKC Fast Facts - Poop Chart - 5 2017 PDFDocument1 pageNKC Fast Facts - Poop Chart - 5 2017 PDFFaniaNo ratings yet
- BruvaxDocument1 pageBruvaxArif K BashaNo ratings yet
- Chain of InfectionDocument13 pagesChain of InfectionPrince Jhessie L. AbellaNo ratings yet
- Kode IcdDocument5 pagesKode IcdNurul FatimahNo ratings yet
- Mortalidad AnestesicaDocument10 pagesMortalidad AnestesicaPaula Andrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mumps Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & PreventionDocument14 pagesMumps Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & PreventionChristian JonathanNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections in Cattle in A Gaushala at Jaipur: Haryana Vet. 49 (December, 2010), PP 62-63Document2 pagesFungal Infections in Cattle in A Gaushala at Jaipur: Haryana Vet. 49 (December, 2010), PP 62-63Mahavir DamakaleNo ratings yet
- Appendix - 1: List of ICI Journal Titles Pending EvaluationDocument7 pagesAppendix - 1: List of ICI Journal Titles Pending EvaluationMultan Singh BhatiNo ratings yet
- 1040 A Day in The Life of A Veterinary Technician PDFDocument7 pages1040 A Day in The Life of A Veterinary Technician PDFSedat KorkmazNo ratings yet
- Form P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDDocument2 pagesForm P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDRavi ParmarNo ratings yet
- What Is Mumps in ChildrenDocument4 pagesWhat Is Mumps in ChildrenFoster K KaundaNo ratings yet
- Alexis Wolter ResumeDocument2 pagesAlexis Wolter Resumeapi-610069547No ratings yet
- Droplet Infection: Tuberkulosis (TB) ParuDocument2 pagesDroplet Infection: Tuberkulosis (TB) ParuMiiniieNo ratings yet
- Basic TB FactsDocument8 pagesBasic TB FactshatemfaroukNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Variants Persistent Infections Emerging Viruses Antigenic Variation Zoonotic DiseaseDocument28 pagesPathogenic Variants Persistent Infections Emerging Viruses Antigenic Variation Zoonotic DiseaseSantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Ayulia 2023Document13 pagesCompany Profile Ayulia 2023Willia HospitalNo ratings yet
- Epi ReviewerDocument4 pagesEpi ReviewerHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Iceberg DiseasesDocument18 pagesIceberg Diseasesachuth29No ratings yet
- Recapitulare TestDocument38 pagesRecapitulare TestDana ChitoiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report: Name: MR .Sandeep Mane Patient ID: P80359Document1 pageLaboratory Report: Name: MR .Sandeep Mane Patient ID: P80359akash srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Centre For Health Protection, Department of Health July 2019Document17 pagesDengue Fever: Centre For Health Protection, Department of Health July 2019Melissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Backyard Poultry Medicine and Surgery - A Guide For Veterinary Practitioners, 2nd EditionDocument672 pagesBackyard Poultry Medicine and Surgery - A Guide For Veterinary Practitioners, 2nd EditionAbubakar Tahir Ramay100% (1)
- Chickenpox (Varicella) : A Communicable DiseaseDocument12 pagesChickenpox (Varicella) : A Communicable DiseaseEizel Nhey G. JADENo ratings yet
- Virology Learning TableDocument6 pagesVirology Learning Table//No ratings yet